Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inorganic Chem Reviewer
Inorganic Chem Reviewer
Uploaded by
kez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesInorganic chemistry involves the study of compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. Key topics covered include the classification of elements and compounds, as well as states of matter.
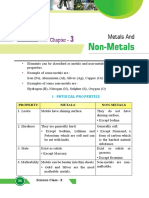
Elements are composed of atoms and are classified as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or semimetals. Metals are usually solid, ductile, and good conductors. Nonmetals are usually colorless gases or brittle solids that are poor conductors. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals.
Compounds are made of two or more elements and can be classified as acids, bases, salts, or oxides. Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and with bases to produce
Original Description:
Original Title
Inorganic Chem reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInorganic chemistry involves the study of compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. Key topics covered include the classification of elements and compounds, as well as states of matter.
Elements are composed of atoms and are classified as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or semimetals. Metals are usually solid, ductile, and good conductors. Nonmetals are usually colorless gases or brittle solids that are poor conductors. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals.
Compounds are made of two or more elements and can be classified as acids, bases, salts, or oxides. Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and with bases to produce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesInorganic Chem Reviewer
Inorganic Chem Reviewer
Uploaded by
kezInorganic chemistry involves the study of compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. Key topics covered include the classification of elements and compounds, as well as states of matter.
Elements are composed of atoms and are classified as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or semimetals. Metals are usually solid, ductile, and good conductors. Nonmetals are usually colorless gases or brittle solids that are poor conductors. Metalloids have properties between metals and nonmetals.
Compounds are made of two or more elements and can be classified as acids, bases, salts, or oxides. Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and with bases to produce
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
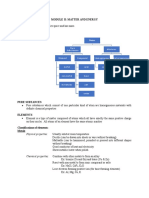
Inorganic Chem Elements excellent semiconductor
- Study of the formation, synthesis, and -Composed of atoms (Si, Ge)
properties of compounds that do not contain - are Metals, nonmetals, metalloids, semimetals Compounds
carbon-hydrogen bonds. -Made up of two or more ELEMENTS
Classification of Elements -Chemically combine elements
Matter • Metals Classification of compounds
-Anything that occupies space and has mass o Physical properties 1. Acid
▪ Usually solid at room -Hydrogen compound whose hydrogen can
Structure of an atom tempt. be replaced by a metal
1. Atomic nucleus ▪ Ductile Properties of acid:
-Protons ▪ Malleable o Sour taste
-Neutrons ▪ Good conductor of heat o Reaction with certain
2. Electrons and electricity metals=produces
State of matter o Chemical properties Hydrogen
Solid ▪ When combine with other o Reaction with
-definite volume and definite shape metals, it forms alloy Bases=produces salt and
Types of solid (Bronze; Cu & Sn) water
1. Crystalline substances ▪ It reacts with non-metal to
-have a definite arrangement form ionic compounds or
-Assume a definite geometric shape or salts 2. Base
figure ▪ Lose electron forming -Hydroxides of metal – hydroxide anion and
Ex. Table sugar, salt, diamond positive ion (Al, Mg, Ca, metallic cations
K) Properties of base:
2. Amorphous substances o Bitter taste
-no definite form • Non-metals o Soapy or slippery feeling
- supercooled liquids o Physical P. o Reaction with
Ex. Wax, paraffin, glass, plastic ▪ Colorless or brilliant color acid=produces salt &
▪ Gases at room temp. water
▪ Brittle 3. Salt
Liquids
▪ Poor conductor of heat -substances consist of metallic radical
- Definite volume but no definite shape
and electricity -combined w/ non-metal or acid radical
- Incompressible
o Chemical P. Types of salt:
▪ Non-metals combine with a. Normal salts (NaCl)
Gases b. Basic salts – contain 1 or more
non-metals forms covalent
-no definite shape, no definite volume OH radicals
compounds (CO2)
Plasma c. Acid salts – hydrogen of an acid
▪ Gain electrons forming a
-Ionize Gas replaced by a metal
negative ion
-result from breaking off an atom or molecule of gas d. Double salts – 2 metals combined
• Metalloids or semi-metals
-contains free electrons and free positive ions with 1 radical
▪ Have properties that lie
between metal and non- 4. Oxide
Classification of matters metals -oxygen & only one other element
Pure substances ▪ Look like metal but brittle Kinds of oxide:
-One particular kind of atom like non-metal a. Metallic oxide
-Homogenous materials with definite chemical ▪ Neither conductor nor -metal + oxygen
properties insulator but make b. Basic anhydride
c. Non-metallic oxide
d. Acid anhydride Physical Change (Triangle) Atomic Symbols
Note: Anhydride = no oxygen L->S = Freezing Mass # = Protons + Neutrons
Mixtures L->G =Evaporation Atomic #, Protons, Electrons = same
-Contains two or more SUBSTANCES S->L = Melting
Types of mixture: S->G = Sublimation
a. Homogeneous Mixture G->S = Reverse Sublimation
-Made up of only one phase G->L = Condensation Put the function of the given radioisotopes
Ex. Sugar solution 1. Iodine – 131 &123
b. Heterogeneous Mixture Chem. Changes (Nasa PPT) 2. Strontium -90
-Components are easily identified 3. Cobalt 59 & 60
Ex. Oil and water 2. Extensive Property 4. Thallium 201
-Change when the size of the 5. Chromium 151
sample changes
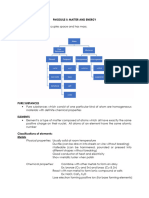
Properties of Matter
1. Intensive Property ENERGY
-Does not change when some Energy Level
samples are taken away Note: 1st part next page
Types of Intensive Property: S = sharp
a. Physical Property/changes – Changes in energy -Spherical shape
affects the state and appearance of - 2 electrons
the matter a. Exothermic change
-Color -Energy is given off P = principal
-taste - Involves heat flow from the system of -Dumbbell shape
-odor surroundings -6 electrons
-volume
-mass b. Endothermic change D = diffuse
-boiling point -Energy is absorbed -four leaf clover (hourglass & ring)
-melting point -Involves heat flow from the surrounding -10 electrons
-freezing point to the system
b. Chemical property/changes –
F = fundamental
Results in the formation of a new
Nuclear change – Change in the composition of -complex shape
chemical substance
nuclei of atoms =14 electrons
-Reactivity; combine w/
a) Nuclear fission
other substance
-separation (Split into two) Electronic configuration
-Combustibility; combine
b) Nuclear fusion
w/ oxygen
-Combine (draw)
-Stability; Resist changes
-Deliquescence; become
wet when exposed to air CHEMICAL SYMBOLS, NOTATIONS, &
-Efflorescence; dry, crisp NOMENCLATURE
& powdery when exposed Modern atomic theory
to air -small nucleus
-Effervescence; forms -3 elementary/subatomic particles (Protons, electrons,
bubbles or foam & Neutrons)
You might also like
- Alkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRDocument20 pagesAlkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRMuzahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Specification For Fuel Gases For Combustion in Heavy-Duty Gas TurbinesDocument24 pagesSpecification For Fuel Gases For Combustion in Heavy-Duty Gas TurbinesGreg EverettNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Jason Robert VictorNo ratings yet
- Metals R0 - 220830Document41 pagesMetals R0 - 220830Kelly Roxelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 NotesDocument47 pagesGen Chem 1 NotesMilescent Rose Juguilon PadillaNo ratings yet
- l6 Minerals - Earth ScienceDocument29 pagesl6 Minerals - Earth ScienceManuel ParillaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PharChemDocument6 pagesChapter 1 PharChemno nameNo ratings yet
- Handwritten: MetalsDocument6 pagesHandwritten: MetalsarjunNo ratings yet
- Matter and EnergyDocument16 pagesMatter and EnergyBiancaQuitasolNo ratings yet
- Solid State - PLPN MhtCetDocument42 pagesSolid State - PLPN MhtCetsiddheshmundlik6No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesChem ReviewerMA. SOFIA ALCUETASNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals - NotesDocument8 pagesMetals and Non Metals - NotesMohita RastogiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Metals)Document4 pagesChemistry Notes (Metals)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas67% (3)
- CHEM-Types of SolidDocument4 pagesCHEM-Types of SolidMark Joseph PulintanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 2Document8 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 2Maithili PanwarNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesStudy Material Class 10 Chapter 3 2017 PDFKaran Pratap67% (3)
- Metal and Non MetalsDocument7 pagesMetal and Non Metalschhabra navdeep100% (1)
- Most Imp Chemistry Full Boards NotesDocument159 pagesMost Imp Chemistry Full Boards NotesAman KumarNo ratings yet
- The Solid State: Chapter - 15Document16 pagesThe Solid State: Chapter - 15Athish MNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 5Document25 pagesPDF Document 5miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Matters and EnergyDocument17 pagesMatters and EnergyCyrisse MONTANONo ratings yet
- Comparison of Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals and Non - MetalsDocument3 pagesComparison of Physical and Chemical Properties of Metals and Non - MetalsSWATINo ratings yet
- Metal and Nonmetal ElementsDocument64 pagesMetal and Nonmetal ElementsSherly Christina OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Full PDFDocument35 pagesChem Notes Full PDFVishal Kunnathur Senthilkumar100% (2)
- Metal and Non MetalsDocument7 pagesMetal and Non Metalschhabra navdeep100% (1)
- Chem M1 PDFDocument11 pagesChem M1 PDFZarylle De AsasNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Review Notes PDF FreeDocument34 pagesGrade 10 Science Review Notes PDF FreeChristian Dar CabotajeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry RevisionDocument3 pagesChemistry RevisionIram GulfarazNo ratings yet
- CHM111 RevDocument2 pagesCHM111 RevLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- C1 - Notes 1 of 2 - Solid StateDocument5 pagesC1 - Notes 1 of 2 - Solid StateAtharva BhavsarNo ratings yet
- S Block (Landscape)Document8 pagesS Block (Landscape)Drastic Pranksters Inc.No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesAzeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedDocument15 pagesMetals and Non-Metals Notes - RemovedCyber Atharv100% (1)
- S Block ElementsDocument31 pagesS Block ElementsMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 CHEMISTRY Chapter 3 PART - 1Document3 pagesGRADE 10 CHEMISTRY Chapter 3 PART - 1Mihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals NotesDocument18 pagesMetals and Non-Metals NotesMustafa Khan100% (1)
- Groupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaDocument6 pagesGroupings of Elements in The Periodic Table Group I A - The Alkali Metals NaGlad YsNo ratings yet
- Candy S - Science 09 ChemistryDocument2 pagesCandy S - Science 09 ChemistryTasneem SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument15 pagesMetals and Non Metalskebepef613No ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument20 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsDevyansh MishraNo ratings yet
- S Block ElementsDocument8 pagesS Block ElementsSwati Jadhav100% (3)
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Class XDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding: Class XGeorge Stephen TharakanNo ratings yet
- Chem PrintsDocument18 pagesChem Printsanayaa agarwalNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and PeriodicityYash BhattNo ratings yet
- c-01 - Theory Solid State FinalDocument26 pagesc-01 - Theory Solid State FinalShivambu Dev PandeyNo ratings yet
- Crop Production & ManagementDocument14 pagesCrop Production & ManagementAnkit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 Metals - and - Non - Metals NewRahul IngleNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument9 pagesChemistryJonah SesayNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Metals and Non - Metals Gist of The LessonDocument8 pagesChapter - 3 Metals and Non - Metals Gist of The LessonPrasadNo ratings yet
- Types and Properties of SolidsDocument13 pagesTypes and Properties of SolidsShaila DelatorreNo ratings yet
- Che 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringDocument19 pagesChe 513 Introduction To Polymer EngineeringHappyNo ratings yet
- Metals ReviewerDocument8 pagesMetals ReviewerCyber DomingoNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 Classification of MatterDocument2 pagesChem 11 Classification of MattershandominiquefelicitycaneteNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsDocument19 pagesLesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsLemonadeNo ratings yet
- Dalal Class 8 Elements Compounds Mixtures New Simplified ICSE Chemistry ICSEHELPDocument11 pagesDalal Class 8 Elements Compounds Mixtures New Simplified ICSE Chemistry ICSEHELPRajesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Element Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesElement Classification of Elements: Class-X Chapter - 3 Metals and Non-MetalsInsha Hasan 10DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Engineering Geology-2024Document67 pagesChapter 2 - Engineering Geology-2024Dawit HaileNo ratings yet
- Complete S Block ElementsDocument108 pagesComplete S Block ElementsDrushya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Molecular Collisions: R.M.S. Speed Z Collision FrequencyDocument8 pagesMolecular Collisions: R.M.S. Speed Z Collision FrequencyMaria ZvolinskayaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plans For MEC442-2017Document2 pagesLecture Plans For MEC442-2017hahahaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Properties of Pure Substances: P, Kpa T, V, M U, KJ/KGDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 - Properties of Pure Substances: P, Kpa T, V, M U, KJ/KGSong LingNo ratings yet
- Absorption ColumnDocument29 pagesAbsorption ColumnSRINIVAS TNo ratings yet
- Structure of Matter Class7Document12 pagesStructure of Matter Class7eas grade04100% (1)
- Question On Welding 42 PDFDocument1 pageQuestion On Welding 42 PDFXerexNo ratings yet
- Gas Cylinder Sizes and Volumes - Read Info at Elgas LPGDocument1 pageGas Cylinder Sizes and Volumes - Read Info at Elgas LPGFahiez Bin JusdeanNo ratings yet
- Landau Level Crossing in Two-Subband Systems in Tilted Magnetic Field - Phys. Rev. B (76) 075346Document8 pagesLandau Level Crossing in Two-Subband Systems in Tilted Magnetic Field - Phys. Rev. B (76) 075346Celso DuarteNo ratings yet
- Evaporator: CH250 - Heat TransferDocument21 pagesEvaporator: CH250 - Heat TransferManas AkashNo ratings yet
- ANew Approach of Splitting C6 CompoDocument7 pagesANew Approach of Splitting C6 CompoMantiqiNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws NOTESDocument2 pagesGas Laws NOTESKimberly MutangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Fig.12.a. Flow Diagram of Simple Vapour Compression SystemDocument15 pagesChapter Four: Fig.12.a. Flow Diagram of Simple Vapour Compression SystemAnonymous 5HYsyrddpNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Packet 2 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesGas Laws Packet 2 ANSWERSCenando BodanioNo ratings yet
- Fizkem Seminar ExDocument22 pagesFizkem Seminar ExZsolt Dürvanger100% (1)
- Freeze Drying & Freeze ConcentrationDocument16 pagesFreeze Drying & Freeze ConcentrationRizka Arifani KromodimedjoNo ratings yet
- Energy Optimization Study - WorkingDocument17 pagesEnergy Optimization Study - WorkingMufleh IdrisNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabian Oil Company: Instrument Specification Sheet - Pressure and Differential Pressure GaugesDocument2 pagesSaudi Arabian Oil Company: Instrument Specification Sheet - Pressure and Differential Pressure GaugesMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- 4VOL R02ipDocument30 pages4VOL R02ipzhyhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 Properties of Natural GasDocument89 pagesChapter 1.2 Properties of Natural GashugoNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1: Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Document22 pagesAppendix 1: Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Anissyuhada NizamNo ratings yet
- MTO Module 5Document128 pagesMTO Module 5Oğuzhan KocaoğluNo ratings yet
- Instant IceDocument2 pagesInstant Iceapi-505898069No ratings yet
- Helium GAS PDFDocument3 pagesHelium GAS PDFAmit Kumar JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Engg Thermodynamics Final Exam Fall 2016 Che 212Document2 pagesAgricultural Engg Thermodynamics Final Exam Fall 2016 Che 212falmubaddelNo ratings yet
- Buku Biomaterials A Basic Introduction - Tjok Tirta-35-58Document24 pagesBuku Biomaterials A Basic Introduction - Tjok Tirta-35-58Arya PutraNo ratings yet
- Practice 2Document30 pagesPractice 2Najmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanics IOE Old Questions-2Document11 pagesFluidMechanics IOE Old Questions-2Abishek AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Offshore Natural Gas Liquefaction Process and Development IssuesDocument7 pagesOffshore Natural Gas Liquefaction Process and Development Issuesthlim19078656No ratings yet