Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3
Uploaded by
Allysa Kim DumpOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3
Uploaded by
Allysa Kim DumpCopyright:
Available Formats
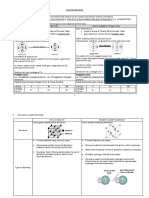
ChemIstry
General Chemistry II
Exist between molecules Hydrogen
Different types of attractive forces Bond
Determines the physical London
Brief History of Chemistry properties of a Dispersion
compound Force
• Chemistry – study of matter; study of everything
that occupies space and has mass
o Organic Chemistry Intermolecular
o Physical Chemistry
o Biological Chemistry
o Analytical Chemistry
o Inorganic Chemistry
• Antoine Van Lavoisier – Father of Modern
Chemistry Intramolecular Intramolecular
• Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev – Father of Periodic
Table
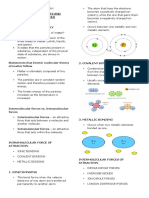
Intermolecular Forces
• Positive Ions (Cation) – an atom that loses an
electron in its valence shell - Forces between individual particles such as
• Negative Ions (Anion) – atoms that gains an atoms, ions and molecules.
electron in its valence shell - Cations (positively ion) are attracted to Anions
• Valence Shell - outermost shell of any atom (negatively ion) therefore connecting the two
• Octet Rule - tendency of atoms to prefer to have intramolecular bond through an intermolecular
eight electrons in the valence shell. force
• 1000 B.C. – Ancient Egypt considered chemistry as - Directly related to the properties of solid, liquid,
an art and gas
o perform embalming on the dead o Strong Attractive Forces in Gas – can cause
(mummification) gas behavior to deviate to the ideal gas
o uses chemistry to make cosmetics (kohl) o Strong Attractive Forces in Liquid – properties
o uses chemistry to make paper made up of such as boiling point, heat of vaporization,
papyrus plant vapor pressure, vapor pressure and viscosity
• Great Roman Empire – melted alloy to remold depend greatly on the forces
metal into different things o Strong Attractive Forces in Solid - properties
• 15th Century – alchemist appeared and attempted such as melting point and heat of fusion are
to use chemistry to make them immortal and solely dependent on the forces
convert metal into gold but they failed and left their
apparatuses and pave the way for the modern 1. Ionic Compound
scientist to discover analytical chemistry - Formula unit (smallest representative unit)
- Electrostatic attraction between a metal and a
Types of Forces
non-metal ion
1. Intramolecular Forces – bond within the - No sharing of electrons in bonds
molecule - Each negative ion is surrounded by positive ions
and vice versa
2. Intermolecular Forces – attractive forces
- The greater the charged density of ions in a crystal,
between molecules
the stronger the forces of attraction, and the
Forces Description Examples:
stronger the force of attraction, the higher the
Intramolecular Bonding Forces Ionic
boiling and melting points and other related
Compound
properties
Exist Within Molecules Covalent
o High Charged Density – an ion with a relatively
Compound
small size and relatively high charge
Determine the chemical Metallic
properties of a Compound
compound
Intermolecular Attractive Forces (non- Dipole-Dipole
binding)
ChemIstry
General Chemistry II
• List of Ionic Compounds Based on their Groups
• Group 1 Metals – Loses
one electron (Na, K, Rb,
Cs, Li, Fr)
• Group 7 Non-Metals –
Gains one electron (F, Cl,
Br, I, At)
• Group 2 Metals – Loses 2 electrons (Be, Mg, 3. Metallic Compound - atomic unit (smallest
Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra) representative unit); ex: Iron Sheet
• Group 6 Non-Metals – Gains 2 electrons (O,
S, Se, Te, Po)
• Group 1 Metals – Loses 1
electron (Na, K, Rb, Cs, Li, Intramolecular Forces
Fr)
1. Dipole-Dipole Forces
• Group 6 Non-Metals –
• Dipole - polarized molecule having partially
Gains 2 electrons (O, S, Se,
positive and negative poles
Te, Po)
• Polarity – molecule having a region of partial
charge either positive or negative
• Group 2 Metals – Loses 2 electrons (Be, Mg,
Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
• Group 7 Non-Metals – Gains 1 electron (F, Cl,
Br, I, At)
- It is not a chemical bond
- Occurs between polar covalent bond where one
part of the molecules has a partial positive charge
and the other part of a partial negative charge
EX:
2. Covalent Compound
- molecular unit (smallest representative unit)
- consists of the mutual sharing of one or more
pairs of electrons between two atoms Dipole
• Polar Covalent Bond - unequal sharing of
electrons resulting in partial charges of atoms; ex: Dipole-Dipole
HCl, SO2 Force
• Non-Polar Covalent Bond - equal sharing of
electrons therefore having no charges in atoms; ex:
Cl2, O2
You might also like
- Basic ChemistryDocument43 pagesBasic ChemistryKarim Wasi100% (6)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Chem PDFDocument37 pagesChem PDFJhonsen BarengNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Chem SummaryDocument75 pagesO Level Pure Chem SummaryEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- Forces of Attraction Unit 1 CAPE Chem (PDF)Document70 pagesForces of Attraction Unit 1 CAPE Chem (PDF)Shadecia Dinnall100% (1)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- GenChem (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)abgolena5238valNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- 6.1 SolidDocument30 pages6.1 SolidAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- PHYSCI - First Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesPHYSCI - First Quarter NotesCjNo ratings yet
- 06 CB Notes 2022Document6 pages06 CB Notes 2022Fitri armaya Jeffri (Greendaless)No ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Matter Mol Scale Part 2Document25 pagesMatter Mol Scale Part 2naomikarenbellNo ratings yet
- C2 Revision Slides V3 Questions MS HDocument35 pagesC2 Revision Slides V3 Questions MS HNeen NaazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - States of MatterDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - States of MatternnooorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Bonding in SolidsDocument27 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Bonding in Solidsmhay martinezNo ratings yet
- 1 3-BondingDocument20 pages1 3-BondingBhPO2023No ratings yet
- 9 Chemical BondsDocument19 pages9 Chemical BondsAdiba TasnimNo ratings yet
- General - Chemistry-ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral - Chemistry-ReviewerShiela Mae VisayaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 002Document7 pagesGen Chem 002jazz vergsNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLDocument46 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 4 Intermolecular Forces JLFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Materials - Lect 2Document38 pagesThe Nature of Materials - Lect 2Safi Ullah WarraichNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Materials - Lect 2Document38 pagesThe Nature of Materials - Lect 2Safi Ullah WarraichNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDocument31 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsvpetro250No ratings yet
- GenChem 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGenChem 2 ReviewerPia Aure MartinezNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument1 pageStructure and BondingeohomegrownappsNo ratings yet
- MLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyDocument15 pagesMLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Crystalline Solids: 4. Clean Cleavage With KnifeDocument5 pagesCrystalline Solids: 4. Clean Cleavage With KnifeShin Se KyungNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Lesson 1Document5 pagesUnit 3 - Lesson 1api-320784618No ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- EOG 11e Lecture Ch02Document9 pagesEOG 11e Lecture Ch02Kadde RichardNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesChemical BondsARDIUZNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructureDocument5 pagesGrade 12 1st Quarter - Week Three Chemical Bonds and Lewis Structurenicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Unidad 61Document36 pagesUnidad 61Eloisa OvandoNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument3 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- First Topic - Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesFirst Topic - Chemical BondingSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pages2 2 2 Bonding and StructureAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument17 pagesMetallic Bondingaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State: Dr. Amiya PriyamDocument82 pagesIntroduction To Solid State: Dr. Amiya PriyamVishal VaibhavNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lesson 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lesson 2Andrea Marie LaquiñaNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioDocument7 pages2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioRayumaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Short NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry Short NotesZainab HassanNo ratings yet
- Compilation of DUDE and Name Reactions 2Document24 pagesCompilation of DUDE and Name Reactions 2Pratham SinghNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document45 pagesModule 1Leigh Kyster BenlotNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Notes Semester 2Document37 pagesChemistry Exam Notes Semester 2AnjaliNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Lecture 3Document74 pages1st Year Chemistry Lecture 3Sarosh NaqviNo ratings yet
- Defining RockDocument24 pagesDefining Rockgeneabi012No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Document26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Minerals ChemistryDocument25 pagesLecture 2 Minerals ChemistryJonathan Lucas HilliardNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- q3 Engacprof ReviewerDocument3 pagesq3 Engacprof ReviewerAllysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion/Research/Career Advocacy/Culminating ActivityDocument5 pagesWork Immersion/Research/Career Advocacy/Culminating ActivityAllysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- General Physics IIDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics IIAllysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- English: For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument3 pagesEnglish: For Academic and Professional PurposesAllysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet