Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GenChem (Lesson 1)
Uploaded by
abgolena5238val0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThis document discusses the kinetic molecular theory and intermolecular forces of attraction. It defines the kinetic molecular theory and describes the states of matter in terms of particle motion and interaction. It then describes the different types of intramolecular and intermolecular forces, including ionic, covalent, metallic and hydrogen bonds. It discusses how intermolecular forces differ between solids, liquids and gases.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the kinetic molecular theory and intermolecular forces of attraction. It defines the kinetic molecular theory and describes the states of matter in terms of particle motion and interaction. It then describes the different types of intramolecular and intermolecular forces, including ionic, covalent, metallic and hydrogen bonds. It discusses how intermolecular forces differ between solids, liquids and gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)
Uploaded by
abgolena5238valThis document discusses the kinetic molecular theory and intermolecular forces of attraction. It defines the kinetic molecular theory and describes the states of matter in terms of particle motion and interaction. It then describes the different types of intramolecular and intermolecular forces, including ionic, covalent, metallic and hydrogen bonds. It discusses how intermolecular forces differ between solids, liquids and gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
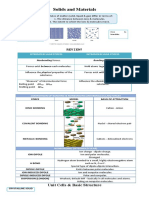
Lesson 1: Kinetic Molecular Model and Intermolecular Forces of Attraction
Forces
- Any type of force causing objects to come close
to each other.
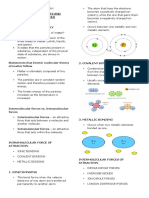
Kinetic Molecular Theory Types of Forces of Attraction
- Properties of matter in terms of intermolecular 1. Intramolecular Forces (inside)
forces of attraction and kinetic energy of - Attractive forces between atoms of molecules.
individual particles. 2. Intermolecular Forces (outside)
- All matter is made up of tiny particles that are - Attraction between molecules.
constantly in motion. - Weaker than intramolecular forces.
- Speed of particles = temperature.
- Solids, liquids, and gases differ in distance,
freedom of motion, and interaction of particles. Types of Intramolecular Forces
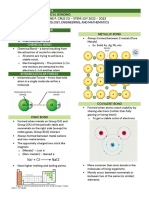
Solid Liquid Gas 1. Metallic Bond
Volume and Fixed shape Fixed Unfixed - Consists of positive ions and a sea of electrons.
Shape and volume. volume, shape and - Metallic elements.
unfixed volume. 2. Ionic Bond
shape. - Attraction between two oppositely charged
Compressib Almost Slightly Compressi ions.
ility incompressi compressi ble.
- Metal and non-metallic elements.
ble. ble.
3. Covalent Bond
Density High High Low
- Sharing of electrons to form electron pairs
Motion Vibration in Random, Random,
place. medium fast, between atoms.
speed, covers - Non-metallic elements.
limited large Types of Covalent Bond
distances. distances.
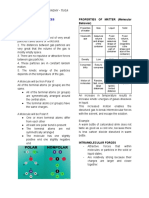
1. Polar Bond
- Uneven sharing of electrons.
Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and Liquids
2. Non-Polar Bond
- Solids and liquids are in condensed state. - Equal sharing of electrons.
Compacted.
Ways to Determine Bond Polarity
1. Difference in electronegativity of atoms.
Molecules of Solid Molecules of Liquid - Ability of an atom to attract itself to the
Closely packed and Closed together with electrons in a chemical bond.
arrange in an organized little spaces between - Elements with high electronegativity have a
manner. each other. greater tendency to attract electrons than the
Vibrating around fixed Higher collision rate than elements with low electronegativity.
locations. gases 2. Dipole Moment.
Always in constant In constant motion, - Occurs when there is a separation of charge.
motion. moving past one another. - A quantitative measure of the polarity of a
Held together by strong Held together by bond.
intermolecular forces. attractive intermolecular
forces.
charge and the other part a partial negative
charge.
4. Hydrogen Bond
- Attraction between a highly electronegative
atom (N, O, and F) and a hydrogen atom.
Intermolecular Forces
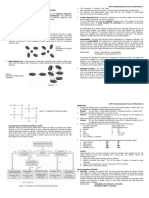
1. Ion-Dipole Bond
- Attractive forces between an ion and a polar
molecule.
- Dipole
Bond or molecule whose ends have
opposite charges.
2. London Dispersion (Van der Waals Forces)
- Occurs when the electrons around a molecule
are unevenly distributed causing a temporary
dipole.
3. Dipole-Dipole Bond
- occurs between polar covalent molecules where
one part of the molecule has a partial positive
You might also like
- Acoustics and Vibrations - Noise and Vibration Control - Beranek - Noise and Vibration Control Engineering - Wiley - 1992 - Ch11 Vibration IsolationDocument22 pagesAcoustics and Vibrations - Noise and Vibration Control - Beranek - Noise and Vibration Control Engineering - Wiley - 1992 - Ch11 Vibration IsolationgrymiNo ratings yet
- Shiloh 2019Document24 pagesShiloh 2019Daniel Ojevwe100% (1)
- General Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIJoven EstebanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- GENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3Document2 pagesGENCHM2 Reviewer Week2&3Allysa Kim DumpNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- General - Chemistry-ReviewerDocument11 pagesGeneral - Chemistry-ReviewerShiela Mae VisayaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: © 20 Pearson Education, IncKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Genchem2Document12 pagesLESSON 4 Genchem2J NavarroNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidJohanna Rachel S. VillasisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- GenChem 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGenChem 2 ReviewerPia Aure MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter # 04Document2 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter # 04AimanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAbigail OconNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem IMFADocument2 pagesGen Chem IMFArhonz.hildawaNo ratings yet
- Bonding 2005Document28 pagesBonding 2005anoopchauhanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A General Chemistry 2Ganilyn Ponciano0% (3)
- Gen - Chem - R1Document3 pagesGen - Chem - R1Kevin JamilNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Ii LecturesDocument18 pagesGen Chem Ii LecturesHANNA ROLISH DIGAMONNo ratings yet
- Composition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthDocument3 pagesComposition: Can Be Found Inside The EarthGabNo ratings yet
- First Topic - Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesFirst Topic - Chemical BondingSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- MLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyDocument15 pagesMLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 1 - CDocument3 pagesQ3 Lesson 1 - CCamille Guzman CabisoNo ratings yet
- General Chem 2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesGeneral Chem 2 ReviewerBeverly A PanganibanNo ratings yet
- CHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0102 FDDocument22 pagesCHM2 11 - 12 Q3 0102 FDJerome ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022Document6 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Chemistry 2 Quarter 3 - Module 1 - AY 2021 - 2022almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Chem ReviewerNIKKI GRACE MAGDALI100% (1)
- PHYS SCI NotesDocument3 pagesPHYS SCI Notesciara galimbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- IMF Liquids and SolidsDocument29 pagesIMF Liquids and SolidsAly HannahNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document24 pagesGen Chem 2jkierstencvergaraNo ratings yet
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Document26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Why To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentDocument22 pagesWhy To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentdNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LectureDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding LectureSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Chem ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Bonding & Structure NotesDocument11 pagesBonding & Structure NotesKamran TajbakhshNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionJose Ferdinand Marcos Jay SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- Attracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsDocument6 pagesAttracted To Intermolecular Forces Part A: Frayer Model of Liquids and SolidsGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocument49 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsfuatNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary BondingDocument6 pagesPrimary and Secondary BondingosmondNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular and Intramolecular MoleculeDocument2 pagesIntermolecular and Intramolecular MoleculeIvy SepeNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioDocument7 pages2 Chemical Basis - AnaphysioRayumaaaNo ratings yet
- Chang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesDocument35 pagesChang - Lecture Slides of Chap11-Intermolecular ForcesJiselle GoconNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem - LectureDocument7 pagesGen Chem - LectureKean MercadoNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- 1 3-BondingDocument20 pages1 3-BondingBhPO2023No ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 11 Solids and LiquidsDocument13 pagesGen - Chem 11 Solids and Liquidschasesawadjaan142No ratings yet
- Crystalline Solids: 4. Clean Cleavage With KnifeDocument5 pagesCrystalline Solids: 4. Clean Cleavage With KnifeShin Se KyungNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument16 pagesBondingactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- C2-Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pagesC2-Chemical Basis of LifeLorrine MagramoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- FORM 5 VariationDocument35 pagesFORM 5 VariationAMOS YAP WEI KANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Impact On Performance in Student-Athletes - Reality AnDocument36 pagesNutritional Impact On Performance in Student-Athletes - Reality AnAbbygail WasilNo ratings yet
- ILSAS DistributionDocument15 pagesILSAS DistributionFaizal FezalNo ratings yet
- Recipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaDocument11 pagesRecipe For BPP Ncii UaqteaPJ ProcoratoNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 7 - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesMock Test 7 - Answer KeyThuỳ Linh Đinh TháiNo ratings yet
- Beacon Atlantic Short Spec R1 141118 NBDocument4 pagesBeacon Atlantic Short Spec R1 141118 NBRayodcNo ratings yet
- Isotermas de Sorcion ManzanaDocument12 pagesIsotermas de Sorcion ManzanaFELIPEGORE ArbeláezNo ratings yet
- AEE-Civil & Mechanical - KeyDocument47 pagesAEE-Civil & Mechanical - KeymadhugangulaNo ratings yet
- MOV S ManualDocument84 pagesMOV S ManualAbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- BookDocument182 pagesBookSebastian Aguayo FritzNo ratings yet
- T1001W6F011Document1 pageT1001W6F011Asim SaleemNo ratings yet
- 21 Lesson For 21st CenturyDocument16 pages21 Lesson For 21st CenturySamia GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsDocument35 pagesSilo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsAhmed TalaatNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Lie in PregnancyDocument2 pagesAbnormal Lie in PregnancyAlexander EnnesNo ratings yet
- Bit Bank (KSM)Document96 pagesBit Bank (KSM)nagendra.jodhaNo ratings yet
- Krishna Kathamrita Bindu 167Document5 pagesKrishna Kathamrita Bindu 167Citraka dasaNo ratings yet
- Traverse SurveyingDocument2 pagesTraverse Surveyingchaudharylucky1818.sNo ratings yet
- TDS - Pidicryl 120V - UpdatedDocument1 pageTDS - Pidicryl 120V - Updatedhai nguyenNo ratings yet
- Past-Sensitive Pointer Analysis For Symbolic ExecutionDocument12 pagesPast-Sensitive Pointer Analysis For Symbolic Execution石远翔No ratings yet
- March, 2023 Domestic: Customer Number: Billing Month: Tariff/Customer Class: Bill ID: 158856022712Document1 pageMarch, 2023 Domestic: Customer Number: Billing Month: Tariff/Customer Class: Bill ID: 158856022712Yasir KhanNo ratings yet
- What and Who Is A Human PersonDocument22 pagesWhat and Who Is A Human Personjay100% (1)
- Laughlin - A Comparison of Turbine Pulley Design Philosophies With Historical PerspectiveDocument3 pagesLaughlin - A Comparison of Turbine Pulley Design Philosophies With Historical Perspectivedarkwing888No ratings yet
- SP 187 BDocument4 pagesSP 187 BBryan CarvacheNo ratings yet
- Work From Home Project: Peshawar Model SchoolDocument4 pagesWork From Home Project: Peshawar Model SchoolShabir RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: 01 Vectors and Vector Operations: Part A: Triangle - Open The Vector SimulationDocument7 pagesLab Assignment: 01 Vectors and Vector Operations: Part A: Triangle - Open The Vector SimulationRahik IhttipasNo ratings yet
- Ansi Ies RP-8-21Document547 pagesAnsi Ies RP-8-21cristianbaileyeNo ratings yet
- Robotic: Differential Motion and JacobianDocument37 pagesRobotic: Differential Motion and Jacobian李尚倫33% (3)
- Combined Cycle Power Plant - Summary StudyDocument3 pagesCombined Cycle Power Plant - Summary StudydndudcNo ratings yet