Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Important Questions for Second Year
Uploaded by
yashwant0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views5 pagesOriginal Title
physics 2 yr important question (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
87 views5 pagesPhysics Important Questions for Second Year
Uploaded by
yashwantCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
SECOND YEAR PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
Very short Answer type Questions (2Marks)
Ray optics and optical instruments
1. what is dispersion? Which color gets more dispersed?
2. What is myopia? How can it be corrected?
3. What is hypermetropia? How can it be corrected?
4. Define power of a convex lens. What is its units?
5. A small angled prism of 4o deviates a ray through 2.48o. Find the refractive
index of the prism.
6. Define focal length and radius of curvature of a concave lens.
7. What do you understand by the terms focus and principle focus in the
context of lenses?
Moving charges and magnetism
8. Distinguish between ammeter and voltmeter.
9. What is a force on a conductor of length l carrying current I placed in a
magnetic field of induction B? when does it becomes maximum.
10.What is force on a charged particle of charge q moving with a velocity v in a
uniform magnetic field of induction B?
11.What is the relation between permittivity of free space and permeability of
free space and the speed of light in vacuum.
12.How do you convert a moving coil galvanometer in to voltmeter.
13.How do you convert a moving coil galvanometer in to ammeter.
14.What is the importance of Oersted’s experiment?
15.A circular coil of radius r having N turns carries a current i, what is its
magnetic moment?
16.What is the principle of moving coil Galvanometer?
Magnetism and matter
17.Define magnetic inclination or magnetic dip.
18.Magnetic lines from continues closed loops. Why?
19.What is the magnetic moment associated with the solenoid?
20.Define magnetic declination.
21.Classify the following materials with regard to magnetism.
Manganese, Cobalt, Nickle, Bismuth, Oxygen , Copper
22.What are the SI units of magnetic moment, magnetic induction and magnetic
field?
Alternating Current
23.What is the phenomenon involved in the working of a transformer?
24.A transformer converts 200 V ac into 2000V ac. Calculate the number of
turns in the secondary if the primary has 10 turns?
25.What is meant by wattless component of current?
26.What type of transformer is used in a 6V bed lamp?
27.What is transformer ratio?
28.Write the expression for the reactance of (i) an inductor (ii) a capacitor.
29.What is the phase difference between AC emf and AC current in the
following: Pure resistor, pure inductor, and pure capacitor.
EM waves
30.Give two used of infrared rays?
31.Microwaves are used in Radars. Why?
32.What are the applications of microwaves?
33.If the wave length of electromagnetic radiation is doubled, what happens to
the energy of the photon?
Duel Nature of Radiation
34.What are cathode rays?
35.What is work function?
36.What is photoelectric effect?
37.Write down Einstein’s photo electric equation.
38.Write down de Broglie’s relation and explain the terms there in.
39.State Heisenberg’s Uncertainty principle?
40.Give example of photo sensitive substances? Why are they called so?
Semiconductors
41.What is n-type semiconductor? What are the majority and minority charge
carriers in it?
42.What are intrinsic and extrinsic semi conductors?
43.Draw the circuit symbols for p-n-p and n-p-n transistors?
44.In which bias can a Zener diode be used as voltage regulator?
45.Which gates are called universal gates?
46.What is a p-n junction diode? Define depletion layer.
Communication systems
47.Define modulation. Why is it necessary?
48.Mention the basic methods of modulation?
49.Which type of communication in employed in Mobile phones?
50.What is sky wave propagation?
51.What are the basic blocks of a communication system?
Short answer type questions (4Marks)
Ray Optics
1. Define Critical angle. Explain total internal reflection using neat diagram.
2. Explain the formation of a mirage?
3. With a neat labelled diagram explain the formation of image in a simple
microscope.
4. Explain the formation of a rainbow?
Wave Optics
5. Explain the Doppler’s effect in light. Distinguish between red shift and blue
shift.
6. How do you determine the resolving power of your eye?
7. Derive the expression for the intensity at a point where the interference of
light occurs.
8. Does the principle of conservation of energy hold for interference and
diffraction phenomenon? Explain briefly?
Electric Charges and Fields
9. State and explain Coulomb’s law in electricity.
10.State Gauss’s law in electrostatics and explain its importance?
11.Derive the equation for the couple acting on an electric dipole in a uniform
electric field.
12.Derive an expression for the intensity of the electric field at a point on the
axial plane of an electric dipoles.
Electric potential and Capacitance
13.Derive an expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
14.Derive the formula for equivalent capacitance when the capacitors are in
series.
15.Derive the formula for equivalent capacitance when the capacitors are in
parallel.
16.Derive expression for the electric potential for point charge?
Moving Charges and Magnetism
17.State and explain Biot Savart law.
18.State and explain Ampere’s law.
19.Derive an expression for the magnetic induction at the Centre of a current
carrying circular coil using Biot Savart law.
20.Derive an expression for the magnetic dipole moment of a revolving
electron.
21.Derive an expression for the magnetic induction at a point on the axis of a
current carrying circular coil using Biot Savart law.
Electromagnetic Induction
22.Describe the ways in which Eddy current are used to advantage.
23.Obtain an expression for the emf induced across a conductor which is
moved in a uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to the plane of
motion?
24.Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co axial
solenoids.
Atoms
25.Explain the different types of spectral series.
26.What is impact parameter and angle of scattering? How are they related to
each other?
27.What are the limitations of Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom?
28.Describe the Rutherford atom model. What are the draw backs of this
model?
29.Write a short note of De Broglie’s explanation of Bohr’s second postulate of
quantization.
Semiconductors
30.What is rectification? Explain the working of a full wave rectifier.
31.Describe how a semi conductor diode is used as a half wave rectifier.
32.Distinguish between Half wave rectifier and Full wave rectifier.
33.Define NAND and NOR gates, and give their truth tables.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (8Marks)
WAVES
1. Explain the formation of stationary waves in air column enclosed in open
pipe. Derive the equations for the frequencies of the harmonics produced.
2. How are stationary waves formed in a closed pipes? Explain the various
modes of vibration and obtain relations for their frequencies.
3. Explain the formation of stationary waves in a stretched strings. Hence
deduce the laws of transverse waves in a stretched string.
4. What is Doppler effect? Obtain an expression for the apparent frequency of
sound heard when the source is in motion with respect to an observer at rest.
CURRENT ELECRICITY
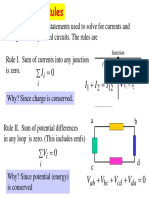
5. State Kirchhoff’s law for an electrical network. Using these laws deduce the
condition for the balance in a Whetstone bridge.
6. State the working principle of a potentiometer. Explain with the help of
circuit diagram how the emf of two primary cells are compared by using the
potentiometer.
7. State the working principle of potentiometer. Explain with the help of circuit
diagram how the potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of
the given primary cell.
NUCLEI
8. Explain the principle and working of a nuclear reactor with the help of a
labelled diagram.
9. What is radioactivity? State the law of radioactive decay show that
radioactive decay is exponential in nature?
You might also like
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsFrom EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo ratings yet
- REVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsDocument2 pagesREVISION Important 5&3 Marks Xii PhysicsGeethika gorakala100% (1)
- Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter Wise Important QuestionsTechnical Hacks100% (1)
- SR Physics - Ipe - Important Questions: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument8 pagesSR Physics - Ipe - Important Questions: Very Short Answer QuestionsRithik Reddy100% (1)
- Senior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Document10 pagesSenior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Soumendu KonaeNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Yr BDocument3 pagesPhysics 2nd Yr BShahrukh KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics questions by C.ShankarDocument5 pagesPhysics questions by C.ShankarVishnu DasNo ratings yet
- Phy - II Pu Previous Year Questions (Electric Charges & Fields and Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance)Document2 pagesPhy - II Pu Previous Year Questions (Electric Charges & Fields and Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance)Madhu ammuNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Derive de Broglie wavelength and solve problems on optics, electronics, communication, atomic physics and nuclear physicsDocument3 pagesDerive de Broglie wavelength and solve problems on optics, electronics, communication, atomic physics and nuclear physicsRakesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSDocument8 pagesChapter Wise Important Questions XII PHYSICSsavitridevi9668No ratings yet
- Phsys Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesPhsys Important QuestionsRamya. RNo ratings yet
- 09-03-2023 - Jr-Chemistry-Ipe Pre-Final-Iii-Batch-Ii - Q.PDocument2 pages09-03-2023 - Jr-Chemistry-Ipe Pre-Final-Iii-Batch-Ii - Q.PGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations of Physics Class 12 CBSEDocument11 pagesImportant Derivations of Physics Class 12 CBSEPadma kannaNo ratings yet
- II PUC CHEMISTRY IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR SOLID STATEDocument29 pagesII PUC CHEMISTRY IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR SOLID STATEom sri sai enterprisesNo ratings yet
- Puc Ii PCMB Board Question Bank PDFDocument439 pagesPuc Ii PCMB Board Question Bank PDFkatti1084154100% (3)
- Wave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesDocument16 pagesWave Optics (Xiii) Teaching NotesSankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course PhysicsDocument39 pagesBridge Course PhysicsWinDroidErNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TopicwiseDocument19 pagesUnit 1 TopicwiseSimran singhNo ratings yet
- Assignment PotentialDocument4 pagesAssignment Potentialshruti baruaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Chemistry QuestionsDocument4 pagesMid-Term Chemistry QuestionsRavindar PurohitNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Board Exam 2019 Revision GuideDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Board Exam 2019 Revision GuideKrishan Lohan100% (1)
- Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesRevision QuestionsShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Chemistry Sample Paper 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry Sample Paper 1 SolutionsSangeetaNo ratings yet
- LIQUID SOLUTIONS CONCENTRATIONDocument33 pagesLIQUID SOLUTIONS CONCENTRATIONSandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 3 (Electrochemistry) Important Unsolved QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass 12th Chemistry Chapter 3 (Electrochemistry) Important Unsolved QuestionsI L0vE SHiTNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields Chapterwise QuestionsDocument19 pagesElectric Charges and Fields Chapterwise QuestionsTejaswini S.kNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Forces, Charges and FieldsDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Forces, Charges and FieldsDeepak PachauriNo ratings yet
- Physics 2nd Year Important Questions 2021Document6 pagesPhysics 2nd Year Important Questions 2021Adnan100% (1)
- Math 2nd Puc Imp QuestionsDocument11 pagesMath 2nd Puc Imp QuestionsNoo EntryNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics Important Questions emDocument11 pages11th Physics Important Questions emRevathi Sivashankar0% (1)
- Physics2-2 Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersDocument3 pagesPhysics2-2 Intermediate II Year Model Question PapersAkshay Pandey100% (3)
- Bloch TheoremDocument2 pagesBloch TheoremSurajNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 11 Important QuestionDocument2 pagesPhysics Class 11 Important QuestionBanna Mohit Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- (Template) Physics Cls 12Document9 pages(Template) Physics Cls 12sreelakshmiNo ratings yet
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Xii ChemistryDocument35 pagesXii ChemistryPratikNo ratings yet
- MLL Chemistry 2024Document6 pagesMLL Chemistry 2024prembabumahawar782No ratings yet
- Question Bank of Chemistry (SEM 1) : Unit I: Atomic and Molecular StructureDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank of Chemistry (SEM 1) : Unit I: Atomic and Molecular StructureDrGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- BEE Question Bank 1 PDFDocument2 pagesBEE Question Bank 1 PDFchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Gauss's Law PDFDocument52 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Gauss's Law PDFkumarnpccNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy Jr INTER PRE-FINAL QPDocument2 pagesSri Chaitanya IIT Academy Jr INTER PRE-FINAL QPrammNo ratings yet
- Proposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsDocument17 pagesProposed Pre Final-1 Time Table With Weightage.. MPC, Bipc&Civils-AP&TsAbhiram muddanaNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Document9 pagesPhysics XII Assignment 1 M.M 30 Part A (1 Marks Question)Nisha RajnwalNo ratings yet
- Ramaiah Entrance Test PaperDocument4 pagesRamaiah Entrance Test PaperNaren Parashar100% (1)
- Level - I: Solutions (Set-1)Document14 pagesLevel - I: Solutions (Set-1)Dwi RomadhonNo ratings yet
- AIPMT 2009 Solved PaperDocument27 pagesAIPMT 2009 Solved PaperFirdosh Khan100% (3)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - PYQ Chemistry Class 11 PDF DownloadDocument9 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - PYQ Chemistry Class 11 PDF DownloadamreshNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Important Questions With SolutionsDocument41 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Important Questions With SolutionsDimpal BisenNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Previous QuestionsDocument12 pagesClass XII Physics Previous QuestionsAnonymous dW6e9PusZNo ratings yet
- EAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71Document25 pagesEAMCET QR Chemistry JR Chem 3.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 42 71pvnchem67% (3)
- Physics Sectionwise Analysis of PYQs (2024) - 5242689b Cf3f 4967 96d6 410f33dd7567 1Document4 pagesPhysics Sectionwise Analysis of PYQs (2024) - 5242689b Cf3f 4967 96d6 410f33dd7567 1lakhbhat2020No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Induction - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024Test UserNo ratings yet
- Class X CBSE Science Question PaperDocument10 pagesClass X CBSE Science Question PaperVinayak Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Liquid Crystal PolymersDocument19 pagesLiquid Crystal Polymersleovaldez3059No ratings yet
- Crystal Field TheoryDocument58 pagesCrystal Field TheoryAakash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- Quantum Phenomenon MS PDFDocument3 pagesQuantum Phenomenon MS PDFyuvrajdohilNo ratings yet
- Construction and Types of Armature Windings in Synchronous GeneratorsDocument57 pagesConstruction and Types of Armature Windings in Synchronous GeneratorsJagath ArchonNo ratings yet
- CSE 250 Assignment 01Document8 pagesCSE 250 Assignment 01Ziana BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- 03 Current ElectricityDocument60 pages03 Current ElectricityDivyanshi KhareNo ratings yet
- Rytmd80-Ata 24Document83 pagesRytmd80-Ata 24KHA ZING WU LIANGNo ratings yet
- 16.objective Questions - EdsDocument13 pages16.objective Questions - EdsSatishdhora SiddanaNo ratings yet
- (Page 249-391) PARTS MANUAL 4Document147 pages(Page 249-391) PARTS MANUAL 4Pranav ShekharNo ratings yet
- PQ - Current Electricty 150Document18 pagesPQ - Current Electricty 150dongoke2019No ratings yet
- 06.electromagnetic Induction FDocument44 pages06.electromagnetic Induction Fmahlom06No ratings yet
- DispersionDocument2 pagesDispersionshweta khannaNo ratings yet
- Daewoo B30S Electric ForkLift Service ManualDocument153 pagesDaewoo B30S Electric ForkLift Service ManualReid AllawayNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Electical & Electronics Measurement Question BankDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Electical & Electronics Measurement Question Bankvijay patilNo ratings yet
- Test 2 PhyDocument5 pagesTest 2 PhyHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's RulesDocument15 pagesKirchhoff's RulesKaye RamosNo ratings yet
- Practical Circuits: Exercise 12.2 Using the Internal Resistance EquationsDocument2 pagesPractical Circuits: Exercise 12.2 Using the Internal Resistance EquationsKaren MartinNo ratings yet
- Rojas 02-12-2023 20.08Document17 pagesRojas 02-12-2023 20.08Juphil PletoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Conductors, Insulators, and SemiconductorsDocument2 pagesLecture Notes Conductors, Insulators, and Semiconductorsoduleke davidNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 10 - ECE Board Exam - AnswersDocument19 pagesMCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 10 - ECE Board Exam - AnswersOne PieceNo ratings yet
- SCIE 4 LP 4a's (Physics)Document6 pagesSCIE 4 LP 4a's (Physics)zachharveyneilNo ratings yet
- Carr's Flying Saucer Theories and ExperimentsDocument30 pagesCarr's Flying Saucer Theories and ExperimentsSavouretNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields 1Document15 pagesMagnetic Fields 111alevelNo ratings yet
- Electrical CircuitsDocument24 pagesElectrical CircuitsJoseph Kinley V. LumosadNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Topical Past Papers PhysicsDocument64 pagesIGCSE Topical Past Papers PhysicsHubert DMelloNo ratings yet
- 2nd PUC Impt 5 Mark Qs and Ans PDFDocument24 pages2nd PUC Impt 5 Mark Qs and Ans PDFRamya. RNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ScriptDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Scriptrobinislam2002khanNo ratings yet
- Singularities in Kerr-28Document21 pagesSingularities in Kerr-28gigajohnNo ratings yet
- PHYS 212 AnswersDocument19 pagesPHYS 212 AnswersJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Theory of General RelativityDocument1 pageTheory of General RelativityEINSTEINNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Physics 12Document2 pagesFormula Sheet Physics 12RyanVgames MCNo ratings yet