Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Candy S - Science 09 Chemistry
Candy S - Science 09 Chemistry
Uploaded by
Tasneem SiddiqueOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Candy S - Science 09 Chemistry
Candy S - Science 09 Chemistry
Uploaded by
Tasneem SiddiqueCopyright:
Available Formats
Science 09 - Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by candy_s via cheatography.com/46463/cs/13765/
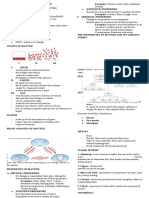
Matter, Mass, Volume Chemical Property Non-Metals
mat - anything with mass & volume ability to react chemically with other substances properties - gas or brittle solid at room
mas - quantity of substance contained, usually to form new substances temperature, not malleable or ductile, dull, poor
conductors of heat and electricity
measured in grams or kilograms can only establish when composition of matter
v - amount of space occupied, usually is altered (ex: reactivity) right of the staircase
measured in millilitres, litres, or cubic
centermetres Pure substances Metalloids
homogenous - uniform apperance elements that shares some properties of
Density metals and non-metals
has a unique set of properties
ratio of mass to volume, m/v properties - brittle solid, can be dull or shiny,
cannot turn into simpler substances by physical
may conduct electricity, poor conductor of heat
means
State of Matter & Fluid
can be further classified as element or
Hydrogen & Oxygen
solid - fixed mass, volume, and shape compound
H - makes up 90% of the atoms in the universe
liquid/fluid - fixed mass and volume
Elements & Compounds O - produced by plants as a by-product of
gas/fluid - fixed mass and container has fixed
photosynthesis, combined w/ sugar in our cells
volume e - simplest pure substance, cannot be broken
down or separated into simpler substances to release energy
fluid - matter that can flow (ex: liquid, gas), no
fixed shapes, takes on the shape of the reason - it's already simple since each
Iron, Silver, Mercury, Mercury Vapour
container elements is made of 1 kind of atom
have different names in different languages Fe - an important material in structures, mixed
Physical Property w/ carbon makes steel, can rust when exposed
chemical symbols consist of 1 or 2 letters, 1st is
to water & oxygen
p - type of characteristics that can be observed capitalized
or measured w/out changing its identity of Ag - better than other metal at conducting heat
c - composed of 2 or more elements in a
& electricity and reflecting light
specific way, can be changed into simpler
Qualtitative substances by chemical means Hg - a poisonous metal as liquid at room
temperature
not measurable
Mixture
malleable - able to be flattened into sheets Chlorine, Silicon, Semiconductor
made of 2 or more substances, physically put
ductile - able to be stretched into wires
together Cl - forms table salt when combined w/ sodium
crystalline structure - shape of appearance of
can be separated into simpler substances by Si - 2nd most common element, after oxygen in
crystals
physical means earth's crust, widely used as a semiconductor
in manufacturing computer chips and hardware
Quantitative
Metals s - a poor conductor of electricity at low
measurable temperature but a good c at high temperature
properties - hard, shiny, malleable, ductile,
solubility - ability to dissolve in water
good conductors of heat and electricity
Physical Change
conductivity - ability to conduct electricity tor
left of the staircase of Periodic Table
heat occurs when no new substances form, but there
density - ratio of mass to volume may be a change in appearance
viscosity - resistance to flow
By candy_s Not published yet. Sponsored by CrosswordCheats.com
cheatography.com/candy-s/ Last updated 6th December, 2017. Learn to solve cryptic crosswords!
Page 1 of 2. http://crosswordcheats.com
Science 09 - Chemistry Cheat Sheet
by candy_s via cheatography.com/46463/cs/13765/
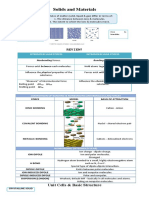
Chemical Change & Precipitate Thermal Energy, Heat, Collision, Temperature which Change of State Occurs
Temperature (cont)
occurs when substances combine (react) to melting point - temperature where solid melts o
form new substances c - particles transferring kinetic energy liquid (ex: 0 celcius for water)
evidence: colour change, heat, light, or sound t - the average kinetic energy of the particle in a boiling point - temperature where liquid boils to
produced, bubbles of gas, precipitate substance gas (100 celcius for water), substances
condense at the same temp at which they boil
p - solid produced in mixing 2 solutions particles in hot objects have more kinetic
energy and move faster freezing point - temperature where liquid
Reactants & Products freezes to solid, same temperature as melting
Kinetic Molecular Theory point, substances freeze at the same temp at
r - substances that are going to react
which they melt
explains how changes in the kinetic energy of
p - new substances that are produced
the particles can result in changes in state
Chemical Bonds (Chemical & Physical)
Chemistry energy makes particles move, more energy the
c - new substances are produced in the
particles have from heating, the faster they
study of matter and its change process of breaking existing chemical bonds
move and farther apart they get
and forming new bonds
includes: facts & observations about matter,
summarize patterns of behaviour in matter, Thermal Expansion, Thermal Contraction chemical bonds - forces that hold 2 or more
theories that explain the patterns of behaviour in atoms together
matter increase in volume of a substance when its
a change in composition occurs, changes are
temperature is raised
difficult to reverse
Models the decreased in volume of a substance when
p - bonds hold atoms together (in molecules
its temperature is lowered
help to visualize objects or processes that and ions), do not change, easier to reverse
cannot be seen directly
Change of State by Heating
Energy Change, Exothermic, Endothermic
Theory particles in solids are tightly packed together =
ec - energy is either released to the
cannot move freely (fixed in position), holds a
provides a scientific explanation based on the environment or absorbed from the environment
definite shape, can and do vibrate constantly
results of experimentation due to energy change in matter chemical
as heat is added, kinetic energy of the par change
increase and begin to collide w/ each other =
Particle Model of Matter energy change in a chemical change might or
more spaces is created between the particles
might not be noticeable
all matter is made of small particles that are too if enough heat is aded, the solid will melt
small to be seen with eye and even a ex - release of energy in the form of heat and
par in liquid are close (in contact w/each other) light
microscope
but have enough space to slide past, don not
there are spaces between the particles, the en - absorption of energy
hold a shape instead take on the shape of its
amount of spaces varies w/ the state of matter container
(greatest in gas, least in solid) Corrosion (Chemical Change)
as heat is added to a liquid, kinetic energy of
the particles are always moving, collides w/ pars increase, collide more = more space the process where metals are broken down
each other & the container in liquid & gas created rusting - corrosion of iron, rust is produced in a
particles are attracted to one another, strength some par gain enough energy to break free, w/ chemical reaction between iron and water
depends on the type of particles enough heat , the liquid will boil containing dissolved oxygen gas = structural
failure
pars in gas are highly energetic, can move
Thermal Energy, Heat, Collision,
freely and quickly in all directions, spread out
Temperature
to fill their container, gas is mostly empty space
te - the total kinetic energy of all the particles in as pars are far apart
a substance
h - thermal energy that is transferred from 1
body to another
By candy_s Not published yet. Sponsored by CrosswordCheats.com
cheatography.com/candy-s/ Last updated 6th December, 2017. Learn to solve cryptic crosswords!
Page 2 of 2. http://crosswordcheats.com
You might also like
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes Full PDFDocument35 pagesChem Notes Full PDFVishal Kunnathur Senthilkumar100% (2)
- Ebook PDF Business Statistics Communicating With Numbers 3rd Edition PDFDocument47 pagesEbook PDF Business Statistics Communicating With Numbers 3rd Edition PDFmathew.floyd85793% (42)
- Electronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElectronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Air BrakeDocument55 pagesVacuum Air BrakeAnshul Gupta100% (1)
- Catalogo Caldwell Observacion AstronomiaDocument4 pagesCatalogo Caldwell Observacion AstronomiaOscar GómezNo ratings yet
- S & S 2 MarksDocument30 pagesS & S 2 MarkspriyajegaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design As Per ACI & BowlesDocument17 pagesFoundation Design As Per ACI & BowlessivakumarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Primary Injection Testing of Protection System For Wiring Errors Between VTsDocument7 pagesPrimary Injection Testing of Protection System For Wiring Errors Between VTsThirumalNo ratings yet
- KMC-950 Service ManualDocument172 pagesKMC-950 Service Manualdavid100% (4)
- CHEM 20024 Learning Module 1 To 3Document23 pagesCHEM 20024 Learning Module 1 To 3Cjerome Casaul100% (1)
- Experiment No. 02: Aim: To Study and Design of Knuckle Joint. TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: Aim: To Study and Design of Knuckle Joint. TheoryAnubhav Singh0% (1)
- Barangay Resident Record Management and Certificate Issuance System PDF Documentation Manual Method and Problems EncounteredDocument4 pagesBarangay Resident Record Management and Certificate Issuance System PDF Documentation Manual Method and Problems EncounteredLimon Michael50% (2)
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- First Semester General Chemistry IDocument2 pagesFirst Semester General Chemistry ICarl Zeus TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chem1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChem1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Science MaterialDocument3 pagesScience Materialpraba.albaniNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument2 pagesGeneral ChemistryKezia CuencoNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument7 pagesGen ChemBrian MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewDocument5 pagesChemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy Alyn Tapleras, MSPH - RPHDocument26 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Bachelor of Science in Pharmacy Alyn Tapleras, MSPH - RPHNur-aine HajijulNo ratings yet
- Inorganic IntroductionDocument24 pagesInorganic IntroductionCarloNo ratings yet
- Genchem ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenchem ReviewerKarylle PingolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 - General ChemistryDocument6 pagesStem 11 - General ChemistryLance CastroNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsDocument19 pagesLesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsLemonadeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document3 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- C1 - Notes 1 of 2 - Solid StateDocument5 pagesC1 - Notes 1 of 2 - Solid StateAtharva BhavsarNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Chem M1 PDFDocument11 pagesChem M1 PDFZarylle De AsasNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.3Document6 pagesLecture 1.3wemata7962No ratings yet
- Gen. Chem MATTER - NotesDocument4 pagesGen. Chem MATTER - NotesKrisha GatocNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Unit 1Document9 pagesGeneral Chemistry Unit 1Yuann AranjuezNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryRhea Kristine C. MateoNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade-7-Handout-2-Element Vs CompoundDocument5 pagesScience-Grade-7-Handout-2-Element Vs CompoundClinton YmbongNo ratings yet
- Chem LabDocument10 pagesChem LabJenna RosalesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- Example: Sun or Any StarDocument3 pagesExample: Sun or Any StarNiki KevinNo ratings yet
- 통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표Document1 page통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표예준오No ratings yet
- 통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표Document1 page통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표예준오No ratings yet
- 통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표Document1 page통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표예준오No ratings yet
- Elements and The Periodic Table: Mendeleev's ProposalDocument1 pageElements and The Periodic Table: Mendeleev's Proposal예준오No ratings yet
- 통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표Document1 page통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표예준오No ratings yet
- 통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표Document1 page통합과학A 읽기자료 주기율표예준오No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document21 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1mariayvankaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem NatennnDocument5 pagesGen Chem NatennnAriaane Grace DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Document40 pagesLesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Evelyn Battuac de AustriaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document2 pagesGen Chem 2Joan Claire FajardoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document2 pagesGen Chem 2Joan Claire FajardoNo ratings yet
- Dalal Class 8 Elements Compounds Mixtures New Simplified ICSE Chemistry ICSEHELPDocument11 pagesDalal Class 8 Elements Compounds Mixtures New Simplified ICSE Chemistry ICSEHELPRajesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument11 pagesPeriodic TableMichelle AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesInorganic Chem ReviewerkezNo ratings yet
- Y9keywords AtomDocument5 pagesY9keywords AtomfugzieNo ratings yet
- Chemical PropertiesDocument1 pageChemical PropertiesjassgNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Ch. 1: The Solid State Points To RememberDocument10 pagesXII Chemistry Ch. 1: The Solid State Points To RememberANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry NotesDocument157 pagesXii Chemistry NotesksvvijNo ratings yet
- Metals Word SheetsDocument2 pagesMetals Word SheetsWaqas BangashNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 3Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 3shareeandradaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument1 pageScienceDANIEL MARTINUS HENWARD TAMUNUNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Matter and Its PropertiesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Bonds ActivityDocument6 pagesBonds ActivityAna MtzNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids SummaryDocument2 pagesBonding in Solids SummaryarachnidkatNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument10 pagesChem ReviewerMA. SOFIA ALCUETASNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter ReviewerDocument2 pagesClassification of Matter ReviewerXhantelle De LanxiNo ratings yet
- PS Lesson 3Document2 pagesPS Lesson 3euginNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- S.6 Paper 3 - Mock Kololo S.SDocument10 pagesS.6 Paper 3 - Mock Kololo S.SW. Joseph the chemistNo ratings yet
- Carrot and RadishDocument35 pagesCarrot and Radishnithya0% (1)
- Computer Class X 2021 Ed1Document12 pagesComputer Class X 2021 Ed1Snehashis Naskar, Class-10 ScienceNo ratings yet
- 9.4 The Simplex Method: Minimization: X W X XDocument11 pages9.4 The Simplex Method: Minimization: X W X XAnas Abdul-MalikNo ratings yet
- MARIE Simulator MARIE Simulator: Dr. Qi Zhu Zhuq@uhv - EduDocument23 pagesMARIE Simulator MARIE Simulator: Dr. Qi Zhu Zhuq@uhv - Eduttt4234No ratings yet
- Logic Design June 2010Document2 pagesLogic Design June 2010Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Curriculum BsitDocument2 pagesCurriculum BsitMichael DelimNo ratings yet
- WSG-SF Order Form: General DataDocument4 pagesWSG-SF Order Form: General DataLe Huynh LongNo ratings yet
- Name L.T Class Y9G Date 11/26/2020 1 Students Set Up The Apparatus Shown BelowDocument9 pagesName L.T Class Y9G Date 11/26/2020 1 Students Set Up The Apparatus Shown BelowThomasNo ratings yet
- Redesigning & Optimization of Conveyor PulleyDocument6 pagesRedesigning & Optimization of Conveyor PulleyJosue21SNo ratings yet
- B 84567 SB MM1 SPC ST 00 0301 - 1 - AOC - Seal Gas Mercury Guard BedDocument7 pagesB 84567 SB MM1 SPC ST 00 0301 - 1 - AOC - Seal Gas Mercury Guard BedpragatheeskNo ratings yet
- Ijser: Experimental Study On Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument3 pagesIjser: Experimental Study On Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced ConcreteAlejandra LópezNo ratings yet
- All February 2020 Papers (MedExam Expert-StudyMate) PDFDocument54 pagesAll February 2020 Papers (MedExam Expert-StudyMate) PDFSaroj YadavNo ratings yet
- MAHLE Contamination Indicators General Catalogue en PDFDocument10 pagesMAHLE Contamination Indicators General Catalogue en PDFLuisFranciscoMarinMedranoNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of MicroservicesDocument9 pagesPerformance Evaluation of MicroservicesRaja Churchill DassNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Noble GasesDocument53 pagesThe Chemistry of Noble GasesNguyeb PhucNo ratings yet
- MicrophoneDocument11 pagesMicrophoneChew Kah MengNo ratings yet
- 04-331 PP 722.9 Print (FH) 02-18-04Document53 pages04-331 PP 722.9 Print (FH) 02-18-04nicolae7887169No ratings yet
- ANSI B16 5 Bridas y AccesoriosDocument157 pagesANSI B16 5 Bridas y AccesoriosDaniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Nietzsches Panpsychism Ulfers Cohen PDFDocument31 pagesNietzsches Panpsychism Ulfers Cohen PDFRaul Araujo100% (1)