Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Respiration: Chapter 16 Respiration in Plants
Definition of Respiration: Chapter 16 Respiration in Plants
Uploaded by
24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesPlants undergo respiration to release energy from organic compounds like glucose. Glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Gaseous exchange in plants occurs through stomata on leaves, lenticels on stems, and root hairs. During photosynthesis oxygen is released and some is used in tissue respiration, while carbon dioxide must diffuse into leaves from the atmosphere for food production since respiration alone does not produce enough. Experiments show that oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide produced during plant respiration.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlants undergo respiration to release energy from organic compounds like glucose. Glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Gaseous exchange in plants occurs through stomata on leaves, lenticels on stems, and root hairs. During photosynthesis oxygen is released and some is used in tissue respiration, while carbon dioxide must diffuse into leaves from the atmosphere for food production since respiration alone does not produce enough. Experiments show that oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide produced during plant respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesDefinition of Respiration: Chapter 16 Respiration in Plants
Definition of Respiration: Chapter 16 Respiration in Plants
Uploaded by
24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊Plants undergo respiration to release energy from organic compounds like glucose. Glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Gaseous exchange in plants occurs through stomata on leaves, lenticels on stems, and root hairs. During photosynthesis oxygen is released and some is used in tissue respiration, while carbon dioxide must diffuse into leaves from the atmosphere for food production since respiration alone does not produce enough. Experiments show that oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide produced during plant respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
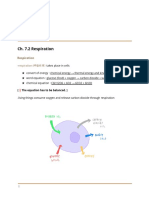
CHAPTER 16 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
Definition of respiration
-organic food substances are oxidised 被氧化 to release energy which can be used by living
cells to carry out many vital process
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Gaseous exchange in plant take place
a) Stomata 气孔 in leaves (principal sites)
-The simple diffusion 扩散 of gases is sufficient
to meet their needs.
b) lenticels in stems 茎部的皮孔
c) root hairs 根毛
Gaseous exchange in plants
• During photosynthesis, oxygen is set free and some of this oxygen is used for tissue
respiration
• In bright sunlight, the rate of photosynthesis is much greater than the rate of respiration
• excess oxygen diffuse out of the leaves through the stomata
• Since the amount of carbon dioxide produce during tissue respiration is not sufficient for
food-making, more carbon dioxide has to diffuse into the leaf from the outside atmosphere
Experiment
A) To prove that oxygen is taken up during respiration
-Calcium hydroxide 氢氧化钙 becomes milky 乳白色
-the splint stop to burn, showing that there is no oxygen in the flask
Conclusion
1. Due to the pressure in the flask decrease, water rises the glass tube.
2. Oxygen is absorbed by the plant during respiration.
B) To prove that respiration produces carbon dioxide
-lime water turned milky
Pg51 在课本 自己背吧(加油!!!
You might also like
- 17-Respiration in PlantDocument19 pages17-Respiration in PlantqingxuguNo ratings yet
- X Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRDocument4 pagesX Cbse Science Unit Test - Solutions: Life Processes-Nutrition & Respiration Marks: 30 Test Code: 10SUT103 Duration: 1 HRdayanandan1No ratings yet
- Practical 6Document9 pagesPractical 6Athira ThyraNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 7Document9 pagesBiology Ch. 7sumsumNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument7 pagesLife Processestasmitha98No ratings yet
- Solution 971085Document4 pagesSolution 971085disha thapa 7625No ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)Document7 pagesNutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)John Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Medical (Inter-I)Document19 pagesReading Material Medical (Inter-I)a18193499No ratings yet
- Living Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument38 pagesLiving Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionWen Shan ChuaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Ans Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceDocument2 pagesAns Key Class 7 Worksheet CH 10 ScienceAishwarya DattaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document24 pagesChapter 13 Biology 1st Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT BY FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)Document4 pagesRespiration in Humans: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 197)lee67% (3)
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Plant LifeDocument5 pagesPlant LifeSanhitha RameshNo ratings yet
- Answers in Questions PDFDocument53 pagesAnswers in Questions PDFArasiveluNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05Document7 pagesIGCSE Answers Chapters 01 05María Eugenia MolteniNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheets New 1Document94 pagesScience Worksheets New 1Jose Manuel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesRespiration Handoutkiran2000tripathiNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument16 pagesRespirationTeacher AlexNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Grade 11Document12 pagesPhotosynthesis Grade 11T Sivajini100% (1)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- Gurukrupa College of Education &research, Kalyan (W) : Co-Teaching Lesson 12Document12 pagesGurukrupa College of Education &research, Kalyan (W) : Co-Teaching Lesson 12Sameer SmartyNo ratings yet
- Purwanchal Vidyamandir SESSION: 2021-2022 Class: Ix Subject: BiologyDocument8 pagesPurwanchal Vidyamandir SESSION: 2021-2022 Class: Ix Subject: BiologyKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- CH.7 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Class 9 Notes IcseDocument7 pagesCH.7 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Class 9 Notes IcseFebin GeorgeNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisAuthor ClubNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Document10 pagesBiology Chapter Life Processes Class 10Âåřøhī MāhåjáňNo ratings yet
- L - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkDocument7 pagesL - Life Processes - Respiration Notes and Questions For Note Book WorkNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Raja Fayaz AliDocument12 pagesRespiration: Raja Fayaz AliSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument39 pagesPlant Nutritionapi-3059093250% (1)
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- s.3 Bio. Respiration and Gaseous Exchange NotesDocument25 pagess.3 Bio. Respiration and Gaseous Exchange NotesKyopaire TobiaNo ratings yet
- 3 Plant Processes: Plants Perform Certain Processes Necessary For SurvivalDocument34 pages3 Plant Processes: Plants Perform Certain Processes Necessary For SurvivalDedy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument6 pagesGas Exchange in PlantsAbi RNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document8 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 10opsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision GuideDocument22 pagesBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- Practice Test 3 PDFDocument5 pagesPractice Test 3 PDFJEAB KONGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 RespirationDocument5 pagesChapter 12 RespirationKai TongNo ratings yet
- Respiration Labco 5Document5 pagesRespiration Labco 5smithsashay74No ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 4Document73 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 4Andeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas Exchange 11.1Document20 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchange 11.1BushraNo ratings yet
- Respiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PosterDocument7 pagesRespiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PostererinaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project KBDocument35 pagesBiology Project KBHarshita ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1.1 and 1.2 and 1.3Document35 pagesPhotosynthesis 1.1 and 1.2 and 1.3heenamehta2702No ratings yet
- Class 7 Lesson 6Document3 pagesClass 7 Lesson 6gunjanrichaNo ratings yet
- 08-Respiration and Gaseous Exchange-1Document22 pages08-Respiration and Gaseous Exchange-1Maku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Bio TestDocument24 pagesBio Testjunaid mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (Eng)Document4 pagesWorksheet (Eng)s2322336No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument39 pagesRespirationRayan LourikiNo ratings yet
- 6-Life ProcessesDocument39 pages6-Life ProcessesKaushal Solanke0% (1)
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAnushreeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Breathing and RespirationDocument8 pagesDifference Between Breathing and RespirationpreethaNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- Celluar RespirationDocument16 pagesCelluar Respirationpetra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- 6.plant Nutrition OverviewDocument26 pages6.plant Nutrition OverviewShlok KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Life Processes-Question BankDocument9 pagesLife Processes-Question Bankkfjg47zq26No ratings yet
- Physics NoteDocument9 pagesPhysics Note24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Essay Good SentenceDocument3 pagesEssay Good Sentence24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 RespirationDocument4 pagesChapter 16 Respiration24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Enzyme: DigestionDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Digestion24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet