Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Cell (1-5) G. Echavez
Uploaded by
Lemon AdeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Cell (1-5) G. Echavez
Uploaded by
Lemon AdeCopyright:
Available Formats
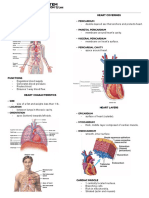
1 Nucleus
2 Nucleolus
3 Nuclear membrane
11 Cell wall
9 Chloroplast
Cell Structure Function
Nucleus Brecht (2021) stated that the nucleus is known
as the “brain” of the cell. Genes and genetic
information are located in the nucleus of the cell.
Proteins, lipids, vitamins, compounds, and more
that the cell requires are activated by the
expression of these genes. The nucleus also
manages growth and metabolism.
Nucleolus The nucleolus is a spherical component of the
nucleus whose primary function is to assemble
and generate ribosomes. Moreover, ribosomal
RNA genes are processed in the nucleolus
(Morris, n.d.).
Nuclear membrane According to Robb (2021), the nuclear
membrane is the outer layer of a nucleus. It
keeps the DNA protected by dividing the nucleus
from the surrounding cytoplasm. Plant cells
completely lack centrosomes and use the
nuclear membrane during mitosis to arrange the
chromosomes. The nuclear membrane also
controls what passes through nuclear pores and
nuclear localization signals to enter and exit the
nucleus.
Cell wall As affirmed by Brecht (2021), the cell wall is
responsible for providing rigidity and support to
the cell and enabling the circulation of water and
minerals. By acting as a barrier, separating the
inside of the cell from the outside, the cell wall
helps to protect against diseases. There is a
primary cell wall and a secondary cell wall in
some circumstances. The primary cell wall is
more flexible than the secondary one, enabling
plant growth. As the plant stops developing, the
secondary cell wall typically grows inside the
main wall.
Chloroplast Chloroplasts are components of eukaryotic cells
that play a role in photosynthesis. During
photosynthesis, glucose and oxygen are
produced using carbon dioxide, water, and light
energy. Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in
the chloroplast, it is essential for capturing the
sunlight's energy for photosynthesis (Molnar &
Gair, 2015).
REFERENCES
Brecht, M. (2021, August 2). Plant Cell Form and Function. study.com.
https://study.com/learn/lesson/plant-cell-anatomy-functions.html#:~:text=The
%20parts%20of%20a%20plant%20cell%20and%20plant%20cell
%20components,cytoplasm%2C%20cytoskeleton%2C%20and%20plastids.
Molnar, C., & Gair, J. (2015, May 14). 3.3 Eukaryotic Cells. Pressbooks.
https://opentextbc.ca/biology/chapter/3-3-eukaryotic-cells/
Robb, A. (2021, March 30). Nuclear Membrane Function & Structure | What is a Nuclear
Membrane? study.com. https://study.com/learn/lesson/nuclear-membrane-function-
structure.html
Morris, S. (n.d.). Nucleolus. Genome.gov.
https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Nucleolus#:~:text=Definition&text=The
%20nucleolus%20is%20a%20spherical,ribosomal%20RNA%20genes%20are
%20transcribed
You might also like
- Test Bank For Human Anatomy 9th Edition by MartiniDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Human Anatomy 9th Edition by MartiniAnthony Cohen100% (38)
- Mitosis PPT EdittedDocument21 pagesMitosis PPT EdittedabdNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Biology Bmat Section 2Document20 pagesBiology Bmat Section 2celiNo ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument40 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt Dimacali100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument16 pagesCell BiologyKlint Rodney Mark Lule100% (1)
- Virtual Laboratory Exercise 2Document4 pagesVirtual Laboratory Exercise 2Jung Somin100% (1)
- IB Biology Unit 1.6 QuestionsDocument4 pagesIB Biology Unit 1.6 QuestionsLaura WNo ratings yet
- 1st Ch. CellsDocument27 pages1st Ch. CellsAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Mitosis Meiosis ComparedDocument1 pageMitosis Meiosis ComparedDURU ALTINKAYA100% (1)
- Cell Test IB BIO HL 123Document7 pagesCell Test IB BIO HL 123AdamNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Teacher: Reda QuidetJuanito MerciNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Cell - Learn Science at ScitableChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 1 NotesDocument6 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notesmohan.shenoy52No ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaapi-3714451100% (2)
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesTerm 1 - Grade 8 Science CH 7 Cell Structure and Functionprakashjoshi23aprilNo ratings yet
- Infografia de BiologiaDocument4 pagesInfografia de BiologiafrancosebastianbcNo ratings yet
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 2 and 3Document26 pagesLESSON - 2 and 3Kerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Ultrastructure Nucleus: BiologyDocument14 pagesUltrastructure Nucleus: BiologyAshu ShewaleNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Cells NoteDocument6 pagesCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Note - BDB FiitjeeDocument5 pagesCell Note - BDB FiitjeeSankar MandalNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Plant CellsDocument6 pagesLesson 2: Plant CellslalaNo ratings yet
- CELulas 2Document21 pagesCELulas 2lizetteNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 1Rock MarkNo ratings yet
- Pes CellsDocument7 pagesPes CellsPrince Vincent AlcedoNo ratings yet
- Found-1 Science NotesDocument15 pagesFound-1 Science NotesSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFDocument2 pagesNucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFsathya50% (2)
- CELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryDocument10 pagesCELLS 2.1: Outline: To Give A Brief Account or SummaryHrithik SolaniNo ratings yet
- Foundation - 1 RecapDocument15 pagesFoundation - 1 RecapSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellDocument11 pagesLabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellGlyndel ArcillasNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cell TypesDocument4 pagesGen Bio Cell TypesRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells and Their Cell Bodies (Baluska Et Al., 2004)Document24 pagesEukaryotic Cells and Their Cell Bodies (Baluska Et Al., 2004)ej valerioNo ratings yet
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- CelsszDocument6 pagesCelsszHITANSH NIJHAWANNo ratings yet
- List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesList All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsAira Shane MargesNo ratings yet
- 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pages5 The Fundamental Unit of Lifekishan jhaNo ratings yet
- UPCAT REVIEWER - ScienceDocument4 pagesUPCAT REVIEWER - ScienceNicole de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - ContentDocument12 pagesMODULE 3 - Contentjameshajiyavudeen001No ratings yet
- Write The Similarities and Differences: Between-Dysplasia-And-MetaplasiaDocument5 pagesWrite The Similarities and Differences: Between-Dysplasia-And-MetaplasiaAngel PicoNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgA SX2Document7 pagesACFrOgA SX2Nadhine MacalinaoNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCell As A Unit of LifeRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument4 pages1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotescarlNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument7 pagesChapter-5, The Fundamental Unit of LifeMonika Mehan100% (20)
- Unit-I Basic Cell BiologyDocument116 pagesUnit-I Basic Cell Biologyvishav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3Document34 pagesKelompok 3Gresia HutagaolNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane: Lesson 1: Cell Parts and Their Functions ReferenceDocument5 pagesCell Membrane: Lesson 1: Cell Parts and Their Functions ReferenceChristine Gabuya CagasNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Document2 pagesBacteria and Archaea Are Classified As Prokaryotes ( Pro Before Karyon - Nucleus)Sekar AyuNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellEster Ariza CruzadoNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science CellsDocument1 pageKS3 Science Cellsejljn1No ratings yet
- Biology Unleashed: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering the Science of LifeFrom EverandBiology Unleashed: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering the Science of LifeNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Gweneth Echavez - Quiz #3Document1 pageGweneth Echavez - Quiz #3Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- RLE List of MaterialsDocument1 pageRLE List of MaterialsLemon AdeNo ratings yet
- CHEM14LAB - Experiment 1Document10 pagesCHEM14LAB - Experiment 1Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- (CLEAN) - Experiment2 With AnswersDocument4 pages(CLEAN) - Experiment2 With AnswersLemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Document6 pagesCardiovascular System - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Blood - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Document5 pagesBlood - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Lec PointersDocument1 pageLec PointersLemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Draft EthicsDocument2 pagesDraft EthicsLemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University: Department of BiologyDocument4 pagesCentral Mindanao University: Department of BiologyNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKent Justine BarrogaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477No ratings yet
- L&G Belts Cross RefDocument31 pagesL&G Belts Cross RefashielanieNo ratings yet
- S1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationDocument19 pagesS1 C2.1 Cell - Structure, Function and OrganisationANGELA HO SHU YEANNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeDaljeet SinghNo ratings yet
- As Level Chapter 1 Cell StructureDocument52 pagesAs Level Chapter 1 Cell StructureNajma Previa Jati100% (1)
- PHCG 201 CytologyDocument113 pagesPHCG 201 CytologyIbn HaarūnNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Students Book 2nd Edition (C. J. Clegg, Geoff Goodwin) (Z-Lib - Org) 1Document5 pagesExtracted Pages From Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Students Book 2nd Edition (C. J. Clegg, Geoff Goodwin) (Z-Lib - Org) 1BonnyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 - Module 7-MitosisandmeiosisDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 - Module 7-Mitosisandmeiosisエアーア ラシブNo ratings yet
- Cell - Unit of Life BiohackDocument14 pagesCell - Unit of Life BiohackArghya PaulNo ratings yet
- Dissecting Pig and Chicken'S Heart: EukaryoticDocument3 pagesDissecting Pig and Chicken'S Heart: EukaryoticRosemarie R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument15 pagesMitosisJorge MurieteNo ratings yet
- BiotDocument13 pagesBiotJOSCEL SYJONGTIANNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Unit 5 Study GuideDocument15 pagesScience 7 Unit 5 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 2 Additional MaterialDocument7 pagesModule 1 2 Additional MaterialEli Joshua EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function EhswebDocument80 pagesChapter 4 Cell Structure and Function EhswebDrAmit Verma0% (2)
- Cell Structure: Lesson Quiz ReviewDocument2 pagesCell Structure: Lesson Quiz ReviewAbdulkarim AlrefaeNo ratings yet
- Class IX Online - CELL - 14-05-22Document5 pagesClass IX Online - CELL - 14-05-22avijayprasad2207No ratings yet
- Cells Alive WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Alive WebquestMegha ModugulaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopediabookchapter PDFDocument13 pagesEncyclopediabookchapter PDFJamesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PDFDocument12 pagesExperiment 1 PDFAdrianne L. de GraciaNo ratings yet
- Ynice Bostic - 8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells-SDocument7 pagesYnice Bostic - 8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells-SYnice BosticNo ratings yet