Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intermolecular and Intramolecular Molecule
Uploaded by
Ivy SepeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intermolecular and Intramolecular Molecule
Uploaded by
Ivy SepeCopyright:
Available Formats
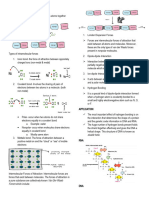
Intermolecular force and
intramolecular force
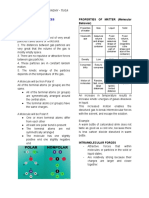
INTERMOLECULAR INTRAMOLECULAR
FORCE FORCE
Forces that hold molecules in a
SIMILARITIES Forces that hold atoms in a
substance. molecule
Determine the state of matter Determine chemical behavior
(solid/liquid/gas) and their They have their own types
of a substance
They are both types of forces
physical properties such as Chemical bonds.
that determine the chemical
melting/ boiling point etc. Stronger than intermolecular
and physical characteristics of
Attractive forces. forces.
substances
Weaker than intramolecular Categorized into covalent,
forces. ionic, and metal bonds.
categorized into dipole-dipole
forces, London dispersion forces,
and hydrogen bonding forces.
Sepe, Carina Ivy Marie A.
ABM 11-Y1-3A
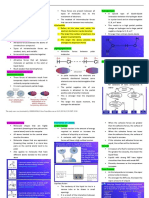
Intermolecular force and
intramolecular force
INTERMOLECULAR INTRAMOLECULAR
FORCES FORCES
IONIC BOND
VAN DER WAAL'S FORCE OF
- This bond is formed by the complete
ATTRACTION transfer of valence electron(s) between
- This force of attraction is due to the atoms.
interaction between uncharged chemical COVALENT BOND
species such as atoms and molecules. - This bond is formed between atoms that
DIPOLE-DIPOLE FORCE OF have similar electronegativities—the affinity
ATTRACTION or desire for electrons.
- Occurs only when the attracting a. nonpolar covalent bond is formed
between same atoms or atoms with very
molecules are permanently polar.
similar electronegativities.
HYDROGEN BONDING OH H-
b. A polar covalent bond is formed when
BONDING atoms of slightly different electronegativities
- This is a special kind of dipole-dipole share electrons.
interaction that occurs specifically METALLIC BONDING
between a hydrogen atom bonded to - This type of covalent bonding specifically
either oxygen, nitrogen, and a fluorine occurs between atoms of metals, in which the
atom. valence electrons are free to move through
the lattice.
Sepe, Carina Ivy Marie A.
ABM 11-Y1-3A
You might also like
- Chemistry 2Document7 pagesChemistry 2Kizzy Rae SolitoNo ratings yet
- Phyphar Chapter 2Document7 pagesPhyphar Chapter 2KATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Pointers To Review ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Chem 2 Pointers To Review ReviewerAlkin RaymundoNo ratings yet
- GenChem 2 ReviewerDocument13 pagesGenChem 2 ReviewerPia Aure MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and LiquidJohanna Rachel S. VillasisNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument3 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionJose Ferdinand Marcos Jay SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral ChemistryJoana Jane MarquezNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesGen Chem ReviewerLawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 1Document16 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 1blackmage016No ratings yet
- Lesson2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pagesLesson2 Intermolecular ForcesJenny Rose Butac Ocden100% (1)
- 3rd QTR - Notes 3 - Chemical StructuresDocument7 pages3rd QTR - Notes 3 - Chemical StructuresDolor GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Document26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Chemical Bonding and Polarity: MetalsDocument2 pagesRevisiting Chemical Bonding and Polarity: MetalsChristma Adyneth EboraNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY 3rd Quarter ReviewerJanelle NopuetoNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGenChem2 ReviewerAshley TupasNo ratings yet
- L I L I: Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesL I L I: Chemical BondingMark IanNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesDocument19 pagesIntramolecular Forces and Intermolecular ForcesAly ReyesNo ratings yet
- Quibot, Mikaela (BSCE 1A) - Discussion Post No. 2Document1 pageQuibot, Mikaela (BSCE 1A) - Discussion Post No. 2Mikaela QuibotNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1 PDFDocument4 pagesReviewer 1 PDFNorjiel BrandinoNo ratings yet
- Compound Type of Intramolecular Force/Chemical Bond Strongest Type of Intermolecular Force Present Reason For ClassifyingDocument2 pagesCompound Type of Intramolecular Force/Chemical Bond Strongest Type of Intermolecular Force Present Reason For ClassifyingTrisha GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Chemical BondingJanchel BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces Liquids and SolidsDocument87 pagesIntermolecular Forces Liquids and SolidsMikey Bryant BonbonNo ratings yet
- Shs Module v2020 #m3.1-1Document4 pagesShs Module v2020 #m3.1-1Adrienne ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem w1-2Document6 pagesGen Chem w1-2Cyril FaithNo ratings yet
- 1 Intermolecular ForcesDocument14 pages1 Intermolecular ForcesKhianne Jayle CarilloNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsFransisca ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument37 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohnnardBelenNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument9 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular ModelSaralyn Mawallil AmilhamjaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 2 Intermolecular ForcesDocument10 pagesActivity Sheet 2 Intermolecular Forces9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Between Atoms Within A Molecule or Formula Unit Are Called Between Molecules Are CalledDocument34 pagesBetween Atoms Within A Molecule or Formula Unit Are Called Between Molecules Are CalledPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Matter: Kinetic EnergyDocument16 pagesMatter: Kinetic EnergyRazel ForrosueloNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 NotesDocument20 pagesGenchem 2 Notesmoss headNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces 2Document74 pagesIntermolecular Forces 2ytheresetiuNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument14 pagesPhysical Sciencejared alonzoNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Bonding 2016Document34 pagesIntermolecular Bonding 2016agony trageNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem - LectureDocument7 pagesGen Chem - LectureKean MercadoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIJoven EstebanNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 General ChemistryDocument83 pagesGrade 11 General ChemistryHannah De VeraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 General Chemistry 2 Synchronous ClassDocument18 pagesLesson 1 General Chemistry 2 Synchronous ClassJustine FabieNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument107 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenGopal GopinathNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Ii LecturesDocument18 pagesGen Chem Ii LecturesHANNA ROLISH DIGAMONNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular ModelChristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document4 pagesModule 1welpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - States of MatterDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - States of MatternnooorNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 ReviewerDuke FaciolNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary BondingDocument6 pagesPrimary and Secondary BondingosmondNo ratings yet
- Lec. 1 States of Matter (Part 1) (2 Slides Per Page)Document24 pagesLec. 1 States of Matter (Part 1) (2 Slides Per Page)Jayrine MonteroNo ratings yet
- GenChem (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesGenChem (Lesson 1)abgolena5238valNo ratings yet
- 1Q - Week 3 Physical ScienceDocument14 pages1Q - Week 3 Physical ScienceJEBONIE TUBICE100% (1)
- General ChemistryDocument10 pagesGeneral ChemistryKatrine Visitacion Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Chem ReviewerNIKKI GRACE MAGDALI100% (1)
- Unit 1 State of MatterDocument108 pagesUnit 1 State of MatterVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids & Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids & Intermolecular ForcesJeromeNo ratings yet
- IMF PogilDocument6 pagesIMF PogilsungminindiaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument6 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryJM FelixNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesIntermolecular ForcesRhane Marielle LeidiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- 11th Worksheet 2022-23 Unit 7,8,12,13Document8 pages11th Worksheet 2022-23 Unit 7,8,12,13ADITYA SONINo ratings yet
- Experiment 5A - Ca Analysis by Flame Photometry - BackgroundDocument9 pagesExperiment 5A - Ca Analysis by Flame Photometry - BackgroundLuis Mejía RuizNo ratings yet
- NPTEL - Electrical Properties in NanomaterialsDocument26 pagesNPTEL - Electrical Properties in NanomaterialsShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Elementary Particles: Griffith'S First ChapterDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Elementary Particles: Griffith'S First ChapterShankar NairNo ratings yet
- Yrk Mohan 2ND Puc Chemistry 2023 Model QuestionsDocument5 pagesYrk Mohan 2ND Puc Chemistry 2023 Model QuestionsNaga Raj S100% (1)
- The Solid State MCQDocument7 pagesThe Solid State MCQAlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. D & F Block Elements (Board Notes)Document12 pagesChapter 8. D & F Block Elements (Board Notes)Akash KoulNo ratings yet
- C. JouleDocument62 pagesC. JouleRehan PrinceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Microproject 1Document12 pagesChemistry Microproject 1Aachal GulhaneNo ratings yet
- Physics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022Document3 pagesPhysics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022BalaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Question BankDocument78 pagesCarbon Question Bankvvg .S0631No ratings yet
- Earth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test BankDocument36 pagesEarth An Introduction To Physical Geology Canadian 4th Edition Tarbuck Test Bankpanabase.trevat.puhh6e100% (26)
- IOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendDocument8 pagesIOC - IRP - Home Test-1 (Without Answer) - SendNicholas BourbakiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Periodic Table and Periodic PropertiesDocument7 pagesChemistry - Periodic Table and Periodic PropertiesHarshad SSNo ratings yet
- 5054 w22 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages5054 w22 QP 11 PDFAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer.: Half Book Test (2021) Class 9thDocument3 pagesChoose The Correct Answer.: Half Book Test (2021) Class 9thZeeshan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Are We Really Made of StarsDocument7 pagesAre We Really Made of StarsMerlita TuralbaNo ratings yet
- Black Holes and The Information ParadoxDocument32 pagesBlack Holes and The Information ParadoxAnonymous BPFIMnCdNo ratings yet
- Fundamental PrinciplesDocument4 pagesFundamental PrinciplesNadeem HassanNo ratings yet
- C2 - Key Recall QuestionsDocument18 pagesC2 - Key Recall QuestionsYashkur Al-ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- Diamond Battery and It's FeasiblityDocument1 pageDiamond Battery and It's FeasiblityVergin JoseNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear Atom 3 MSDocument4 pagesThe Nuclear Atom 3 MSmuhammadzariyanshafiqueNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 8 - ECE Board Exam - AnswersDocument29 pagesMCQ in Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Part 8 - ECE Board Exam - AnswersOne PieceNo ratings yet
- Unsur Golongan TransisiDocument18 pagesUnsur Golongan TransisiRomzi Al Amiri ZainNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnergy Transformation Worksheetgabrielle.r.halimNo ratings yet
- Rbse Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2024Document10 pagesRbse Class 12 Physics Syllabus 2024vishnoimukshNo ratings yet
- Paramedical UG: RUHS Entrance Examination 2019 Question PaperDocument17 pagesParamedical UG: RUHS Entrance Examination 2019 Question PaperAhmd UllahNo ratings yet
- Que&Ans Neet 2021 (Code O3)Document27 pagesQue&Ans Neet 2021 (Code O3)Muhammad Sahil KhanNo ratings yet
- SLK G7 Q3wk8 Mongcopa RevisedDocument11 pagesSLK G7 Q3wk8 Mongcopa RevisedTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- 2-s2.0-84961120848 (1) Abbas ImportantDocument9 pages2-s2.0-84961120848 (1) Abbas Importantfarah al-sudaniNo ratings yet