Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10.4 Answer Homeostasis-1
10.4 Answer Homeostasis-1
Uploaded by
صالح ابراهيمOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10.4 Answer Homeostasis-1
10.4 Answer Homeostasis-1
Uploaded by
صالح ابراهيمCopyright:
Available Formats
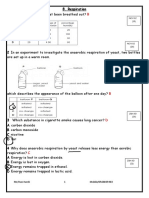
10.
4 Homeostasis
1 How do sweat glands and blood vessels near the skin surface respond when body temperature
rises above normal? D
NOV 04
(21)
2 What is needed in the diet of a man working hard in a hot climate? C
NOV 05
(14)
3 The diagram shows the small intestine, the liver and blood vessel P that joins them.
NOV 05
(15)
Which carbohydrate is found in blood vessel P and which carbohydrate is found in the liver? A
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
4 What happens when the body temperature rises above normal? D
NOV 05
(23)
5 During a long-distance race, the body temperature of an athlete begins to rise.
Which changes occur to help return the body temperature to normal? D
JUN 05
(25)
6 The diagram shows structures within human skin under two different external conditions.
JUN 06
(23)
What are external conditions 1 and 2? A
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
7 What is an example of homeostasis? B JUN 07
A breathing in oxygen (22)
B regulating blood glucose
C removing undigested food through the anus
D urinating to empty the bladder
8 Capillaries near the surface of the skin become wider after drinking large amounts of alcohol.
Why does this cause the body temperature to drop? A
JUN 08
A It allows heat to be lost rapidly from the skin. (22)
B It causes vasoconstriction.
C It prevents vasodilation.
D It stops the person from sweating.
9 After a meal, the concentration of blood glucose increases.
What then causes the concentration of blood glucose to return to normal?
A adrenalin
B blood cells
C insulin
D platelets
10 What is true for a runner, at the end of a marathon race, in a hot climate? B
A sweating and vasoconstriction JUN 09
(23)
B sweating and vasodilation
C vasoconstriction only
D vasodilation only
11 The diagram shows some blood vessels near the surface of the skin.
NOV 10
(23)
If vasoconstriction occurs at X, what happens to the blood flow at Y and Z? A
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
12 The diagram shows blood vessel P which carries digested food from the small intestine to
the liver.
NOV 10
(18)
Which row describes the level of glucose in blood vessel P and the level of glycogen in the liver,
shortly after a meal containing carbohydrates? B
13 What happens when the body temperature rises above normal? D
JUN 10
(22)
14 The graph shows the variation in a person’s body temperature over a period of time.
Which temperature change is likely to cause most sweating? B
NOV 11
P11 (23)
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
15 During a long race, an athlete’s skin temperature rises.
NOV 12
(26)
What causes this? D
A increased sweating
B opening of the pores in the skin
C vasoconstriction of the blood vessels in the skin
D vasodilation of the blood vessels in the skin
16 During a long race, an athlete’s skin temperature rises.
NOV 12
What causes this? D P12 (24)
A increased sweating
B opening of the pores in the skin
C vasoconstriction of the blood vessels in the skin
D vasodilation of the blood vessels in the skin
17 When the body temperature rises above 37°C, which changes help to return the
temperature to normal? D
NOV 12
P13 (25)
18 Read the following sentence.
order to prevent the human body from losing heat, the arterioles supplying the skin become
narrow.
Which process does this sentence describe? A JUN 12
(25)
A constriction
B shivering
C sweating
D vasodilation
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
19 During a long-distance race, the body temperature of an athlete begins to rise.
Which changes occur to help return the body temperature to normal? D
JUN 12
P12 (22)
20 The diagram shows some blood vessels near the surface of the skin.
NOV 13
P11 (23)
If vasoconstriction occurs at X, what happens to the blood flow at Y and Z? A
21 How does sweating cool the body? D
A Sweating causes vasodilation. NOV 13
P11 (26)
B Sweating decreases the water content of the blood.
C Urea and salt are lost from the body in sweat.
D Water in sweat evaporates from the skin.
22 What is the main function of sweating? D
A to excrete urea
NOV 13
B to remove excess salts P13 (25)
C to clean the pores
D to cool the body
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
23 How does insulin move from the pancreas, where it is produced, to the cell where it acts? B
A along nerves JUN 14
B in the blood P11 (17)
C through the digestive system
D through the pancreatic duct
24 The graph shows the energy released by two animals through respiration as the external
temperature changes.
JUN 14
P11 (18)
Which conclusion can be drawn from the graph? D
A Animals 1 and 2 release the least energy at 23 °C.
B Animal 2 always respires faster than animal 1.
C As the temperature rises, respiration always increases.
D The rate of respiration is the same for both animals at 23°C.
25 Which responses occur when a person is too hot? D
JUN 14
P12 (23)
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
26 Which numbered parts form the central nervous system? B Q25 0610/22/F/M/22
A 1 only B 1 and 2 C 2 and 3 D 3 only
Q26 0610/22/F/M/22
27 The diagram shows a section through the eye of an octopus. Octopuses have eyes that are
similar in structure and function to human eyes. D
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
Q27 0610/22/F/M/22
28 A person eats a large bowl of rice. Rice contains starch. What happens to the amounts of
insulin and glucagon in their body? C
Q24 0610/23/M/J/22
29 The diagram shows the junction between two neurones.
What is labelled at X? C
A neurotransmitter
B vesicle
C neurotransmitter receptor molecule
D synaptic cleft
Q25 0610/23/M/J/22
30 The diagram shows the density of rods and cones across a section of the retina. What is the
position of the fovea? A
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
31 What is the synthetic plant hormone 2,4-D used for? C Q26 0610/23/M/J/22
A genetic engineering
B inhibiting phototropism
C killing weeds
D promoting germination
MR. Hani tarek 0568035983
You might also like
- Combined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisDocument76 pagesCombined Past Paper Questions On Excretion and HomeostasisRamesh Iyer81% (26)
- BIO271 - Practice MCQDocument6 pagesBIO271 - Practice MCQEric LuongNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Revised A5Document720 pagesAnaesthesia Revised A5barn003100% (1)
- Coordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 2 QPDocument14 pagesCoordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 2 QPIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 2 QPDocument14 pagesCoordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 2 QPNathan Ssekamatte100% (1)
- NERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM (IB-DP BIOLOGY) - Multiple Choice Type QuestionsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 3Document6 pagesUntitled 3Chyntia D. RahadiaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologia Do Sistema Cardiovascular II e III - TextoDocument6 pagesFisiologia Do Sistema Cardiovascular II e III - TextoDavidson De AraújoNo ratings yet
- Ulangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Document99 pagesUlangkaji Berfokus SPM 2015 p1 Theme 2Norizan DarawiNo ratings yet
- Sure UnsureDocument20 pagesSure Unsureohemgee wowNo ratings yet
- Water Injection BodyDocument13 pagesWater Injection BodyoviangNo ratings yet
- Water, ElectrolyteDocument15 pagesWater, Electrolytevicky_law_2No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Jphysiol 2014 272104Document18 pagesJphysiol 2014 272104mustakNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 1Document6 pagesHomeostasis 1challista amandaNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument23 pagesCoordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 1 QPIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)Document22 pages2020 Form 5 Biology Mock Exam: A Saliva Secretion Is An Involuntary Action Controlled by U (Medulla)UniversityJCNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 1 QP PDFDocument23 pagesCoordination & Response (Multiple Choice) 1 QP PDFClinton Chikengezha0% (1)
- Biology MCQsDocument18 pagesBiology MCQsZaw Linn PhyoNo ratings yet
- PhisioDocument15 pagesPhisiojohnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For 9th IgcseDocument14 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For 9th IgcseFatma Zorlu100% (1)
- Class X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesDocument2 pagesClass X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesBornil Bikash BhuyanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument19 pagesBIOLOGYAnum ObaidNo ratings yet
- Excretion Question AnsweredDocument9 pagesExcretion Question AnsweredKeelah BennNo ratings yet
- Https Smiletutor - SG Wp-Content Uploads 2021 05 Sec-4-Pure-Biology-2018Document456 pagesHttps Smiletutor - SG Wp-Content Uploads 2021 05 Sec-4-Pure-Biology-2018Neilson Alexandro TjheNo ratings yet
- Previous Exam Paper PHBG 3716Document8 pagesPrevious Exam Paper PHBG 3716TsholofeloNo ratings yet
- Control of Blood Tissue Blood Flow: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDDocument25 pagesControl of Blood Tissue Blood Flow: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDNermeinKhattabNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 7 9 2Document19 pagesHomeostasis 7 9 2Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cell, Blood and Muscle PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCell, Blood and Muscle PhysiologyMaheen AnwaarNo ratings yet
- Careful With That Colloid, Eugene..Document36 pagesCareful With That Colloid, Eugene..Tom WoodcockNo ratings yet
- 12 The Blood Circulatory System - AnswersDocument4 pages12 The Blood Circulatory System - AnswersDonnabell PagaraNo ratings yet
- Classified - Enzymes and Metabolism - DR Haitham AbdAllahDocument14 pagesClassified - Enzymes and Metabolism - DR Haitham AbdAllahJojo AmirNo ratings yet
- Renal Function in The Malnourished Child: Gustavo Gordillo-Paniagua and Silvestre FrenktDocument20 pagesRenal Function in The Malnourished Child: Gustavo Gordillo-Paniagua and Silvestre FrenktAgnihotram GopinathNo ratings yet
- MRCS Crtical CareDocument135 pagesMRCS Crtical CareArijeet77No ratings yet
- Gr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)Document13 pagesGr. 10 Bio Semester 2 Revision Sheet Answer Key (2023-2024)8fr4xqpcb8No ratings yet
- Instructions:: Section A: (30 Marks)Document30 pagesInstructions:: Section A: (30 Marks)李安逸No ratings yet
- Body Fluid and Circulation - Board Pattern Test (BPT)Document2 pagesBody Fluid and Circulation - Board Pattern Test (BPT)Dr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Coordination and ResponseDocument1 pageChapter 3: Coordination and ResponseNurfatin JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Surmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Document20 pagesSurmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1leone shikukuNo ratings yet
- Penelitian PenyelamanDocument4 pagesPenelitian PenyelamanErick SupondhaNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GDocument55 pagesRenal Physiol-OGY: DR I.GAmanuel DinaNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Test Yourself 12.1 (Page 246)Document3 pagesHomeostasis: Test Yourself 12.1 (Page 246)lee100% (1)
- MedCosmos Surgery - MCQ - General SurgeryDocument167 pagesMedCosmos Surgery - MCQ - General SurgeryEmmanuel DanielsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Principles of Fluid Management Apr 2020Document2 pagesLecture Notes On Principles of Fluid Management Apr 2020Den PeraNo ratings yet
- Are Set Up in A Warm RoomDocument27 pagesAre Set Up in A Warm Roomصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22Document3 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Sample Mock Paper Term 2 Exam 2021 22VedantNo ratings yet
- (OS201) E06 T06 SGD Concepts in RegulationDocument8 pages(OS201) E06 T06 SGD Concepts in RegulationJoe JoeNo ratings yet
- Bio P1 SPMTrialDocument23 pagesBio P1 SPMTrialCikgu Zaid IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Fat Emboli in LiposuctionDocument34 pagesFat Emboli in LiposuctionRicky Herdianto100% (1)
- Physiology Feedback: Finals Sem1 Ay 2017-2018: D. Both A & B (Phospagen andDocument4 pagesPhysiology Feedback: Finals Sem1 Ay 2017-2018: D. Both A & B (Phospagen andvicbart11No ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument82 pagesCase PresentationChadi Alraies100% (8)
- Ans02 HomeostasisDocument6 pagesAns02 Homeostasisngsuan.2020No ratings yet
- CH 11+12 MCQDocument13 pagesCH 11+12 MCQHungryPanda’s KitchenNo ratings yet
- CH 11+12 MCQDocument13 pagesCH 11+12 MCQHungryPanda’s KitchenNo ratings yet
- A4 QB-MC Ch18 HomeostasisDocument13 pagesA4 QB-MC Ch18 HomeostasisReg ChooNo ratings yet
- 23-26 An Autopsy Case of Decompression Sickness. Hemorrhages in The Fat Tissue and Fat EmbolismDocument4 pages23-26 An Autopsy Case of Decompression Sickness. Hemorrhages in The Fat Tissue and Fat EmbolismLoredana MorosanuNo ratings yet
- REVISION TEST U-1,2,7,12 Science: Class 10 STDDocument2 pagesREVISION TEST U-1,2,7,12 Science: Class 10 STDDynamicdharsan 31XOR1No ratings yet
- 5090 w12 QP 12Document20 pages5090 w12 QP 12mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Biology Test Class 11Document6 pagesBiology Test Class 11orphic20007No ratings yet
- Year 12 Cat Make Up Bio TRSDocument10 pagesYear 12 Cat Make Up Bio TRSNjoroNo ratings yet
- G5 W1 Answer KeyDocument4 pagesG5 W1 Answer Keyصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Inspire International Academy Social Studies Second Term Worksheet 2 Grade 5 - Time and ClimateDocument3 pagesInspire International Academy Social Studies Second Term Worksheet 2 Grade 5 - Time and Climateصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Q4 DrugsDocument2 pagesQ4 Drugsصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Case Study "Ethical Aims" Book Page 65 (Answers)Document1 pageCase Study "Ethical Aims" Book Page 65 (Answers)صالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/11Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/11صالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42صالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Are Set Up in A Warm RoomDocument27 pagesAre Set Up in A Warm Roomصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- 4 (B) (I) Largest Clear Area / Has Prevented Most Growth / Killed The Most Bacteria / AVPDocument2 pages4 (B) (I) Largest Clear Area / Has Prevented Most Growth / Killed The Most Bacteria / AVPصالح ابراهيمNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument48 pagesIntestinal ObstructionMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Updated Directory of Iwc As of April 24, 2012Document7 pagesUpdated Directory of Iwc As of April 24, 2012Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Case Report PresentationDocument19 pagesCase Report PresentationCheyenne PetersNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Standards For Physiotherapy and Service DeliveryDocument54 pagesQuality Assurance Standards For Physiotherapy and Service DeliveryNestor Balboa0% (1)
- Holaway Et Al Intolerance of Uncertainty in OCD and GAD J Anxiety Disorders 2006Document17 pagesHolaway Et Al Intolerance of Uncertainty in OCD and GAD J Anxiety Disorders 2006Jean BoutiereNo ratings yet
- Medical InventoryDocument33 pagesMedical InventoryMiguel Elias Mustafa MichelNo ratings yet
- CRESOPHENE, Solution For Dental Use: Physicians Prescribing InformationDocument1 pageCRESOPHENE, Solution For Dental Use: Physicians Prescribing InformationTasyaSoeriaAtmadja100% (1)
- A GUIDE TO AIM GLOBAL BUSINESS - Uganda PDFDocument40 pagesA GUIDE TO AIM GLOBAL BUSINESS - Uganda PDFWa Tu LeeNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument2 pagesScriptCas FortesNo ratings yet
- Paper 33 Evaluation of Clinical Laboratory Tests' Turnaround Time in A Tertiary Hospital in Democratic Republic of The CongoDocument16 pagesPaper 33 Evaluation of Clinical Laboratory Tests' Turnaround Time in A Tertiary Hospital in Democratic Republic of The CongoDiego PérezNo ratings yet
- Manuskrip: Oleh: Dias Syaima Husniyah NIM. 1501009Document12 pagesManuskrip: Oleh: Dias Syaima Husniyah NIM. 1501009elsaNo ratings yet
- Life of Rizal Act 3Document2 pagesLife of Rizal Act 3Arian Keith AquinoNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSienaNo ratings yet
- FCFRP Relatório BCRP - Periódicos Não DesdobradosDocument500 pagesFCFRP Relatório BCRP - Periódicos Não Desdobradosmarcelo_vpfNo ratings yet
- AddDocument4 pagesAddteacherashleyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Airway ManagementDocument54 pagesPediatric Airway ManagementCardiacCareCenterMCHNo ratings yet
- Dental Arch Morphology in Normal OcclusionsDocument4 pagesDental Arch Morphology in Normal Occlusionsdianpn27No ratings yet
- CaffeineDocument6 pagesCaffeinejust_checkingNo ratings yet
- Ethic in NursingDocument246 pagesEthic in Nursingsyikir100% (1)
- Medical Disorders and OrthodonticsDocument21 pagesMedical Disorders and OrthodonticsfarisNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia For Neurosurgery-PIIS1472029919302656Document6 pagesAnaesthesia For Neurosurgery-PIIS1472029919302656james Wilson09No ratings yet
- Changes in The Body Following DeathDocument3 pagesChanges in The Body Following Deathbreech_16loveNo ratings yet
- Refraction 2Document47 pagesRefraction 2RuDy RaviNo ratings yet
- CHN - CoparDocument51 pagesCHN - Coparljealou2002No ratings yet
- OncologyDocument7 pagesOncologyTrincyNo ratings yet
- Degradation of PurineDocument36 pagesDegradation of PurineShrey SundriyalNo ratings yet
- Summer - 2023 Phase - III Time Table Remaining UG - PG and University Courses University Theory Examinations - 190523Document66 pagesSummer - 2023 Phase - III Time Table Remaining UG - PG and University Courses University Theory Examinations - 190523shivaNo ratings yet
- MsdsDocument4 pagesMsdsAdrian MerinoNo ratings yet