Professional Documents
Culture Documents
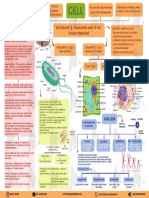
Functions:: Transport of Substances Through The Plasma Membrane
Uploaded by
Shamiun NaharOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Functions:: Transport of Substances Through The Plasma Membrane
Uploaded by
Shamiun NaharCopyright:
Available Formats
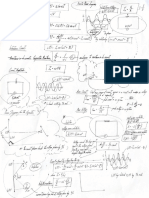
lei!
T
he Ba\1( U /
nt1 or 111 , / ( ,
f-ien'lbrane Covering the Cell "' ~ >
, Cha,.... _
-__,,.. · · rlstlc Features
.... ..- • Semi-trans .
...... wall structure membrane
parent m
embrane surround·
cell
Cell wall • It is multicellul ing the plasma
p1asmodesma 1 p. ar usual! h .
2· r_,mary cell Wall y av,ng three layers
. Middle lamella
Cytoplasm
• ~ ro! e~ond~ry cell Wall
e middle lamella
Vacuole connect one cell t ' plasmodesmata .
0 another arise which
cell wall Functions:
• Provides a framework to th
• Provides d fi . e cell
e nite shape to th
• Gives ri g'd'ty e cells
plants ' I and support to the tissues in
• Gives me h ·
c anical strength to the II
• Helps in balanci ng d . . _ ce
pressure an maintaining osmotic
• Prevents bursting of cells
• Protects protoplasm against infections
• HI elps _i n the transport of water and minerals over
~e;c==============--~============= ====='==,~o;;,;n~g~d:,:;1s:ta
: n~c~e:,
s"='
Transport of Substances through the Plasma Membrane
The passage of substances across the cell membrane takes place by three ways, wh'1Ch are liste d as £allows.
1. Passive transport
2. Active transport
3. Bulle transport
Passive Transport
Passive tr~nsport is a mode of transport that takes place without the expenditure 0£energy. It takes place by either diffusion
or osmosis.
Diffusion
Dilfusion is the process--in which movement of molecules takes place from higher to lower concentrations until thi
concentrations become equal. It is generally applicable to the movement of gaseous substances. With diffusion, the plan1
rake in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen during the process of photosynthesis. The taking in of oxygen int
the blood from lungs and the release of carbon dioxide from the lungs into the blood also take place by diffusion.
Osmosis is vital to many body processes, including the functioning of the kidney and the nerves.
You might also like
- Controller Installation and Adjustment Procedures For ModelsDocument34 pagesController Installation and Adjustment Procedures For ModelsJonathan RoblesNo ratings yet
- CAT - 3126E.3126E With Prefix LEFDocument11 pagesCAT - 3126E.3126E With Prefix LEFPhil B.No ratings yet
- TBR Bio1 OptDocument333 pagesTBR Bio1 OptChris Daniels90% (10)
- Chapter 4 TissuesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 TissuesAl-Shuaib Astami Son100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument98 pagesAnimal Tissuesfit3akmal100% (3)
- Basic HistologyDocument8 pagesBasic Histologyroy_dubouzetNo ratings yet
- Pipe Network AnalysisDocument32 pagesPipe Network AnalysisRANJINI02VNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Lam Nguyen - Worksheet - Plant Animal CellsDocument2 pagesKami Export - Lam Nguyen - Worksheet - Plant Animal Cellsapi-552399149No ratings yet
- Market Technician No63Document12 pagesMarket Technician No63ppfahdNo ratings yet
- Klangfarbenmelodie Amongst The Darmstadt Circle: Atmosphères at The Donaueschinger Musiktage, He WroteDocument48 pagesKlangfarbenmelodie Amongst The Darmstadt Circle: Atmosphères at The Donaueschinger Musiktage, He WroteBrandon McguireNo ratings yet
- JW TICO Product Guide Issue 1-18 PDFDocument48 pagesJW TICO Product Guide Issue 1-18 PDFgkdora574No ratings yet
- Unleash Your Speed: Thinking Forward. Challenging LimitsDocument3 pagesUnleash Your Speed: Thinking Forward. Challenging Limitsanon_19722876No ratings yet
- Belt and Pulley SystemsDocument5 pagesBelt and Pulley SystemsNBRellos50% (2)
- Class 10 BiologyDocument2 pagesClass 10 BiologyShamiun NaharNo ratings yet
- Primitive Unit Cells - MSEstudentComDocument20 pagesPrimitive Unit Cells - MSEstudentComJuano Valls FerrerNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 pagesEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Growth Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue Growth Worksheet AnswersuyenNo ratings yet
- Histology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document22 pagesHistology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Fea Kristine PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument23 pagesAnimal TissueMadhav KhanalNo ratings yet
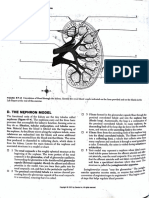
- D. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresDocument6 pagesD. The Ne Phron Model: Ul'lnary TructuresCatherine BelonioNo ratings yet
- DLC PracticalDocument6 pagesDLC PracticalAngoruz Gohain BaruahNo ratings yet
- PDF Cell Biology Scioly Notes Regional - CompressDocument3 pagesPDF Cell Biology Scioly Notes Regional - CompressChinmay KalakondaNo ratings yet
- Lessson Plan PushpaDocument9 pagesLessson Plan Pushpashivani dasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 Cell As Unit of LifeDocument21 pagesChapter - 8 Cell As Unit of Lifeavishank584No ratings yet
- Bio Questions ch1 3Document2 pagesBio Questions ch1 3Remar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- ITBS Cell NotesDocument13 pagesITBS Cell NotesSufiyan BegNo ratings yet
- Chordate E&D PDFDocument14 pagesChordate E&D PDFPatience HeduvorNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Transes PDFDocument11 pagesEpithelial Tissue Transes PDFFAUL MANGAYANo ratings yet
- Plant Animal Cell DiagramsDocument5 pagesPlant Animal Cell Diagramssalagi28No ratings yet
- The Cell and Biological Membranes Structure and FunctionDocument9 pagesThe Cell and Biological Membranes Structure and FunctionAvaneesh HNo ratings yet
- 8 Bio L1Document13 pages8 Bio L1Abirami SathishNo ratings yet
- Section - A: Model Paper - 1 Diploma in Medical Lab Technician Second Year Paper - IDocument19 pagesSection - A: Model Paper - 1 Diploma in Medical Lab Technician Second Year Paper - IMohammed MjdNo ratings yet
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDocument8 pagesHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 03 Jan 2024Document11 pagesAdobe Scan 03 Jan 2024riteshraj07082007No ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument34 pages3.1 Cell Structure and OrganisationMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- A8 Cell Unit of LifeDocument1 pageA8 Cell Unit of LiferajjoNo ratings yet
- Simple and Complex Permanent TissuesDocument8 pagesSimple and Complex Permanent TissuesMatthew Reyes RemegiaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Bioeng-1: Mrs Daramola BellstechDocument30 pagesMolecular Bioeng-1: Mrs Daramola BellstechSamuel EkpoNo ratings yet
- 4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument49 pages4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsabhishek80562506877No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumVanyVillegasNo ratings yet
- محاضره 1 انسجهDocument32 pagesمحاضره 1 انسجهYahya Daham Zafeer SakhrNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument4 pagesCilia and FlagellaAnurag chavan100% (1)
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsMaggieSamNo ratings yet
- GS Biology 2Document70 pagesGS Biology 2LalruatdikiNo ratings yet
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- Exercise 15 Serial Transverse Section of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument5 pagesExercise 15 Serial Transverse Section of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument18 pagesCell Structure and OrganizationMuhammad SamhanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Tissue and Integumentary System10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Class 10 BiologyDocument3 pagesClass 10 BiologyShamiun NaharNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument18 pagesTissuesAndrea Elaine Joy TorrentoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1ayush aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Unit-1Document16 pagesBiochemistry Unit-1sushantxenomaniaNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Class IxDocument46 pagesAnimal Tissues: Class IxDHARSHAN BOOPALANNo ratings yet
- AP03-TissuesDocument12 pagesAP03-TissuesLyn YmiNo ratings yet
- 07 Animal TissuesDocument12 pages07 Animal TissuesKeisha Clarice AdaroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Histology and Epithelium TissueDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Histology and Epithelium TissuejabirNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document18 pagesCell 2pranavdarkundeNo ratings yet
- 9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Document29 pages9tissuesppt 150802072720 Lva1 App6892Vipul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biology AssignmentDocument5 pagesBiology AssignmentAlishan BangashNo ratings yet
- Type of Epidermis & Thermoregulation BasicDocument14 pagesType of Epidermis & Thermoregulation BasicJJRG PrintingNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabDocument34 pagesMidterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabkabukibearNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial Tissue3010babitaguptasvjcNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- 26 03 2022 - 241421Document9 pages26 03 2022 - 241421Vedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument53 pagesAnimal TissuesIpshita PathakNo ratings yet
- The Living Barrier: A Primer on Transfer across Biological MembranesFrom EverandThe Living Barrier: A Primer on Transfer across Biological MembranesNo ratings yet
- Channels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportFrom EverandChannels, Carriers, and Pumps: An Introduction to Membrane TransportNo ratings yet
- QRAS TutorialDocument98 pagesQRAS TutorialAnderson RochaNo ratings yet
- T G 1653646560 Time Zones Powerpoint Ver 1Document8 pagesT G 1653646560 Time Zones Powerpoint Ver 1Malvika BalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Smart Technologies For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument420 pagesSmart Technologies For Sustainable DevelopmentMaria Rafaela Bezerra de Macêdo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Micropulse Transducers: Magnet Rod SeriesDocument2 pagesMicropulse Transducers: Magnet Rod SeriesAlexander GochevNo ratings yet
- VMC Advance 1 Paper 1Document11 pagesVMC Advance 1 Paper 1amogh kumarNo ratings yet
- Groff and MomDocument12 pagesGroff and MomSalomon SalomonNo ratings yet
- Bahan PPT PPICDocument19 pagesBahan PPT PPICAoc SidomulyoNo ratings yet
- DS Arf27Document1 pageDS Arf27BogdanNo ratings yet
- Column Design For Unbraced Columns Via Ec2Document5 pagesColumn Design For Unbraced Columns Via Ec2Muhammad Wazim AkramNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Lab ReportDocument6 pagesProjectile Motion Lab ReportThu Phuong LeNo ratings yet
- Physics II Honors E&M Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics II Honors E&M Cheat SheetCeline ShawNo ratings yet
- CH Wise Stats IMP Questions by HM Hasnan Jan-24Document75 pagesCH Wise Stats IMP Questions by HM Hasnan Jan-24Harris QureshiNo ratings yet
- PROBABILITY It Is A Numerical Measure Which Indicates The ChanceDocument20 pagesPROBABILITY It Is A Numerical Measure Which Indicates The ChancePolice stationNo ratings yet
- Segmented Shaft Seal Brochure Apr 08Document4 pagesSegmented Shaft Seal Brochure Apr 08Zohaib AnserNo ratings yet
- MAPEH (Arts) : Quarter 2Document40 pagesMAPEH (Arts) : Quarter 2Eiay CommsNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Eaton 93 STS - Static Transfer SwitchDocument2 pagesDatasheet Eaton 93 STS - Static Transfer SwitchWilliam QuintelaNo ratings yet
- BoT-IoT - GenerationDocument40 pagesBoT-IoT - GenerationHassina KouachiNo ratings yet
- UH8 RF V2 1.5 LR ManualDocument12 pagesUH8 RF V2 1.5 LR Manualgarys12No ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument5 pagesData SheetMindSet MarcosNo ratings yet
- PCon - Planner System RequirementsDocument2 pagesPCon - Planner System RequirementsKristof MCNo ratings yet
- Handouts General MathematicsDocument70 pagesHandouts General Mathematicskhalid4vuNo ratings yet
- DPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Document12 pagesDPP - Electricity (Prashant Kirad)Abhinav SinghNo ratings yet