Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in Elements
Uploaded by
Fransisca Chevalier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagessadssdd
Original Title
Bonding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsadssdd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesMetallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in Elements
Uploaded by
Fransisca Chevaliersadssdd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Metallic bonding Ionic bonding
Ionic bonding is the
electrostatic force of attraction
between positively and
negatively charged ions.
A result of a transfer of
electrons between two atoms
with a large difference in
electronegativities.
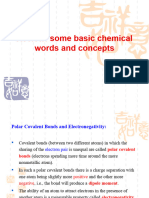
Pure covalent bonding Polar covalent bonding
Covalent bonds with unequal electron
Pure covalent bonding is only found in sharing are called polar covalent bonds.
elements.
The intermolecular forces of attraction considered here are: (in order of strength)
Van der Waals' forces
permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
hydrogen bonding
Van der Waals' forces
They are only significant in atoms and
molecules which have no other types of
intermolecular forces of attraction, for
example, discrete non-polar molecules and
the Group 0 elements.
Van der Waals' forces are a result of
electrostatic attraction between temporary
dipoles and induced dipoles caused by
movement of electrons in atoms and
molecules.
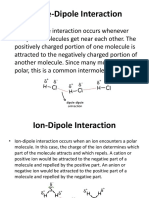
Permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions
A molecule can be described as polar if it has a permanent dipole. A permanent dipole
is due to a difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved in a covalent
bond.
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonds are permanent dipole-
permanent dipole interactions.
Bonds consisting of a hydrogen atom
bonded to an atom of a strongly
electronegative element such as fluorine,
oxygen or nitrogen are highly polar.
Hydrogen bonds are electrostatic forces of
attraction between molecules which contain
these highly polar bonds.
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- L I L I: Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesL I L I: Chemical BondingMark IanNo ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ProjectDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding ProjectOtto Bauer0% (1)
- Module3 Chemi BitsDocument3 pagesModule3 Chemi BitsPalNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument16 pagesIntermolecular ForcesAlvin RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- Dipole-Dipole Interaction PDFDocument4 pagesDipole-Dipole Interaction PDFEireen Rose JornacionNo ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding Lec 02Document14 pagesStructure & Bonding Lec 02tishagirkar074No ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument3 pagesForces of AttractionMoya-Dean WalcottNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument16 pagesBondingactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Bonding Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageBonding Knowledge Organisermya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Phys. Sci. Module 5Document3 pagesPhys. Sci. Module 5TE RENo ratings yet
- Phyphar Chapter 2Document7 pagesPhyphar Chapter 2KATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- Intermolecular-Forces JIE FINDocument22 pagesIntermolecular-Forces JIE FINKathlyn PlacenteNo ratings yet
- CH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionDocument33 pagesCH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionHARPACANo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument30 pagesRadioactivitybrianna brownNo ratings yet
- Polarity & ForcesDocument13 pagesPolarity & ForcesElsayed ElazazyNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Bonding & Structure NotesDocument11 pagesBonding & Structure NotesKamran TajbakhshNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?rahulinder1234No ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pearson Chemistry Chapter 8 Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesPearson Chemistry Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizletأستغفرالله واتوب اليهNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Materials Lecture 4Document24 pagesChemistry of Materials Lecture 4sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondsDocument1 pageIonic BondsDivya ShahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular and Intramolecular MoleculeDocument2 pagesIntermolecular and Intramolecular MoleculeIvy SepeNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument19 pagesChemical Bondingrabiullah.edu987No ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The EarthDocument58 pagesChemical Composition of The EarthPutik Nurul ArasyNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Document26 pagesIntermolecular Forces: General Chemistry 2Cielo GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument1 pageChemical Bondingsurvey callNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument1 pageChemical Bondingsurvey callNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document7 pagesChemistry 2Kizzy Rae SolitoNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit1Document14 pagesChem Unit1Hussain JassimNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIJoven EstebanNo ratings yet
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document36 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?aditya_2013No ratings yet
- ReviewDocument12 pagesReviewjannatul80002No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Attraction 1. Dipole-Dipole ForceDocument2 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Attraction 1. Dipole-Dipole ForceNica GamesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds ReviewDocument1 pageChemical Bonds ReviewGeorgeNo ratings yet
- 02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingDocument10 pages02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingShreyash ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Introduction Adhesives1Document36 pagesIntroduction Adhesives1Pathik ShahNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular FORCES 2Document19 pagesIntermolecular FORCES 2hiba nisarNo ratings yet
- MoleculesDocument3 pagesMoleculesMoktar EsmailNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition of The EarthDocument58 pagesChemical Composition of The EarthPutik Nurul ArasyNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet