Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Note Water Hammer2
Uploaded by
Tuna RaisaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Note Water Hammer2
Uploaded by
Tuna RaisaCopyright:
Available Formats
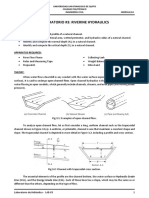
Water Hammer
University of Tasmania
School of Engineering
Experimental Procedure Experimental Records
Aim: Measure transient pressure variation due to water hammer for a known initial flow speed During the lab, you will collect a number of transient pressure records following water hammer events.
These records will appear similar to those shown in Figure 2.
Procedure:
1. Measure: pipe section lengths, heights, diameter, thickness
2. Calibrate the pressure transducers by sequentially exposing each to atmospheric pressure and then
static head + atmospheric pressure
3. Measure steady state flow rate using V-notch weir
4. Acquire water hammer transient records using the LabView software
Apparatus
A basic sketch of the apparatus is shown in Figure 1. It consists of a pump drawing fluid from the lower
Figure 2: Typical transient pressure record following a water hammer event.
reservoir into a header tank of approximately constant head which is maintained by a large overflow
rate within the tank, such that the flow drawn through the pipeline is relatively small compared to the
overflow.
Analysis
Predict the pressure rise, wave speed and transient timing of the first positive pressure wave and first
Water flows through a copper pipe which is fitted with two pressure transducers located at approximately
suction wave. As the system is open to atmosphere the suction wave amplitude is restricted atmospheric
L/3 and 2L/3, where L is the distance from the reservoir to the outlet. At the downstream end a series
pressure + static head. Use the predictions to construct a theoretical transient pressure record and
of control valves are installed to control the flow and allow air to be bled from the system. The last
compare to experimental data.
valve on the pipeline is a rapid acting axial valve which is used to generate water hammer events. A
v-notch weir is positioned after the outlet to enable steady flow rates to be measured.
NOTE: The pressure transducer calibration is negative. i.e. A negative voltage peak corresponds to a
positive pressure peak.
Water Hammer Valve The wave speed for the pressure front in an elastic pipe is given by
Upstream Pressure Transducer
Downstream Pressure Transducer
And the amplitude of the pressure wave is given by
U d𝑃 = 𝜌 c d𝑢
Water Hammer Valve
l1
l2 Nomenclature
l3
z1 z2 ρ - Fluid density [kg m−3] K - Bulk Modulus [Pa]
E - Young’s Modulus D - Inner pipe diameter [m]
e - Pipe wall thickness [m] dU - Change in flow speed [m s−1]
c - Wave Speed [m s ]−1 dP - Pressure change due to water hammer [Pa]
Figure 1: A rough sketch of the apparatus indicating the major features.
You might also like
- Charts For Determining Size of Surge SuppressorsDocument3 pagesCharts For Determining Size of Surge Suppressorsnikolai.ortizNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument70 pagesFluid DynamicsH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Analysis and SolutionsDocument12 pagesWater Hammer Analysis and SolutionsAhmed Salah HassanNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer PDFDocument30 pagesWater Hammer PDFbhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument30 pagesWater Hammerbhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Characterisation of Friction Loss in Pipe FlowDocument6 pagesCharacterisation of Friction Loss in Pipe FlowRoshan RameshNo ratings yet
- Pipe Friction For Laminar...Document6 pagesPipe Friction For Laminar...charanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics & Hydrology (CVE 705)-Module 6Document52 pagesHydraulics & Hydrology (CVE 705)-Module 6mohammed adoNo ratings yet
- Lab - #3. - Riverine HydraulicsDocument8 pagesLab - #3. - Riverine HydraulicsJuan CallesNo ratings yet
- Ceg 503 Lecture Note 3 Water HammerDocument15 pagesCeg 503 Lecture Note 3 Water Hammerayodejiayinde765No ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Irrigation Engineering Lab ManualDocument43 pagesHydraulics and Irrigation Engineering Lab ManualMuhammad Faisal AsifNo ratings yet
- AUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerFrancis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument57 pagesWater HammervikrammotiNo ratings yet
- Allievi PDFDocument33 pagesAllievi PDFluis_enrique_cv100% (1)
- CE016 Module 1 With Solution CES32S3Document79 pagesCE016 Module 1 With Solution CES32S3RALPH LAWRENCE BAXTERNo ratings yet
- Pipe Design 4Document6 pagesPipe Design 4raghebomNo ratings yet
- FM & HM - Manual - 2019-2020Document34 pagesFM & HM - Manual - 2019-2020madhu sudhanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument25 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Manualeklavya kumarNo ratings yet
- Water Hammering Effects in Pipe System and Dynamic Stress PredictionDocument8 pagesWater Hammering Effects in Pipe System and Dynamic Stress PredictionDuzzysNo ratings yet
- 30-31 Water HammeringDocument14 pages30-31 Water HammeringujjancricketNo ratings yet
- Energy Analysis of Pipes and FittingsDocument4 pagesEnergy Analysis of Pipes and FittingsEymann JalaNo ratings yet
- Tijsseling-Bergant 2018Document7 pagesTijsseling-Bergant 2018uroskNo ratings yet
- 10 1051@epjconf@20146702042Document5 pages10 1051@epjconf@20146702042Baja BajabajasziNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Lesson - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Lesson - Water HammerEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- Water hammer pressure and celerityDocument6 pagesWater hammer pressure and celerityEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammering in Fire Fighting InstallationDocument13 pagesWater Hammering in Fire Fighting InstallationsaishankarlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Lasandu WanniarachchiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Lab Manual 2017Document48 pagesHydraulic Lab Manual 2017Muhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Analysis ReportDocument22 pagesWater Hammer Analysis ReportAh Leng LauNo ratings yet
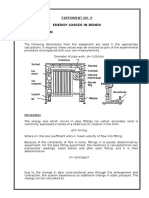
- Energy Losses in Bends I.: Experiment No. 9Document10 pagesEnergy Losses in Bends I.: Experiment No. 9Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual (Hydraulics Engineering)Document34 pagesLab Manual (Hydraulics Engineering)Shahid Kamran63% (8)
- NAME 254 LabsheetDocument56 pagesNAME 254 LabsheetFarhana TaherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - 2Document35 pagesLecture 1 - 2Professor GobozaNo ratings yet
- Basic Hydraulics Engineering ConceptsDocument125 pagesBasic Hydraulics Engineering ConceptsClaire Rizsha QuilonNo ratings yet
- Experiment Level Control: 1. Objectives of The ExperimentDocument17 pagesExperiment Level Control: 1. Objectives of The ExperimentAnonymous mvM7yzsfNo ratings yet
- Energy Losses in Pipes ExperimentDocument4 pagesEnergy Losses in Pipes ExperimentAditya MehtaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer PressuresDocument39 pagesWater Hammer PressurescharbelNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer ArticleDocument14 pagesWater Hammer ArticleayoungaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Production and Design Measures in Piping SystemsDocument16 pagesWater Hammer Production and Design Measures in Piping SystemsSivashankar DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Flow Analysis & Pressure DropDocument31 pagesFlow Analysis & Pressure DropAltin DorriNo ratings yet
- L1 Water HammerDocument19 pagesL1 Water HammerOPONo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Irrigation Engineering Lab Manual UpdatedDocument37 pagesHydraulics and Irrigation Engineering Lab Manual UpdatedKamalnath GNo ratings yet
- Orifice MeterDocument6 pagesOrifice MeterShiva YadavNo ratings yet
- Volume flow rate guideDocument8 pagesVolume flow rate guidetfkthe46No ratings yet
- Wave CharacteriStic MethodDocument0 pagesWave CharacteriStic MethodSuranji RathnayakaNo ratings yet
- Unit-3-Flow Through Pipes FMDocument75 pagesUnit-3-Flow Through Pipes FMPrãfûl Wådhãî100% (2)
- Cive4307 LecturesDocument374 pagesCive4307 Lecturesrizwan ghafoor100% (1)
- Fluid friction pipe experimentDocument15 pagesFluid friction pipe experimentxxxxx100% (3)
- One-Way Air Chambers For Pumping Plants: J. T. Kephart, JRDocument3 pagesOne-Way Air Chambers For Pumping Plants: J. T. Kephart, JREdevar Luvizotto JuniorNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument20 pagesFluid DynamicsMohammad Zunaied Bin Harun, Lecturer , CEENo ratings yet
- R Gid Solutions: Review School For Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesR Gid Solutions: Review School For Civil EngineeringLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- Viscosity of Water: Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesViscosity of Water: Laminar FlowgunawansoloNo ratings yet
- Experimental Flume: Operation ManualDocument28 pagesExperimental Flume: Operation ManualUzair BukhariNo ratings yet
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Document1 pageNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Mr. Mark B.100% (1)
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFDocument1 pageNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFMr. Mark B.No ratings yet
- 3750 Pulpress Pressurisation Unit: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument14 pages3750 Pulpress Pressurisation Unit: Installation and Operating InstructionsRonNo ratings yet
- Stauff Accumulators - Maintenance InstructionsDocument6 pagesStauff Accumulators - Maintenance InstructionsBill MurrayNo ratings yet
- 2017 PPR Pipes PVC PlumbingDocument5 pages2017 PPR Pipes PVC PlumbingRichpaulNo ratings yet
- Ground Water EngineeringDocument3 pagesGround Water EngineeringAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- VC101 condenser design and materials document summaryDocument2 pagesVC101 condenser design and materials document summaryboeiniNo ratings yet
- ASME VIII Unfired Vessel Relief ValvesDocument53 pagesASME VIII Unfired Vessel Relief Valvessaid530No ratings yet
- Inpro Group Products Guide: Fuel Handling Equipments ForDocument78 pagesInpro Group Products Guide: Fuel Handling Equipments ForRathikaNo ratings yet
- Valves 2015-16Document63 pagesValves 2015-16Sethu MadhavNo ratings yet
- ManualsDocument7 pagesManualsRicardo Calderon ClarosNo ratings yet
- BC-6000 - Air Dynamic and Liquid System - V3.0 - ENDocument59 pagesBC-6000 - Air Dynamic and Liquid System - V3.0 - ENKevin BravoNo ratings yet
- Coil Tubing - IwcfDocument26 pagesCoil Tubing - IwcfWH Baloch67% (3)
- FDC PDFDocument1 pageFDC PDFمحمد مجديNo ratings yet
- 5 431529563391000589Document1 page5 431529563391000589mNo ratings yet
- Re92711 - 2021 05 17Document48 pagesRe92711 - 2021 05 17Andie KesumaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Bench ExperimentsDocument18 pagesHydraulic Bench Experimentschesca marasigan100% (1)
- BE-80 Gear Pump Parts ListDocument1 pageBE-80 Gear Pump Parts ListMauricio Ariel H. OrellanaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Specialty CatalogueDocument50 pagesPlumbing Specialty CatalogueFAIYAZ AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Specification Sheet: Customer Name PO Number Vendor Name Vendor Reference Document Title Revision NoDocument13 pagesSpecification Sheet: Customer Name PO Number Vendor Name Vendor Reference Document Title Revision NoAmit SurtiNo ratings yet
- Code Notes SprinklerDocument13 pagesCode Notes Sprinklernarasimha raoNo ratings yet
- Series 5000 TexsteamDocument24 pagesSeries 5000 TexsteamDaniel Dambo100% (4)
- Project 1Document1 pageProject 1hk6868991No ratings yet
- Serial IndexDocument8 pagesSerial IndexJoan Cz100% (4)
- Control Station and Control Valve in The Process Piping - Make Piping EasyDocument15 pagesControl Station and Control Valve in The Process Piping - Make Piping EasyEjaz Ahmed RanaNo ratings yet
- TESTO ITC KORINNA 28mm Allargato: Monoblock Directional Control ValveDocument32 pagesTESTO ITC KORINNA 28mm Allargato: Monoblock Directional Control ValveAnonymous v7XdaQuNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalación Bomba Quintuplex Pentair MA-300Document32 pagesManual de Instalación Bomba Quintuplex Pentair MA-300zayagoraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Hydraulic ComponentsDocument592 pagesStructure and Function of Hydraulic ComponentsDarwin RoseroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Plumbing FixturesDocument57 pagesLecture 4 Plumbing FixturesSamille GarciaNo ratings yet
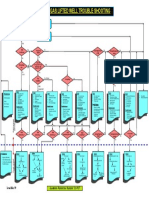
- Attachment-1: Gas Lifted Well Trouble ShootingDocument1 pageAttachment-1: Gas Lifted Well Trouble ShootingDaurenNo ratings yet
- Despiece Filtro de ArenaDocument8 pagesDespiece Filtro de Arenaluisote05No ratings yet
- Course2a-Energy Efficiency PDFDocument59 pagesCourse2a-Energy Efficiency PDFNazaruddin SinagaNo ratings yet
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemFrom EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNo ratings yet
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowFrom EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNo ratings yet
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsFrom EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinFrom EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationFrom EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsFrom EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesFrom EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsFrom EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)