Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio (Reproduction)
Uploaded by
dark sparkOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio (Reproduction)
Uploaded by
dark sparkCopyright:
Available Formats
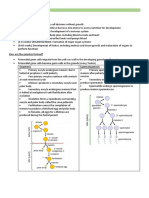
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition:
• The process in which organisms can reproduce individuals of the same species.
• Is the mechanism that produces new generation and maintains a species population.
(Two) Types of Reproduction:
• Sexual reproduction
o Two parents are needed.
o Male and female gametes are formed (gametogenesis)
o Fertilization takes place.
o Offspring is not identical to the parents.
o Some variations are produced.
o Variation is helpful to adapting in the environment.
• Asexual reproduction
o One parent is needed.
o Male and female gametes are not formed.
o Fertilization does not take place.
o Offspring are identical to the parents.
o No variations are produced.
Reproduction in humans
Male reproductive system:
It consists of:
• Pair of testes in a sac like structure called as scrotum.
• Male copulatory organ used to transfer the sperms in the female reproductive system.
The main function of the male reproductive tract includes:
• Sperm production.
• Secretion of testosterone.
• Spermatogenesis.
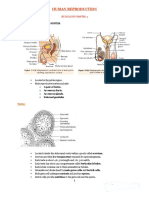
• Each testis consists of highly coiled tubules called seminiferous tubules.
• Epithelium of seminiferous tubules is called germinal epithelium.
• The cells of the germinal epithelium divide by mitosis to produce spermatogonia.
• Spermatogonia increases in size and differentiated into primary spermatocytes.
• Primary spermatocytes divide by meiosis to secondary spermatocytes or spermatids.
• Eventually the spermatids differentiate into the mature sperms.
• Fluid secreted by glands provides liquid medium which provides protection, and
nourishment to the sperms while they are in tubules.
• The sperms are then transferred to vas deferens.
• The germinal end of vas deferens is highly convoluted is called epididymis.
• The sperms are stored are stored in the epididymis.
Female reproductive system:
It consists of:
• Ovaries.
• Oviducts.
• Uterus.
• External genitalia.
• A pair of the ovaries lies within the body cavity of the females.
The process of the egg production(oogenesis):
• Germ cells in the ovary divide by mitosis to form the primary oocytes which are enclosed in
the group of the follicular cells.
• The primary oocytes divide by meiosis I to form haploid secondary oocyte and first polar
body meiosis.
• The secondary oocyte divides by meiosis II as far as metaphase but is not completed until
oocyte is fertilized.
• Immediately after fertilization the egg is converted into ova(egg).
• In huma only one egg is released from the ovary and the process is called ovulation.
Fertilization:
• Eggs are released into the oviduct during the ovulation.
• The sperms will travel and most active one will reach the egg first in the oviduct.
• Then the nuclei of the sperm and egg fuse with each other to form zygote which is called
fertilization.
• Oviduct is the site of fertilization.
Implantation:
1) After fertilization zygote is formed.
2) Zygote divides by mitosis to form embryo.
3) Embryo starts moving slowly towards the uterus.
4) When it reaches the uterus, it gets embedded into the endometrium (uterine wall).
5) This process is called implantation.
Development of the embryo into the fetus:
• After implantation the embryo starts growing.
• Placenta is developed between embryo and the uterine wall.
• The embryo develops into the fetus.
• When the development is complete, the contractions start in the uterine wall.
• Due to the contraction of the uterine wall the fetus is pushed out of the female body.
• This process is called birth.
You might also like
- Anatomy AssignmentDocument77 pagesAnatomy AssignmentTonmoy BasuNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Part 1Document20 pagesSexual Reproduction Part 1Jurez N. EvansNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Reproductive SytemDocument21 pagesLesson 1. Reproductive Sytemseanbalangcod29No ratings yet
- Male SubfertilityDocument41 pagesMale SubfertilityIshaThapaNo ratings yet
- Genetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentDocument54 pagesGenetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentBiraito TakanaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Document10 pagesHuman Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Vishal UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Animal Development & Human ReproductionDocument121 pagesAnimal Development & Human ReproductionAmethystNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalDocument5 pagesReproduction in AnimalRANJIT KUMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 f5Document231 pagesChapter 4 f5Jo YeeNo ratings yet
- Form 5 HSB Session 9-12Document83 pagesForm 5 HSB Session 9-12Alysha NeilsNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- ANAT0001 Fertilisation and CleavageDocument7 pagesANAT0001 Fertilisation and CleavageOmed ZarifiNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument20 pagesReproductionTisha GangulyNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument35 pagesSexual ReproductionTanyaradzwa MugutaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human DevelopmentDocument78 pagesIntroduction To Human DevelopmentAbdul QaharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embryology.Document24 pagesIntroduction To Embryology.Mercy AdeolaNo ratings yet
- EMBRYO Oogenesis, Comparison of GametesDocument20 pagesEMBRYO Oogenesis, Comparison of Gametessolatayesha16No ratings yet
- Embryology Study GuideDocument255 pagesEmbryology Study GuideSiddharth KatyalNo ratings yet
- Human Life Cycle & Male Reproductive System: Dr. Muhjah Falah Hasan PH.D in Infertility & Clinical ReproductionDocument32 pagesHuman Life Cycle & Male Reproductive System: Dr. Muhjah Falah Hasan PH.D in Infertility & Clinical Reproductionsuad aliNo ratings yet
- Gamete Comparison: Oogenesis vs SpermatogenesisDocument7 pagesGamete Comparison: Oogenesis vs SpermatogenesisUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument82 pagesReproductionBIJAY GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument42 pagesLesson 8 - How Do Organisms ReproduceriyanshuNo ratings yet
- GametogenisisDocument43 pagesGametogenisisaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Animal DevelopmentDocument43 pagesAnimal DevelopmentZach ThorpeNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Human Reproduction SystemDocument48 pagesPhysiology of Human Reproduction SystemWivan Havilian DjohanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Gamete FormationDocument17 pages4.1 Gamete FormationKasmahwati MattailNo ratings yet
- 7 GametogenesisDocument35 pages7 GametogenesisBlè SsìngsNo ratings yet
- Chap 19 - The Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesChap 19 - The Reproductive SystemHATLERNo ratings yet
- Development of Urogenital SystemDocument31 pagesDevelopment of Urogenital SystemPraney SlathiaNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 10 - Reproductive SystemRYLE IBANEZNo ratings yet
- CXC BIOLOGY LECTURE SERIES COVERS KEY TOPICSDocument58 pagesCXC BIOLOGY LECTURE SERIES COVERS KEY TOPICSShantay BurtonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: Chapter 9 - The Final Chapter in Animal PhysiologyDocument15 pagesReproduction in Humans: Chapter 9 - The Final Chapter in Animal PhysiologyZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsDocument38 pagesHuman Sexuality Unit: Reproductive SystemsMary Grace CacalNo ratings yet
- 16.4 Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument63 pages16.4 Sexual Reproduction in Humansnie20060301No ratings yet
- 2 Spermatogenesis DR - GosaiDocument31 pages2 Spermatogenesis DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.3 Human ReproductionDocument39 pagesLesson 6.3 Human ReproductionJohn Victor MalupaNo ratings yet
- Rhsi, LSDocument56 pagesRhsi, LSMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis ExplainedDocument21 pagesGametogenesis ExplainedLorna McGinleyNo ratings yet
- Biology 9 - RepoductionDocument10 pagesBiology 9 - Repoductionolivia.mar.sanNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis: The Process of Creating GametesDocument25 pagesGametogenesis: The Process of Creating GametesJoanne Crishna MiguelNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction 2019Document138 pagesHuman Reproduction 2019daylinallie2007No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesMale Reproductive SystemChinju Jose SajithNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument21 pagesHuman ReproductionShazia KhatoonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humanssnoops moopsNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Life CyclesDocument29 pagesReproduction and Life CyclesDHEERAJ ADINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEsriharshitha darapuNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in HumansDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in HumansRhondene WintNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- Presentation StudentDocument61 pagesPresentation Studentvsvm2009No ratings yet
- Note1 - Reproduction in HumansDocument2 pagesNote1 - Reproduction in HumansSandalu Romeshika PereraNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument11 pagesHuman ReproductionAdesh BhullarNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument24 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceShubhada WarakeNo ratings yet
- SpermatogenisisDocument30 pagesSpermatogenisismayssenbenmaad1970No ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- 7 Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of The MaleDocument78 pages7 Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of The MaleClarissa CletNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis: The Formation of Eggs and SpermDocument52 pagesGametogenesis: The Formation of Eggs and SpermMUDIN ABDELLANo ratings yet
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Document21 pagesLife Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Shyamal AryalNo ratings yet
- EOT StructureDocument27 pagesEOT StructureNKANo ratings yet
- ChemistryFormative (Ch12)Document2 pagesChemistryFormative (Ch12)dark sparkNo ratings yet
- ChemistryFormative (Ch12)Document2 pagesChemistryFormative (Ch12)dark sparkNo ratings yet
- Bio (Reproduction)Document2 pagesBio (Reproduction)dark sparkNo ratings yet
- ChemistryFormative (Ch13)Document1 pageChemistryFormative (Ch13)dark sparkNo ratings yet
- Bio (Skeletel System)Document3 pagesBio (Skeletel System)dark sparkNo ratings yet
- Global AwarenessDocument8 pagesGlobal Awarenessdark sparkNo ratings yet
- SAT Syllabus Includes Courses Which Students Have Already Covered in Their School Curriculum Over The Years. Syllabus For SAT Exam Includes: Reading Section Writing MathematicsDocument3 pagesSAT Syllabus Includes Courses Which Students Have Already Covered in Their School Curriculum Over The Years. Syllabus For SAT Exam Includes: Reading Section Writing Mathematicsdark sparkNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations Practice Test ADocument3 pagesElectron Configurations Practice Test Adark sparkNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test A: Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in AtomsDocument5 pagesChapter Test A: Chapter: Arrangement of Electrons in Atomsdark sparkNo ratings yet
- Extracting DNA From Strawberries: Name: Abdulmajeed Mamdouh Alhartani Grade: 11BDocument14 pagesExtracting DNA From Strawberries: Name: Abdulmajeed Mamdouh Alhartani Grade: 11Bdark sparkNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Sec 3Document2 pagesCH 4 Sec 3dark sparkNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations Practice Test ADocument3 pagesElectron Configurations Practice Test Adark sparkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Review Sheets - KeysDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Review Sheets - Keysdark sparkNo ratings yet
- ObsNGyn - Contraception AtfDocument12 pagesObsNGyn - Contraception AtfarongeremewNo ratings yet
- BIOL30001 Course Summary Notes Table of ContentsDocument11 pagesBIOL30001 Course Summary Notes Table of ContentsHoney BaseriNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Oral Contraceptive PillsDocument3 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Oral Contraceptive PillsbebytycoNo ratings yet
- Vety Endocrine PharmaDocument59 pagesVety Endocrine PharmaSunilNo ratings yet
- Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (Ais)Document18 pagesAndrogen Insensitivity Syndrome (Ais)Junbek nov23No ratings yet
- Sexual Health and Fertility ClassDocument14 pagesSexual Health and Fertility ClassJaymih Santos AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Maternal Lec Week 1 3Document4 pagesMaternal Lec Week 1 3Althea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- 1 ReproductioninOrganismsDocument22 pages1 ReproductioninOrganismsPriNce KhatriNo ratings yet
- Puberty Changes in Boys and GirlsDocument47 pagesPuberty Changes in Boys and GirlsAvi :DNo ratings yet
- Materi 4 - Kanker Pada Perempuan - DR - Tofan, SP - Og (K)Document41 pagesMateri 4 - Kanker Pada Perempuan - DR - Tofan, SP - Og (K)Tuti KristantiNo ratings yet
- Biology: Sexual ReproductionDocument7 pagesBiology: Sexual ReproductionAllan BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Document3 pagesCot 1 Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10Arlen FuentebellaNo ratings yet
- Cockroach BioHackDocument10 pagesCockroach BioHackMohammed HamedNo ratings yet
- Tog 12667Document10 pagesTog 12667saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion on Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument55 pagesCase Discussion on Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeGenevie Ombao100% (1)
- Post Cycle TherapyDocument2 pagesPost Cycle TherapyXBBXNo ratings yet
- Penile Length-Somatometric Parameters Relationship in Healthy Egyptian MenDocument5 pagesPenile Length-Somatometric Parameters Relationship in Healthy Egyptian Mengohary18047No ratings yet
- Assisted ReproductionDocument3 pagesAssisted ReproductionFernando GonzalezNo ratings yet
- AMH and PCODocument10 pagesAMH and PCOwaleedaliNo ratings yet
- Surigao Sur Colleges: DIRECTIONS: Research An Example of A Lesson Plan With Topic On HumanDocument5 pagesSurigao Sur Colleges: DIRECTIONS: Research An Example of A Lesson Plan With Topic On HumanFonzy RoneNo ratings yet
- Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Human Sperm Bound to Zona Pellucida or Hyaluronic AcidDocument9 pagesTyrosine Phosphorylation in Human Sperm Bound to Zona Pellucida or Hyaluronic Acidira rahmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology QuestionsDocument10 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Questionskrishna chandrakani100% (2)
- Effects of Pumpkin and Bitter Leaf Extracts on Rat SpermDocument33 pagesEffects of Pumpkin and Bitter Leaf Extracts on Rat SpermThompson E IghaloNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology NotesDocument175 pagesGynaecology NotesNathaniel Mbiu TimNo ratings yet
- Martin 1991 - The Egg and The SpermDocument17 pagesMartin 1991 - The Egg and The SpermYolly ChenNo ratings yet
- BMSN2202 Physiology & Biochemistry ReviewDocument11 pagesBMSN2202 Physiology & Biochemistry ReviewMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives A. Content Standards: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument8 pagesI. Objectives A. Content Standards: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayMaribel NayadNo ratings yet
- Gas Module 1 PDFDocument58 pagesGas Module 1 PDFHIEZEL BAYUGNo ratings yet
- Section A-Objective Type (MCQ & AR Questions) : CHAPTER - 3 Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesSection A-Objective Type (MCQ & AR Questions) : CHAPTER - 3 Human ReproductionnbmNo ratings yet