Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Molecular Genetics Review
Uploaded by
shya3640 shya36400 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageOriginal Title
Molecular+Genetics+Review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageMolecular Genetics Review
Uploaded by
shya3640 shya3640Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Molecular Genetics Review
1. Outline the following scientist’s role in the discovery of DNA:
a) Meischer d) Avery, McLeod and McCarty
b) Griffith e) Rosalind Franklin
c) Hershey and Chase f) Watson and Crick
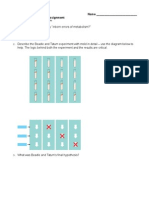
2. Describe the Structure of DNA.
3. Explain how DNA structure helps DNA replicate itself.
4. Explain the role of enzymes in the replication of DNA.
5. Explain the central dogma.
6. Briefly(ish) explain transcription.
7. Briefly(ish) explain translation.
8. Briefly explain the three main post transcriptional modifications.
9. What are retroviruses? How do they work?
10. What are the four levels of control for gene expression? P. 255
11. Using the lac operon, explain how a gene can be turned on when necessary.
12. Using the trp operon, explain how a gene can be turned off when not needed.
13. Explain the following mutations:
a) point mutations f) nonsense mutations
b) translocation mutations g) frameshift mutations
c) substitution mutations h) deletion mutations
d) silent mutations i) insertion mutations
e) missense mutations
14. What are mutagenic agents? Name some.
15. Explain the organization of eukaryotic DNA.
16. Briefly explain the role of the following tools in genetic engineering:
a) restriction endonucleases
b) methylases
c) DNA ligase
d) Gel electrophoresis
e) Plasmids
17. Briefly outline the steps required to clone a gene in a bacterium.
18. Distinguish between EcoRI and SmaI
19. What is PCR? What is it used for?
20. Briefly outline how PCR works.
21. What is RFLP? What is it used for?
22. What is Southern blotting? Explain how it produces a DNA fingerprint.
23. Explain why the Sanger Dideoxy method is also called chain termination technique.
24. What is barcoding and how is it created? How is this information useful?
25. What is CRISPR-Cas9? What is the significance of this technology?
Complete the following questions from the text:
p. 229 # 11 - 16 p. 274 # 2, 7, 13
p. 230 # 5, 9, 14 p. 319 # 13
p. 273 # 13 - 16 p. 320 # 1, 2, 6, 14, 17, 18, 22
You might also like
- BIOLOGYDocument3 pagesBIOLOGYAadit “ThePROkiller”No ratings yet
- DNA Quiz ReviewDocument2 pagesDNA Quiz ReviewsvitlanaNo ratings yet
- 107普生期末Document4 pages107普生期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceeDocument4 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceePROFESSORNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument2 pagesAssignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceJai Bharat0% (1)
- Microbiology Lecture Exam Unit #2 Study Guide Essential Biology and Survey of The Microbial WorldDocument6 pagesMicrobiology Lecture Exam Unit #2 Study Guide Essential Biology and Survey of The Microbial WorldTatum MastermanNo ratings yet
- CH 20 Guided ReadingDocument9 pagesCH 20 Guided ReadingSylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Guided Reading Chapter 16Document5 pagesGuided Reading Chapter 16Tara Gambetta50% (4)
- Important Questions Genetic EngineeringDocument4 pagesImportant Questions Genetic EngineeringKishore TadinadaNo ratings yet
- Hapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N RnaDocument6 pagesHapter 7 Essay Questions Enzyme, Dna N Rnamaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- AO1 Quiz DNA, Cell CycleDocument3 pagesAO1 Quiz DNA, Cell CycleFaiza HamidNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument106 pagesCombine PDFМөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- D.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument9 pagesD.A.V School: Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai 88 Class 12 BIOLOGY Chapter 11 BIOTECHNOLOGYMaheswari RajnarayananNo ratings yet
- Possible Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesPossible Exam QuestionsJofreyNo ratings yet
- Dna Review AnswersDocument2 pagesDna Review AnswersShi Jie100% (1)
- DNA Structure of PolynucleotidechainDocument22 pagesDNA Structure of PolynucleotidechainNasla AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.Document2 pagesClass 12 Biology Zoology EM Chapter 5. Molecular Genetics Question Bank by Rana Sakthi Durga, Puducherry.joshan jayapaul pandiyan100% (1)
- Bioscience Imp QuesDocument2 pagesBioscience Imp QuesdearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Biology Question BankDocument67 pagesStd. XII Biology Question BankShashank RautNo ratings yet
- Review SheetDocument2 pagesReview Sheetapi-289866381No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsDocument7 pagesMolecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsKrutika SNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Asm 2022-23Document33 pagesUnit-Ii Asm 2022-23AnshnuNo ratings yet
- Post Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesPost Assessment Module 3: Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyRyan CuisonNo ratings yet
- Class 12 DDP 1Document4 pagesClass 12 DDP 1sumitsorout294No ratings yet
- Biology Question Bank Unit-Vii Chapter - Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument3 pagesBiology Question Bank Unit-Vii Chapter - Molecular Basis of InheritanceTanmay DograNo ratings yet
- AP BioDocument12 pagesAP BioThomas Lim100% (2)
- SBI4U Assignmentfor Unit 3 Mini Summative Chapter 6 YuchucaoDocument5 pagesSBI4U Assignmentfor Unit 3 Mini Summative Chapter 6 Yuchucaoyao fengNo ratings yet
- Genetics Unit Test ReviewDocument3 pagesGenetics Unit Test ReviewvexelleNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardDocument1 pageAp Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardAbhi ShahNo ratings yet
- 1 Mark Questions: $QV 1 6LJPD FactorDocument19 pages1 Mark Questions: $QV 1 6LJPD FactorJames OrtegaNo ratings yet
- BioK DP Notes 7.1Document10 pagesBioK DP Notes 7.1Lal ÖzşahinNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk100% (26)
- 7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument1 page7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationGihansa VidhanelageNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Questions - Chapter 1Document5 pagesBiotechnology Questions - Chapter 1Marwa SurveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 13 Test A RNA and Protein Synthesis ANSWERS PDFxspiiirONo ratings yet
- Grade-12a - Biology - Worksheet-5 (08.09.23)Document4 pagesGrade-12a - Biology - Worksheet-5 (08.09.23)Dhavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesChapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceMahesh T MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityDocument6 pagesExercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityHiroshi MatsushimaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument9 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceVINOD KUMAR M TNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Chapt 10, 11, 12Document2 pagesHomework 4 Chapt 10, 11, 12ButterlesstoastNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Chapter 5 and 7Document2 pagesTutorial Questions Chapter 5 and 7tshegomatsebaNo ratings yet
- 2. Exam 2 Sample Questions (Жагупаров)Document3 pages2. Exam 2 Sample Questions (Жагупаров)respect_6opicNo ratings yet
- MCQS Paper Molecular BiologyDocument10 pagesMCQS Paper Molecular Biologymariam zameerNo ratings yet
- Pyq Cbse 2021-1-2Document19 pagesPyq Cbse 2021-1-2Yuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- Mader Chap012 10eTBDocument17 pagesMader Chap012 10eTBDr. Michael DavidNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning Unit 6 PacketDocument21 pagesDistance Learning Unit 6 Packet苏紫紫No ratings yet
- Designer Genes: Practice - Molecular-Genetic GeneticsDocument26 pagesDesigner Genes: Practice - Molecular-Genetic GeneticsGiovanni TorresNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 17 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument8 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 17 Guided Reading AssignmentSkylerFragozco0% (3)
- 12th Bio Important ALPDocument15 pages12th Bio Important ALPAdnan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology 1st Edition Wessner Test Bankthomasmayoaecfpmwgn100% (29)
- Biotechnology Qns BankDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Qns BankMadhu DhingraNo ratings yet
- Biosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachDocument10 pagesBiosc1940 Molecular Biology Midterm Exam 1: Multiple Choice (2 Pts Each) - Circle One Answer For EachMohamed MounirNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet-1Document3 pagesStudent Worksheet-1brenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- Final Study Guide 13Document8 pagesFinal Study Guide 13tlyons1188No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDeep Kumar BasakNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document11 pagesCH 07Brian Blocks100% (2)
- Fred Review 16Document8 pagesFred Review 16Justin HsuNo ratings yet
- Quiz HistologyDocument28 pagesQuiz HistologyMedShare100% (30)
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncDocument8 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Genome Stability: From Virus to Human ApplicationFrom EverandGenome Stability: From Virus to Human ApplicationIgor KovalchukNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesPhysics Exam Reviewshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Rate of ChangeDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Rate of Changeshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Phys 1.3Document6 pagesPhys 1.3shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Polynomial Functions MSDocument4 pagesUnit 3 - Polynomial Functions MSshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power Problems 2 Solutions 2Document4 pagesWork Energy Power Problems 2 Solutions 2shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
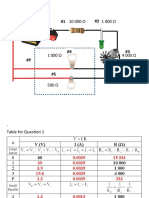
- Assignment Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesAssignment Circuit Analysisshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- The Case of Brenda Brown WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Case of Brenda Brown Worksheetshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Bottled WaterDocument1 pageBottled Watershya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Phys 1.6Document3 pagesPhys 1.6shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- BleachDocument1 pageBleachshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Journal 19Document1 pageJournal 19shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Molecular Kit Assignment WSDocument1 pageMolecular Kit Assignment WSshya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Journal #4Document1 pageJournal #4shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Journal 12Document1 pageJournal 12shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Journal #5Document1 pageJournal #5shya3640 shya3640No ratings yet
- Info Cad Engb FestoDocument14 pagesInfo Cad Engb FestoBayu RahmansyahNo ratings yet
- Sales Purchases Returns Day BookDocument8 pagesSales Purchases Returns Day BookAung Zaw HtweNo ratings yet
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDocument26 pagesWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNo ratings yet
- Gender Religion and CasteDocument41 pagesGender Religion and CasteSamir MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Erotic Massage MasteryDocument61 pagesErotic Massage MasteryChristian Omar Marroquin75% (4)
- Causing v. ComelecDocument13 pagesCausing v. ComelecChristian Edward CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Donna Haraway - A Cyborg Manifesto - An OutlineDocument2 pagesDonna Haraway - A Cyborg Manifesto - An OutlineKirill RostovtsevNo ratings yet
- English VowelDocument6 pagesEnglish Vowelqais yasinNo ratings yet
- Hussain Kapadawala 1Document56 pagesHussain Kapadawala 1hussainkapda7276No ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)Document28 pagesOrganisational Behaviour - II India Yamaha Motors Interim PPT (Download To View Full Presentation)mahtaabkNo ratings yet
- KANDIDAT (Jurnal Mahasiswa Universitas Abulyatama)Document8 pagesKANDIDAT (Jurnal Mahasiswa Universitas Abulyatama)intan fazlianiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Document3 pagesCambridge Latin Course Book I Vocabulary Stage 1 Stage 2Aden BanksNo ratings yet
- Management of Breast CancerDocument53 pagesManagement of Breast CancerGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- History RizalDocument6 pagesHistory RizalIrvin LevieNo ratings yet
- Accenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFDocument8 pagesAccenture 172199U SAP S4HANA Conversion Brochure US Web PDFrajesh2kakkasseryNo ratings yet
- Developing Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkDocument6 pagesDeveloping Mental Health-Care Quality Indicators: Toward A Common FrameworkCarl FisherNo ratings yet
- AIW Unit Plan - Ind. Tech ExampleDocument4 pagesAIW Unit Plan - Ind. Tech ExampleMary McDonnellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Nuc - PhyDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Nuc - PhyHaris ShahidNo ratings yet
- Practical Power Plant Engineering A Guide For Early Career Engineers PDFDocument652 pagesPractical Power Plant Engineering A Guide For Early Career Engineers PDFsahli medNo ratings yet
- Molina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKDocument2 pagesMolina Vs de La Riva 6 Phil 12 INOKErick Jay InokNo ratings yet
- Iver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDocument7 pagesIver Brevik, Olesya Gorbunova and Diego Saez-Gomez - Casimir Effects Near The Big Rip Singularity in Viscous CosmologyDex30KMNo ratings yet
- Niper SyllabusDocument9 pagesNiper SyllabusdirghayuNo ratings yet
- 02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyDocument10 pages02 - Nature and Role of Science in SocietyMarcos Jose AveNo ratings yet
- Press ReleaseDocument1 pagePress Releaseapi-303080489No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Review QuestionsSouthernGurl99No ratings yet
- Operations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanDocument8 pagesOperations Research Letters: Meichun Lin, Woonghee Tim Huh, Guohua WanQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Investment Opportunities: Equity MarketsDocument38 pagesInvestment Opportunities: Equity MarketsRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- John Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God EnglishDocument2 pagesJohn Dee - Sigillum Dei Aemeth or Seal of The Truth of God Englishsatyr70286% (7)
- Analysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Effectiveness of Heat Exchanger Shell and Tube Type One Shell Two Tube Pass As Cooling OilHendrik V SihombingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 101-160Document297 pagesChapter 101-160Dipankar BoruahNo ratings yet