Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electricity and Magnetism 6
Uploaded by
Julia KarakiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electricity and Magnetism 6
Uploaded by
Julia KarakiCopyright:
Available Formats
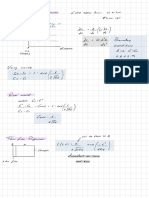
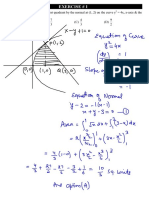
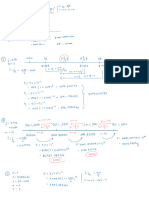
Repulsive and Attractive Forces
for like
charges : for opposite charges :
-
the product 9192 is positive .
the product 9192 is negative
f is positive f is
- .
negative
-
The
charges repel each other .
The
charges attract each other
worked example
distance ,
r= 2.00mm = 2.0×10-3 m
9C
'
elementary charge
-
,
e = I. 6 ✗ to
-
the elementary charge e is the charge of a
proton
-
an alpha particle has 2 protons
80 91=2 ( I. 6×10 9) 3.2
' 9
C
_
'
10
-
× = ✗
-
a gold nucleus ☒as 79 protons
% 79 (1.6 10-19) '
7C
92
-
◦ = × × = 1.264 ✗ 10
↳ f- = K 91 (8.99×109) ( 3.2 ✗ to
- '
9) (1.264 × 10-17)
92 = ×
2
r2 (2.0 × 10-3)
f- = 9. I ✗ 10
- 21
N
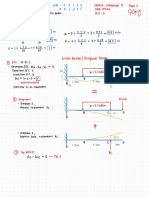
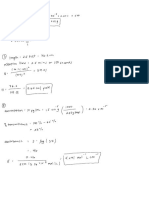
5.2 Heating Effect of Electric Currents
Circuits
Circuit Diagrams
Circuit Symbols : Functions of Most common
components :
.
switch it turns the circuit -
on
(closed) ,
or off (open)
.
fixed resistor it limits : the flow
of current
-
as electrons flow through
a resistor , they transform
electrical potential energy
.
Variable resistor : a resistor with a
slider that can be used to change
its resistance .
resistance of the
variable
-
as the
increases resistor ,
the
current in the circuit decreases
and vice versa .
•
thermistor a resistor whose :
resistance depends its
temperature
on
-
as temperature increases ,
the
decreases
resistance of a thermistor
and vice versa .
.
light dependent resistor ( LDR) a :
depends
resistor whose resistance
light intensity on the
-
as eight intensity increases ,
decreases
the resistance of a LDR
and vice versa .
You might also like
- Ncert Diamond Question CH 1 To 8Document13 pagesNcert Diamond Question CH 1 To 8pravchoo2006No ratings yet
- EX9 Una BombaDocument2 pagesEX9 Una BombaRoger UnoxxNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument13 pagesElectric Charges and Fieldssatanikdas3No ratings yet
- EcuacionesDocument10 pagesEcuacionesJuan Álvaro CobosNo ratings yet
- Hifiuibrii: GivenDocument43 pagesHifiuibrii: GivenShreyas PrabhuNo ratings yet
- EMA3050 Oct 17Document5 pagesEMA3050 Oct 17Alicina DaleNo ratings yet
- Ce226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegDocument12 pagesCe226 Q6 Corpuz J 3cegJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- CB2201 5Document1 pageCB2201 5grisha.unusovNo ratings yet
- TD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryDocument15 pagesTD 4 Experimental Base of Quantum TheoryusaroufNo ratings yet
- Pizarra, Sesión 13 - 10 de DiciembreDocument5 pagesPizarra, Sesión 13 - 10 de DiciembreFelipe FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection PDFDocument7 pagesBeam Deflection PDFHaikal HakimNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry NotesDocument4 pagesTrigonometry NoteschexNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledElla TorresNo ratings yet
- Httpsdoc 08 0s Docs - Googleusercontent.comdocssecurescjh066je4vgdvk3h6d71bq9jqgonq0qtn8f3ok81bqm4cq0uh9nnsiij8ha3iapb3164Document4 pagesHttpsdoc 08 0s Docs - Googleusercontent.comdocssecurescjh066je4vgdvk3h6d71bq9jqgonq0qtn8f3ok81bqm4cq0uh9nnsiij8ha3iapb3164ItZIbus RNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSHW2Document2 pagesPHYSICSHW2fenasikerimNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument24 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwansuyash KumarNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Ejercicios T7 Gulag FreeDocument4 pagesWuolah Free Ejercicios T7 Gulag FreeuserwuolahNo ratings yet
- Strengths of Materials TutorialDocument2 pagesStrengths of Materials TutorialCharl CronjeNo ratings yet
- Untitled Notebook PDFDocument5 pagesUntitled Notebook PDFShehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- HW11 (Aot)Document2 pagesHW11 (Aot)Sam BNo ratings yet
- Formula CheatsheetDocument1 pageFormula CheatsheetGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- 9P 1.602xto": ProtonDocument5 pages9P 1.602xto": ProtonZoha FaisalNo ratings yet
- Ofgasolineused - .IM?yrg (Ggs - kg1m3: Furs 13.89ms 12.79NDocument1 pageOfgasolineused - .IM?yrg (Ggs - kg1m3: Furs 13.89ms 12.79Nchee xiongyewNo ratings yet
- Fisika Mandiri 11: Try ZTFZDocument7 pagesFisika Mandiri 11: Try ZTFZAzka Rahmah MeisaNo ratings yet
- Murtaza - Quiz 1 MatrekDocument2 pagesMurtaza - Quiz 1 Matrekmur tazaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan PDFDocument48 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan PDFMRIDUL VYAS94% (54)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan (1) - RemovedDocument31 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan (1) - RemovedAarush Gaming100% (3)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument14 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwankjfnk,jg100% (2)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDocument6 pagesClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwanaastha.sawlaniNo ratings yet
- P-C SurplusesDocument4 pagesP-C SurplusesWajiha RajaniNo ratings yet
- Y Nen: PointDocument14 pagesY Nen: PointMohit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ill I: SlopeDocument10 pagesIll I: SlopeMohit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Binding Energy 231023 164202Document5 pagesNuclear Binding Energy 231023 164202shreemit2020No ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Notes - Ii: Amit Kumar Jha (Iitian)Document15 pagesQuantum Mechanics Notes - Ii: Amit Kumar Jha (Iitian)Tiasha DevNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument4 pagesEquationsRahul RoopchandNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument1 page2 PDFSim Pei YingNo ratings yet
- Cee 235a HWDocument21 pagesCee 235a HWNguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- T Im#-Eex4Ixs E4MDocument5 pagesT Im#-Eex4Ixs E4Mcarol108tsaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effects of CurrentCHINMAY UPADHYAYA X-DNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic 1 Page NotesDocument4 pagesElectrostatic 1 Page Notesmonishbro41No ratings yet
- Null 2Document3 pagesNull 2techeducation807No ratings yet
- Physics All DerivationDocument48 pagesPhysics All Derivationdhruvvegda1000100% (1)
- Be184p m1 SolDocument2 pagesBe184p m1 SolDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- 576d8v49yuy41 JPGDocument1 page576d8v49yuy41 JPGliliplayz123No ratings yet
- 진동공학 0904Document7 pages진동공학 0904SangMin ShinNo ratings yet
- ImageDocument1 pageImageaditya dwi fantaraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry P1 Unsolved - 231015 - 193252Document18 pagesTrigonometry P1 Unsolved - 231015 - 193252inaayaNo ratings yet
- Addition PolymerisationDocument3 pagesAddition PolymerisationNoura NawafNo ratings yet
- Janjang ArithmetikDocument15 pagesJanjang ArithmetikHaninii Suhaila HKNo ratings yet
- Ramraj: SolutionDocument8 pagesRamraj: SolutionRajat Verma X D 39No ratings yet
- HarshDocument20 pagesHarshHarsh Vashishtha67% (3)
- CrystallographyDocument1 pageCrystallographySUNANDAN PANDANo ratings yet
- Tixf6 - : AlgebraDocument7 pagesTixf6 - : AlgebraShireen KiranNo ratings yet
- 4 Implications For Report - Boston - RavenDocument5 pages4 Implications For Report - Boston - Ravensbracca1No ratings yet
- Alita - Math119 Test3 NoteDocument3 pagesAlita - Math119 Test3 Note4jcvphvr6mNo ratings yet
- Population: BinomialDocument10 pagesPopulation: Binomialnaghamaoun.13No ratings yet
- Ch4 HWDocument1 pageCh4 HWhzfmzh1313No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Measurements and UncertaintiesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Measurements and UncertaintiesJulia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 5Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 5Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 7Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 7Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 10Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 10Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 9Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 9Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 4Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 4Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 3Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 3Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument1 pageElectricity and MagnetismJulia KarakiNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism 8Document1 pageElectricity and Magnetism 8Julia KarakiNo ratings yet
- SC D353Document168 pagesSC D353Ricardo SidotiNo ratings yet
- Manual DCM300GDocument40 pagesManual DCM300GLuis SerranoNo ratings yet
- LTspice-model of Thermoelectric Peltier-Seebeck ElementDocument5 pagesLTspice-model of Thermoelectric Peltier-Seebeck ElementVinicius Silva OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 10jhao XXXXSD PDFDocument1 page10jhao XXXXSD PDFGustavo CochachínNo ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engineering 2009 PDFDocument48 pagesIES Electrical Engineering 2009 PDFSuresh christ rajNo ratings yet
- Intro To BJT Small SignalDocument35 pagesIntro To BJT Small Signaldaserock83100% (1)
- Password Based Circuit BreakerDocument16 pagesPassword Based Circuit BreakerEEE GreenCornerNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents: Revised: 3/21/08Document68 pagesTable of Contents: Revised: 3/21/08Mario Leonel Torres MartinezNo ratings yet
- SEMIKRON Application Manual Power Semiconductors English en 2015 LIBRO (001 001)Document100 pagesSEMIKRON Application Manual Power Semiconductors English en 2015 LIBRO (001 001)Gilman Robert MontalvoNo ratings yet
- AC Installation - Testing Form Template - Chiller UnitDocument6 pagesAC Installation - Testing Form Template - Chiller UnitVincent LeeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Accessories PDFDocument28 pagesCircuit Breaker Accessories PDFMax Tajima MatsuharaNo ratings yet
- Ul MCCBDocument112 pagesUl MCCBbsunanda01No ratings yet
- 2022 03 Kre High - Temperature - Solutions DigitalDocument6 pages2022 03 Kre High - Temperature - Solutions DigitalJose Rafael CastroNo ratings yet
- ATS01eCatalog PDFDocument48 pagesATS01eCatalog PDFJuanCarlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Emerson Hktv13 Chassis Cn-001nk SvcmnlsDocument38 pagesEmerson Hktv13 Chassis Cn-001nk SvcmnlsAvr Electronica ChileNo ratings yet
- Sulalitha PhysicsDocument72 pagesSulalitha PhysicsVarun s90% (135)
- CH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class NotesDocument7 pagesCH 3-Renewable Energy Resources Class Notesmerooney desanchesNo ratings yet
- Circuit-Protection-Con Polyswitch-Fundamentals PDFDocument13 pagesCircuit-Protection-Con Polyswitch-Fundamentals PDFd.c.delatorre2200No ratings yet
- Sine Wave PWM (SPWM) Circuit Using Opamp - Homemade Circuit ProjectsDocument28 pagesSine Wave PWM (SPWM) Circuit Using Opamp - Homemade Circuit Projectsdudulemarc100% (1)
- Unit 2 PDFDocument39 pagesUnit 2 PDFMoulod Mouloud100% (1)
- Hfe JBL s4800Document3 pagesHfe JBL s4800Steve WalschotNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety PDFDocument16 pagesElectrical Safety PDFARPITA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Cursos Pararrayos SIEMENS PDFDocument32 pagesCursos Pararrayos SIEMENS PDFedwinoria100% (1)
- Airport Electrical StandardsDocument580 pagesAirport Electrical StandardsJayadevDamodaran50% (2)
- A Seminar On: Battery Energy Storage For Enabling Distributed Solar Power GenerationDocument25 pagesA Seminar On: Battery Energy Storage For Enabling Distributed Solar Power GenerationUvarajGopalNo ratings yet
- Ec8261 CD Lab ManualDocument92 pagesEc8261 CD Lab ManualthasleemaNo ratings yet
- OMMIC GaN ProcessDocument22 pagesOMMIC GaN ProcessMario San Miguel MontesdeocaNo ratings yet
- ECO100 Platform V3Document27 pagesECO100 Platform V3Fabio GomesNo ratings yet
- QRP SuperRM Assembly ManualDocument26 pagesQRP SuperRM Assembly ManualBenjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- VS501Z 54481-01 - 97 - ADocument8 pagesVS501Z 54481-01 - 97 - AanderskrauseNo ratings yet