Professional Documents
Culture Documents
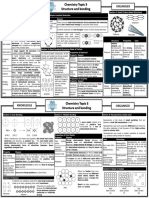
Bonding Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
mya thet htar swe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageBonding Knowledge Organiser
Uploaded by
mya thet htar sweCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
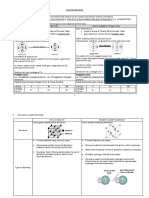
Anion A negatively charged ion
Bonding Knowledge Organiser Boiling point
Cation
Temperature at which substance changes from a liquid to a gas
A positively charged ion
Covalent bond A shared pair of electrons between atoms
Atoms want to have a full outer shell as this makes them stable. To do this they form bonds with Delocalised electrons Free moving electrons from the outer shell of metal atoms. Form a
other atoms. strong attraction with metal ions
Ionic Bonds Dot and cross diagram Diagram showing how electrons are arranged in a molecule or ion (dots
for one atom, crosses for another atom)
Metals and non-metals will form ionic bonds. The metal Electrical conductivity Measure of how well a substance conducts electricity
atom loses electrons to become a positive ion(cation) and Electron Negatively charged sub atomic particle
the non-metal atom gains electrons to become a negative Electron transfer Movement of electrons from one atom to another
ion (anion). Electrostatic attraction Force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Intermolecular force Relatively weak force of attraction between molecules that keeps them
The electrons from the metal transfer to the together
non-metal so that both toms have a full outer Ion Particle with a charge, positive or negative
shell. Ionic bond Forms between metals and non-metals. Oppositely charged ions attract
to form an ionic bond.
The ions formed are attracted by an
electrostatic force. Ionic formula How ionic compounds are represented
Ionic lattice Regular arrangement of positive ions surrounded by negative ions
Ionic compounds forma giant structure called a lattice. Melting point Temperature at which substance changes from a solid to a liquid
Metal ions Positively charged atom in a metal
The electrostatic attraction is strong meaning ionic compounds have a high Metallic bond Forces that keep atoms together in a metal
melting point as a lot of energy is needed to overcome the attraction. Molecule Two or more atoms chemically joined
Ionic compounds don’t conduct when solid because the ions are locked in Simple covalent molecule Substance that contains only a few non-metal atoms held together by
covalent bonds
position. When molten the ions are free to move and can conduct.
Stable An atom is stable when it has a full outer shell
Covalent Bonds Metallic Bonds
Two non-metals will form a covalent bond. The atoms Although the covalent bond is strong the Metallic bonds are metal ions surrounded by delocalised
share electrons to make themselves stable. simple molecules are held together by weak electrons.
intermolecular forces. This means they have
low boiling points. Metals con duct electricity because the electrons are free to
move.
The covalent molecules don’t conduct
The metallic bond is strong so they have a high melting point.
electricity because there are no free electrons.
Metals are malleable because the layers are able to slide over
each other.
You might also like
- Types of SolidsDocument5 pagesTypes of SolidsBianca RolstonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesBonding and StructureYusma KhanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- L I L I: Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesL I L I: Chemical BondingMark IanNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument30 pagesRadioactivitybrianna brownNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsFransisca ChevalierNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Ion Formation (SummarizedDocument8 pages7.1 Ion Formation (Summarizedahmdhjw24No ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Science Presentation in Blue Light Blue Hand Drawn StyleDocument6 pagesChemical Reactions Science Presentation in Blue Light Blue Hand Drawn StyleskiphmelodyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Project: Ionic, Covalent, and Periodic TrendsDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding Project: Ionic, Covalent, and Periodic TrendsOtto Bauer0% (1)
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Chemical PropertiesDocument32 pagesLesson 3 Chemical PropertiesJohann LeoncitoNo ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding Lec 02Document14 pagesStructure & Bonding Lec 02tishagirkar074No ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument1 pageStructure and BondingeohomegrownappsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructuresDocument5 pagesChemical Bonds and Lewis Structuresnicole MenesNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Icm ScienceDocument2 pagesIcm Scienceapi-345381848No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding NotesDocument1 pageIonic Bonding Notesevango21No ratings yet
- Module-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Document193 pagesModule-Ii Chemical Bonding: General Chemistry CHEM-1001Shivansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- Elements and Their Corresponding ColorDocument6 pagesElements and Their Corresponding ColorAdonis MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- rjjrfpjrfprDocument7 pagesrjjrfpjrfprZemmerCCNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- AQA Combined Science Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesAQA Combined Science Structure and Bondingali.a.226No ratings yet
- Why To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentDocument22 pagesWhy To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentdNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument15 pagesIonic Bondemy.sajesajeNo ratings yet
- 3-Ionic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3-Ionic Bonding PDFTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure-ReviewDocument1 pageBonding and Structure-Reviewcandyli3788No ratings yet
- 化学考点Document1 page化学考点Long Eks XuNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer (Chemical Bonding) 3Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer (Chemical Bonding) 3Yohan Kleir PuruggananNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- ch-3,chemDocument6 pagesch-3,chemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartArcelie Alberca EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingfDocument25 pagesChemical BondingfRobelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- 06 CB Notes 2022Document6 pages06 CB Notes 2022Fitri armaya Jeffri (Greendaless)No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceDocument2 pagesMODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceEmma Cristie BalahadiaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Ionic, Covalent, MetallicDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: Ionic, Covalent, MetallickalumamuNo ratings yet
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pages2 2 2 Bonding and StructureAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument8 pagesThe Chemical Basis of LifeSemper Ann LawagueyNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionDocument10 pagesGrade 10 IB Bridging Course Chemistry: Flow of This SectionMarc LoNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Compounds Properties & Metals and IonsDocument42 pagesIonic and Covalent Compounds Properties & Metals and IonsHillary DalitNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Chemical BondingDocument50 pages3.0 Chemical Bondingparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- "Different Types of Bonds and There Models": Y.B. Patil Polytechnic, AkurdiDocument2 pages"Different Types of Bonds and There Models": Y.B. Patil Polytechnic, AkurdiSwapnil GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Biochemlec Mod 1 6Document50 pagesBiochemlec Mod 1 6Sean Michael ComprendioNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- Bond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical BondsDocument29 pagesBond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical Bondseric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds ReviewDocument1 pageChemical Bonds ReviewGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 4. Structure of The Atom (10 June 2022)Document6 pagesUnit 4. Structure of The Atom (10 June 2022)mya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Group 7 ElementsDocument11 pagesChemistry-Group 7 Elementsmya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 (Energy Changes)Document16 pagesUnit 5 (Energy Changes)mya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Group 1 Metals Like Lithium, Sodium and Potassium in WaterDocument4 pagesReactions of Group 1 Metals Like Lithium, Sodium and Potassium in Watermya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Structure of the Atom ExplainedDocument16 pagesStructure of the Atom Explainedmya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- Teacher Mya's Yr-9 Chemistry on Noble GasesDocument9 pagesTeacher Mya's Yr-9 Chemistry on Noble Gasesmya thet htar swe100% (1)
- Chemistry-Group 7 ElementsDocument11 pagesChemistry-Group 7 Elementsmya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- 8 SaltsDocument13 pages8 SaltswanyanaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For General Organic and Biological Chemistry 4th Edition Laura D FrostDocument21 pagesTest Bank For General Organic and Biological Chemistry 4th Edition Laura D FrostPierre Wetzel100% (36)
- Class 12 Part TestDocument39 pagesClass 12 Part TestshrawantiyaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid-Protecting Groups: Albert Isidro-Llobet, Mercedes Álvarez, Fernando AlbericioDocument117 pagesAmino Acid-Protecting Groups: Albert Isidro-Llobet, Mercedes Álvarez, Fernando AlbericioAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ChemistryDocument5 pagesLesson Plan ChemistryFatin Atiyah100% (1)
- Module 6 Portfolio PDFDocument3 pagesModule 6 Portfolio PDFAndrea Celine AurealNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Study and Revision GuideDocument342 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Study and Revision GuideMayank Maddula33% (3)
- R315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSDocument8 pagesR315 AbenojaJL HYDROCARBONSJL AbenojaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: HV-25L HV-50L HV-85L HV-110LDocument41 pagesOperating Manual: HV-25L HV-50L HV-85L HV-110LrafaelNo ratings yet
- Final Dissertation FYP Naqiyuddin 14282Document49 pagesFinal Dissertation FYP Naqiyuddin 14282Edinson Diaz RojasNo ratings yet
- Sand Lime Bricks For Masonry ConstructionDocument7 pagesSand Lime Bricks For Masonry ConstructionAnjanaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Sodium CitrateDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Sodium CitrateMutia Nurul OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AlkanesDocument37 pagesChapter 2 AlkanesLionel MessiNo ratings yet
- Hydrophilic-Lipophilic BalanceDocument56 pagesHydrophilic-Lipophilic Balancealanmarr100% (1)
- 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument23 pages3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Spectroscopy - Oct2020-Feb2021Document7 pagesAssignment 1-Spectroscopy - Oct2020-Feb2021Amirah AzlanNo ratings yet
- CURRENT RESEARCH IN CLAY MINERALOGYDocument9 pagesCURRENT RESEARCH IN CLAY MINERALOGYGraceNo ratings yet
- Color Changing Milk 01Document2 pagesColor Changing Milk 01api-259780711No ratings yet
- Marbling 2Document2 pagesMarbling 2John AngNo ratings yet
- XyzDocument9 pagesXyzankit singh100% (1)
- Thermosets & ThermoplasticsDocument7 pagesThermosets & ThermoplasticsManjunath Keshav D MNo ratings yet
- Handouts 7 CPI 5 - Pulp and Paper IndustriesDocument72 pagesHandouts 7 CPI 5 - Pulp and Paper IndustriesRushane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Hydrogen Peroxide Durox LR-3Document8 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Hydrogen Peroxide Durox LR-3nanenarayanaNo ratings yet
- GCSE - A Level Chemistry Transition Gcse Questions.199272016Document13 pagesGCSE - A Level Chemistry Transition Gcse Questions.199272016miyu kanzakiNo ratings yet
- Atomic World I (up to chemical bonding) -SQ: Key concepts and practice questionsDocument2 pagesAtomic World I (up to chemical bonding) -SQ: Key concepts and practice questionsEngland NgNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Organic ChemistryDocument112 pagesBasic Concepts of Organic ChemistryPakardan TeaNo ratings yet
- Is 4041 2006Document19 pagesIs 4041 2006Khan ShahzebNo ratings yet
- Hot Dip Galvanizing Process ExplainedDocument13 pagesHot Dip Galvanizing Process ExplainedaselabollegalaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HL Paper 2 TZ1Document36 pagesChemistry HL Paper 2 TZ1Hasnatul Khaira100% (1)
- Puri Sharma Kalia Inorganic Chemistry PDF Sharma Kalia Inorganic Chemistry PDF Do PDFDocument2 pagesPuri Sharma Kalia Inorganic Chemistry PDF Sharma Kalia Inorganic Chemistry PDF Do PDFVaishnu S. Nair56% (9)