Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction of 21st Century Literacies Reviewer
Uploaded by
Haxx LovieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction of 21st Century Literacies Reviewer
Uploaded by
Haxx LovieCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION OF 21ST CENTURY LITERACIES and create information.
7. Digital Literacy – The ability to use digital technology,
What is literacy communication tools or networks to locate, evaluate, use and
create information.
The word “Literacy” stems from the word “literate”, which first appeared
in the 15th century and is in turn derived from the Latin word Litteratus, The university of pittsburgh library system calls the new literacy as
meaning “ (a person) marked with letters” that is distinguished or the “21st century literacies,” which covers visual literacy, media literacy,
identified by letters” and it carried with it the idea that such a person technology literacy, network literacy, and cultural.
was cultured and educated.
1.Visual literacy- constructing meaning from images and
Miller (1973) expressing oneself in terms of visually while recognizing the validity
and accuracy of those images.
Basic literacy- correspond visual shape to spoken
sounds in order to decode written materials and translate Example of integration into library instruction: use images from
them into oral language. flickr to compare and contrast primary & secondary sources.
Comprehensive literacy- to understand the meaning of
what is being read. 2. Media Literacy- Critical understanding of media in a variety of
Functional or Practical Literacy- to read (decode and formats and an understanding of the impact of various media on the
comprehend) written materials needed to perform individual and society.
vocational tasks.
Example of integration into library instruction: Use a variety of
Some definition of literarcy media (print & online newspapers, Wikipedia, etc.) to find and
evaluate
Literacy, defined most simply, is the ability to read and information on a current news topic.
write.
Literacy is a process by which one expands one’s 3. Technology Literacy- Critical thinking and problem solving skills
knowledge of reading and writing in order to develop related to digital technology and communication.
one’s thinking and learning for the purpose of
understanding oneself and the world Example of integration into library instruction: Have students
Literacy is the capacity to communicate using inscribed, create a wiki to collaborate on an annotated bibliography.
printed, or electronic signs or symbols for representing 4. Network Literacy- Understanding of the tools and skills related to
language networked communication and the ability to use those skills to make
Literacy is the ability to identify, understand, interpret, informed decisions.
create, communicate and compute, using printed and
written materials associated with varying contexts. Example of integration into library instruction: Use a shared
Literacy involves a continuum of learning in enabling catalog such as WorldCat to locate a list of resources
individuals to achieve their goals, to develop their
knowledge and potential, and to participate fully in their 5. Cultural Literacy- Analyzing and understanding culture and society
community and wider society. and showing familiarity and compassion towards other cultures.
Literacy is the ability to read, view, write, design, speak and listen in a Example of integration into library instruction: Have students
way that allows you to communicate effectively. The power of literacy find topics in The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy.
lies not just in the ability to read and write, but rather in a person’s
capacity to apply these skills to effectively connect, interpret and LESSON 2: The 21st century literacies and skills
discern the intricacies of the world in which they live.
Globalization
Traditional Literacy Versus New Literacies
is the process of interaction and integration between people,
Traditional literacy is defined as "the quality of being literate; business entities, governments, and cultures from other
knowledge of letters; condition in respect to education, esp. nations, driven by international trade and investment and
ability to read and write" It is the building block for all other supported by information technology.
literacies; without it, they would be impossible to master. is the word used to describe the growing interdependence of
The new literacies encompass much more. Their utility lies in the world's economies, cultures, and populations, brought
online reading comprehension and learning skills, or 21st about by cross-border trade in goods and services, technology,
century skills, required by the internet and other information and flows of investment, people, and information.
and communication technologies (icts), including content
Effects of globalization
found on wikis, blogs, video sites, audio sites, and in e-mail.
They require the ability not just to "read" but also to navigate Economic, political, and military dependence and
the world wide web, locate information, evaluate it critically, interdependence between nations
synthesize it and communicate it-all skills that are becoming Expanded flow of individual people among societies
vital to success in this century's economy. Interdependence of expressive culture among nations
Types of New Literacies Expanded flow of instrumental culture around the world.
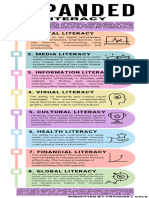
1. Traditional Literacy – Reading, writing, speaking and listening. Cultural literacy
2. Information Literacy – The ability to identify what information is
• Cultural literacy is the knowledge and understanding of the life
needed and the ability to locate, evaluate, and use information.
of a culture to the point where one can fluently participate in
3. Visual Literacy – The ability to understand and produce visual
the activities of the said culture. This includes, but is not
messages.
limited to, its languages, traditions, values, beliefs, forms of
4. Critical Literacy – The ability to question, challenge and
entertainment, and worldviews.
evaluate the meanings and purposes of texts.
Cultural literacy in the Philippines
5. Media Literacy – The ability to question, analyze, interpret,
evaluate, and create media messages. The National Commission for Culture and the Arts (NCCA)
6. Tool Literacy – The ability to use tools to manage, consume is the government body tasked with the documentation,
preservation, and dissemination of Philippine culture, both • Blogging
locally and abroad.
Philippine Cultural Education Program (PECP) together • Class website
with the Department of Education (DepEd), tasked to
formulate the cultural heritage education programs both • Video conferencing
local and overseas Filipinos that are to be an integral part
• Social networking site
of the Philippine education in all its aspect.
Challenges for cultural literacy in the philippines Ways to incorporate social literacy in a face to face social environment;
What kind of knowledge constitute cultural literacy? Is it • Group projects
knowing facts, names, and dates, or is it something more • Peer reviewing
experiental like being familiar with a story or a particular song.
If culture is more “ caught the taught” should cultural literacy • Fieldtrips
be one of the goals of education? If yes, how does one teach
it? • Group activities
Whose cultures must be literate in to be considered “ culturally Types of Social skills
literate”? Who decides which cultures are included and which
ones are excluded, and on what bases? • Greetings- It is the first step in social interaction. It is done not
Is cultural literacy education simply a means for the dominant only in words but also in facial expression, tone of voice and
culturebto express its dominance over minority cultures. gesture.
How is cultural literacy to be assessed and evaluated? How
can we know someone is “ culturally literate”? • Initiating conversation- Child must be able initiate, maintain,
and close conversation appropriately. This requires good
Multicultural literacy listening and attention skills, as well as the ability to take turns
and probe for missing information.
• It is the knowledge and skills necessary to ensure that any
communication with a culture different from our own is clear, • Understanding the listener - Once a conversation is
productive, and respectful such that their differences are iniatated, it has to be maintained. In order to do that it is
celebrated and neither culture is demeaned or treated as important to understand the audience one is talking. ( think the
inferior. way they think)
Skills and knowledge required to be multi-culturally literate • Empathizing - Emphaty is more than perspective taking; it
means that one able to feel what the other persons feels.
Selflessness Empathy allows one to really connect with other people.
Knowledge that good and useful things can ( and do)
come from those different from us. • Reading social cues - Cues are the hint and signals that
Willingness to compromise guide us to the next thing to say or to do. Social cues can be
Acceptance that there are limits verbal or non verbal.
Idea that we cannot be friends with everyone.
• Previewing or planning- Conversations also require that one
Issues in teaching and learning MULTICULTURAL LITERACY IN THE previews or thinks about what effect the words or actions may
PHILIPPINES have on the listener before he/she says or does them.
Nationalistic/regionalistic pushback • Problem solving - How ones react to a conflict depends on
The persistence of the problem how good her problem solving skills.
The question of value • Apologizing - A person with a good social skills is confident
enough to make a sincere apology for her error. This is
Social literacy
courageous act and a sign of humble and mature character.
Social literacy, from the perspective of the social-cultural theory, is
Role Of Parents And Teacher In Teaching Social Skills To Children
more than the ability to read and write, and more than mastering
literacy skills. Children can learn literacy through social interaction 4-Part Strategy
between themselves and children and/or adults in or outside school.
1. Practicing- A parent can help a child substitute a specific
Social literacy spans across interacting of peers, family, co workers, appropriate response for a specific inappropriate one. This
teachers, and even people who have not we met face to face. might mean brainstorming with the child about different
alternative responses and then practicing one or more with
Social literacy concern itself with the development of social skills,
child.
knowledge, and positive human values that enable human beings to
2. Praise- Often children are not eager to work on new skills so
act positively and responsibly in range of social setting.
parent must reward their children with praise when the new
How was social literacy change over time? skills are practiced a way of helping the skills become habits.
3. Point Out- Parents can use opportunities to point out when
In the past, social literacy was understood as students ability others are using the desired skills. It might be specific
communicate in social settings. This definition broadened and behavior of the parent, other adult, a child, or even a character
continuous to broaden into more and more social realms. Over time, in a book or on tv. This idea is to give children examples and
and especially recently, social settings is changing from just face to role models of people engaging in the appropriate social skill.
face environment. For the students to competently interact socially and 4. Prompt- Without nagging, parents can greatly remind their
communicate effectively includes a newer and very present realm. child to use a new skill when the opportunity arises .
Ways to incorporate social literacy online; Children can be fall into 4 basic categories in the school setting;
Rejected- children who are consistently subjected to ridicule, Payment methods, cost, and benefits of each
bullying and harassment by classmates. Budgeting and classification of expenses
Satisfaction, determinants of demand, cost of information
Isolated- student who, although not openly rejected, are ignored
by classmates and are uninvolved in the social aspects of school. search, cost of product durability
Controversial- Students who have established a circle of friends SAVING
based upon common interests or proximity but seldom move
beyond that circle. Concept of saving and interest
How people save money, where people can save money
Popular- Students who have successfully established positive and why people save money
relationships within a variety of groups. The factors determining the value of a person's savings
over time
Teaching social literacy in school is not as easy as it appears to
be due to; Saving for retirement
Subjective standards of morality- Subjective morality says morals USING CREDIT
are human-made and can vary from person to person. While there are Concept of credit and the cost of using credit
strong morals in many humans, such as rules against harming others.
Why people use credit and the source of credit
Human Nature- While we would all like to believe that people are Why interest rates vary across borrowers
inherently good experience has taught us that the inherent goodness of Basic calculation related to borrowing (principal and
humanity is, at best,, unreliable: sometimes it is there, often it is not. interest)
We are not quick to champion the cause of moral uprightness, justice, Consumer protection laws
and equity, but balk when our words and actions come under their
FINANCIAL INVESTING
scrutiny.
Situational awareness in the work place- An ability to read social Concept of financial investment
situations illustrates strength to employers – quick picking up on client’s Variety of possible investments
mood or expectations in a various business or cross cultural situations Calculate rates of return
can be the difference between success and failure.
PROTECTING AND INSURING
Social intelligence in technological communication- Text-speak and
Concept of financial risk and loss
technology use have affected many young people ‘s ability to
Insurance
communicate. While email deformalized much of the communication
process, students still need to ensure their writing denotes respect and Managing risk
provides enough context for professors or future employers to readily Identity theft
respond. Life insurance products
Social intelligence in traditional communication- While email has BENEFITS OF FINANCIAL LITERACY
taken over as the primary method of communication traditional modes
WE NEED TO FINANCIALLY LITERATE SO THAT;
of discourse still exist. For example, many employers still expect cover
letters in addition to resumes, and lack of thank you note for a gift is 1. We know how to manage our finances
often perceive as more than a simple social oversight. 2. We can control the use of money
3. We can increase our savings for financial stability
Financial Literacy
4. We will know how and where to invest
Financial literacy is the ability to understand how money works,
how someone makes, manage and invest it and also expends
it.
Standards and key concept of Financial Literacy
EARNING INCOME
Income earned or received by people.
Different types of job as well as different forms of income
earned or received
Benefits and cost of increasing income through the
acquisition
Government programs that affect income
Types of income and taxes
Labor market
BUYING GOODS AND SERVICES
Scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost
Factors that influence spending choices, such as
advertising, peer pressure, spending choices of others
Comparing the costs and benefits of spending decisions
Basics of budgeting and planning
Making a spending decision
Six Major Characteristic types of people view money
FRUGAL
- Frugal people seek financial security by living below their
means and saving money.
PLEASURE
- Pleasure seekers use money to bring pleasure to themselves
and to others.
STATUS
- Some people use money to express their social status. They
like to purchase and show off their branded items.
INDIFFERENCE
- some people place very little importance on having money and would
rather grow their own food and craft their own clothes. It is as if having
too much money makes them nervous.
POWERFUL
-powerful people use money to express power or control over others
SELF-WORTH
-people who spend money for self worth value how much they
accumulate and tend to judge others based on the amount of money
they
have.
You might also like
- READ IT: NSA's Full Glossary of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion TermsDocument34 pagesREAD IT: NSA's Full Glossary of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion TermsDaily Wire Investigations Team75% (4)
- CHAPTER 1-Building AND EnhancingDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 1-Building AND EnhancingJess Arceo100% (9)
- Smoking QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesSmoking QuestionnaireNeric Ico Magleo100% (1)
- Module 2: Literacy in The 21 CenturyDocument3 pagesModule 2: Literacy in The 21 CenturyJuliet Ardales0% (1)
- English CG 2023Document217 pagesEnglish CG 2023Melody BadillaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literacies IntroductionDocument11 pages21st Century Literacies IntroductionPELAEZ, JOANNA MAY L.No ratings yet
- Building Ang EnhancingDocument7 pagesBuilding Ang EnhancingYessia Mae E. ArandaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 10 - Building and Enhancing New LiteraciesDocument21 pagesEDUC 10 - Building and Enhancing New LiteraciesMeliza CasipitNo ratings yet
- Educ 6-3Document5 pagesEduc 6-3Rica NarioNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4 Notes (Building and Enhancing)Document14 pagesModule 3 and 4 Notes (Building and Enhancing)John Kiere F. CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Building and Enhancing NewDocument29 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Building and Enhancing NewDanilo de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Profed08 Chapter 1Document10 pagesProfed08 Chapter 1Monica Mae CodillaNo ratings yet
- L1Document4 pagesL1Shaira LiabanNo ratings yet
- L1-BENLACDocument38 pagesL1-BENLACCABRERA ABIGAIL P.No ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across CurriculumDocument10 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across CurriculumKlaimark Ramento CadelinaNo ratings yet
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum: Educ 323Document33 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum: Educ 323Abegail Lucapa100% (7)
- Module 3 Building New Literacy in The 21ST Century2Document19 pagesModule 3 Building New Literacy in The 21ST Century2Realyn FababaerNo ratings yet
- Concept of Literacy and Its Significance On Society - Group 1Document9 pagesConcept of Literacy and Its Significance On Society - Group 1Myeth BendalNo ratings yet
- EDUC-110-NOTESDocument5 pagesEDUC-110-NOTESHannahNo ratings yet
- local_media555487452840911793Document11 pageslocal_media555487452840911793its03mae14No ratings yet
- Prof Educ 2 Module 1Document7 pagesProf Educ 2 Module 1Erica Mae Sionicio0% (1)
- General Education Final Exam Covers New LiteraciesDocument3 pagesGeneral Education Final Exam Covers New LiteraciesDaewin SeratoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Basic-LiteracyDocument22 pagesLesson 3 - Basic-LiteracyShyra Kate CatalyaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literacy SkillsDocument28 pages21st Century Literacy SkillsKristine Lapada TanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To The Concept of New LiteracyDocument16 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To The Concept of New LiteracyRodelin Manding100% (1)
- Medinfolit 1Document7 pagesMedinfolit 1JASIS JULIA NOELYN V.No ratings yet
- Educ102 Prelim-FinalDocument8 pagesEduc102 Prelim-FinalCressa MaloneNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 10 Module 1 Preliminaty TopicsDocument4 pagesProf Ed 10 Module 1 Preliminaty TopicsRhina Mae ArguezaNo ratings yet
- BENLAC-MODULE 3-DE LEONDocument48 pagesBENLAC-MODULE 3-DE LEONMary Angeline De LeonNo ratings yet
- 5fa9547986fd360027cb85f9 1635128249 1. Introduction To The 21st Century LiteraciesDocument9 pages5fa9547986fd360027cb85f9 1635128249 1. Introduction To The 21st Century LiteraciesJharmie Vie Redoble VLNo ratings yet
- Information LiteracyDocument12 pagesInformation LiteracyKirsten GoNo ratings yet
- LITERACYDocument5 pagesLITERACYJemay JamitoNo ratings yet
- New LiteraciesDocument14 pagesNew LiteraciesJULES DOMINIC CATULAYNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 21ST Century Literacy GRP 1Document3 pagesIntroduction To 21ST Century Literacy GRP 1Jhiemalyn RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Module 3-BENLACDocument65 pagesModule 3-BENLACElleonor Abatay100% (1)
- Ed 110 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEd 110 Reviewerjulieanna gupitNo ratings yet
- MINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterDocument2 pagesMINLIT1 Prelims 2nd Semestermarcuspanopio91787No ratings yet
- Communications ReviewerDocument8 pagesCommunications ReviewerAubrey MarinNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Sir RYAN)Document48 pagesModule 3 (Sir RYAN)Jayla Mae MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- MINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterDocument2 pagesMINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterantekeithNo ratings yet
- U1L2 - Definitions of 21st Century LiteraciesDocument19 pagesU1L2 - Definitions of 21st Century LiteraciesJerry Glenn Latorre CastilloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Mil PDFDocument17 pagesReviewer in Mil PDFJulius Cesar CuderaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 111 Topic 1Document7 pagesProf Ed 111 Topic 1Angel Joy LunetaNo ratings yet
- Exam Ed102Document92 pagesExam Ed102Lowell VenerableNo ratings yet
- Activity in Extended LiteracyDocument1 pageActivity in Extended LiteracyFrances ColeNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts of LiteracyDocument3 pagesKey Concepts of Literacyaleth ofiladaNo ratings yet
- BENLACDocument24 pagesBENLACVanessa Garfin TambanNo ratings yet
- BENLAC REVIEWERDocument5 pagesBENLAC REVIEWERJho MalditahNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 10Document16 pagesProf Ed 10John Michael A PalerNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Definitions of The 21 Century Literacies: Sheila Mae AguadoDocument3 pagesModule 2 - Definitions of The 21 Century Literacies: Sheila Mae AguadoSheila AguadoNo ratings yet
- San Jose Community CollegeDocument6 pagesSan Jose Community CollegeSimple HeavenNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication Skills Course OutlineDocument8 pagesEffective Communication Skills Course OutlineKC Panaligan100% (1)
- Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum - Introduction To 21ST CenturyDocument5 pagesBuilding and Enhancing New Literacies Across The Curriculum - Introduction To 21ST CenturyJenny Rose GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Module 1-8 (21ST) PDFDocument266 pagesModule 1-8 (21ST) PDFHannah Mae LucasNo ratings yet
- Oinarrizko Konpetenziak Ingelesa LHDocument9 pagesOinarrizko Konpetenziak Ingelesa LHNekane GastaminzaNo ratings yet
- MSC 6 MODULE 3 REPORTDocument6 pagesMSC 6 MODULE 3 REPORTMary Angeline De LeonNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document14 pagesModule 3ROSE ANN MAULANANo ratings yet
- Mil Og ReviewerDocument6 pagesMil Og ReviewerMarian ColoradoNo ratings yet
- Orange and Cream Illustrative Learning English PresentationDocument46 pagesOrange and Cream Illustrative Learning English Presentationkristine buñaNo ratings yet
- Media and Digital LiteracyDocument21 pagesMedia and Digital LiteracyJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1kylerubyjaneNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lesson 1 PED 203Document7 pagesWeek 1 Lesson 1 PED 203Syvil Mae GerotapeNo ratings yet
- Cultural Intelligence: Thriving in a Diverse Global MarketplaceFrom EverandCultural Intelligence: Thriving in a Diverse Global MarketplaceNo ratings yet
- 19 Intl JChild Rts 547Document25 pages19 Intl JChild Rts 547Aslı AlkışNo ratings yet
- The Ability To Read and Write.: Media The Physical Objects Used To Communicate With, or The Mass CommunicationDocument3 pagesThe Ability To Read and Write.: Media The Physical Objects Used To Communicate With, or The Mass CommunicationRachel MonesNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm ExamKaleb Drey GuancoNo ratings yet
- Benlac ReviewerDocument4 pagesBenlac ReviewerRonalyn Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mil QuizDocument3 pagesMil QuizDlanor Nablag100% (1)
- Notes in Media and Information LiteracyDocument5 pagesNotes in Media and Information LiteracyMel GBNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument18 pagesMedia LiteracyShy PaguiganNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Parallel Test - M3 & M4Document2 pagesWeek 2 - Parallel Test - M3 & M4Oliver JaguinesNo ratings yet
- English For Media Literacy Syllabus: Instructor InformationDocument5 pagesEnglish For Media Literacy Syllabus: Instructor InformationAhmed Ra'efNo ratings yet
- Weekly Plan MILDocument8 pagesWeekly Plan MILEdelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Media Literacy Week 1Document3 pagesMedia Literacy Week 1Annalei Tumaliuan-TaguinodNo ratings yet
- Filipino Students - Competency in Evaluating Digital Media Content Credibility - Beginning - To - Emerging - LevelsDocument13 pagesFilipino Students - Competency in Evaluating Digital Media Content Credibility - Beginning - To - Emerging - LevelsdumpyreireiNo ratings yet
- BowDocument3 pagesBowAriel CancinoNo ratings yet
- Media Literacy 8th Edition Potter Test BankDocument7 pagesMedia Literacy 8th Edition Potter Test Banksophiechaurfqnz100% (27)
- BENLAC Syllabus 2021Document10 pagesBENLAC Syllabus 2021EFren N. NOceteNo ratings yet
- Access, Equity, and Empowerment - Supporting Digital Literacies For All LearnersDocument20 pagesAccess, Equity, and Empowerment - Supporting Digital Literacies For All LearnersUIC College of EducationNo ratings yet
- MIL - Module 7 - Lesson 9 - Media and Information Literate IndividualDocument4 pagesMIL - Module 7 - Lesson 9 - Media and Information Literate IndividualLOREEN BERNICE LACSONNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 Communication Media and InformationDocument39 pagesWEEK 1 Communication Media and InformationIan ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information DesignDocument3 pagesMedia and Information DesignRachell Ann BarrogoNo ratings yet
- THESIS As of 5-21-19 For Clean Copy Print 1Document110 pagesTHESIS As of 5-21-19 For Clean Copy Print 1Shane MAGDAY BATARANo ratings yet
- DLL Mil Week 1 2022 This Is A Daily Lesson Log For Week 1 of The First Semester in Media and InformationDocument5 pagesDLL Mil Week 1 2022 This Is A Daily Lesson Log For Week 1 of The First Semester in Media and InformationHanz Albrech AbellaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Media LiteracyDocument13 pagesModule 8 Media LiteracyEfigenia Macadaan Fontillas100% (6)
- 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World 1.1Document4 pages21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The World 1.1Kiefer SebastianNo ratings yet
- Multimedia and Information Literacy Quarter 1-Module 2Document7 pagesMultimedia and Information Literacy Quarter 1-Module 2Marieezze ParkNo ratings yet
- Prince CharmingDocument18 pagesPrince CharmingIsabelleArthurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and InformationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Media and InformationArnel AcojedoNo ratings yet
- EVR College Viscom UG Syll 2018Document37 pagesEVR College Viscom UG Syll 2018AnjacNo ratings yet