Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ENTRANCE TEST CHEMISTRY
Uploaded by
जggerNaut ClassesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENTRANCE TEST CHEMISTRY
Uploaded by
जggerNaut ClassesCopyright:
Available Formats
ENTRANCE TEST
SET C Grade-XI
Chemistry
TIME: 30 minutes Marks: 30
1) With increase of temperature, which of these changes?
(A) Molality (B) Weight fraction of solute (C) Molarity (D) Mole fraction
2) In a compound C, H and N atoms are present in 9 : 1 : 3.5 by weight . Molecular weight of the
compound is 108 g mol-1 . Molecular formula of compound is
(A) C6H8N2(B) C3H4N2 (C) C4H6N (D) C12H16N4
3) The work function of sodium metal is 4.41 × 10–19 J. If photons of wavelength 300 nm are incident on
the metal, the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons will be (h = 6.63 × 10–34 J s; c = 3 × 108 m/s)
________ × 10–21 J?
(A) 222 (B) 444 (C) 333 (D) 111
4) As the temperature is raised from 20°C to 40°C, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes
by a factor of which of the following?
(A) 313/293 (B) 1/2 (C) √313/√293 (D) 1/√2
5) Consider the following reaction:
xMnO4−+yC2O42− + zH+ → xMn2+ + 2yCO 2 + z2H2O
The value's of x, y and z in the reaction are, respectively :
(A) 2,5,and 8 (B) 2,5,and16 (C) 2,7and 8 (D) 2,7and 16
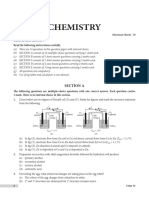
6) The magnitude of work done by a gas that undergoes a reversible expansion along the path ABC
shown in the figure is _______.
(A) 48 (B) 96 (C) 72 (D) 36
7) The Born-Haber cycle for KCl is evaluated with the following data :
ΔfHΘ for KCl = −436.7 kJ mol−1 ;
ΔsubHΘ for K = 89.2 kJ mol−1 ;
ΔionizationHΘ for K = 419.0 kJ mol−1 ;
ΔelectrongainHΘ for Cl (g) = −348.6 kJ mol−1 ;
ΔbondHΘ for Cl 2 = 243.0 kJ mol −1
The magnitude of lattice enthalpy of KCl in kJ mol −1 is _____________ (Nearest integer)
(A) 418 (B) 618 (C) 518 (D) 718
8) The standard Gibbs energy change at 300 K for the reaction 2A ⇋ B + C is 2494.2 J. At a given time,
the composition of the reaction mixture is [A] = 1/2, [B] = 2 and [C] = 1/2. The reaction proceeds in
the: [R = 8.314 J/K/mol, e = 2.718].
(A) Reverse direction because Q<KC
(B) Reverse direction because Q>KC
(C) Forward direction because Q<KC
(D) Forward direction because Q>KC
(From Question 9 to Question 15) Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is
labelled as Reason R.
9.) Assertion (A) : Lithium salts are hydrated.
Reason (R) : Lithium has higher polarising power than other alkali metal group members
10.) Assertion (A) : Dissolved substances can be removed from a colloidal solution by diffusion through a
parchment paper.
Reason (R): Particles in a true solution cannot pass through parchment paper but the colloidal particles
can pass through the parchment paper.
11.) Assertion (A) : Magnesium can reduce Al2O3 at a temperature below 1350C, while above 1350C, while
above 1350C aluminium can reduce MgO.
Reason (R) : The melting and boiling points of magnesium are lower than those of aluminium.
12.) Assertion (A) : During the boiling of water having temporary hardness, Mg(HCO3)2 is converted to
MgCO3.
Reason (R) : The solubility product of Mg(OH)2 is greater than that of MgCO3.
13.) Assertion A : SO 2(g) is absorbed to a large extent than H 2(g) on activated charcoal.
Reason R : SO 2(g) has a higher critical temperature than H 2(g).
14.) Assertion A : Activated charcoal adsorbs SO2 more efficiently than CH4.
Reason R : Gases with lower critical temperatures are readily adsorbed by activated charcoal.
15.) Assertion A: Amylose is insoluble in water.
Reason R: Amylose is a long linear molecule with more than 200 glucose units.
(From Question 9 to Question 15) Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A. Both A and R are true and R is correct Explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true but R is not correct Explanation of A
C. A is true but R is False
D. A is false but R is true
E. Both A and R are False
Answers
1. C
2. A
3. A
4. A
5. B
6. A
7. D
8. B
9. B
10. C
11. C
12. E
13. A
14. D
15. D
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Xii Chem QPDocument6 pagesXii Chem QPnrusinghsamal2006No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Sample PaperDocument6 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Sample PaperDamodar KasukurthiNo ratings yet
- Exam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1Document10 pagesExam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1asjawolverineNo ratings yet
- neet 20Document6 pagesneet 20h47xa4t5No ratings yet
- MSSN Mock Chm101 - 100422Document5 pagesMSSN Mock Chm101 - 100422Adebayo TaiwoNo ratings yet
- SL Paper 1 MsDocument14 pagesSL Paper 1 MsKali stringsNo ratings yet
- JEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperDocument12 pagesJEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- All India Test Series For Iit-JeeDocument16 pagesAll India Test Series For Iit-JeeApex Institute100% (1)
- IIT-JEE Advanced Revision Package: Physical ChemistryDocument172 pagesIIT-JEE Advanced Revision Package: Physical ChemistryprathamNo ratings yet
- XIIth ChemistryDocument7 pagesXIIth ChemistryRiya MalikNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 QDocument4 pagesCHM 101 Qbalikisolayemi2005No ratings yet
- Chemistry ExamDocument8 pagesChemistry ExamAnubrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- QP 3 Xi Chem Paper 3Document5 pagesQP 3 Xi Chem Paper 3technical SiteNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IInd Law PC EDocument14 pagesThermodynamics IInd Law PC Eb72hbapqiNo ratings yet
- JAM 2006 CHEMISTRY TEST PAPERDocument12 pagesJAM 2006 CHEMISTRY TEST PAPERSreedevi KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- Downloading - Viswa Niketan Secondary School (11 & 12)Document32 pagesDownloading - Viswa Niketan Secondary School (11 & 12)Sāŕőj ÝáđåvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 SolutionsDocument25 pagesChapter 14 Solutionsjmb1421No ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1st Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pages1st Exam Multiple Choice Questionsnick200808No ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: Fill in The BlanksDocument13 pagesChemical Energetics: Fill in The BlanksAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistryrs9070515No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument16 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentramanji1021No ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)Document9 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang STPM Trial Exam L6 Semester 1 2019 (Chemistry)AlyciaLeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document17 pagesChemistry: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020QSQFNo ratings yet
- SET 2 Question PaperDocument8 pagesSET 2 Question PaperKrityapriya BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper I: IIT JEE 2010Document9 pagesChemistry Paper I: IIT JEE 2010Jaswinder SamraNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY G-12 (Practice Paper Class 12)Document4 pagesCHEMISTRY G-12 (Practice Paper Class 12)pushkardeshmukh75No ratings yet
- MC & FR Questions For The AP Chemistry Examination (Part 3)Document98 pagesMC & FR Questions For The AP Chemistry Examination (Part 3)Jihyun YeonNo ratings yet
- NAT January SET-2 XI to XIIDocument4 pagesNAT January SET-2 XI to XIIAayush NagpalNo ratings yet
- QP - Chemistry - 12 - Set 1Document6 pagesQP - Chemistry - 12 - Set 1Akash SureshNo ratings yet
- 1markedimpquestions - D24 Mar 2022Document22 pages1markedimpquestions - D24 Mar 2022f20230345No ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Set 1 QuestionsDocument5 pagesChemistry Sample Set 1 QuestionsvksumanthNo ratings yet
- West Bengal University of TechnologyDocument4 pagesWest Bengal University of Technologysayan_dasNo ratings yet
- KV Gurugram Class 12 Chemistry Practice Paper SolutionsDocument10 pagesKV Gurugram Class 12 Chemistry Practice Paper SolutionsSANAJ BSNo ratings yet
- Section-I: IIT - JEE 2014 TW Test MARKS: 65 Time: 1Hr Topics:Chemical EquilibriumDocument5 pagesSection-I: IIT - JEE 2014 TW Test MARKS: 65 Time: 1Hr Topics:Chemical EquilibriumAnshul JindalNo ratings yet
- Phase Test - 1 (Class Xi) First Five ChapterDocument4 pagesPhase Test - 1 (Class Xi) First Five ChapterChutzpahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 151 Final Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesChemistry 151 Final Exam ReviewNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Question PaperDocument10 pagesChem 1 Question PaperAgkayNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Thermodynamics MCQsDocument7 pagesIIT-JEE Thermodynamics MCQsAtharva Sheersh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Modified Xi Chem Hy QP PaperDocument6 pagesModified Xi Chem Hy QP PaperxdhustlesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Papers Class XiDocument26 pagesChemistry Sample Papers Class Xijayanti obcNo ratings yet
- CLIP - Chemical Kinetics PDFDocument4 pagesCLIP - Chemical Kinetics PDFAman JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Gate Chemistry 2015Document12 pagesGate Chemistry 2015cabdiraxmaanlaagoNo ratings yet
- Time: 3.00 Hours) /maximum Marks: 100: This Question Paper Contains 8 Printed PagesDocument8 pagesTime: 3.00 Hours) /maximum Marks: 100: This Question Paper Contains 8 Printed PagesOmpratapNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Document5 pagesXI Chemistry Pre-Annual 02.02.2022Ankit TanwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 213Document7 pagesChemistry 213KoladeNo ratings yet
- QP 4 Xi Chem Paper 4Document5 pagesQP 4 Xi Chem Paper 4technical SiteNo ratings yet
- pH Calculations and Reaction MechanismsDocument14 pagespH Calculations and Reaction MechanismsRaj Nayan DattaNo ratings yet
- GUJCET_D22-Mar-2024Document13 pagesGUJCET_D22-Mar-20249bshrutiyadav16No ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document5 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)DeeptanshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QP - PB XiiDocument5 pagesChemistry QP - PB XiiSnehaNo ratings yet
- PhychemDocument7 pagesPhychemChrystylyn VictorioNo ratings yet
- Chemisstry FormulaDocument11 pagesChemisstry FormulaSharifah RenahNo ratings yet
- Monica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Document65 pagesMonica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Alkash BaigNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Paper QuestionsDocument10 pagesChemistry Practice Paper QuestionsSANAJ BSNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry XII PaperDocument4 pages12 Chemistry XII PaperPrinceNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 & 2Document4 pagesChem 1 & 2Fashola AbdulhamidNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Water AssignmentDocument2 pagesWater AssignmentजggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations 1Document7 pagesChemical Equations 1जggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Water: The Essential Substance for LifeDocument112 pagesWater: The Essential Substance for LifeजggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Allem: - B 3tT-xDocument5 pagesAllem: - B 3tT-xजggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Set BDocument3 pagesSet BजggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Grade-XII Chemistry Entrance Test SolutionsDocument3 pagesGrade-XII Chemistry Entrance Test SolutionsजggerNaut ClassesNo ratings yet
- Mock Nata 2: Read The Instructions CarefullyDocument38 pagesMock Nata 2: Read The Instructions Carefullyvivek vallakatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Belt FrictionDocument8 pagesLab Report Belt Frictionasnaliffah94No ratings yet
- De150103 BMDDocument3 pagesDe150103 BMDseve1No ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument11 pagesExercisestomrannosaurusNo ratings yet
- Board Questions Chapter 1Document15 pagesBoard Questions Chapter 1nehapriyadharshini cbeiarchNo ratings yet
- 36 - Other Electrical SystemDocument52 pages36 - Other Electrical Systemirwan yuniardiNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Q4 Week 3 Module 11Document13 pagesBasic Calculus Q4 Week 3 Module 11Christian EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Silicon Zener Diodes for Stabilizing and Clipping CircuitsDocument4 pagesSilicon Zener Diodes for Stabilizing and Clipping CircuitsMohamad Toufan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Local Manufacture of Cast Resin Transformers: Transmission and DistributionDocument2 pagesLocal Manufacture of Cast Resin Transformers: Transmission and DistributionSharafat AliNo ratings yet
- 01 Service Manual SV600 V4.0 enDocument384 pages01 Service Manual SV600 V4.0 enLuis Felipe Romero100% (3)
- Lecture - Notes - Chemistry - Final - 10232018 PDFDocument130 pagesLecture - Notes - Chemistry - Final - 10232018 PDFAlvin DeliroNo ratings yet
- Holmes 1995Document5 pagesHolmes 1995Milutin MelkaNo ratings yet
- High Conductance Fast Diode: Absolute Maximum Ratings Sym Parameter Value UnitsDocument2 pagesHigh Conductance Fast Diode: Absolute Maximum Ratings Sym Parameter Value UnitsZoltán ÁgostonNo ratings yet
- PHY370 - Chapter 4.0 - Nuclear PhysicsDocument34 pagesPHY370 - Chapter 4.0 - Nuclear PhysicsaisyahNo ratings yet
- Astm F 1281Document12 pagesAstm F 1281Attef BedaweNo ratings yet
- Danfoss Reciprocating Compressors: MT / MTZ / NTZ / VTZDocument16 pagesDanfoss Reciprocating Compressors: MT / MTZ / NTZ / VTZCarlos SilvaNo ratings yet
- The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test Executive SummaryDocument1 pageThe Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test Executive SummaryULdialogueNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 2 Probe TestDocument8 pagesEXPERIMENT 2 Probe TestNur BazilahNo ratings yet
- ABB Price Book 424Document1 pageABB Price Book 424EliasNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument21 pagesSeminar ReportVishnu100% (1)
- Tn-38 Bolt Torque Flanged JointsDocument37 pagesTn-38 Bolt Torque Flanged Jointsprabu prasadNo ratings yet
- Z & H ParameterDocument14 pagesZ & H ParameterTajatNo ratings yet
- 798 - Third Party Testing of HYSD Reinforcement F 500 DSteelDocument1 page798 - Third Party Testing of HYSD Reinforcement F 500 DSteelp.v.n. lakshmanNo ratings yet
- English Full Catalouge Facing UpDocument96 pagesEnglish Full Catalouge Facing Updaboo sanatNo ratings yet
- GEKA - 2 CYLINDER MACHINES Hydracrop Series, Bendicrop 60 and 85Document69 pagesGEKA - 2 CYLINDER MACHINES Hydracrop Series, Bendicrop 60 and 85David Ramirez100% (1)
- Mechanical Professional ElectiveDocument310 pagesMechanical Professional ElectivearunrajNo ratings yet
- Mastery Test in Science 1Document3 pagesMastery Test in Science 1Michelle SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Complex01cssa SolDocument42 pagesComplex01cssa SolZohair KadriNo ratings yet
- EHV AC TransmissionDocument14 pagesEHV AC TransmissionShyamkantVasekarNo ratings yet
- BS en 10109-3-1996Document14 pagesBS en 10109-3-1996Martijn GrootNo ratings yet