Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integumentary To Endocrine Draft
Uploaded by
Angela Jasmin Quitevis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
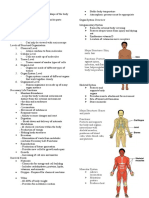
3 views1 pageThe integumentary system acts as a physical barrier protecting the body from harm and regulates temperature, stores nutrients and helps the immune system. The skeletal system maintains body structure, equilibrium and protects organs while storing and releasing minerals and fat. The muscular system allows movement, circulates fluids and produces heat to aid digestion and circulation. The nervous system acts as the command center interpreting senses and regulating functions through electrochemical impulses. The endocrine system regulates growth, metabolism and day-to-day functions through hormones.
Original Description:
Original Title
Integumentary to Endocrine Draft
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe integumentary system acts as a physical barrier protecting the body from harm and regulates temperature, stores nutrients and helps the immune system. The skeletal system maintains body structure, equilibrium and protects organs while storing and releasing minerals and fat. The muscular system allows movement, circulates fluids and produces heat to aid digestion and circulation. The nervous system acts as the command center interpreting senses and regulating functions through electrochemical impulses. The endocrine system regulates growth, metabolism and day-to-day functions through hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageIntegumentary To Endocrine Draft
Uploaded by
Angela Jasmin QuitevisThe integumentary system acts as a physical barrier protecting the body from harm and regulates temperature, stores nutrients and helps the immune system. The skeletal system maintains body structure, equilibrium and protects organs while storing and releasing minerals and fat. The muscular system allows movement, circulates fluids and produces heat to aid digestion and circulation. The nervous system acts as the command center interpreting senses and regulating functions through electrochemical impulses. The endocrine system regulates growth, metabolism and day-to-day functions through hormones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
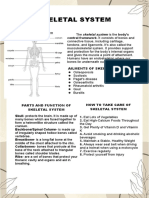
Integumentary Acts as a physical barrier skin, subcutaneous tissue
which protects the body from
bacteria, infection, chemicals,
injury, and sunlight.
Regulates body temperature.
Stores fat, water, glucose, and
vitamin D, and helps the
immune system do its job of
keeping the body healthy and
disease-free.
Skeletal Aids in maintaining body bones, ligaments, cartilage,
equilibrium tendons
Offers a structure for
muscular action.
Helps keep internal organs
and bone marrow safe
It acts as a mineral and fat
storage and release organ.
Creates red blood cells
Muscular Moves the skeleton/allows bones, muscles, tendons,
movement ligaments, soft tissues
Moves fluids through vessels
in the circulatory system
Produces heat
Aids in moving food through
the digestive system
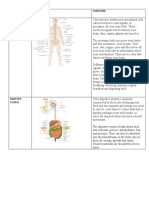
Nervous Acts as the body’s command brain, nerves, eyes, ears
center which interprets
sensory information.
Regulates body functions
such as movement by means
of electrochemical impulses
Endocrine Regulates body functions thyroid gland, pituitary gland,
such as growth and pancreas
reproduction by means of
hormones.
Regulates day-to-day
metabolism by means of
hormones
You might also like
- Mod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalDocument8 pagesMod 5 Organ Systems and Animal SurvivalrasingtanyaroseNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2Document12 pagesMODULE 1 & 2 - General Biology 2John Michael LopezNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Bodyjavier andres martinez100% (1)
- CelllllDocument9 pagesCelllllbasman1212No ratings yet
- Sas 3Document1 pageSas 3zimoneNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument11 pagesBIOLOGYElla May TimoteoNo ratings yet
- 12 Body SystemsDocument2 pages12 Body Systemsasif khanNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument3 pagesBody SystemsA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesJamaica SimanganNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Integrated Function Organ - Kel 2Document20 pagesIntegrated Function Organ - Kel 2Rashif AnbiaNo ratings yet
- NOTES ReportingsDocument16 pagesNOTES Reportings2240739No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnonymous 2k0o6az6lNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Reviewer - Ch1 To Ch6Document30 pagesReviewer - Ch1 To Ch6cpagente01No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesHimiko JacksonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Body SystemsDocument1 pageIntegumentary System: Body SystemsIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganDocument8 pagesAnatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheDocument7 pagesDiaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheRizzalyn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Argyll ProjectDocument10 pagesArgyll ProjectPark Lee ツNo ratings yet
- Eals ACT2 ValdezDocument4 pagesEals ACT2 ValdezMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- M3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Document27 pagesM3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Muskan HomeNo ratings yet
- Organ System PDFDocument73 pagesOrgan System PDFbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesActivity #1 Anatomy and PhysiologyJenny Sumangil EspejoNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues and Human TissuesDocument8 pagesAnimal Tissues and Human Tissuesismail.hassanineNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument8 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 7 - Earth and Life ScienceKristine Alcordo100% (1)
- LABORATORY EXERCISE NO. 1 Introduction To Food & NutritionDocument8 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE NO. 1 Introduction To Food & NutritionkawaiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PretestDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PretestMary Regine BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- Name: Serrato, Princess B. Subject CODE: D9 Course and Schedule: TUESDAY 4-6:00 PM 1 SEMESTER S/Y 2021-2022 Instructor: Ms. Joyce Ann PerezDocument3 pagesName: Serrato, Princess B. Subject CODE: D9 Course and Schedule: TUESDAY 4-6:00 PM 1 SEMESTER S/Y 2021-2022 Instructor: Ms. Joyce Ann PerezPrincess Binondo SerratoNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali MohammedDocument22 pagesHuman Biology: Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali MohammedAli HarthNo ratings yet
- Health and Social Care Assignment Sample PDFDocument11 pagesHealth and Social Care Assignment Sample PDFWilliamRiley100% (2)
- 3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodyDocument5 pages3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodySabrina PorcoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes - Lecture 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Notes - Lecture 1ellieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ANPH 1001 Anatomy PhysiologyDocument4 pagesChapter 1 ANPH 1001 Anatomy PhysiologyKaraNo ratings yet
- Organ System 1Document15 pagesOrgan System 1LeoNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell OrganizationDocument27 pages1 Cell OrganizationLawrence RayappenNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q2 - CLAS1 - Organs of Each Organ System That Work Together - v6 - Liezl ArosioDocument10 pagesScience6 - q2 - CLAS1 - Organs of Each Organ System That Work Together - v6 - Liezl ArosioJeffrey VigonteNo ratings yet
- System Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemDocument1 pageSystem Structure Purpose Interaction With Other SystemLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Funda ReviewerDocument15 pagesFunda ReviewerKate LagundiNo ratings yet
- Biology Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document36 pagesBiology Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- Body Cells: Skin Cells Red Blood Cells Bones andDocument17 pagesBody Cells: Skin Cells Red Blood Cells Bones andHj LifeNo ratings yet
- These Tasks:: General Biology 2Document8 pagesThese Tasks:: General Biology 2Mary Rose MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDanielle LeighNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Reviewerain't your saintessNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Document29 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 2qq23588% (68)
- Types of Body SystemDocument4 pagesTypes of Body SystemLatowed RemuelNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyAngel vyne borbonNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 5 - Animal Organ SystemsDocument34 pagesBiology Module 5 - Animal Organ SystemsfloNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Processes in Various Organ SystemsDocument25 pagesMetabolic Processes in Various Organ SystemsSANTIAGO, David Joshua B.No ratings yet
- Report in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesReport in Anatomy and Physiologydowngrade840No ratings yet
- PAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Document5 pagesPAP Review KEY - Unit 7 CBA 2016-2017Tom PunnenNo ratings yet
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionDocument8 pagesAssignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionJefferNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Notes Human Body Cells TissuesDocument21 pagesAnaPhy Notes Human Body Cells TissuesRON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet