Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonds Review
Uploaded by
GeorgeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonds Review
Uploaded by
GeorgeCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMICAL BONDS
A chemical bond is an attraction between two or more ions that enables the
formation of chemical compounds. Bonds are formed when valence electrons,
the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, interact. The bond may result
from the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions as in
ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds.
There are three primary types of chemical bonding:
IONIC
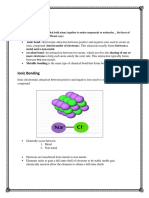
An ionic bond is a type of linkage formed from the
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged
ions in a chemical compound. Such a bond forms when
the valence electrons of one atom are transferred
permanently to another atom.
COVALENT
A covalent bond is a type linkage that results
from the sharing of an electron pair between two
atoms. The binding arises from the electrostatic
attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons.
METALLIC
A metallic bond is a force that holds atoms
together in a metallic substance. In the “electron
sea” model, atoms in a metallic solid lose their
outer electrons and form a regular lattice of
positive metallic ions.
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Chemical BondsDocument17 pagesChemical BondsAnonymousGodiswithyouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Bondingahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Article (Bonding&Structure)Document3 pagesArticle (Bonding&Structure)Fawzan Fahad MDNo ratings yet
- Formation of Covalent BondDocument8 pagesFormation of Covalent BondShyra Mae MagpusaoNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument2 pagesIonic BondP. BrucoyNo ratings yet
- L I L I: Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesL I L I: Chemical BondingMark IanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ProjectDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding ProjectOtto Bauer0% (1)
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument19 pagesChemistry37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- 化学考点Document1 page化学考点Long Eks XuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Why Do Atoms Bond?Document3 pagesChemical Bonding: Why Do Atoms Bond?Saavelo WinlandNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Science PTDocument19 pagesScience PTGamerPlays 0192No ratings yet
- Chem BondsDocument1 pageChem BondsMeenakshi DeepakNo ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument1 pageChemical BondingSukmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and Chemical CompoundsDocument8 pagesChemical Bonds and Chemical Compoundsmargareth bumatayNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Chemical Compounds: Ntended Learning OutcomesDocument27 pagesChemical Bonds Chemical Compounds: Ntended Learning OutcomesAlias SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Pearson Chemistry Chapter 8 Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesPearson Chemistry Chapter 8 Flashcards - Quizletأستغفرالله واتوب اليهNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsDocument68 pagesChemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsRalph RebugioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ionic Bond PPDocument10 pagesChemistry Ionic Bond PPSaya KacakNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding LNDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding LNCenjie Niña Hayag SongcalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesCovalent Bonds vs. Ionic Bonds: Comparison ChartArcelie Alberca EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Sci 73A.2Document3 pagesSci 73A.2Andreev ImutanNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Warm Up 11/8/2010: in Your Own Words, Answer The FollowingDocument11 pagesWarm Up 11/8/2010: in Your Own Words, Answer The Followingdwolfe25No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument2 pagesChemical BondHadaramNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE To ReviewDocument4 pagesSCIENCE To ReviewMichaela Gwyneth SantosNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument30 pagesRadioactivitybrianna brownNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Webquest Background EssayDocument1 pageChemical Bonding Webquest Background Essayapi-303294518No ratings yet
- IkatanDocument3 pagesIkatanPutri KemeNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Chemical BondingDocument50 pages3.0 Chemical Bondingparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondsDocument1 pageIonic BondsDivya ShahNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument3 pagesForces of AttractionMoya-Dean WalcottNo ratings yet
- CH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionDocument33 pagesCH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionHARPACANo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Ion Formation (SummarizedDocument8 pages7.1 Ion Formation (Summarizedahmdhjw24No ratings yet
- Introduction Adhesives1Document36 pagesIntroduction Adhesives1Pathik ShahNo ratings yet
- Chem BondDocument10 pagesChem BondMIRIAM BATHANNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Material Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesMaterial Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingCsir RimlaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding, Structure and Shapes of Molecules and CompoundsDocument70 pagesChemical Bonding, Structure and Shapes of Molecules and Compoundsann wamburaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument26 pagesChemical BondingShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING - NotesDocument30 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING - NotesP YNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsdanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemical BondingAhmed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Cell One - IB PreparationDocument2 pagesCell One - IB PreparationGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Losing Sense of Fairness: How Information About A Level Playing Field Reduces Selfish BehaviorDocument10 pagesLosing Sense of Fairness: How Information About A Level Playing Field Reduces Selfish BehaviorGeorgeNo ratings yet
- A Private Experience Part 1Document2 pagesA Private Experience Part 1GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Aba 2Document6 pagesAba 2GeorgeNo ratings yet