Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q3wi Scaffold 1
Uploaded by
CHRIST GAMING0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Q3WI SCAFFOLD 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesQ3wi Scaffold 1
Uploaded by
CHRIST GAMINGCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
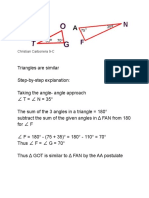
1.
Based on the videos, what volcanic
hazards caused the injuries and deaths of
humans?
- This combination gave rise to wet ash, increasing loading on structures with a large
proportion of the 847 death toll due to roof collapse.
2. What data/information from the videos
shows specific needs of the situation?
-If you are instructed to remain in your home, close all windows, doors, and other points of
entry for ash. Bring pets inside and move livestock to shelters, when at all possible. Avoid
running air conditioning systems, fans, and heaters during or immediately after an eruption,
since they can pull in volcanic gasses and ash. Also, fill large containers, sinks, and bathtubs
with clean water since eruptions can cause disruptions or contamination of water supplies.
3. What are the barriers to meeting the
needs?
-volcanoes rouse from sleep with some notice—shaking the ground, bulging their flanks, or
shifting the gasses wafting from their craters and vents. And for many volcanoes near
populations, scientists closely watch their every move, which allows them to better understand
when they might burst to life.
So if you live near a volcano, or plan to visit one, familiarize yourself with the local monitoring
agencies. Understand where you can safely tromp and where you need to steer clear, regions
known as exclusion zones. It’s also important to look up evacuation routes and hazards specific
to your location.
4. What can be designed/planned to
address the barriers?
-Avoid low-lying areas, areas downwind of the volcano, and river valleys downstream of the
volcano. Debris and ash will be carried by wind and gravity. Stay in areas where you will not be
further exposed to volcanic eruption hazards
You might also like
- Finaleddddddd Sci 9Document13 pagesFinaleddddddd Sci 9Khirlsty Mae Gonzales BaloNo ratings yet
- Module 7 ErupTIONDocument5 pagesModule 7 ErupTIONHannah VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Volcano Hazard: Learning Content Standard: Performance Standard: The Learners Develop A Family EmergencyDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Volcano Hazard: Learning Content Standard: Performance Standard: The Learners Develop A Family EmergencyEsther CalawiganNo ratings yet
- How To Know Whether A Volcano Is About To EruptDocument2 pagesHow To Know Whether A Volcano Is About To EruptsaadNo ratings yet
- 3D VolcanoDocument5 pages3D VolcanoNeslyn EquipajeNo ratings yet
- GQA Science 9 Q3 Wk2 Volcanic Erutptions and Its Effect On Society - LrqaDocument15 pagesGQA Science 9 Q3 Wk2 Volcanic Erutptions and Its Effect On Society - LrqaRichelle DolarNo ratings yet
- Pokemon2 161001051034Document28 pagesPokemon2 161001051034Regie G. GalangNo ratings yet
- DRRR Handout Volcanic HazardDocument4 pagesDRRR Handout Volcanic HazardAnonymous fKViHeaw0% (1)
- Volcanic Hazard EssayDocument4 pagesVolcanic Hazard EssayPrincess Manelle de VeraNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLP 59 - Precautionary Measures On Volcanic Eruptions - Repair PDFDocument10 pagesScience 6 DLP 59 - Precautionary Measures On Volcanic Eruptions - Repair PDFJemar Prajes100% (2)
- Volcano (Precautionary Measures and Facts)Document4 pagesVolcano (Precautionary Measures and Facts)Nazarene Perez100% (1)
- 6 Volcano PrepDocument29 pages6 Volcano PrepGLoria, Danica Joy A.No ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument1 pageVolcanoesmarvin fajardoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet - Science 9 - Week 2.1 For Posting in GCDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet - Science 9 - Week 2.1 For Posting in GCKent Kyle PalingcodNo ratings yet
- Volanoes BrochureDocument3 pagesVolanoes Brochureasdwe0% (1)
- What To Do BeforeDocument3 pagesWhat To Do BeforeDane Richmon SajulNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument31 pagesDRRRdeleonroccel7No ratings yet
- DRRR Las 10Document4 pagesDRRR Las 10Casther Troy FraynaNo ratings yet
- Volcanic HazardsDocument32 pagesVolcanic HazardsCherry Pie RenonNo ratings yet
- Volcanic EruptionDocument15 pagesVolcanic EruptionArnel DelingonNo ratings yet
- Safety Precautions Before, During, and After Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionDocument12 pagesSafety Precautions Before, During, and After Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionAndré SanchezNo ratings yet
- G7 TCSHS Volcanic Hazards and Impacts and DRRM Plan Notes and WorksheetDocument7 pagesG7 TCSHS Volcanic Hazards and Impacts and DRRM Plan Notes and WorksheetAthena JadeehNo ratings yet
- Sulit, Ella Mae M. Final DemoDocument35 pagesSulit, Ella Mae M. Final DemoElla Mae Mendoza SulitNo ratings yet
- Volcano HazardsDocument65 pagesVolcano Hazardsjohndeocampo14No ratings yet
- What To Do Before, During and After A Volcanic Eruption: Awareness CampaignDocument11 pagesWhat To Do Before, During and After A Volcanic Eruption: Awareness CampaignshilameyNo ratings yet
- Science 4THDocument7 pagesScience 4THAlthea AndresNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint PresentationDocument18 pagesPowerpoint PresentationMichelle ReynoNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption Awareness Campaign: Presentation by Group 1Document16 pagesVolcanic Eruption Awareness Campaign: Presentation by Group 1Xcel MoralesNo ratings yet
- During A Volcanic EruptionDocument4 pagesDuring A Volcanic EruptionJosie Alonzo AndradeNo ratings yet
- EFFECTS OF VOLCANIC ERUPTION - PPSXDocument19 pagesEFFECTS OF VOLCANIC ERUPTION - PPSXMyla Balingit AdiNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q1 M4 Volcanic HazardsDocument4 pagesDRRR Q1 M4 Volcanic HazardsMs.Muriel MorongNo ratings yet
- What To Do BEFORE, DURING, and AFTER Volcanic EruptionDocument20 pagesWhat To Do BEFORE, DURING, and AFTER Volcanic EruptionRizaNo ratings yet
- Taal VolcanoDocument8 pagesTaal VolcanoShervin Angelo DumangcasNo ratings yet
- Safety Plan To Reduce The Risk of Volcanic HazardsDocument27 pagesSafety Plan To Reduce The Risk of Volcanic HazardsAlesandra PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Preparedness On Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionDocument17 pagesDisaster Preparedness On Earthquake and Volcanic EruptionRUEL PELAYONo ratings yet
- Science 4qaDocument7 pagesScience 4qaAlthea AndresNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Hydrometreological HazardDocument50 pagesModule 6-Hydrometreological HazardAlodia PastorizoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Natural Hazards, Mitigation and Adaptation: A. EarthquakeDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Natural Hazards, Mitigation and Adaptation: A. EarthquakeJac Nama Garcia100% (4)
- Week3Q4 LAS Science6 FinalDocument8 pagesWeek3Q4 LAS Science6 FinalFrances Quibuyen DatuinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Volcanic EruptionDocument30 pagesLesson 2 Volcanic EruptionJBNo ratings yet
- Signs of Impending Volcanic Eruption Grade 9.odpDocument14 pagesSigns of Impending Volcanic Eruption Grade 9.odpAce Richard P. ClimacoNo ratings yet
- GamalDocument4 pagesGamalKai JieNo ratings yet
- Mt. Bulusan: An Active Volcano Case StudyDocument9 pagesMt. Bulusan: An Active Volcano Case StudyRaichu PikachuNo ratings yet
- PHED 213 MODULE PRELIM-okDocument19 pagesPHED 213 MODULE PRELIM-okSarah DiazNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Hazard Awareness DriveDocument3 pagesVolcanic Hazard Awareness DriveJames Carlo AlertaNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption: Are You Prepared?: Ma. Rachel B. EspinoDocument22 pagesVolcanic Eruption: Are You Prepared?: Ma. Rachel B. EspinoChristopher CelisNo ratings yet
- DRRR Lesson On VolcanoDocument25 pagesDRRR Lesson On VolcanoRam KuizonNo ratings yet
- Rocel Pamulagan NG Section Antares 2Document13 pagesRocel Pamulagan NG Section Antares 2Juriel Elohim GolvinNo ratings yet
- During A Volcanic Eruption: BeforeDocument7 pagesDuring A Volcanic Eruption: BeforeCoshie DelcorNo ratings yet
- During A Volcanic Eruption: BeforeDocument7 pagesDuring A Volcanic Eruption: BeforeCoshie DelcorNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Vo LDocument60 pagesEarthquake Vo LFree VideosNo ratings yet
- Science Q3W2Document3 pagesScience Q3W2jermelie coñaNo ratings yet
- Performance Task #1: Earl Alekxis PactolDocument12 pagesPerformance Task #1: Earl Alekxis PactolBor RubinNo ratings yet
- Pyroclastic Density CurrentsDocument4 pagesPyroclastic Density CurrentsRheann Marie BugtongNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument2 pagesVolcanoesJarel MarabutNo ratings yet
- Appropriate-Measures (DRRRM)Document2 pagesAppropriate-Measures (DRRRM)Kristine Mae Orong OyawanNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument59 pagesVolcanoGhavine RoldanNo ratings yet
- Volcano 6Document4 pagesVolcano 6johnmichaelgregorio640No ratings yet
- How to Prepare for Every Natural Disaster: Including First Aid InstructionsFrom EverandHow to Prepare for Every Natural Disaster: Including First Aid InstructionsNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Process QuestionsDocument1 pageProcess QuestionsCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
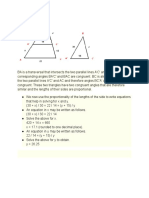
- Scaffold 3Document1 pageScaffold 3CHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Conditioning ExercisesDocument5 pagesConditioning ExercisesCHRIST GAMING100% (1)
- Q3 Performance Task TemplateDocument2 pagesQ3 Performance Task TemplateCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Math PTDocument1 pageMath PTCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Cast AwayDocument1 pageCast AwayCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Gospel Reflection 1Document1 pageGospel Reflection 1CHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet
- My EscapeDocument2 pagesMy EscapeCHRIST GAMINGNo ratings yet