Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2
Uploaded by
Juren LasagaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2
Uploaded by
Juren LasagaCopyright:
Available Formats
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
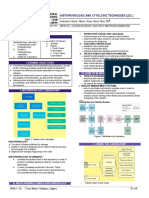
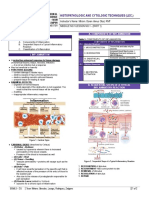
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
● Assessment of female hormonal activity. (sterility &
OUTLINE endocrine disorders) - maturity index
I. Exfoliative Cytology → is achieved by microscopic evaluation for determination of
A. Purpose maturation index (MI), based on examination of smears
B. Preparation taken from the lateral vaginal walls
C. Smear Preparation → Especially as females, we can identify what are the cells
D. Adhesion present during menstrual phase, pre-menstrual phase, and
E. Specimens after the menstruation.
F. Staining Method ● Determination of genetic sex - Barr Bodies (conglomeration
G. Cells found in Cervico-Vaginal Smear of chromatin, XX chromosome)
H. Criteria for the Cytologic Diagnosis of Normal Pregnancy → most of the nuclei of females exhibit conglomeration of
I. Report for Cytologic Smear for Diagnosis of Cancer chromatin, representing XX chromosomes (Barr body), which
J. Other Microscopic Examination Techniques of Cytologic may be demonstrated in the smears from buccal or vaginal
Smears mucosa
● Detects the presence of possible infection.
I. EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
● CYTOLOGY
→ histology of exfoliated, abraded or desquamated cells
▪ This is the study or histology of the cells that are being
removed from the body. Cells that were scraped from the
body.
▪ Give an example of body fluid that is being removed from
the body:
− CNS - Cerebrospinal Fluid Figure 1. Barr body in Females
● IMPRINT/ABRADED CYTOLOGY
→ Study of cells directly taken from surfaces of excised B. PREPARATION
specimens by touching them to a clean glass slide ● Material from fluids of the body may be examined either by:
▪ To clean glass slides. So, we will go back a little bit to the → Preparation of Smears
different fresh tissue preparations from the last prelims. → Preparation of Tissue Blocks (Cell Blocks)
Most of the preparations that we are performing for
exfoliative cytology will include the use of slides,
smearing, spreading on the slides.
● EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
→ Microscopic study of desquamated cells from epithelial
surfaces.
→ Study of cells that have been shed or physically removed
▪ We will be studying those cells that are being removed
physically on the body
BOOK INFORMATION: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
▪ Exfoliated cells may be found in smears that have been
Figure 2. Tissue/Cell Blocks
spontaneously shed or physically removed from epithelial and
mucous membranes. ● Various Regions
▪ Specimens can be collected from the epithelial surfaces by → Vaginal Smear
lightly scraping the surface, by swabbing, aspirating or → Endometrial and endocervical smear
washing the surfaces. → Prostatic and breast secretion
→ Gastric or bronchial secretions
A. PURPOSE → Pleural or peritoneal fluids
● Assessing cancerous conditions (staging) → Sputum
→ With these body fluids, we can identify what is the stage of → Smears of urine sediment
the cancer ng patient. If it is on the critical stage, or early → Cerebrospinal fluid
stage. ▪ (PPVE - PGP - SSC)
● Detection of asymptomatic cancers
→ Asymptomatic Cancer example - Cervical Cancer C. SMEAR PREPARATION
▪ Cervical cancer, upon diagnosis, usually it’s on stage ● Make smears from fresh and moist material on clean slide;
three. Usually, stage 1 and 2, it has no signs and should not have clumps
symptoms. So that is why. We are familiar with Pap Smear → When we are making a smear, make sure that it is not too
no? That is an example of the test to identify this thin or not too thick. It must be uniformly spread on our slide.
asymptomatic cancer. Because this pap smear class, it is It should not have clumps.
a screening test. So, it can identify early if you have this ● Diamond pen Is used to put Identifiers on the smear (name,
cancer - cervical cancer. age, date, and type of smear); frosted-end slides may also be
used
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 1 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
→ During labeling, diamond pen or lead pencil must be used ▪ Air drying is avoided with smears for cytological detection of
neoplasia because it changes the appearances of the cells.
▪ Slides bearing blood or bone marrow smears, on the other
hand, are usually air-dried. Marrow smears are stained in
parallel to sections of the bone marrow core biopsy.
SMEAR PREPARATION CONCENTRATION:
NOTE:
● Best (yet flammable) fixative - 95% ethanol-ether
● Routinely used fixative - 95% ethanol
If smears cannot be made immediately, place the collected
material in 50% alcohol (for all types of effusions) —> replaced
. by Saccamono’s preservative
Figure 3. Diamond Pen ● Saccamono’s Components: 50% ethanol , 2% carbowax
● Immerse smears immediately in fixative by a single There are instances that we cannot perform the smear
uninterrupted motion (exfoliated cells decompose rapidly immediately, what would be our remedy for this? So we will place
● Spray fixatives: 12 Inches or 1 foot away it in a 50% alcohol and then replace it with Saccamono’s
→ If it is used near the slide, there will be an increase of Preservative
pressure, then the tissue will be erased.
● Storage: add ROH & refrigerate. (If we are going to store
our sample, we will add alcohol and refrigerate it with the
following concentration.)
→ 50% - pleural / peritoneal
→ 70% - sputum
→ 95% - urine, bronchial, gastric
● Mailed Specimen: air-dry for 10-15 minutes after 2 hrs fixation
& place in a container
● If specimen Is more than a few drops:
Figure 4. Spray Fixatives → Centrifuge at 2,000 rpm for 2 minutes.
→ Afterwards, decant the supernatant, and smear the sediment
● Avoid in the container to prevent the cells from dislodged directly to the glass slide, or cytocentrifuge directly on the
● Optimal time: 1 hour to allow dehydration; adhesion and slide with albumin.
maximal penetration of the fixative
→ Extra sediment can be used for cell block technique.
Figure 2. Smear Preparation
BOOK INFORMATION: (Smear Preparation)
▪ Smears should be made from fresh material, prepared in the
doctor's office or radiology units.
▪ Specimens can be collected from the epithelial surfaces by
lightly scraping the surface, by swabbing, aspirating or
washing the surfaces
▪ The commonly received cytoprep is that of the “thin prep.” Figure 4. Smear Preparation if specimen is more than a few drops
These smears are wet-fixed in 95% ethanol immediately after
preparation to preserve the fine structure of the chromatin and
help in the evaluation of nuclear changes.
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 2 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
GENERAL PROCESSING: A. RESPIRATORY SPECIMENS
General Processing ● SPUTUM
Viscous specimen Immerse in Ether ROH ASAP → Demonstrate abnormal cells early in disease
● Cervical, Vaginal, → Fresh, unifixed, at least 3 consecutive early morning
Prostate Secretion sputum
Mucoid Specimens Dry smear edges before fixing (to ▪ We must give clear instructions. Patients are the
● Sputum, Bronchial avoid runoff) ones that will collect the sample in their
and Stomach houses, early in the morning.
Secretions ▪ We must instruct the patient to collect three
Bloody specimens RBC can be destroyed by adding consecutive samples. The patient must have
2-5 mL of conc. Acetic acid per CONTAINER 1, CONTAINER 2, CONTAINER 3.
100 mL of the specimen ▪ So collection of this one must have 1 hour
For example, we received a interval
sample na CSF. To destroy RBC ▪ Since it is early morning, It is important to put the
present in the CSF (have time, so that we can identify what is the first one,
problems with the collection), add second, etc.
concentrated acetic acid per 100 → Patients unable to produce sputum: INDUCED
mL of the specimen. SPUTUM by inhalation of aerosol solution for 20
minutes
▪ If ever the patient has undergone repeat collection
many times, we can give them aerosol solution.
Inhalation lang for 20 minutes.
▪ Why aerosol solution? Because it can trigger
Water Specimens (urine, Specimen is centrifuged first and asthma. There will be sputum formation.
exudate, aspirate) the sediment is smeared in an ▪ Not recommended to everyone. Upon the
albumin coated glass slide. In the recommendation of the doctor.
event that there is excess → Wide mouthed bottle w/ Saccomanos's fluid
sediment, it may be subjected to ▪ The container must have a wide mouth
biopsy ▪ The sample needs to be preserved since the
sample came from the patient’s house.
D. ADHESION → After collection:
● For adequate adhesion of smeared material, ▪ Pour specimen in petri dish, examine for solid or
● Albumin not recommended because it will retain the OG of blood flecked particles
Pap stain ▪ Remove particles, place on slide, crush w/
● Specimens That Require Adhesives : another slide. Evenly distribute
→ Urinary sediment ▪ Fix for a minimum of 1 hour
→ BAL − After receiving the sample, we are going to
→ Specimens with proteolytic enzymes (saliva) prepare it using the crushing technique.
→ Concentrated sputum → Absence of histiocytes and alveolar macrophages
● Characteristics of Adhesives: indicate that only saliva was collected
→ permeable to both fixative & stain ▪ If saliva is collected, repeat the collection.
● Examples of Good Adhesives : ▪ How to collect the sample? It must be a deep
→ Pooled Serum / Plasma cough.
→ Celloidin Ether Alcohol ▪ We are going to look for histiocytes and alveolar
→ Leuconostoc Culture macrophages.
E. SPECIMENS BOOK INFORMATION: (sputum smear)
● Generally divided into two major areas. We have ▪ Collect early morning sputum by a deep cough in a wide
non-gynecologic specimens and gynecologic specimens. -mouthed jar containing Saccomanno fluid (50% ethyl alcohol
→ If gynecologic, they are samples from females. Other and 2% carbowax).
samples like sputum, urine, and others, non-gynecologic. ▪ If a more extensive study is to be made, it is recommended
● Non-gynecologic Specimens that a minimum of 2-4 slides be prepared, and one is air dried
→ Respiratory Specimens for Giemsa staining. At least two slides should be stained by
→ Gastrointestinal Specimens Papanicolaou method.
→ Peritoneal, Pleural & Pericardial Smears ▪ If no solid particles are found, an attempt should be made to
→ Urine secure representative samples from both thin and thick
→ Breast Secretions portions. With the end of a wooden applicator stick, these
→ CSF samples are evenly spread on the slides and immediately
→ Prostatic Secretion placed in fixative for a minimum of one hour.
● Gynecologic Specimens ▪ Sputum collected should have been coughed from
"down-deep" to ensure that the specimen is a true
I. NON-GYNECOLOGIC SPECIMENS representative of the sputum and not just saliva. The mucus
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 3 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
present preserves the cell constituents; however, it is highly → smear must contain epithelial cells (ciliated bronchial
recommended that the specimen be as fresh as possible cells) + RBC and WBC
when examined, if better cellular detail is to be appreciated. → If specimen is scanty, prepare smear in OR to prevent
drying
● BRONCHIAL BRUSHING
→ Directly smear on two slides using Pull-apart
technique
→ Fix immediately to avoid production of Air drying
artifacts
Figure 7. Bronchial Aspirates
Figure 5. Bronchial Brushing
BOOK INFORMATION: (bronchial brushing)
▪ The slides are then fixed by a spray fixative or immediately
immersed in 95%alcohol. Failure to fix the slides within a few
seconds will produce unsatisfactory cytologic results due to
air drying artifact.
● BRONCHOALVEOLAR LAVAGE (BAL)/ BRONCHIAL
WASHING Has cilia; an indication of the doctor that is really a bronchial
→ Performed in patients with AIDS to rule out aspirate
Pneumocystis jirovecii infection Among these four, sputum lang ang patient ang mag collect.
▪ Also the causative agent of pneumonia The rest, si doctor na ang mag collect.
BOOK INFORMATION: (bronchial aspirate)
▪ The secretion obtained at bronchoscopy are collected either
by aspiration into a glass suction apparatus or by washing the
bronchi with 1-2 cc. of saline, into a cup, if sufficient in
amount, and sent immediately to the laboratory for
preparation and examination.
B. GASTROINTESTINAL SPECIMENS
● 2 methods: Through the mouth or Levine method -
through nasogastric
● GASTRIC LAVAGE, GASTRIC BRUSH, SUBMUCOSAL
LESION FNA
Figure 6. Bronchial Washing → Collection:
▪ Irrigation
BOOK INFORMATION: (bronchial washing) ▪ Aspiration
→ Difficult due to inaccessibility and presence of gastric
▪ Bronchial Washing specimens are freshly collected in the
fluid
bronchoscopy collection container and hand delivered to the
→ Examine ASAP
laboratory
▪ Sample must be processed as soon as possible
→ 8 hours fasting before gastric washing; even water is
● BRONCHIAL ASPIRATES
prohibited
→ Collection:
▪ Even water is prohibited
▪ aspiration (with glass suction apparatus) or
▪ washing (with saline)
→ Show evidence of malignancy in advanced stage for
20-30 minutes, medium speed
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 4 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
after spending extended time period in acid
environment in the bladder
▪ In the morning, urine stays longer in the bladder
→ Female - catheterized
● At least 50 mL is needed
● For more reliable evaluation, urine may be collected and
examined twice: early morning and later in the day
● Use of preservative is not recommended
→ For diagnosis urothelial malignancy and not for
prostatic carcinomas
▪ Malignancy in the bladder, urethra, or renal pelvis
▪ Not on the prostate
Figure 8. Gastric Washing
BOOK INFORMATION: (gastric smear preparations)
▪ Specimen should be examined as soon as possible since any
delay of more than I /2 hour, before fixation, will digest the
cells and make the specimen unsatisfactory for evaluation.
▪ The patient should have fasted for at least 8 hours before
gastric washing is performed. Esophageal washings are to be
examined immediately
C. PERITONEAL, PLEURAL, & PERICARDIAL SMEARS
● Paracentesis
→ For the extraction of peritoneal, pleural, pericardial
fluid Figure 10. Urine
● Collection: same as bronchial specimens
→ Increased fluid indicates pathologic process BOOK INFORMATION: (urinary tract)
→ Presence of malignant cells usually indicate ▪ Voided urine from males is usually sufficient for cytological
metastasis evaluation, but for female patients, a catheterized specimen is
→ Add 300 units of heparin per 100 mL of aspirate to recommended to prevent contamination of specimen with
avoid clots vulvar cells.
▪ Because peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial ▪ Early morning specimen yields the greatest number of cells,
samples are prone to clotting but such cells are usually distorted due to prolonged bladder
retention
▪ Smears of sediments should be prepared and fixed as soon
as possible after collection. Since a great proportion of cells
become detached during fixation, unsatisfactory smears may
result in false negative diagnosis.
▪ The collection technique should be always mentioned on the
requisition form. The cytomorphologic features of low grade
urothelial carcinomas may be indistinguishable from those of
Figure 9. Peritoneal, Pleural, & Pericardial Smears
reactive urothelial hyperplasia.
BOOK INFORMATION: (serous effusion)
E. BREAST SECRETION
▪ The presence of malignant cells in serous effusions usually ● Collection: Spontaneous nipple discharge
indicate metastatic involvement and, therefore, a higher stage ● Materials: cotton swab or touch prep (Touch the nipple
of cancer directly during discharge using the slide or cotton swab)
▪ They can be collected in tubes or syringes that may be either → For hormonal imbalance testing
plain or pre-heparinized, to prevent coagulation ▪ Not an indication or phase of cancer
▪ Freshly tapped specimens are preferred for cytology. If → Benign breast lesion or endocrine problems
immediate processing is not possible, it can be preserved in → Extremely low diagnostic yield for breast carcinoma
the refrigerator for a period of 24-48 hours or pre-fixed in 50% diagnosis
ethanol. Albuminized slides should be used to prepare → If bloody, benign intraductal papilloma
smears from prefixed sample.
D. URINE
● Collection:
→ Male - Second voided urine
▪ First morning is not recommended for cytologic
evaluation because the cells may degenerate
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 5 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
BOOK INFORMATION: (CSF)
▪ Cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples degenerate very
quickly and are usually present in very low numbers. Once the
slide has been prepared, it should be rapidly air dried before
staining. The addition of an equal amount of ethyl alcohol to
the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is recommended if a delay in
processing is anticipated. For CSF specimens, a minimum
amount of 1 cc. is necessary for cytologic evaluation
G. PROSTATIC SECRETION
● 3 Specimen:
Figure 11. Breast Secretion → Voided urine before massage
→ smear of prostatic secretion by massage
BOOK INFORMATION: (breast secretion) → urine after massage
▪ Spontaneous nipple discharge is usually a result of hormonal ▪ Label the container with ‘before’ and ‘after’ to
imbalance in young patients, and when the secretion is bloody distinguish the time of urine collection
a benign intraductal papilloma should be considered clinically. ▪ If unproductive massage = urine should still be
▪ The spontaneous nipple discharge should be smeared on a passed
clean glass slide, and immediately placed in fixative. ● Cytologic examination of 3rd specimen after
▪ In women, except during lactation and the immediate unproductive massage is recommended
post-lactation period, any discharge from the nipple is
abnormal .
▪ The nipple discharge is usually due to a benign breast lesion
such as duct ectasia and papilloma , or due to endocrine
problems.
▪ However the major value of cytologic examination of nipple
discharge is potential detection of malignant cells in a patient
with clinically undetected carcinoma.
Collection Technique:
▪ Gently strip the subareolar area and nipple using the thumb
and forefinger.
▪ Place the labeled slide upon the nipple and draw it quickly
across the nipple.
▪ If more than a drop is collected, use another slide to smear
with a pull-up technique.
▪ Immediately drop slide in a bottle of 95% isopropanol or use
spray fixative. Figure 13. Prostatic Secretion
▪ If the secretion is scanty in amount, smears should be
restricted to a small area of the slide to prevent drying. II. GYNECOLOGIC SPECIMENS
▪ Secretions obtained from both breasts should be properly A. VAGINAL AND CERVICAL SMEARS
identified as left or right. ● Screening test for precancerous condition
▪ For localized breast lesions producing discharge upon → Not an identification for cancer
pressure, the secretion may be smeared directly on the slide → Recommended for females (35 yrs old and above)
after expressing material from the breast ▪ If the female has a child = recommended to
undergo Pap Smear
F. CEREBROSPINAL FLUID ● Not diagnostic
● Minimum of 1 mL is necessary ● Transformation zone (T-zone: junction of the
● Manner of extraction: Lumbar Puncture endocervical mucosa)
● Collection: aspiration of posterior fornix, swabbing,
● Instruments:
→ 8 inch glass pipette & rubber bulb (for cancer
cytology)
→ Sterile tongue depressor (for hormonal studies)
→ Ayre’s spatula
→ Cervix brush
Figure 12. Cerebrospinal Fluid
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 6 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
endocervix, smeared on glass slides and stained by the
Papanicolaou (Pap) method. The entire procedure is known
as Pap smear. Because cervical cytology is a screening test,
abnormal findings must be confirmed histologically.
▪ The patient should abstain from coitus, not douche the vagina
for at least a day, and not apply intravaginal preparations for
at least one week before the examination. Smears should not
be taken during menstrual bleeding, because of
contamination with blood, endometrial component, and tissue
debris that can obscure the cells during smear examination.
▪ Various collecting systems such as cotton swabs, wooden or
plastic spatula, and cervical brushes, so-called cytobrushes,
are generally used to collect gynecology cells. In brush
biopsies, more endocervical cells and blood may be present
in the smears, and this may lead to valuation difficulties. The
use of cotton swab for collection of cervical smear is to be
discouraged because of the drying artifacts and loss of cells
that are caused by this method. Wooden spatula is preferable
to plastic spatula, because of its mildly rough surface that can
collect more material. Endo-cervical brushing is used strictly
for taking materials from endocervix.
▪ After smear collection, the sample is evenly smeared on to
the center of the non-frosted area of the glass slide and fixed
immediately. Excessively thin or thick smears can result in
false-negative reports.
CYTOLOGIC COLLECTION AND PREPARATION:
Cytologic Collection and Preparation
Figure 14. Vaginal and Cervical Smears Instruments Endocervical brush samples of endocervical canal
● PRECAUTIONS FOR VAGINAL SMEAR PREP Vaginal scrape patients with hysterectomy
→ Patient must avoid vaginal exam’n or douching 24-48
hours before collection. Lateral vaginal scrape for hormonal evaluation
→ Spread smear thinly in a rotary motion
→ Glass pipette must be absolutely dry Four quadrant vaginal scrape for localization of vaginal
→ No lubricant or powder must be used adenosis
Vulvar scrape for detection of herpetic
lesions or carcinoma
Figure 15. Precautions Figure 16. Cytologic Collection and Preparation
BOOK INFORMATION: (cervical smear) F. STAINING METHOD
● PAPANICOLAU STAINING METHOD
▪ Cancer of the uterine cervix is the commonest cancer that can
→ Staining method of choice
be detected even at the pre-invasive stage. Cervical cytology
→ Developed by Dr. George Papanicolao (1940)
screening involves the microscopic examination of cell
→ Detecting human uterine & cervical CA.
samples that have been taken primarily from the ecto- and
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 7 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
→ Cytologic evaluation of other secretions → Upper lateral 3rd of vaginal wall (less contamination &
→ Transparent blue staining of cytoplasm accessible)
▪ due to the action of high alcoholic content of the → Wooden spatula is recommended only in vaginal hormonal
cytoplasmic counterstain, allowing overlapping cells to be studies
seen and identified. → LPO:
→ Excellent nuclear detail is produced ▪ Assess smear & staining quality
→ Color range is predictable ▪ Detect RBC & WBC
▪ and of great value in identification and classification of ▪ Detect type of exfoliated cells
cells, producing a good differential coloring of basophilic ▪ Rough assessment of cell proportion
and acidophilic cells → HPO: Quantitate
→ Valuable in comparing cellular appearances in smears
▪ with their counterpart in similarly stained sections.
MAKE USE OF 3 STAINS:
Stain Cells stained
Hematoxylin Nuclear structure
OG6 (orange green) Cytoplasm of mature cell
Eosin Azure Cytoplasm of immature cell
Figure 17. Vaginal Hormonal Cytology
Components:
Eosin
PTA
G. CELLS FOUND IN CERVICO-VAGINAL SMEARS
Light green stain (36, 50, 65) 1. Mature superficial cells
Lithium carbonate 2. Intermediate cells
Bismarck brown 3. Parabasal cells
4. Basal cells
5. Endometrial cells
6. Endocervical glandular cells
7. Doderlein bacilli
Figure 17. 3 Stains
● MODIFIED PAP’S METHOD
→ It omitted the Bismarck brown dye from EA solution
→ Sharpness of color and brilliant staining reactions are
improved
BOOK INFORMATION: (papanicolaou stain)
▪ Papanicolaou's stain (also known as Pap stain) is a
multichromatic staining cytological technique that is used to
Figure 18. Cells found in cervico-vaginal smears
differentiate cells in smear preparations of various bodily
secretions, including gynecological smears (Pap smears),
sputum, brushings, washings, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, MATURE SUPERFICIAL CELLS
abdominal fluid, pleural fluid, synovial fluid, seminal fluid, fine ● Polygonal
needle aspiration material, tumor touch samples, or other ● Pale pink cytoplasm
materials containing cells. ● Dark pyknotic nuclei (< 6 µ)
● Abundant during proliferative phase
● VAGINAL HORMONAL CYTOLOGY → Before menstruation
→ Inexpensive ● True acidophilia (due to estrogen)
→ Not commonly used nowadays → Due to estrogen
→ performed regularly even in pregnant women without undue ● Pseudoacidophilia:
risk → Vaginal prolapse and drying
→ No prior vaginal examination or douching in the last 24 hours → Drying of smears
→ Infection
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 8 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
→ Chemicals
Figure 19. Mature superficial cells.
INTERMEDIATE CELLS
● Medium sized polyhedral or elongated cells
● Basophilic cytoplasm with vacuoles
Figure 21. Parabasal Cells
● Abundant during secretory phase (influenced by progesterone)
A. NAVICULAR CELLS
BASAL CELLS
→ Boat shaped; folds / curls on edges ● Small, round to slightly oval cells
→ Estrogen progesterone effect ● Large nuclei (> half of cell vol.)
→ Latter half of menstrual cycle, pregnancy, & ● Strongly basophilic cytoplasm
menopause ● Found before puberty & after menopause
B. PREGNANCY CELLS
→ Round, oval cells
→ Translucent basophilic cytoplasm at the center of cell
d/t central glycogen accumulation
→ Eccentric nucleus
→ Double walled boundary with deep blue stain at the
cytoplasmic periphery
Figure 20. Intermediate cells. Figure 22. Basal Cells
PARABASAL CELLS ENDOMETRIAL CELLS
● Smaller than intermediate cells ● Like parabasal cells; slightly cylindrical
● Thick, round to oval ● Less basophilic cytoplasm
● Smaller strongly basophilic cytoplasmic area ● During & 1-4 days after menstruation
● Larger vesicular nucleus than intermediate cells
● 2 weeks of age to puberty, after childbirth, abortions & after
menopause
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 9 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
Figure 25. Doderlein Bacilli
FERNING PHENOMENON
● “fern”/palm-leaf pattern of salt crystals
Figure 23. Endometrial Cells ● seen on dried cervical mucus
● signifies persistent estrogen effect
ENDOCERVICAL GLANDULAR CELLS ● basis for diagnosing early pregnancy
● Occur in large group or sheets
● Honeycomb appearance
● Finely vacuolated pale blue/gray cytoplasm
Figure 26. Ferning Phenomenon (positive & negative results)
H. CRITERIA FOR THE CYTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS OF
NORMAL PREGNANCY
1. Marked progesterone effect
2. At least 50% of intermediate cells in cluster
3. At least some typical pregnancy cells are present
4. Less than 30% mature superficial cells
5. Doderlein-filled dirty background
Figure 24. Endocervical Glandular Cells
QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION FOR VAGINAL CYTOLOGY
Quantitative Evaluation for Vaginal Cytology
DODERLEIN CELLS
Maturation Index The percentage of cells from the main
● Lactobacillus acidophilus
(MI) layers of vaginal epithelium (superficial,
● most common normal vaginal flora
intermediate and deep)
● blue to lavender w/ Pap’s
Criterion: Pyknosis
● Increased number indicates healthy vagina
● Numerous in: last trimester of pregnancy, infection, estrogen Acidophilic Index (AI) The percentage of cells staining
deficiency, DM pink-orange to red with Pap’s smear.
● Decreased number leads to increase in population of invasive This is not a reliable index due to
Lepthothrix species; comes with presence of Trichomonas possible pseudoacidophilia
vaginalis Pyknotic Index (PI) The percentage of cells with shrunken,
dark and small structure-less nuclei
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 10 of 11
SCHOOL OF MEDICAL
LABORATORY SCIENCE
HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LEC.)
SAN PEDRO COLLEGE – MAIN
CAMPUS
Instructor’s Name: Ma’am. Doren Venus Otod, RMT
AY 2022 – 2023 - 2ND SEMESTER LESSON 2: EXFOLIATIVE CYTOLOGY
I. REPORT FOR CYTOLOGIC SMEAR FOR
DIAGNOSIS OF CANCER
CLASS I Absence of Atypical or abnormal cells
CLASS II Atypical Cytologic Picture but no evidence of
malignancy
CLASS III Cytologic picture suggestive but not conclusive
of malignancy
CLASS IV Cytologic picture strongly suggestive of
malignancy
CLASS V Cytologic picture conclusive of malignancy
J. OTHER MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
TECHNIQUES OF CYTOLOGIC SMEARS
1. ACRIDINE ORANGE FLUORESCENT TECHNIQUE
a. Binds DNA -> green/yellow
i. If increased (↑): MALIGNANCY
b. Binds RNA -> brick-orange red
i. If increased (↑): GROWTH
2. PHASE CONTRAST MICROSCOPY
a. The second best choice after Pap’s staining
b. Used for hormonal evaluation of gynecologic specimen
and for cancer detection
3. INTERFERENCE MICROSCOPY
a. Determines the dry weight of individual cells or cellular
constituents
b. Very expensive and complex
BSMLS – 2G Team Writers: Bersabe, Lasaga, Rodriguez, Zwijgers 11 of 11
You might also like
- Lesson-21 Exfoliative Cytology PDFDocument4 pagesLesson-21 Exfoliative Cytology PDFSasa AbassNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Krizza UrmazaNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative CytologyDocument9 pagesExfoliative Cytologymiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Histopath CompiledDocument155 pagesHistopath Compiledp27z9vg2yfNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument39 pagesIntroductionarellanokristelleNo ratings yet
- Cytological TechniquesDocument4 pagesCytological TechniquesJamie100% (1)
- (PH156) 15 Introduction To CytologyDocument5 pages(PH156) 15 Introduction To CytologyRosshlein Marian YangsonNo ratings yet
- Cytology Sample Collection and Preparation For Veterinary PractitionersDocument8 pagesCytology Sample Collection and Preparation For Veterinary PractitionersKmo mastnNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 6Document6 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 6Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Cytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHDocument201 pagesCytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHbusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- 3rd Seminar Exfoliative CytologyDocument57 pages3rd Seminar Exfoliative CytologydevikaNo ratings yet
- CytopathologyDocument6 pagesCytopathologynevelle4667No ratings yet
- 7 Diagnostic CytologyDocument4 pages7 Diagnostic CytologyJovelyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lecture Part 1 3 Hanz Santos Merged 1Document21 pagesHistopath Lecture Part 1 3 Hanz Santos Merged 1joal bunagNo ratings yet
- Internship: Genetics and Pre-Natal Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) LaborotaryDocument9 pagesInternship: Genetics and Pre-Natal Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) LaborotaryPratika NagpalNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Fresh TissueDocument3 pagesPreparation of Fresh TissueMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- Histopath 1Document3 pagesHistopath 1Winnie Gay UanangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 21 PDFShirmayne TangNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument27 pagesTissuesAngela Nicole Udan100% (1)
- Barr Body Lab.4 PDFDocument13 pagesBarr Body Lab.4 PDFكرار 2No ratings yet
- Proceedings - J Brazzell1Document130 pagesProceedings - J Brazzell1Ganesh Dasara100% (1)
- Clinical PathologyDocument4 pagesClinical PathologyMicky FantaNo ratings yet
- Clinpara Finals LabDocument81 pagesClinpara Finals LabAnne CabreraNo ratings yet
- 001 - Gphc100: Intro To Quality ControlDocument7 pages001 - Gphc100: Intro To Quality ControlEricka MasakayanNo ratings yet
- Histopathology: 1. Routine Histopathologic ExaminationDocument2 pagesHistopathology: 1. Routine Histopathologic ExaminationPat DazaNo ratings yet
- Mycoplasma Spp.Document14 pagesMycoplasma Spp.Sowon wiNo ratings yet
- 5 Lect 5 Pract 23-24leishmaniaDocument14 pages5 Lect 5 Pract 23-24leishmaniaSaadNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged-2Document8 pagesIlovepdf Merged-2Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Part 1 PDFDocument12 pagesHistopathology Part 1 PDFJanneth MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination - HistopathDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination - HistopathIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- PARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Document5 pagesPARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection Processing Modified VersionDocument10 pagesSpecimen Collection Processing Modified VersionJohn Vincent TacalNo ratings yet
- Histopath Topic 3 PrelimDocument103 pagesHistopath Topic 3 PrelimKatrina JornadalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic CytologyDocument32 pagesDiagnostic Cytologyclaw foreSK TeamNo ratings yet
- Trans Histopath 3Document5 pagesTrans Histopath 33A PEÑA AndreaNo ratings yet
- dv09069 PDFDocument3 pagesdv09069 PDFIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cytology and Cytological Techniques-Dbb40103 2019Document41 pagesIntroduction To Cytology and Cytological Techniques-Dbb40103 2019Bintu AmirudinNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Cytopathology: Dr. Sanjiv Kumar Asstt. Professor, Deptt. of Pathology, BVC, PatnaDocument51 pagesDiagnostic Cytopathology: Dr. Sanjiv Kumar Asstt. Professor, Deptt. of Pathology, BVC, PatnaMemeowwNo ratings yet
- Histocytologic Technique: Prepared By: EGB, RMTDocument4 pagesHistocytologic Technique: Prepared By: EGB, RMTjuamiakaNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingDocument4 pagesNOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingOdette G. TanNo ratings yet
- 214 Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol - March-April 2009 - Vol 75 - Issue 2Document3 pages214 Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol - March-April 2009 - Vol 75 - Issue 2Cindy MaslagNo ratings yet
- Benign EffusionsDocument7 pagesBenign EffusionsMugomba JuliusNo ratings yet
- LaSala Rocco-SCACM 2017 Workshop-Cyto Histo IntroDocument36 pagesLaSala Rocco-SCACM 2017 Workshop-Cyto Histo Introrut4soloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Histopathology Lec.Document56 pagesClinical Laboratory Histopathology Lec.phd0780No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Bacterial Identification and Processing ModuleDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Bacterial Identification and Processing ModuleTinNo ratings yet
- at NeoplasmDocument50 pagesat NeoplasmNazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SpecimenDocument50 pagesChapter 4 SpecimenCherenet TomaNo ratings yet
- HPCT Lec MidtermsDocument25 pagesHPCT Lec MidtermsKRISTERLEX RUIZNo ratings yet
- Placenta ChecklistDocument2 pagesPlacenta ChecklistNidhi Shivam Ahlawat100% (3)
- Columbia University From Gastrulation To CleavageDocument18 pagesColumbia University From Gastrulation To CleavageKay YgNo ratings yet
- Overview of Pap SmearDocument2 pagesOverview of Pap SmearFaye AlmiraNo ratings yet
- J Bbagrm 2009 02 002Document7 pagesJ Bbagrm 2009 02 002Raymundo Lopez NNo ratings yet
- Proper Processing of Fresh Tissue - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LabDocument4 pagesProper Processing of Fresh Tissue - SPC MLS 2B - Histopath LabMa. Erikah CancioNo ratings yet
- MethodsDocument12 pagesMethodsMohammad_Islam87No ratings yet
- Lesson5.3 LabDiaofTBDocument3 pagesLesson5.3 LabDiaofTBJAY JR. APONNo ratings yet
- Clinical Virology Unit 5 DiagnosisDocument68 pagesClinical Virology Unit 5 DiagnosisTeklewNo ratings yet
- Bacteria, Virus, Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma, Parasite, Toxin, PoisonsDocument5 pagesBacteria, Virus, Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma, Parasite, Toxin, PoisonsNerdyPotatoNo ratings yet
- 0192623308326152Document7 pages0192623308326152DANIELLE JOYCE BACSALNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 3 - Topic 4Document2 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 3 - Topic 4Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Is Lab. Activity 1 ETSDocument6 pagesIs Lab. Activity 1 ETSJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- GRP 04 - Staining of Bone Marrow and Blood ElementsDocument11 pagesGRP 04 - Staining of Bone Marrow and Blood ElementsJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 5 - Topic 7Document8 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 5 - Topic 7Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Trace Elements Clin. Chem. Lab.Document4 pagesTrace Elements Clin. Chem. Lab.Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 6Document6 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 6Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- HIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 7)Document9 pagesHIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 7)Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 5Document5 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 4 - Topic 5Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2Document3 pagesHistopath Lec - Week 2 - Topic 2Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesExperiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesExperiment 8 - Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - STS 100 - During Scientific RevolutionDocument4 pagesLesson 8 - STS 100 - During Scientific RevolutionJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Finals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineDocument17 pagesFinals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Document6 pagesBiochem Lec Transes (Week 4)Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Histo Lec - Female Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesHisto Lec - Female Reproductive SystemJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- His Lab Prelim NotesDocument14 pagesHis Lab Prelim NotesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Week 1: Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocument6 pagesOutline: Week 1: Introduction To Analytical ChemistryJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry Part 3: OutlineDocument6 pagesMidterms: Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry Part 3: OutlineJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- HIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 4)Document3 pagesHIMLS LEC TRANSES (Week 4)Juren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - STS 100 - The Middle AgesDocument5 pagesLesson 6 - STS 100 - The Middle AgesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesOutline: Midterms: Calculations Used in Analytical ChemistryJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - STS 100 - Science and Technology in Pre-Columbian TimesDocument5 pagesLesson 5 - STS 100 - Science and Technology in Pre-Columbian TimesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec - The Nature of Analytical ProcessDocument19 pagesChem Lec - The Nature of Analytical ProcessJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - A STS 100 - Science and Technology During RenaissanceDocument5 pagesLesson 7 - A STS 100 - Science and Technology During RenaissanceJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - B STS 100 - Science and Technology During RenaissanceDocument8 pagesLesson 7 - B STS 100 - Science and Technology During RenaissanceJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- 03 Calibration Standards Pgs 39-84 Date 17-06-10 WebDocument46 pages03 Calibration Standards Pgs 39-84 Date 17-06-10 WebGert ten Brink100% (1)
- Activity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationRoan Eam TanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology-Practical 3Document3 pagesMicrobiology-Practical 3Dhanuja jayamalNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sem Tem FixDocument9 pagesJurnal Sem Tem FixSri Wahyuning Puji Ayu LestariNo ratings yet
- Peripheral SmearDocument12 pagesPeripheral Smearapi-3823785100% (1)
- CDN Ed Biology Exploring The Diversity of Life 2nd Edition Russell Test BankDocument25 pagesCDN Ed Biology Exploring The Diversity of Life 2nd Edition Russell Test BankMichaelMeyerfisp100% (66)
- Influence of Temperature and Thickness On The Off-Axis Behaviour of Short Glass FibreDocument13 pagesInfluence of Temperature and Thickness On The Off-Axis Behaviour of Short Glass FibreAndres Felipe Perez MarinNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument24 pagesEpithelial TissuesyoloNo ratings yet
- High-Power and Femtosecond Lasers: Properties, Materials and Applications: Properties, Materials and Applications, Nova Science PublishersDocument501 pagesHigh-Power and Femtosecond Lasers: Properties, Materials and Applications: Properties, Materials and Applications, Nova Science PublishersShahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- The Giemsa Stain Its History and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesThe Giemsa Stain Its History and ApplicationsMaritza GranadilloNo ratings yet
- User Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesDocument22 pagesUser Manual Trinocular Compound LED Microscope: Model M8311Z SeriesMarcelo WillyNo ratings yet
- A Method For Staining Epoxy PDFDocument6 pagesA Method For Staining Epoxy PDFVansala GanesanNo ratings yet
- Kodak WrattenFilters TextDocument50 pagesKodak WrattenFilters TexttimagalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument13 pagesLecture 1 - Cells - The Building Blocks of Lifekinza yasirNo ratings yet
- What Is Wrong With LAser DiffractionDocument7 pagesWhat Is Wrong With LAser DiffractionMuhammad Alfin Al-MaedaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Non Conventional Energy ResourcesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Non Conventional Energy ResourcesShubham Srivastava80% (5)
- Contoh IjapDocument4 pagesContoh IjapFarihaNo ratings yet
- Cell Analogy ProjectDocument3 pagesCell Analogy ProjectAP - 10KG 732763 John Fraser SSNo ratings yet
- La2 Structure and Function With Growth of BacteriaDocument10 pagesLa2 Structure and Function With Growth of BacteriaRihan RihanNo ratings yet
- Types of MicrosDocument30 pagesTypes of MicrosKarishma100% (1)
- DFS Activity (Villanueva)Document3 pagesDFS Activity (Villanueva)John Carlo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1B: Cells As Organisms Versus Cells in A Social System (I.e., Multi-Cellular Organisms)Document21 pagesLecture 1B: Cells As Organisms Versus Cells in A Social System (I.e., Multi-Cellular Organisms)KingBrazyAskariNo ratings yet
- Confocal MicrosDocument18 pagesConfocal Microsvinayak2314No ratings yet
- Leica LAS X-Brochure en MC-0000071 2019.01.30Document4 pagesLeica LAS X-Brochure en MC-0000071 2019.01.30vaidish1No ratings yet
- Botha Nandipha Loveness 2019 ThesisDocument263 pagesBotha Nandipha Loveness 2019 ThesisKelly GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Nirali 3rd Sem (Book)Document209 pagesMicrobiology Nirali 3rd Sem (Book)Sujay Chakraborty100% (1)
- Mymensingh Medical College, Mymensingh List of Books To Be Purchased During The Year 2008-2009 of The Department of MicrobiologyDocument1 pageMymensingh Medical College, Mymensingh List of Books To Be Purchased During The Year 2008-2009 of The Department of MicrobiologyOsama Bakheet50% (2)
- Chapter 4: Microbial Diversity: Part 1: Acelluar and Prokaryotic MicrobesDocument48 pagesChapter 4: Microbial Diversity: Part 1: Acelluar and Prokaryotic MicrobesMudarab AliNo ratings yet
- Direct Fluorescent Labeling For Efficient Biological Assessment of Inhalable ParticlesDocument12 pagesDirect Fluorescent Labeling For Efficient Biological Assessment of Inhalable ParticlesAD DNo ratings yet
- Isolation, Preservation & Maintenance of Pure CultureDocument37 pagesIsolation, Preservation & Maintenance of Pure CultureShardul DalviNo ratings yet