Professional Documents
Culture Documents
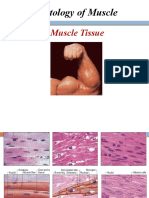
Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Uploaded by
Allyzha Aguilar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThis document summarizes the three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle. It describes their key structural features, including sarcomeres as the basic contractile units in skeletal and cardiac muscle composed of actin and myosin filaments. Contraction occurs via sliding of actin and myosin filaments. The document also outlines the connective tissue coverings of muscle fibers and bundles.
Original Description:
Original Title
Muscle-tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle. It describes their key structural features, including sarcomeres as the basic contractile units in skeletal and cardiac muscle composed of actin and myosin filaments. Contraction occurs via sliding of actin and myosin filaments. The document also outlines the connective tissue coverings of muscle fibers and bundles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesMuscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Uploaded by
Allyzha AguilarThis document summarizes the three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle. It describes their key structural features, including sarcomeres as the basic contractile units in skeletal and cardiac muscle composed of actin and myosin filaments. Contraction occurs via sliding of actin and myosin filaments. The document also outlines the connective tissue coverings of muscle fibers and bundles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
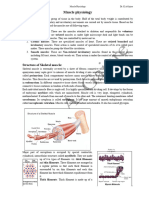
VANA 215 – Muscle Tissue o sarcomere – the unit structure of muscle
contraction, w/c starts in the sarcomere
Muscle Tissue o it includes all myofilaments located between two
group of muscle cells or fibers composed of adjacent sarcomere
organelles and inclusions like any other cell
sarcolemma – the name for the cell membrane; o field of cohnheim is the group of myofilaments
the cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm appear clumps of acidophilic dots
“sarco” means flesh
actin and myosin that comprise the myofilaments
of the fiber enable the muscle to perform the
property of its sarcoplasm (i.e. contractility
responsible for locomotion/movement of the body)
3 Types of Muscle based on their STRUCTURE
1. Smooth/ non-striated/ involuntary muscle
2. Skeletal/ striated/ voluntary muscle
o in relaxed or contracted sarcomere –
3. Cardiac/ striated/ involuntary muscle
o Ordinary Cardiac Muscle (OCM) myofilaments are longitudinally arranged in the
middle, extending to but not reading the ends of
o Special cardiac muscle fiber or Purkinje
sarcomere
o actin filaments extend from the Z line toward the
1. Smooth/ non-striated/ involuntary muscle
middle of each adjacent sarcomere in between
elongated and spindle-shaped cells with tapered
the myosin filaments where they terminate in free
ends
ends before reaching the H band
elongated nucleus is also
o contraction of sarcomere is the result of sliding of
centrally located
actin into the interstices of the myosin where they
muscle fibers are tightly
are interdigitated; pulling the Z lines until at full
paced to form sheet
contraction the free ends of actin meet in the
in longitudinal section,
middle of the sarcomere
fibers forming sheet are
o contracted sarcomere has no H Band
arranged in staggered
fashion o stretched sarcomere , the actin filaments over
middle widest portion of the fiber is adjacent to the extend and slide away from the myosin, resulting
tapered; end of other fiber making the nuclei to a wide H band almost obliterating the A band
appear staggered also
found in the lamina propria of the tunica mucosa
and tunica muscularis of tubular organs
2. Skeletal/ striated/ voluntary muscle
fibers are long and cylindrical with blunt ends
multinucleated located peripherally
special feature is the x-striations of the
sarcoplasm oriented perpendicular to the long
axis of the fiber
striations are the alternating dark or A band and 3. Cardiac/ striated/ involuntary muscle
light or I band 2 types of cardiac muscle
o I band – contains the fine/thin actin filaments
o A band – contains the thick myosin filaments end
of actin = A band is dark
o EM, A band has a narrow light area at the middle
called H band because of the absent actin filament
o represents the gap between the free ends of actin
filaments
o I band is bisected by the middle dark line called Z
line where the actin filament of one sarcomere are
connected to the next sarcomere
o Ordinary cardiac
muscle (OCM) – has
x-striations but
functions but
functions like smooth
muscle
Multinucleated
located at the
center of elongated branched fiber
highly vascular, have intercalated disc, running
transversely on the longitudinal axis of the
fibers, indicating the point of end to end
contact of the muscle
fibers
o Special cardiac muscle fiber
or Purkinje fiber – impulse
conducting cells located from
A-V node to IV septum
Connective tissue
covering of muscle
Epimysium – outer most covering
Perimysium – covers bundle/fascicle of
muscle
Endomysium – covering of muscle fiber
You might also like
- AnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemLM KishimotoNo ratings yet
- OnlineMedEd Clinical Video ListDocument8 pagesOnlineMedEd Clinical Video ListCourtney Holbrook100% (1)
- Classification of MusclesDocument50 pagesClassification of MusclesNoor HaleemNo ratings yet
- Zoology PPT Muscular SystemDocument68 pagesZoology PPT Muscular SystemDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Blood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument71 pagesBlood: Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeCath TabasNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Muscular SystemDocument8 pages7.1 Muscular SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Upper GI Disorders Study GuideDocument10 pagesUpper GI Disorders Study Guidemelpietrowski100% (1)
- Muscles Part1 DoxDocument13 pagesMuscles Part1 DoxjeffdelacruzNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument49 pagesMuscular TissueSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryDocument13 pagesChapter 10: Muscle Tissue: VoluntaryClyde BaltazarNo ratings yet
- The Child With Hematologic DisordersDocument149 pagesThe Child With Hematologic DisordersNics FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Bartolome, Week 4 Course Task PDFDocument5 pagesBartolome, Week 4 Course Task PDFKhate BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Histology of MuscleDocument49 pagesHistology of MuscleTewachew Dessie100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesMuscular SystemTricia Mae LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesReviewer - Muscular SystemIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- HAPP Week VII XDocument32 pagesHAPP Week VII Xxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 7 - Muscular SystemlNo ratings yet
- Célula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoDocument11 pagesCélula Muscular, Macro y MicrobiologicoimanolNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Lecture 1DDocument7 pagesMuscular System Lecture 1DShane PascualNo ratings yet
- 589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyDocument3 pages589bc774 Df1d 47c6 Bc97 B5fd73030ca6muscle PhysiologyMalti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarDocument65 pagesMuscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarYulius SamuelNo ratings yet
- ANPH Midterm NotesDocument44 pagesANPH Midterm NotesClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- 29.-31. SBRC MSK SummaryDocument153 pages29.-31. SBRC MSK SummaryErin HillNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYSIO LEC (Midterms)Document14 pagesANAPHYSIO LEC (Midterms)KIM EUNHANo ratings yet
- Anaphy Notes MidtermDocument10 pagesAnaphy Notes MidtermAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- 04muscle TissueDocument39 pages04muscle Tissueapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Histo MuscleDocument11 pagesHisto MuscleaikaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument3 pagesMuscular System ReviewerRea BrangueloNo ratings yet
- Muscular TDocument18 pagesMuscular TSumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesMuscular SystemReynaldo MontañoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy-Muscular HandoutDocument7 pagesAnaphy-Muscular HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesANAPHY - Muscular SystemSoleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- MUSCOSKELETALDocument6 pagesMUSCOSKELETALN.No ratings yet
- 7 Muscular SystemDocument11 pages7 Muscular SystemmargaretNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy - ContentDocument14 pagesFunctional Anatomy - ContentxanaduNo ratings yet
- Human Histology (Lecture) Lesson 6: Muscle Tissue (Anatomy & Physiology)Document4 pagesHuman Histology (Lecture) Lesson 6: Muscle Tissue (Anatomy & Physiology)AJ MERCADONo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument11 pagesMuscleJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- LPT 321Document103 pagesLPT 321rahul roshanNo ratings yet
- 3D. Muscle TissueDocument47 pages3D. Muscle Tissuejaf123xyNo ratings yet
- Eme 1Document20 pagesEme 1Tara LingatingNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYDocument78 pagesMUSCLE and NERVOUSHISTOLOGYAerielle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemCHRISTIANNE DENISE EBREONo ratings yet
- MascularDocument39 pagesMascularAive BelistaNo ratings yet
- Muscles TransesDocument3 pagesMuscles TranseskimeehhNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument15 pagesNotesGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Nona PeriarceNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleDocument73 pagesHistology of Cardiac and Smooth MuscleShehryar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 PDFDocument6 pagesLec 6 PDFАбу ДжудNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissuesDocument46 pagesMuscular TissuesDAVE CANALETANo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue NotesDocument4 pagesMuscle Tissue NotesTob MoradosNo ratings yet
- Neuron Motor PeriferDocument15 pagesNeuron Motor PerifernunualoneNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument10 pagesMuscular SystemKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument10 pagesMuscular SystemMarie Veatrice JacomilleNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesMuscular SystemChrisjohn Aster OsioNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesMuscular SystemNicoleVideñaNo ratings yet
- Muscles Lab Report - NoDocument3 pagesMuscles Lab Report - Noapi-3801039No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer For MidtermsDocument3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer For MidtermsChristianJoshuaOseaElpedesNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue NotesDocument11 pagesMuscle Tissue NotesAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Notes (HAP)Document7 pagesDay 2 Notes (HAP)Psyche Daclag TumandaNo ratings yet
- UNOANAPHYDocument45 pagesUNOANAPHYGraye SolliNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 pagesMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument25 pagesMuscular Tissue: Anatomy and Physiology LecturehanzNo ratings yet
- Histo Lab Ex 13 17Document57 pagesHisto Lab Ex 13 17Allyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cow's HeartDocument10 pagesCow's HeartAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- BioChem - Experiment 3-Post LabDocument12 pagesBioChem - Experiment 3-Post LabAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Cladogram ActivityDocument4 pagesCladogram ActivityAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Chapter 4 Nuclear PhysicsDocument14 pagesGroup 5 Chapter 4 Nuclear PhysicsAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Filipino Artist in Central LuzonDocument43 pagesFilipino Artist in Central LuzonAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Group 4-Experiment 1 - POST LABDocument16 pagesGroup 4-Experiment 1 - POST LABAllyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- BioChem - Experiment 8Document8 pagesBioChem - Experiment 8Allyzha AguilarNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrilasiDocument5 pagesAtrial FibrilasiAviation MedicineNo ratings yet
- Case Study HypertnsionDocument32 pagesCase Study HypertnsionAnkush Kulat PatilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemRenz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Infants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDateDocument16 pagesInfants of Women With Diabetes - UpToDatethelesphol pascalNo ratings yet
- Blood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)Document1 pageBlood Test Results: CMP Explained: Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)giuzolinNo ratings yet
- Penilaian Awal Pasien SyokDocument33 pagesPenilaian Awal Pasien SyokatikaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram NotesDocument23 pagesElectrocardiogram NotesSanjay RanaNo ratings yet
- Primary+Clinical+Care+Manual +9th+Edition+ +Full+ManualDocument805 pagesPrimary+Clinical+Care+Manual +9th+Edition+ +Full+Manualpaul okelloNo ratings yet
- Esophagus - Anatomic and Physiologic Data, Research Methods, Diseases, Clinic, TreatmentDocument41 pagesEsophagus - Anatomic and Physiologic Data, Research Methods, Diseases, Clinic, TreatmentSASIDHARNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin II Receptor BlockersDocument4 pagesAngiotensin II Receptor BlockersmazfarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)Document21 pagesChapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Milk FeverDocument10 pagesMilk FeverMorad Imad100% (1)
- Folio 2022Document10 pagesFolio 2022fila markNo ratings yet
- Vascular EmergenciesDocument43 pagesVascular EmergenciesMohammad BanisalmanNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Hepatic Artery Aneurysm.a Rare Visceral AneurysmDocument5 pagesCase Report: Hepatic Artery Aneurysm.a Rare Visceral AneurysmIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Drill #1 With RationaleDocument12 pagesDrill #1 With RationaleRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Aca HolterDocument39 pagesGuidelines Aca HolterMiguel PeixotoNo ratings yet
- Aneasth.2 - PHCP2Document11 pagesAneasth.2 - PHCP2أحمد أسامهNo ratings yet
- History of Electrocardiography, From The Past To The PresentDocument37 pagesHistory of Electrocardiography, From The Past To The PresentОксана ЗвягинаNo ratings yet
- NF) S ) JF Cfof) U G) Kfn:Jf:Yo ) JF, HG/N GL (Ë D"X, Xfos KFFRF) + Tx,:6Fkm G (KBSF) V'NNF / CFGTL/S K - Ltof) Lutftds LNLVT K/Liffsf) Kf7/OqmdDocument4 pagesNF) S ) JF Cfof) U G) Kfn:Jf:Yo ) JF, HG/N GL (Ë D"X, Xfos KFFRF) + Tx,:6Fkm G (KBSF) V'NNF / CFGTL/S K - Ltof) Lutftds LNLVT K/Liffsf) Kf7/OqmdAnil BasnetNo ratings yet
- La Ringo MalasiaDocument6 pagesLa Ringo Malasiayunita24No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System: Physical ExaminationMiguel C. Dolot100% (1)
- 8th Edition of The AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Pancreas and Hepatobiliary CancersDocument3 pages8th Edition of The AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Pancreas and Hepatobiliary Cancersmilagros12300No ratings yet
- Amlodipine by HamidDocument21 pagesAmlodipine by HamidShaheen UiiahNo ratings yet