Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap Test 11
Uploaded by
Sameh NoorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap Test 11
Uploaded by
Sameh NoorCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________
Vertebrate Diversity
Chapter Test A
Answer Key
Multiple Choice 21. The branches represent different classes of
1. c vertebrates.
2. b 22. Mammals have hair.
3. b 23. reptilia (Also allow: reptiles.)
4. a 24. an amnion, which encloses an embryo
5. b during development
6. a 25. four limbs
7. a
8. c
9. d
10. c
11. d
12. c
13. d
14. c
15. c
Short Answer
16. Jaws developed from gill arches.
17. The modern fish with jaws would be better
suited, because it could use its jaws to grasp
and devour prey.
18. It reinforces the jaws.
19. The fish is a predator.
20. to support the gills
Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company
Biology 1 Vertebrate Diversity
Name:______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________
Vertebrate Diversity
Chapter Test A
MULTIPLE CHOICE
Choose the letter of the best answer. (15 credits)
_____ 1. Gills are large sheets of thin _____ 3. What passes through a
tissue that chordate’s pharyngeal slits?
a. absorb carbon dioxide. a. blood
b. assist in digesting food. b. water
c. take in dissolved oxygen. c. electrical currents
d. protect a fish’s lungs. d. eggs
_____ 2. The illustration in _____ 4. Lampreys hold on to their
Figure 23.1 shows the prey with their
metamorphosis of a frog. a. suckers.
Which of the following b. jaws.
statements is true? c. tentacles.
d. teeth.
_____ 5. How many groups of jawed
fish still exist?
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
_____ 6. What is the term for the fan-
FIG. 23.1 shaped array of bones in
fish such as goldfish and
a. Frogs live only on dry
tuna?
land.
a. ray-fin
b. Some amphibians lay
b. fin-arch
eggs in the water.
c. gill-arch
c. Tadpoles can live on land
d. fin-support
or in water.
d. Adult frogs can’t survive _____ 7. The coelacanth is a type of
out of water. a. lobe-finned fish.
b. ray-finned fish.
c. cartilaginous fish.
d. amphibian.
Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company
Biology 2 Vertebrate Diversity
Name:______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________
Chapter Test A, continued
_____ 8. Which animals were the _____ 12. Sharks have skeletons made
first to develop four limbs? of
a. reptiles a. chitin.
b. bony fish b. bone.
c. amphibians c. cartilage.
d. birds d. keratin.
_____ 9. Lobe-finned fish that may _____ 13. A fish’s swim bladder
be the closest living helps it
relatives to terrestrial a. swim faster.
vertebrates are b. breathe water.
a. coelacanths c. remove waste.
b. lampreys d. stay afloat.
c. chimeras
d. lungfish _____ 14. Which of the following is a
membranous organ that
_____ 10. What is labeled B in the develops in female
illustration of the sea squirt? mammals during
pregnancy?
a. keratin
b. amniotic egg
c. placenta
d. uterus
_____ 15. A caecilian uses a
hydrostatic skeleton to
stiffen its body to
a. evade predators.
b. attack its prey.
c. move through soil.
d. attract a mate.
FIG. 23.2
a. gills
b. endoskeleton
c. notochord
d. intestine
_____ 11. The first recognizable
vertebrates were
a. birds.
b. amphibians.
c. reptiles.
d. fish.
Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company
Biology 3 Vertebrate Diversity
Name:______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________
Chapter Test A, continued
Short Answer Use the diagram below to answer items 16–20. (5 credits)
FIG. 23.3
16. What does this illustration show about how jaws developed?
_______________________________________________________________
17. Which animal would be better suited to preying on large animals, a jawless
fish or a modern fish? Explain.
_______________________________________________________________
18. In most fish, the fourth gill set is fused to the cranium. How does this structure
help the jaws?
_______________________________________________________________
19. What does the presence of teeth in the modern jawed fish indicate about
its diet?
_______________________________________________________________
20. As the illustration shows, most gill arches have kept their original purpose.
What is that purpose?
_______________________________________________________________
Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company
Biology 4 Vertebrate Diversity
Name:______________________________Class: _________________ Date: _________________
Chapter Test A, continued
Use the diagram below to answer items 21–25. (5 credits)
FIG. 23.4
21. What do the branches of this tree represent?
_______________________________________________________________
22. What, according to the chart, is a basic difference between reptiles and
mammals?
_______________________________________________________________
23. Which class is most closely related to birds?
_______________________________________________________________
24. What, according to the tree, do reptiles, birds, and mammals have in common?
_______________________________________________________________
25. What fundamental characteristic do frogs and birds share?
_______________________________________________________________
Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company
Biology 5 Vertebrate Diversity
You might also like
- Grade 11Document6 pagesGrade 11Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Evolution ReviewerDocument5 pagesEvolution Reviewercuasayprincessnicole4No ratings yet
- Aq. R & E - Set BDocument6 pagesAq. R & E - Set BLaiza UsopNo ratings yet
- Phylum Cnidaria Test PDFDocument7 pagesPhylum Cnidaria Test PDFSHIKHAR SRVSTVNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Arthropods SGDocument2 pagesDiversity of Arthropods SGSusan WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Science6 ST3 Q2Document2 pagesScience6 ST3 Q2Dave Banay Yabo, LPTNo ratings yet
- Evo Final Exam - Bio6lDocument4 pagesEvo Final Exam - Bio6lElyciel FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3rd 9-Weeks Exam Study Guide - Zoology: Multiple ChoiceDocument9 pages3rd 9-Weeks Exam Study Guide - Zoology: Multiple ChoiceAmberlie MaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Reviewer 2 Monthly Test Name: - Score: - SectionDocument7 pagesGrade 6 Science Reviewer 2 Monthly Test Name: - Score: - SectionHaf SahNo ratings yet
- PeopLe and Earth Final Quiz SKHFDocument5 pagesPeopLe and Earth Final Quiz SKHFRodmar SumugatNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test in Science 4Document3 pages2nd Periodical Test in Science 4reysonjoe88% (16)
- Aquatic Science NotesDocument2 pagesAquatic Science NotesJade BellezaNo ratings yet
- LS 2 Sci - and Cri - Thinking SkillsDocument9 pagesLS 2 Sci - and Cri - Thinking SkillsJuvilla BatrinaNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document4 pagesScience 6Rosalie Flores ClavioNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument3 pagesEcosystemReggie HaliliNo ratings yet
- Zoology TestDocument56 pagesZoology TestHero Khan UsafxaiNo ratings yet
- LS 2 Sci - and Cri - Thinking SkillsDocument8 pagesLS 2 Sci - and Cri - Thinking SkillsJuvilla Batrina100% (1)
- Biology 2 Semester Final: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesBiology 2 Semester Final: Multiple Choicejcastill77No ratings yet
- G5 Science Exercise - Food Chain & AdaptationDocument4 pagesG5 Science Exercise - Food Chain & AdaptationLay Rikky Citra sdibcNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test No.3 ScienceDocument2 pages2nd Quarter Summative Test No.3 ScienceMarilou Kimayong-GuazonNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test No.2 ScienceDocument2 pages2nd Quarter Summative Test No.2 ScienceMarilou KimayongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 32 Test 1Document4 pagesChapter 32 Test 1Justin MacDonaldNo ratings yet
- 9th STD Biology OM Que (Unit - 20, 21, 22)Document3 pages9th STD Biology OM Que (Unit - 20, 21, 22)ezhilkzone1109No ratings yet
- Aq. R & E - Set CDocument6 pagesAq. R & E - Set CLaiza Usop100% (1)
- Department of Education: Region III Division of Zambales Subic, Zambales S.Y. 2018-2019Document3 pagesDepartment of Education: Region III Division of Zambales Subic, Zambales S.Y. 2018-2019James Lacuesta TabioloNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 2nd Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 5 2nd Midterm Examleoronquillo20No ratings yet
- Bio 12 Revision Students Notes 2Document21 pagesBio 12 Revision Students Notes 2Saleh AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10 Test Answer KeyDocument9 pagesBiology Chapter 10 Test Answer Keymohamad aliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (1 PT Each)Document5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (1 PT Each)Sekar PuspitaNo ratings yet
- VertebratesanimalsDocument4 pagesVertebratesanimalsDinesh TharangaNo ratings yet
- 1314 Level E Science Revision Sheet Questions CAT1.2Document4 pages1314 Level E Science Revision Sheet Questions CAT1.2Mona EL-SherifNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Biology Test)Document10 pagesScience Reviewer (Biology Test)CHRISTIAN NOE BONGALBALNo ratings yet
- UntigktledDocument23 pagesUntigktledAhsan QadriNo ratings yet
- ANIMALSDocument4 pagesANIMALSSam SamNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Science-PrintDocument2 pages2nd Periodical Science-PrintGuia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Examination: Assumption Montessori SchoolDocument9 pagesComprehensive Examination: Assumption Montessori Schoolshincee23No ratings yet
- g5 Science 1st MonthlyDocument3 pagesg5 Science 1st MonthlyTeacher MaedelNo ratings yet
- CH 34 QZDocument2 pagesCH 34 QZJordyn ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Midterm-Exam-Test-Paper ALONDRADocument6 pagesMidterm-Exam-Test-Paper ALONDRAMae CherryNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Exam Science 6Document3 pages4th Summative Exam Science 6markjoseph regaladoNo ratings yet
- 11 Bio ch7-8 Quiz SolutionDocument4 pages11 Bio ch7-8 Quiz SolutionConnor BrooksNo ratings yet
- Science Day 2 ReviewerDocument29 pagesScience Day 2 ReviewerVeronica C. MeloNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Biology Annual Exam QPDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Biology Annual Exam QPAnirudh KGNo ratings yet
- EIT - General Bio II - Final Exam - 2011Document7 pagesEIT - General Bio II - Final Exam - 2011Yonas Isa'acNo ratings yet
- Let ReviewerDocument20 pagesLet ReviewerMark Anthony SolisNo ratings yet
- Soal Kelas Pts 3Document2 pagesSoal Kelas Pts 3Nawaitus SrNo ratings yet
- ch.25,29,31 QuizDocument7 pagesch.25,29,31 QuizjeksilverstarNo ratings yet
- Reading Form 4Document4 pagesReading Form 4peterpham804No ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test ExploratoryDocument4 pages1st Summative Test ExploratoryJARED DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Name: Surname:: Cacti Have Thick Waxy Skin. Worker Ants Communicate With One Another Using Chemical SignalsDocument2 pagesName: Surname:: Cacti Have Thick Waxy Skin. Worker Ants Communicate With One Another Using Chemical SignalsCatherine JeaneNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Science 5Document4 pagesDiagnostic Test in Science 5Prince John Ladia II100% (3)
- Q2 S2 ScribdDocument6 pagesQ2 S2 ScribdMarie Jaja Tan RoaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Exam 1 FinalDocument17 pages2017 Exam 1 FinalFaisal100% (1)
- Veterinary AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary AnatomyKenneth ShayNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument3 pagesLong Quizfernandezkhryztal30No ratings yet
- Science VDocument1 pageScience Ve_geanga100% (1)
- Islamabad Academy MZD: Class Paper Type Chapter/course Total Marks Time 1 Year Biology Subjective 40 1:50 HrsDocument1 pageIslamabad Academy MZD: Class Paper Type Chapter/course Total Marks Time 1 Year Biology Subjective 40 1:50 HrsPrince ArsalNo ratings yet
- Pisay Exam 7Document8 pagesPisay Exam 7Kim Carlo Aglinao100% (2)
- Biology and Geology of Coral Reefs V3: Biology 2From EverandBiology and Geology of Coral Reefs V3: Biology 2O.A. JonesNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyFrom EverandThe Biology of Stentor: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNo ratings yet
- AP Bio ReviewDocument73 pagesAP Bio ReviewSameh NoorNo ratings yet
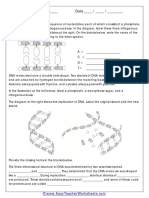
- DNA Worksheet-2Document1 pageDNA Worksheet-2Basma AlharereNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Chapter Test ADocument5 pagesAnswer Key: Chapter Test Aفردوس يسNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test 12Document5 pagesChapter Test 12Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Grade 10mDocument5 pagesGrade 10mSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document5 pagesGrade 9Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- PlantDocument1 pagePlantSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8-13 Study GuideDocument54 pagesChapter 8-13 Study GuideSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Ap B Test: Figure 1. A Cellular ProcessDocument59 pagesAp B Test: Figure 1. A Cellular ProcessSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Ap EnvironmentalDocument24 pagesAp EnvironmentalSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Chapters 3 To 7 Study GuideDocument38 pagesChapters 3 To 7 Study GuideSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- SG Final2023 643ef5b83d5884.643ef5bb6d31e5.20306336Document76 pagesSG Final2023 643ef5b83d5884.643ef5bb6d31e5.20306336Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- TB Final2023 643ef57734b858.643ef57a5a0fb6.40844090Document71 pagesTB Final2023 643ef57734b858.643ef57a5a0fb6.40844090Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Exam 2020Document34 pagesExam 2020Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Learning Express AP Biology Exam 1Document26 pagesLearning Express AP Biology Exam 1Sameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Learning Express AP Biology Exam 2Document19 pagesLearning Express AP Biology Exam 2store_n_stowNo ratings yet
- 9 - 1 H Wood Cabinet Spec Options NelDocument8 pages9 - 1 H Wood Cabinet Spec Options NelinformalitybyusNo ratings yet
- Lpalmer ResumeDocument4 pagesLpalmer Resumeapi-216019096No ratings yet
- BURNS GeneralDocument59 pagesBURNS GeneralValluri MukeshNo ratings yet
- Croma Personal Cooler: Model Name Model Number AZ24 CRLC24LRCA175001 AZ40P CRLC40LRCA175001Document16 pagesCroma Personal Cooler: Model Name Model Number AZ24 CRLC24LRCA175001 AZ40P CRLC40LRCA175001Copy cat Telugu (Ganesh amjuri)No ratings yet
- LivingScience CBSE CompanionDocument56 pagesLivingScience CBSE Companionnjlenovo95% (19)
- Responsibility Accounting Practice ProblemDocument4 pagesResponsibility Accounting Practice ProblemBeomiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasNayre JunmarNo ratings yet
- WP DeltaV Software Update Deployment PDFDocument8 pagesWP DeltaV Software Update Deployment PDFevbaruNo ratings yet
- Kmart PDFDocument105 pagesKmart PDFkaranbhayaNo ratings yet
- Period of Intuitive NursingDocument4 pagesPeriod of Intuitive NursingJhey-ar Toledo100% (1)
- Electrolux EKF7700 Coffee MachineDocument76 pagesElectrolux EKF7700 Coffee MachineTudor Sergiu AndreiNo ratings yet
- MS 1979 2015Document44 pagesMS 1979 2015SHARIFFAH KHAIRUNNISA BINTI SYED MUHAMMAD NASIR A19EE0151No ratings yet
- Uric Acid Mono SL: Clinical SignificanceDocument2 pagesUric Acid Mono SL: Clinical SignificancexlkoNo ratings yet
- Ctaa040 - Ctaf080 - Test 4 Solution - 2023Document7 pagesCtaa040 - Ctaf080 - Test 4 Solution - 2023Given RefilweNo ratings yet
- 5 Keto Pancake RecipesDocument7 pages5 Keto Pancake RecipesBai Morales VidalesNo ratings yet
- Red Winemaking in Cool Climates: Belinda Kemp Karine PedneaultDocument10 pagesRed Winemaking in Cool Climates: Belinda Kemp Karine Pedneaultgjm126No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledSpace HRNo ratings yet
- Minimum Number of Thermocouples-Local PWHTDocument5 pagesMinimum Number of Thermocouples-Local PWHTPradip Goswami100% (1)
- Cervical Changes During Menstrual Cycle (Photos)Document9 pagesCervical Changes During Menstrual Cycle (Photos)divyanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Life Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalDocument16 pagesLife Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalTeeshan VerappenNo ratings yet
- ACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - QuizletDocument18 pagesACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - Quizlet김민길No ratings yet
- 36 Petroland PD Serie DKDocument7 pages36 Petroland PD Serie DKBayu RahmansyahNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Sexual ExstasyDocument63 pagesSecrets of Sexual Exstasy19LucianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 Futures HedgingDocument19 pagesChapter 3.2 Futures HedginglelouchNo ratings yet
- CGMP Training ToolDocument21 pagesCGMP Training Toolbabusure99No ratings yet
- Simple CASC StationsDocument74 pagesSimple CASC Stationssherief marouf100% (2)
- Tropical Fruit CHAPTER-3Document32 pagesTropical Fruit CHAPTER-3Jeylan FekiNo ratings yet
- Keandalan Bangunan Rumah SusunDocument9 pagesKeandalan Bangunan Rumah SusunDewi ARimbiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report KapilDocument66 pagesThesis Report Kapilkapilsharma2686100% (1)
- Allison Burke Adime 4Document8 pagesAllison Burke Adime 4api-317577095No ratings yet