Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Methodology
Methodology
Uploaded by
무제untitledOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Methodology
Methodology
Uploaded by
무제untitledCopyright:
Available Formats
Methodology
The methodology and design concepts that will be employed in the design project are outlined
in this section. When planning a cold storage, there are a few factors to consider, and it is presented as
follows:
Methods of Determining the Design Strategy
The design specifications for the Swine Carcass Refrigeration System will be as follows.
The proposal's principal method is to design and redesign. The cooling load calculations rely
heavily on the parameters of the equipment that will be utilized for cold storage. The roof,
automatic door, lighting, forklift, insulation, pallets, and meat crate are among the equipment.
The blast freezer design is important for increasing the shell life of chopped swine meat
carcasses. Moreover, it is used to keep food secure against microorganism formation and
growth.
The floor dimensions of the swine carcass refrigeration system are 20m W x 25m L x
12m H, with specific rooms such as a dock, office, freezer room, chiller rooms, deboning and
chopping room, and comfort room.
Methods of Determining the Site Location
When selecting a cold storage production site, one of the most crucial aspects to
consider is plant location. When selecting a location, it must have enough construction space to
accommodate the desired design size, and it must also be easily accessible by public transit.
In this project design the proposed floor plan dimension for the swine carcass
refrigeration system is 20 m W x 25 m L x 12 m H, which will be composed of different facilities
such as receiving area, freezer room, chiller room, storage room, cutting, deboning, and
packaging room, main office. The proposed cold storage facility will be situated in Poblacion
Ibaan, Batangas.
Methods of Determining the Temperature Required for the Cold Storage Facility
For the meat of a swine carcass to be maintained for a long period and transported in
good shape, it must maintain a cool temperature. Hence, it is essential to know what the
working temperature will be to cool and preserve the swine carcass meat.
This proposed project design will focus mainly on the two different sections, which are
the blast freezer and chiller room. Depending on their system procedure, this part has their own
room temperature. The blast freezer will operate at a room temperature of -35°C. In addition,
the items will be stored in a chiller room with an operating temperature of around -20°C to
ensure a lengthy storage capacity.
Methods of Determining the Relative Humidity
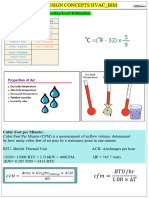
Prior to the design of the facility, the appropriate temperature and humidity must be
considered and determined ad it will help keep the swine carcass meat cool and frozen in cold
storage for longer period. Thus, the relative humidity level should be maintained between 80%
and 90%, to avoid the flesh surface from drying out.
Methods of Determining the Calculation of the Refrigeration Loads
The following are the formulas that will be utilized for the calculation of refrigeration
loads of the swine carcass refrigeration system:
1. Transmission Load
The thermal energy that was transferred to the cold room through the roof, walls, and
floor is known as the transmission load. The following formula can be used to calculate the
transmission load:
U ∙ A ∙ TD∙ 24
Q=
1000
where,
Q is heat transfer (Kwh/day), U is the overall heat transfer coefficient (W/m 2K), A is area
(m2), and TD is the temperature difference between sides of thermal barrier ( oC).
2. Product Load
The heat that is added to the cold room as new goods are delivered is referred to as the
product load. The following formula can be used to calculate the product load:
m ∙C p ( T E−T S )
Q=
3600
where,
Q is heat transfer (Kwh/day), Cp is the specific heat of the product (kJ/kg oC), TE is the
temperature of the product when it enters ( oC), and Ts is the temperature of the room(oC).
3. Infiltration Load
When the door opens, the infiltration load is the amount of heat that is transferred into
the area through the air. The following formula can be used to calculate the infiltration
load:
n ∙ V ∙ E ( T O−T I )
Q=
3600
where,
Q is heat transfer (Kwh/day), n is the number of volume changes per day, V is the volume of
the storage, and E is the energy per cubic meter per oC.
4. Lighting Load
This the calculation of the heat emitted by the lights in the cooled swine carcass storage.
The lighting load is calculated by using the number of lights required to illuminate the entire
cold storage.
Load Lighting = ( No . of Lights ∙Wattage
1000 )(
per Light No . of Hours per day
24 )
5. Occupant Load
The average amount of heat emitted by a person inside a room varies based on the
activity he or she is undertaking. The following formula can be used to compute it:
Load People =HE p ∙ No . of People ( 0.524 )
where,
HEp is the equivalent heat factor of people, and 0.5/24 is a conversion factor.
Methods of Determining the Appropriate Insulation Materials
The use of insulating materials is critical for maintaining the cold storage's temperature.
As a result, it's critical to pick the right insulating material to keep the heat out of the cold
storage. In addition, the insulating material must be cost-effective, practical, and long-lasting.
Methods of Determining the Type of Refrigerant Required
A refrigeration system's thermodynamic efficiency is largely determined by its operating
temperatures. Important practical issues including system design, size, preliminary and
operational costs, safety, dependability, and serviceability, among others, are heavily influenced
by the type of refrigerant chosen for a given application. Hence, choosing the appropriate type
of refrigerant must be taken in consideration to address the issues that might further intervene
in the process.
You might also like
- MEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked RefrigerationDocument25 pagesMEM554 - Thermalfluids Lab Computer Linked Refrigerationsayabudakcomey75% (12)
- E4.3.1-2-3-4-5 - PTB-4-2019 PDFDocument17 pagesE4.3.1-2-3-4-5 - PTB-4-2019 PDFEdison CasallasNo ratings yet
- 01 Hawkins Electrical Guide 1917Document376 pages01 Hawkins Electrical Guide 1917Davide Boreaneze100% (1)
- Refrigeration Heat Load EstimatingDocument17 pagesRefrigeration Heat Load EstimatingAnonymous 1gbsuaafddNo ratings yet
- Phuong Phap Tinh Tai Theo Phan Mem MistralDocument8 pagesPhuong Phap Tinh Tai Theo Phan Mem Mistralntt_121987No ratings yet
- Efficient Display Case Refrigeration: Practical GuideDocument7 pagesEfficient Display Case Refrigeration: Practical GuideCyduck GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load CalculationDocument14 pagesCooling Load CalculationVũ Hằng PhươngNo ratings yet
- Glass Unit V Air-Conditioning Load CalculationDocument26 pagesGlass Unit V Air-Conditioning Load CalculationASWIN KUMAR N SNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: 1.1 Applications and Necessity of RefrigerationDocument21 pagesUnit-I: 1.1 Applications and Necessity of RefrigerationviratNo ratings yet
- Hladnjaca DefrostingDocument6 pagesHladnjaca DefrostingDzana KadricNo ratings yet
- HVAC Cooling Load CalculationDocument98 pagesHVAC Cooling Load CalculationVishnupriya B.100% (1)
- Cooling Load CalculationDocument36 pagesCooling Load Calculationglennmarc.mejascoNo ratings yet
- DR ApichitDocument139 pagesDR ApichitMuh. Yousuf KhanNo ratings yet
- Hvacr 222 AbbieDocument39 pagesHvacr 222 AbbieApril FenolanNo ratings yet
- 2008 ... KULKARNI, Design of Solar Thermal Systems UtilizingDocument14 pages2008 ... KULKARNI, Design of Solar Thermal Systems Utilizingjhonny9204No ratings yet
- Thermosyphon-Assisted Cooling System For Refrigeration ApplicationsDocument12 pagesThermosyphon-Assisted Cooling System For Refrigeration ApplicationsWoo GongNo ratings yet
- DESIGN OF COLD STORAGE FACILITY FOR Anthurium Sp. IN BENGUET PROVINCE, PHILIPPINESDocument13 pagesDESIGN OF COLD STORAGE FACILITY FOR Anthurium Sp. IN BENGUET PROVINCE, PHILIPPINESKimberly OrtizNo ratings yet
- 3 Thermal LoadsDocument19 pages3 Thermal LoadsJaime Fernando Leon TerrazosNo ratings yet
- Searle Engineers HandbookDocument31 pagesSearle Engineers HandbookDavidB1206No ratings yet
- Freezing and Refrigerated Storage in Fisheries - 8. Calculation of Cold Store Refrigeraion Load PDFDocument3 pagesFreezing and Refrigerated Storage in Fisheries - 8. Calculation of Cold Store Refrigeraion Load PDFPrateekNo ratings yet
- DMCDocument7 pagesDMCFares NasserNo ratings yet
- Quick Calculations: For andDocument2 pagesQuick Calculations: For andAhmed AzadNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Calculation: (Aircon Lab)Document24 pagesCooling Load Calculation: (Aircon Lab)matthew ocampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Basic Concepts in RefrigerationDocument113 pagesChapter 1. Basic Concepts in RefrigerationHosnii QamarNo ratings yet
- RAC Handout AC Chapt - 7Document8 pagesRAC Handout AC Chapt - 7Daniel KetemawNo ratings yet
- Designing of Cold Stores and Choosing of Cooling System ElementsDocument15 pagesDesigning of Cold Stores and Choosing of Cooling System Elementsmarzola699No ratings yet
- 3 Thermal LoadsDocument19 pages3 Thermal LoadsLaUpa Ricra PaUlNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load Calculation FormulaDocument2 pagesCooling Load Calculation FormulaYamte VawaNo ratings yet
- 04 MEC 093 Newspaper ArticleDocument7 pages04 MEC 093 Newspaper ArticleJuan Francisco Requejo ZevallosNo ratings yet
- Cooling Load and Heating Load PrincipleDocument18 pagesCooling Load and Heating Load PrincipleSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Ijmet 10 01 065Document7 pagesIjmet 10 01 065IAEME PUBLICATIONNo ratings yet
- Residential Cooling Load CalculationDocument24 pagesResidential Cooling Load CalculationAngeloTomalonNo ratings yet
- Aircon DesignDocument23 pagesAircon DesignAramae DagamiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning ThesisDocument4 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning Thesisfc4b5s7r100% (1)
- Lab 01 RACDocument5 pagesLab 01 RACSaad mubeenNo ratings yet
- Grupo 7Document7 pagesGrupo 7YuneskyNo ratings yet
- HVAC Module 04 Cooling Load 2020Document29 pagesHVAC Module 04 Cooling Load 2020Ziad El SamadNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioner BasicsDocument18 pagesAir Conditioner BasicsBenjamin YusuphNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Storage SystemDocument55 pagesThermal Energy Storage SystemTrain13100% (1)
- Efficient Design, Operation, Maintenance of Cold StorageDocument24 pagesEfficient Design, Operation, Maintenance of Cold StorageVarun V100% (2)
- Cooling Load Estimation For Hibir BoatDocument10 pagesCooling Load Estimation For Hibir BoatAdi WahyudiNo ratings yet
- 4 Load EstimationDocument175 pages4 Load Estimationhasan bishNo ratings yet
- Air Condiitoning Heating & Cooling Load Calculations PDFDocument258 pagesAir Condiitoning Heating & Cooling Load Calculations PDFsaghir meraj100% (1)
- Warehouse Heating and Ventilating: Equipment Selection FactorsDocument8 pagesWarehouse Heating and Ventilating: Equipment Selection FactorsLangzkie NalipaNo ratings yet
- Christoph Reinhart: L12 Thermal Mass and Heat FlowDocument64 pagesChristoph Reinhart: L12 Thermal Mass and Heat FlowT N Roland BourgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7basharatNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines /R&Ac Ic Engines /R&Ac: Course: Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringDocument55 pagesIc Engines /R&Ac Ic Engines /R&Ac: Course: Basic Civil and Mechanical EngineeringSrivikas MathesvaranNo ratings yet
- RefrigeratorDocument1 pageRefrigeratorAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- HAVAC - Design - Cooling Load EstimationDocument11 pagesHAVAC - Design - Cooling Load Estimationchouhanankit0504No ratings yet
- A Lining Management System For Submerged Arc FurnacesDocument10 pagesA Lining Management System For Submerged Arc FurnacesismaglezhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Refrigeration and Air ConditioningCharan Reddy Abbadi100% (2)
- Me Lab Assessment 5Document8 pagesMe Lab Assessment 5Emilio Joaquin FloresNo ratings yet
- Design of Cold Storage Structure For Thousand PDFDocument8 pagesDesign of Cold Storage Structure For Thousand PDFzhyhhNo ratings yet
- Cold Room Heat Load CalculationDocument10 pagesCold Room Heat Load CalculationCd LictawaNo ratings yet
- Load CalculationDocument4 pagesLoad CalculationVirani BharatNo ratings yet
- Reference Design Cold Storage of BeefDocument47 pagesReference Design Cold Storage of Beefhacker poNo ratings yet
- Sun Cam ManualDocument27 pagesSun Cam ManualAzrinshah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Waste Heat Recovery System For Domestic RefrigeratorDocument5 pagesDesign and Development of Waste Heat Recovery System For Domestic RefrigeratorAsifNo ratings yet
- Catalan - Lbyme4a - Ee3 - Design of Experiment - Written ReportDocument5 pagesCatalan - Lbyme4a - Ee3 - Design of Experiment - Written Reportcatalan153709No ratings yet
- Potato Cold Storage Load CalculationsDocument3 pagesPotato Cold Storage Load CalculationsSamiYousif100% (1)
- Cryogenic GuidelinesDocument31 pagesCryogenic Guidelineszvola100No ratings yet
- Design Option 3Document9 pagesDesign Option 3무제untitledNo ratings yet
- Design Options CalculationsDocument10 pagesDesign Options Calculations무제untitledNo ratings yet
- Design FormulasDocument3 pagesDesign Formulas무제untitledNo ratings yet
- Design ComputationsDocument17 pagesDesign Computations무제untitledNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection From Vertical Parallel Plates: An Integral Method SolutionDocument10 pagesNatural Convection From Vertical Parallel Plates: An Integral Method SolutionRenov IdNo ratings yet
- DP024 Chapter 3 Electric Current and Direct Current CircuitDocument37 pagesDP024 Chapter 3 Electric Current and Direct Current CircuitMUHAMAD MUZAMMIL HAKIMI BIN HUSEIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2.2 Forces (Answers)Document8 pagesAssignment 2.2 Forces (Answers)panghua tanNo ratings yet
- Elementary Astronomical Calculations: Lecture-01Document55 pagesElementary Astronomical Calculations: Lecture-01SILENCO ASESINATONo ratings yet
- VSS Lesson 1 Early Atomic Theories Chemistry 12Document11 pagesVSS Lesson 1 Early Atomic Theories Chemistry 12Jaideep GillNo ratings yet
- CL-NG-6460-002-035 Checklist For Circuit Switchers Rev00Document2 pagesCL-NG-6460-002-035 Checklist For Circuit Switchers Rev00WajahatNo ratings yet
- Saidku42129 ch09Document24 pagesSaidku42129 ch09rami wahshehNo ratings yet
- Module ElectronicsDocument20 pagesModule ElectronicsCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- Magnets - Mat and App BookDocument542 pagesMagnets - Mat and App BookHijualpa DanversNo ratings yet
- Clack Sand Filters V2Document2 pagesClack Sand Filters V2Ali KarimNo ratings yet
- General Description Features: 28V/10A Synchronous Ezbuck RegulatorDocument15 pagesGeneral Description Features: 28V/10A Synchronous Ezbuck RegulatorholinsunNo ratings yet
- Transport Properties and Boltzmann EquationDocument25 pagesTransport Properties and Boltzmann EquationSubash PanthiNo ratings yet
- 4.determination of Stefan Boltzmann ConstantDocument3 pages4.determination of Stefan Boltzmann ConstantSuraj RoyNo ratings yet
- 6EP13341LB00 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6EP13341LB00 Datasheet enMihai StefanNo ratings yet
- Power Systems - I Question BankDocument78 pagesPower Systems - I Question BankSuparna DebNo ratings yet
- AC DC Drives Application ConsiderationDocument8 pagesAC DC Drives Application Considerationvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 13 QuestionsDocument64 pagesThermodynamics 13 QuestionsAngelo Luigi Yasay0% (1)
- Tedea: - HuntleighDocument2 pagesTedea: - Huntleighnico_pr82No ratings yet
- Servovalvula Buschjost 82410Document2 pagesServovalvula Buschjost 82410Base SistemasNo ratings yet
- AP Lab Report 6Document10 pagesAP Lab Report 6Talharashid RamzanNo ratings yet
- 9.6MW UPCS PackageDocument10 pages9.6MW UPCS PackagearunghandwalNo ratings yet
- PC Lexan 104Document4 pagesPC Lexan 104countzeroaslNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2tanaya.s.gadkariNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 SolDocument4 pagesAssignment2 SolSrea11No ratings yet
- Questions On Electric Motor With AnswersDocument2 pagesQuestions On Electric Motor With Answersanil1216kumarNo ratings yet
- 3 HM150.08 - Impact of JetDocument15 pages3 HM150.08 - Impact of JetTugau Gates100% (1)
- Balance & Weights: Replicates Observed Weight (G)Document4 pagesBalance & Weights: Replicates Observed Weight (G)Pragya Sharma0% (1)
- 11.1.2 - A53-RF01 - IFC246 Inductive SensorDocument2 pages11.1.2 - A53-RF01 - IFC246 Inductive SensorJul MarteloNo ratings yet