Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ملخص بايو هرمونات تاني
Uploaded by
ahmed nasserOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ملخص بايو هرمونات تاني
Uploaded by
ahmed nasserCopyright:
Available Formats
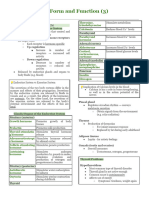
Functions of hormones
Growth Hormone ADH Oxytocin Pancreatic hormones
(somatotropin) Antidiuretic hormone
“Vasopressin”
Growth ✓ Increase water ✓ Milk ejection = milk letting down by Insulin
✓ Physical reabsorption from suckling reflex ✓ CHO: decrease blood glucose level
▪ Bone: distal convoluted ✓ Uterine contraction: ✓ Lipid: lipogenesis
1. deposition of Ca, tubules ▪ has minor role during labor ✓ Protein: anabolism
Phosphate and protein ▪ major role after labor by causing ✓ Electrolytes: increase K uptake by body cells.
in bone ✓ VC leading to involution of uterus and decrease
2. proliferation of Glucagon
increased ABP post-partum hemorrhage.
epiphyseal cartilage. ✓ CHO: increase blood glucose level
and stoppage of ▪ potentiated by estrogen and inhibited
▪ Soft tissue. ✓ Lipid: lipolysis leading increased FFA in blood
bleeding in case by progesterone and catecholamines
✓ Mental and sexual ✓ Protein: anabolism
of hemorrhage ✓ Sexual intercourse: oxytocin causes
▪ No effect ✓ CNS: stimulate appetite center in CNS
uterine contraction leading to suction of
✓ CVS: stimulate cardiac contraction by increasing
Metabolism sperm upward in uterus and sensation of
CAMP
orgasm.
✓ Kidney: natriuresis = increase Na excretion by
✓ CHO: ✓ Help movement of sperm in male sex
kidney.
▪ increase blood glucose level organ toward penis
✓ Lipid: ✓ Stimulate contraction of apocrine sweat Somatostatin
▪ increase FFA in blood gland for sexual attraction between ✓ Anterior pituitary: inhibit release of growth
✓ Protein: animals. hormone
▪ protein anabolism, helped by ✓ Pancreas: inhibit insulin and glucagon release
insulin. from pancreas
✓ Electrolytes: ✓ GIT: inhibit all GIT functions.
▪ increase electrolytes in blood Pancreatic polypeptides
by increasing their absorption
✓ Inhibit release of other pancreatic hormones.
from GIT and kidney
Thyroid hormones Mineralocorticoid = Glucocorticoid = cortisol Catecholamines
Aldosterone
❖ At level of cell ▪ Na reabsorption from DCT • CHO: increase blood glucose level • CNS: decrease reflex time , increase
▪ K secretion from DCT in case alertness by stimulation of reticular
▪ Increase amino acid uptake by cell of hyperkalemia • Lipid: lipolysis leading to increased FFA in activating system.
▪ Stimulate Na-K pump ▪ H secretion from DCT in case blood • CVS: increase all cardiac properties
▪ Stimulate protein synthesis by of acidosis in blood , VD of coronary artery
• Protein:
stimulating DNA and mRNA ▪ Na reabsorption and K or H • Blood vessel: VC of all blood vessel
▪ Stimulate mitochondria for ATP secretion in any secretion in ✓ In liver: - In normal dose: anabolism
except blood vessel of liver,
synthesis body as saliva, milk, sweat. - In high dose: catabolism
skeletal MS and coronary artery
▪ Stimulate lysosomes. ✓ In other tissues: protein catabolism
• Liver: decrease clotting time by
• Antiallergy: stimulating formation of clotting
❖ At level of body: factors 1,2,5
✓ Decrease histamine release from
mast cell and Basophil. • Respiration: initially, it cause
▪ Growth: stimulate physical , mental adrenaline apnea by reflex
✓ Has no effect on antigen-antibody
( by stimulation of myelination of inhibition of respiration center
complex or already Histamines
nerve fibers leading to decrease followed by stimulation of
• Anti-inflammatory:
relax time) and sexual growth. respiration by direct stimulation of
▪ Metabolism: increase glucose and ✓ Inhibit migration of immune cell to respiratory center
O2 consumption for formation of site of inflammation • Pancreas:
ATP
✓ Inhibit release of interleukin 1 from a. increase insulin and glucagon by
▪ CHO: increase blood glucose stimulation of beta receptor
▪ Lipid: lipolysis leading to increased immune cell Leading to inhibition of b. decrease insulin and glucagon by
FFA in blood fever stimulation of alpha receptor
▪ Protein = skeletal ms: c. net result: increase glucagon and
• Anti-stress: see later decrease insulin
✓ in normal level: protein
anabolism • Blood vessel: Cortisol increases synthesis • Smooth MS: bronchodilatation,
mydriasis
✓ while in high level: protein and vascular Reactivity of blood vessels
catabolism and ms breakdown • Skin: pale, moist skin with erected
to catecholamines hair
and weakness
▪ Vitamins: • Blood cells: • Kidney: decrease Na and water loss
✓ convert carotene to vit A ✓ Increase RBCs and neutrophil in urine by VC of renal vessels and
✓ stimulate clearance of vitamin ✓ Decrease basophil , eosinophil , stimulation of rennin angiotensin
leading to increase need for lymphocytes system
vitamins ✓ Involution of lymphoid tissue in • Muscle: orbelli phenomenon: better
✓ stimulate metabolism and puberty contraction and no fatigue by VD
clearance of other drugs as • Gastric effect: Increase HCL and decrease of skeletal MS blood vessels and
digitalis mucous increasing ATP
▪ CVS: increase force of contraction • Permissive: Increase activity of
– increase SBP by increasing COP catecholamine and Glucagon.
and decrease DBP by causing VD • Renal: cortisol stimulate ADH and
by the effect of metabolites leading aldosterone in case dehydration , while
to increased pulse pressure which is inhibit them in case of overhydration.
called water hammer pulse
▪ Blood: increase erythropoietin
hormone which cause osteoporosis,
increase 2,3 DPG which cause shift
to RT of O2 dissociation curve.
▪ Respiration: increase rate of
respiration.
▪ GIT: increase GIT motility and
appetite
▪ Gonad: normal level of thyroxine
maintains gonadal function
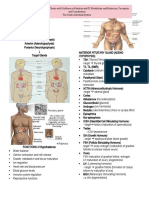
Control of hormones
Growth hormone ADH Insulin Glucagon
▪ Hypothalamus: GHRH: ▪ Hyper osmolarity: Stimulators Stimulators
- stimulate GH, while GHIH - more than 300 m. osmol/l, ✓ CHO: increased blood glucose ✓ Decreased blood glucose
(somatostatin) decrease GH leading to increased ADH ✓ Lipid: increased FFA ✓ Decreased blood FFA
release. secretion ✓ Protein: increase blood amino ✓ Increased blood amino acids
▪ Feedback. ▪ Hypovolemia acid ✓ Growth hormone
▪ Others: ▪ Others: ✓ Glucagon: increases insulin by
Stimulator Stimulators direct paracrine stimulation of Inhibitors
✓ Decreased blood glucose, ✓ Increased temperature beta cell of pancreas, and • العكس
FFA, increased blood amino ✓ Barbiturate, beta agonist indirectly by increasing blood • Somatostatin and pancreatic
acids as arginine ✓ Opiates (morphine) glucose polypeptides
✓ Stress, starvation, sleep ✓ Nicotine ✓ GIT hormones: see GIT
✓ Exercise, estrogen and ✓ Estrogen ✓ Vagus
dopamine ✓ Sulphonyurea ✓ Beta agonist
✓ Ca
Inhibitor Inhibitors ✓K
• Increased blood glucose, • Alpha agonist, PGs ✓ Sulphonyl urea
FFA, decreased amino acid
• Hypercalcemia, increased K
• Obesity, cortisol, increased efflux Inhibitors
GH and IGF • Pancreatic polypeptides,
• Cortisol, chronic water
loading, cold weather somatostatin
• Alpha agonist, PGs
• Diazoxide and phenytoin drugs
• Hypoglycemia, exercise
Thyroid hormone Cortisol Aldosterone Catecholamines
Iodine: ▪ Cortisol formation stimulated in ▪ Rennin angiotensin system: ▪ Controlled by adrenaline secretory
✓ Iodine deficiency leads to stress conditions as exercise, decreased ECF volume leads to center (ASC) in medulla oblongata
decreased thyroid hormone hypoglycemia, cold weather, shock renal ischemia which leads to
formation. activation of RAS and formation ▪ Reticulospinal tract arise from ASC
✓ Excess iodine leads to ▪ Hypothalamus release CRH to of aldosterone to T5:T9 of spinal cord to
inhibition of enzymes leading stimulate release of ACTH from stimulate sympathetic
to decrease hormones ant pituitary ▪ Hyperkalemia and acidosis preganglionic fibers (greater
formation. Called wolf chaikoff splanchnic nerve) which pass to
effect ▪ Ant pituitary release ACTH to ▪ Hyponatremia adrenal medulla to stimulate
stimulate adrenal cortex to release adrenaline secretion
Stress: as cold weather leads to cortisol ▪ ACTH: has minor role in formation
increased thyroid hormone of aldosterone ▪ Adrenaline secretion during rest is
▪ Cortisol is the only adrenal cortical basal
Pregnancy: HCG has TSH activity hormone which has negative
leading to increased thyroid feedback effect. ▪ ASC is affected by:
hormones formation ✓ Hypothalamus,
▪ Cortisol secretion is irregular chemoreceptor, cortisol:
Antithyroid agents= goitrogen: pulsatile more in the morning ➢ stimulate adrenaline
thiouracil present in cabbage, controlled by suprachiasmatic secretion
prevent iodide uptake by thyroid nucleus (biological clock = ✓ Baroreceptor in aortic arch
gland leading to decreased thyroid circadian rhythm) and volume receptor in RT
hormone formation which by atrium:
negative feedback leads to ➢ inhibit adrenaline
increased TSH causing goiter secretion.
Age: thyroid hormone formation
decreases in old age
TSH:
✓ Increase size of thyroid gland
✓ Stimulate thyroid hormone
production by thyroid gland
✓ Increased level of thyroid
hormones leads to decreased
TSH by negative feedback on
pituitary more than
hypothalamus
TSI= thyroid stimulating hormone =
LATS= long acting thyroid
stimulator:
✓ Produced by lymphocyte and
has TSH activity leading to
increased size of thyroid gland
and increase thyroid hormone
formation
✓ No negative feedback between
thyroid hormones and TSI
Disorder of hormones
GH ADH
Dwarfism Gigantism Acromegaly Diabetes insipidus
Decreased GH Increased GH secretion Increased GH Diabetes insipidus Syndrome of inappropriate ADH
secretion in in children before fusion secretion in adult secretion
Cause children before of epiphysis due to after fusion of Cause - Central cause: decreased - Increased ADH secretion due to:
fusion of tumor in somatotrpoes epiphysis due to ADH secretion. ✓ Trauma
- Nephrogenic cause: defect ✓ CNS dse
epiphysis tumor in
in receptor in kidney with Ectopic ADH secretion from lung
somatotropes normal blood level of ADH tumor
Growth:
- Physical -Decreased with -Increased with tall -Coarse features as Manifestation ▪ Polyurea with low specific ▪ Increased water reabsorption
short stature stature (symmetric prognathism, gravity. leading to decreased Na
growth, height = span) enlarged hand and ▪ Polydipsia. concentration in blood resulting in
foot, kyphosis Anorexia and loss of weight headache, dizziness
-Sub mentality due to loss of water-soluble ▪ Increased blood volume leads to
- Mental -No effect -Sub mentality vitamins in urine. stimulation of RT atrial ANP
-Hypogonadism due to secretion
- Sexual -No effect pressure of tumor on -Hypogonadism due Treatment - Central type: give ADH ANP causes Na and water excretion
gonadotrpoes ……. - Peripheral type: not given
ADH
Decrease BMR Increase BMR and Increase BMR and Insulin
Metabolism and blood blood glucose blood glucose Diabetes mellitus
glucose
Blurring of vision and The same as Manifestation:
Vision headache due to gigantism ▪ Hyperglycemia
pressure of tumor on ▪ Glucosuria
optic chiasma ▪ Polyurea
Gynecomastia, ▪ Polydipsia
galactorrhea,
▪ Increased triglyceride in blood with lipolysis
hirsutism due to
Others lactogenic effect of ▪ Formation of ketone bodies which cause blood acidosis
GH. ▪ Mobilization of protein from ms to be used as source of energy leading to
asthenia and loss of weight.
Thyroid hormone Adrenal cortical hormones
Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) Hyperaldosteronism Cushing syndrome Addison dse
Causes - May be: - Caused by excess thyroid hormone Causes - May be: - May be: - Damage of adrenal
▪ 1ry hypothyroidism due to lesion in due to: ▪ 1ry (cons syndrome): ▪ 1ry: due to tumor in cortex by autoimmune dse,
thyroid gland. ▪ Tumor in thyroid gland due to tumor in adrenal adrenal cortex TB and tumor leading to
▪ 2ry hypothyroidism due to lesion in ▪ Tumor in pituitary gland cortex ▪ 2ry due to tumor in decreased cortisol,
pituitary gland. ▪ Graves dse ▪ 2ry due to liver, heart pituitary gland. aldosterone and androgen
- May occur in: and renal dse. ▪ exogenous cortisol
▪ Infant so called cretinism
▪ Adult so called myxedema Manifestation ▪ Hypernatremia, ▪ Exaggerated ▪ Decreased BMR
hypervolemia, mineralocorticoid ▪ Decreased blood
growth: ▪ In cretinism: there is decreased all ▪ Increased mental processes as hypertension and edema activity: as aldosterone glucose
▪ physical types of growth insomnia and tremors ▪ Hypokalemia leasing to ▪ Exaggerated ▪ Anemia
▪ In myxedema: decreased mental ms weakness, periodic androgenic effect: ▪ Abdominal pain
▪ Mental process as slow thinking, slow ▪ Ms weakness paralysis, nephropathy acne, amenorrhea and ▪ Addison crisis: on
reflexes and low concentration. and ECG changes hirsutism exposure to stress, there
▪ Ms weakness (as prominent u wave) ▪ Mental changes: is exaggerated
▪ Impotence in male and ▪ Sexual disturbance as impotence in ▪ Metabolic alkalosis due insomnia, euphoria and condition leading to
oligomenorrhea in female male and polymenorhea in female to H excretion leading to psychosis. shock
▪ Sexual tetany. ▪ Lipid: ▪ Deficient aldosterone
1- thin limb leading to
▪ Appetite ▪ Decreased appetite ▪ Increased appetite 1. 2-moon face hyponatremia,
▪ Bradycardia ▪ Bradycardia ▪ Tachycardia 2. 3-bufflo hump hyperkalemia with
▪ BMR ▪ Decreased BMR: leading to weight ▪ Increased BMR: leading to weight 3. 4-truncal obesity metabolic acidosis.
gain and intolerance (increased loss and intolerance (increased ▪ CHO: hyperglycemia ▪ Dark pigmentation of
sensitivity to cold weather) sensitivity to hot weather) ▪ Protein: protein skin: due to decreased
▪ Constipation ▪ Diarrhea catabolism leading to cortisol which leads to
▪ Constipation ms weakness, bruises, increased ACTH by
stria and osteoporosis. negative feedback
▪ Skin ▪ Skin: ▪ Skin: ▪ Polycythemia (ACTH has MSH activity)
▪ Eye 1. Dry scaly brittle hair due to Warm moist with fine silky hair. ▪ Peptic ulcer
▪ Face decreased vit A. ▪ Eye:
2. Yellowish due to 1. Staring look due to widening of
hypercarotenemia. palpebral fissure due to retraction
3. Pale due to anemia and pressure of upper eye lid
of myxomatous tissue on blood 2. Infrequent blinking Catecholamines
vessels. 3. Lid lag: delay in downward
movement of upper eye lid when
Pheochromocytoma
4. Cold: due to decreased BMR. ▪ Cause: increased catecholamine secretion by tumor in adrenal medulla
▪ Face: following a falling object.
▪ Manifestation:
❖ Dull uninterested with puffy eye 4. Failure of convergence 1- headache 2-blured vision
lid, thick lip and macroglossia (all due to sympathetic overactivity) 3-chest pain 4-palpitation with tachycardia
5. Exophthalamus: due to 5-hyperglycemia 6-hypertention
accumulation of inflammatory cell 7-pale moist skin
and exophthalamus producing ▪ Diagnosis: by finding venyl mandilic acid which is the metabolite of catecholamines in urine
substance behind eye.
Additions Thyroid hormones:
Mechanism of growth hormone action
▪ Pituitary gland release growth hormone which has: T4 (thyroxine) T3
✓ Direct effect on CHO, lipid and electrolytes ▪ Tetraiodothyronine ▪ tri-iodothyronine
✓ Indirect effect on protein anabolism and growth ▪ contain tyrosine+ 4 atoms ▪ contain tyrosine+ 3 atoms
▪ Growth hormone stimulate liver and other tissues to release of iodine of iodine.
somatomedins (insulin like growth factor), then somatomedin ▪ represent 90% of thyroid ▪ represent 10% of thyroid
stimulate protein anabolism and growth hormones hormones
▪ There are two types of somatomedin: 1 in adult, 2 in fetus ▪ long half life = 7 days ▪ short half life = 1 day
▪ Structure of somatomedin is similar to insulin. ▪ less potent . ▪ more potent
Pancreatic hormones (present in tail of pancreas which represent 1% of pancreas): Goiter:
▪ Insulin released by beta cell
Def : Enlargement of thyroid gland with increased or decreased thyroid gland
▪ Glucagon released by alpha cell, also secreted from GIT in the form
activity
of glicentin (glucagon like peptides) Causes:
▪ Somatostatin released by D cell ▪ Goitrogen
▪ Pancreatic polypeptide released by F cell ▪ Graves dse
▪ Iodine deficiency
Mechanism of some hormones : ▪ Physiological goiter in pregnancy
▪ ADH and glucagon: by increasing CAMP ▪ Nodular goiter in stress.
▪ Oxytocin: by increasing Ca inside cell
Adrenal cortex formed of :
Nature of hormones : 1. Zona glomerulosa: outer part, secrete aldosterone which has 90% of
✓ All hormones are polypeptide except: mineralocorticoid activity.
▪ Thyroid hormones and catecholamine are amino acid hormone, formed 2. Zona fasciculata: middle part, secrete cortisol, and corticosterone (less
of tyrosine or phenylalanine active than cortisol)
▪ Adrenal cortical hormones are steroid hormones, formed from 3. Zona reticularis: inner part, secrete androgen
cholesterol, mainly bound to plasma protein to globulin mainly
which is called transcortin. Difference between 1ry and 2ryhyperaldosteronism :
❖ In 1ry hyperaldosteronism: low rennin , mild edema due to :
▪ Heart: secrete ANP to excrete Na followed by water excretion
Insulin is formed with C peptide :
C peptide is equimolar to insulin and measure endogenous insulin secretion. ▪ Kidney: increase GFR (which is called aldosterone escape phenomenon)
❖ In 2ry hyperaldosteronism: there is high rennin , sever edema
Adrenal medulla which is called modified sympathetic Effect of hormones on lipid :
ganglia, formed of two types of cells: ▪ Insulin: cause lipogenesis through:
▪ Cells that secrete epinephrine: 80% ✓ Stimulate lipoprotein lipase in blood which convert lipoprotein to FA
▪ Cells that secrete norepinephrine: 20% which pass to adipose tissue for lipogenesis.
✓ Inhibit lipolysis in adipose tissue
Control of catecholamine secretion: ✓ Convert glucose and protein to fat
▪ Adrenaline secretory center (ASC) in medulla release ▪ Growth hormone , glucagon , cortisol , catecholamine and thyroxine
reticulospinal tract which reach spinal cord (T5-T9) ✓ Stimulate lipolysis leasing to release of FA to blood
▪ From spinal cord, preganglionic sympathetic fibers (called ✓ FA used as source of energy for ms during stress
greater splanchnic nerve) arise to reach adrenal medulla to
stimulate it to release catecholamines. Effect of hormones on protein:
▪ ASC is affected by: ▪ Growth hormone, insulin, thyroid hormone in normal dose , cortisol in
a. Hypothalamus, cortisol and chemoreceptor: stimulate ASC normal dose in liver : stimulate protein anabolism by :
b. Baroreceptor in blood vessels and right atrium: inhibit ASC Increase amino acid uptake by cell
Convert DNA to MRNA to protein
Decrease protein catabolism
Effect of hormones on CHO: ▪ Normal dose of cortisol in other tissues , excess thyroxine : Stimulate
▪ Growth hormone, glucagon, catecholamines: Increase blood protein catabolism
glucose by:
Decrease glucose uptake by cell Hypothalamus and pituitary gland:
Stimulate gluconeogenesis ▪ Hypothalamus control anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) by
Stimulate glycogenolysis and inhibit glycogenesis hypothalamo- hypophyseal portal circulation by releasing stimulatory
▪ Insulin: Decrease blood glucose by العكس and inhibitory factors
▪ Cortisol: net result is increase blood glucose by: ▪ Hypothalamus control posterior pituitary (neuro-hypophysis) through:
Increase blood glucose by: decrease glucose uptake by cell, Posterior pituitary hormones as ADH and oxytocin are formed in
stimulate gluconeogenesis hypothalamus:
Decrease blood glucose by stimulating glycogenesis. ADH: formed in supraoptic nucleus then bound to neurophysin 2
▪ Thyroid hormones: net result is increased blood glucose by: Oxytocin: formed in paraventricular nucleus then bound to neurophysin 1
Increase blood glucose by increasing glucose absorption from
GIT, stimulate gluconeogenesis, stimulate glycogenolysis - After formation in hypothalamus they pass through hypothalamo –
Decrease blood glucose by increasing glucose uptake by cell hypophyseal tract to be stored in herring body which is swelling at end of
tract.
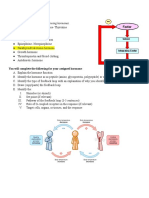
Anterior pituitary formed: Feedback:
▪ Acidophil: two types: somatotropes that release GH, mammotrpoe
that release prolactin Negative feedback Positive feedback
▪ Basophil: that release TSH, FSH and LH, ACTH, MSH ▪ Most common ▪ Less common
Def ▪ Gland A stimulate gland B. ▪ Gland A stimulate gland B
Anterior pituitary control through its trophic hormones: ▪ When hormone B is ▪ When hormone B is
✓ Thyroid, adrenal cortex and gonads and not control pancreas, increased it inhibit gland A. increased, it stimulates
parathyroid and adrenal medulla. gland A
Hypothalamus release both stimulatory and inhibitory factors for - Types: - Types:
GH, prolactin and MSH Types & ▪ Ultrashort: ▪ Occurs only during
Significance ✓ between hormones and ovulation and labor
Hypothalamus release only releasing factors for ACTH, FSH AND its own secreting gland
LH, TSH ▪ Short: - Significance:
✓ between pituitary and ▪ Amplify biological activity
hypothalamus of hormone
▪ Long:
✓ between gland and
pituitary or gland and
hypothalamus.
- Significance:
▪ Maintain hormonal
blood level constant
You might also like
- TEAS 6 Science by KellyDocument22 pagesTEAS 6 Science by KellyLily Garcia100% (1)
- Gyane MCQS 6, 7, 9 Chapter Irfan Masood PDFDocument16 pagesGyane MCQS 6, 7, 9 Chapter Irfan Masood PDFJansher Ali Chohan100% (1)
- Science Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum EditionDocument3 pagesScience Essentials 9 For NSW Stage 5 Australian Curriculum Editionapi-374582387No ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDocument2 pagesBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6No ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 Test 2Document44 pagesMed Surg 2 Test 2Tara ThorntonNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet McatDocument16 pagesReview Sheet McatCal GoNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesMenstrual CycleintanNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Parathyrid Gland FinalDocument63 pagesPathology of Parathyrid Gland FinalGurpreet Kaur SagooNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION+QUESTIONNAIRE+ (Rev 1+2012) PDFDocument1 pageHYPERTENSION+QUESTIONNAIRE+ (Rev 1+2012) PDFZito Amora100% (1)
- DIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)Document8 pagesDIabetes Mellitus ! Patho (Complete)freyaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsDocument4 pagesQuiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsZayne Lucas Gabrielle TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesVitamins Cheat SheetElijah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Draw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesDraw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology TableDocument3 pagesEndocrinology TableWilliam PartonNo ratings yet
- Hormone High Yield InfoDocument5 pagesHormone High Yield InfoHuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone (GH) All Over:: Hormone Origin Which 2 Messenger Target TissueDocument55 pagesGrowth Hormone (GH) All Over:: Hormone Origin Which 2 Messenger Target TissueJoe EpsteinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeMaria Luisa VillalunaNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Hormone and Cell Signaling PresentationDocument10 pagesHormone and Cell Signaling Presentationsean mucNo ratings yet
- Some Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSome Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- AlgoDocument1 pageAlgoErrold Joseph LahaganNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Is A Condition in Which A Person Has A High Blood SugarDocument4 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Is A Condition in Which A Person Has A High Blood SugarisonkutonNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseDocument2 pagesPituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesBenjo Plaza AtoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Patofisiologi Trauma - DR Raden Ajeng Sri WulandariDocument22 pagesKuliah Patofisiologi Trauma - DR Raden Ajeng Sri WulandariAgung Budi SuristioNo ratings yet
- NORCETDocument101 pagesNORCETDiksha DhillonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Endocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesEndocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Kehamilan-1Document34 pagesFisiologi Kehamilan-1Igus UlfayazeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Endocrine PharmacologyDocument22 pagesLesson 3 - Endocrine PharmacologyJayla MarieNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageNursing CS Endocrine SystemLia neNo ratings yet
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- Wala ToDocument3 pagesWala ToLady MidnightNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9: Endocrine System: Prepared by Arianne V. JulianDocument34 pagesLesson 9: Endocrine System: Prepared by Arianne V. JulianGisselleNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesThyroid GlandacNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- NOTZ SUMMARY - PancreasDocument1 pageNOTZ SUMMARY - PancreasAdmin DutiesNo ratings yet
- Scan 08 Apr 2024Document6 pagesScan 08 Apr 2024Rosella Bethany CorreaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDocument5 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDevia OktaviandraNo ratings yet
- Index CardsDocument6 pagesIndex CardsShanley SalemNo ratings yet
- Physio Endo 4Document21 pagesPhysio Endo 4Hoth HothNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument34 pagesHomeostasisAwaid AsimNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesMale Reproductive SystemEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Effects Adrenal Hormones RegebDocument7 pagesEffects Adrenal Hormones RegebPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Refresher Course For Primary Exam May 2008 Endocrine Physiology - Viva/Essay QuestionsDocument7 pagesRefresher Course For Primary Exam May 2008 Endocrine Physiology - Viva/Essay QuestionsanaeshklNo ratings yet
- GI - Secretions - NASPGHAN - Picture RemovedDocument56 pagesGI - Secretions - NASPGHAN - Picture Removedmalikbaseerat32No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Document3 pagesChapter 10 - Endocrine Pituitary Gland: A.) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)Reen BalbaguioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PresentationDocument231 pagesEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Endo ShortlistingDocument3 pagesEndo ShortlistingMamoona RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Part 3Document55 pagesEndocrine System Part 3Cristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Functions of Growth HormoneDocument19 pagesFunctions of Growth HormoneRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- Type of Regulation ChartDocument6 pagesType of Regulation ChartmarNo ratings yet
- GI HormonesDocument1 pageGI HormonesCarla CentenoNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionDocument5 pagesBio 11 - Animal Form and FunctionNikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanism ActivityDocument9 pagesFeedback Mechanism ActivityRohan BhatiaNo ratings yet
- ورق حصة د.الفلاحة بالزيادات كلهاDocument8 pagesورق حصة د.الفلاحة بالزيادات كلهاahmed nasserNo ratings yet
- Community - Catogry + Questions & Answers 2012Document34 pagesCommunity - Catogry + Questions & Answers 2012ahmed nasserNo ratings yet
- MCQ - May, 2015Document7 pagesMCQ - May, 2015ahmed nasser100% (1)
- Oral CommunityDocument9 pagesOral Communityahmed nasserNo ratings yet
- Summer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsDocument7 pagesSummer Vacation Assignment - QuestionsSidra QueenNo ratings yet
- PHYS20050 Tutorial 3 - Student Copy Nov 2017Document2 pagesPHYS20050 Tutorial 3 - Student Copy Nov 2017muhammad haziqNo ratings yet
- Etiologi & Penatalaksanaan Dub: Erald Giovanny Hasiholan Simatupang FAA 115 027Document6 pagesEtiologi & Penatalaksanaan Dub: Erald Giovanny Hasiholan Simatupang FAA 115 027Anonymous 7dsX2F8nNo ratings yet
- CorticosteroidsDocument63 pagesCorticosteroidsRiddhi Jain100% (2)
- Histology Solution AvnDocument11 pagesHistology Solution AvnDrdo rawNo ratings yet
- Sci10 Q3 Module1Document23 pagesSci10 Q3 Module1Jinky AydallaNo ratings yet
- Journal - A Review of Diabetes MellitusDocument6 pagesJournal - A Review of Diabetes Mellitusifaans16No ratings yet
- Cbse Assignments Class - X Biology For Sa-1Document2 pagesCbse Assignments Class - X Biology For Sa-1Purvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Changes at MenopauseDocument14 pagesBiochemical Changes at MenopauseSyedSaqibHussainNo ratings yet
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Document33 pagesEndocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Omed Zarifi100% (1)
- 2003 LG Nefropatia DiabeticaDocument13 pages2003 LG Nefropatia DiabeticaDario ToschiNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyAnnie Laiza BacayNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality Diversity in Contemporary America 9th Edition Yarber Test BankDocument39 pagesHuman Sexuality Diversity in Contemporary America 9th Edition Yarber Test BankJeffreyWoodogcjq100% (15)
- Role of HbA1c in Diabetes MellitusDocument23 pagesRole of HbA1c in Diabetes Mellitusdimple1#100% (1)
- Preanalytical Considerations in Testing Thyroid FunctionDocument10 pagesPreanalytical Considerations in Testing Thyroid FunctionSihem MezNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDocument29 pagesDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKmarina shawkyNo ratings yet
- Le Patologie Autoimmunitarie Del Cavo OraleDocument23 pagesLe Patologie Autoimmunitarie Del Cavo OralealfonsoNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism: Preparation byDocument18 pagesCalcium Metabolism: Preparation byAbhijeet KanjeNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI SyllabusDocument8 pagesNCM 103 Endo, Meta, GI Syllabusjongmartinez100% (1)
- 2 Year Mbbs (Batch-48) of CMC LarkanaDocument1 page2 Year Mbbs (Batch-48) of CMC LarkanaKhanNo ratings yet
- To Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleDocument5 pagesTo Print Cut and Paste Add Photos To TabbbleleleRimaHimeNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentDocument2 pagesTypes of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentKrystale Mae ValdezNo ratings yet
- A Psychoeducational Program ToDocument4 pagesA Psychoeducational Program Togracias vlasNo ratings yet