Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Communications Engineering: Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel Ver 2.4
Uploaded by
Mohamed shabanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Communications Engineering: Dr. Ali Hussein Muqaibel Ver 2.4
Uploaded by
Mohamed shabanaCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO Dr.
Ali Hussein Muqaibel
COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING ver 2.4
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 1
OUTLINES
What Does Communication (or Telecommunication) Mean?
Importance of Communications (by electrical signals)
So What will We Study in This Course?
Examples of Today’s Communication Methods
Simplex vs. Duplex Communications
Basic Construction of Electrical Communication Systems
Basic Terminology
Analog and Digital Communications
Modulation
Why to modulate?
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 2
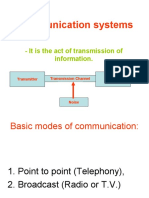
BASIC CONSTRUCTION OF ELECTRICAL COMMUNICATION
SYSTEM Electric Signal
(Like audio and Electric Signal
Electric Signal Electric Signal (Like the outputs of a
video outputs of a
(transmitted signal) (received signal) satellite receiver)
Sound, picture,… video camera) Sound, picture,…
Converts the input Converts the electric
signal from its signal to its original
original form (sound, form (sound,
picture,…) to an picture,…)
electric signal
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 3
WHAT DOES THE CHANNEL DO?
Distortion (Linear vs. nonlinear, distortion vs. distortionless channels)
corrected by equalizers.
Noise (unwanted, unpredictable): is an undesired signal that is
added to (or sometimes multiplied with) a desired transmitted
signal at the receiver. The source of noise may be:
External to the communication system : noise resulting from electric machines, other
communication systems, noise from outer space, lightning, automobile ignition can be
reduced or eliminated.
Internal: caused by thermal motion of electrons in the conductors can be reduced but not
eliminated.
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 4
BASIC TERMINOLOGY USED IN
COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
A Signal: is a function that specifies how a specific variable changes versus an independent
variable such as time, location, height (examples: the age of people versus their coordinates
on Earth, the amount of money in your bank account versus time).
A System: operates on an input signals in a predefined way to generate an output signals.
Analog Signals: are signals with amplitudes that may take any real value out of an infinite
number of values in a specific range (examples: the height of mercury in a –long
thermometer, the weight of people setting in a class room may take any real value between
to (typically)).
Digital Signals: are signals with amplitudes that may take only a specific number of values
(number of possible values is less than infinite) (examples: the number of students registered in
different classes at KFUPM is an integer number between and ).
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 5
CONT. BASIC TERMINOLOGY USED IN
COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is the ratio of the power of the desired signal to
the power of the noise signal. (amplifier does not help!)
Signal Bandwidth (BW) is the width of the frequency range that the signal
occupies. For example the bandwidth of a radio channel in the AM is around
10 kHz and the bandwidth of a radio channel in the FM band is 150 kHz.
Rate of Communication is the speed at which DIGITAL information is
transmitted. A Local Area Network (LAN) can theoretically receive/transmit
information at a rate of 100 M bits/s. Gigabit networks would be able to
receive/transmit information at least 10 times that rate.
What is the advantage of using fiber optics?
Signal Power related to quality, distance, rate….
Capacity, Security,…etc
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 6
ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS
Today, you can find a digital form of almost all types of analog
communication systems. Examples:
TV channels are now broadcasted in digital form (most if not all Ku–band
satellite TV transmission is digital).
Radio now is being broadcasted in digital form (see http://www.siriusxm.com/).
Home phone systems are going digital (a digital phone system is available at
KFUPM).
Cellular phones are now digital.
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 7
ADVANTAGES OF DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
OVER ANALOG COMMUNICATION
Immunity to Noise (possibility of regenerating the original digital signal if signal power
to noise power ratio (SNR) is relatively high by using of devices called repeaters along the
path of transmission).
Efficient use of communication bandwidth (through use of techniques like compression).
Digital communication provides higher security (data encryption).
Error Control Coding : the ability to detect errors and correct them if necessary.
Design and manufacturing of electronics for digital communication systems is much easier
and much cheaper than the design and manufacturing of electronics for analog
communication systems.
What is the price for going digital ?
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 8
Baseband versus Passband (Carrier Modulation)
MODULATION
Modulation is changing one or more of the characteristics of a signal (known
as the carrier signal) based on the value of another signal (known as the
information or modulating signal) to produce a modulated signal.
A carrier is a sinusoidal of high frequency with one of its parameters
(amplitude, phase, or frequency) is varied in proportion to the message
Famous Types:
Amplitude Modulation (AM): varying the amplitude of the carrier based on the
information signal as done for radio channels that are transmitted in the AM radio band.
Phase Modulation (PM): varying the phase of the carrier based on the information signal.
Frequency Modulation (FM):varying the frequency of the carrier based on the information
signal as done for channels transmitted in the FM radio band.
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 9
WHY TO MODULATE?
1. Antenna size is inversely proportional to the frequency, . Antenna size
has to be comparable to the wavelength, . Recall that .
2. To receive transmitted signals from multiple sources without interference
between them, they must be transmitted at different frequencies (frequency
division multiplexing, FDM) by modulating carriers that have different
frequencies with the different information signals. (like painting with colors).
3. To improve the propagation. Low frequency penetrates walls better than
high frequency signals.
4. Other reasons!
DR. ALI HUSSEIN MUQAIBEL 10
You might also like
- Amateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileFrom EverandAmateur Radio Electronics on Your MobileRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?Document5 pagesWhat Does Communication (Or Telecommunication) Mean?tasniNo ratings yet
- DC Notes PDFDocument151 pagesDC Notes PDFSharland GodinhoNo ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Introduction To Communications SystemDocument9 pagesHandout 1 - Introduction To Communications System0322-3713No ratings yet
- Yadav Sir 1Document5 pagesYadav Sir 1AyaneNo ratings yet
- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALSDocument10 pagesANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALSMadhusudhanan.ANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication Systems: Lesson-1Document26 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systems: Lesson-1Kennedy MutaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To CommDocument32 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To CommhaftamunigusNo ratings yet
- How Image, Audio, and Video Signals are DigitizedDocument20 pagesHow Image, Audio, and Video Signals are DigitizedMary Rachelle Anne EliangNo ratings yet
- Explaining Communication System BlocksDocument26 pagesExplaining Communication System BlocksBhalchandra ChandakkarNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCommunication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringAyad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 1Document127 pagesEc8395 Ce Notes 1makNo ratings yet
- Adc Unit 1 Material PDFDocument79 pagesAdc Unit 1 Material PDFsrinithaNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument17 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationeceelectroNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 Phy IntroDocument20 pagesLecture02 Phy IntroDr. Pallabi SaikiaNo ratings yet
- A Communication System Conveys Information From Its Source To A Destination. - ExamplesDocument59 pagesA Communication System Conveys Information From Its Source To A Destination. - ExamplesminoshmaNo ratings yet
- 1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemDocument29 pages1 A) Draw The Basic Block Diagram of Communication SystemBhargava GNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Historical Notes-Communication SystemsDocument55 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Historical Notes-Communication Systemsbad is good tatyaNo ratings yet
- Cse Notes PDFDocument77 pagesCse Notes PDFAshutosh AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Wireless Physical Layer, Channel, and Capacity Lecture 2: Wireless Physical Layer, Channel, and CapacityDocument20 pagesLecture 2: Wireless Physical Layer, Channel, and Capacity Lecture 2: Wireless Physical Layer, Channel, and CapacityChaitanyaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer FecnDocument2 pagesReviewer FecnNathan ash ClintonNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATION SYSTEM - Module-IDocument84 pagesCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM - Module-ICOMPETITIVE GURU JINo ratings yet
- What Is CommunicationDocument3 pagesWhat Is CommunicationKevin DanyNo ratings yet
- GaddaDocument119 pagesGaddaMurthyNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 & 4 - Amplitude Modulation - DoneDocument73 pagesLecture3 & 4 - Amplitude Modulation - Donerizwanahmed06No ratings yet
- 4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. CollegeDocument5 pages4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. Collegeajaykumar988No ratings yet
- Module 5 NewDocument43 pagesModule 5 NewMythri RangaswamyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemsSolomon Tadesse AthlawNo ratings yet
- Basics 1Document5 pagesBasics 1Manoj Kumar 1183No ratings yet
- Physics Communication System CoachingDocument9 pagesPhysics Communication System Coachingvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- ECE 7 ActivityDocument4 pagesECE 7 Activitywilmar cadungogNo ratings yet
- CS Assignment: 1) Week 1 SummaryDocument8 pagesCS Assignment: 1) Week 1 SummaryAyeshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Communication SystemDocument10 pages1 Introduction To Communication SystemMOHAB MAHMOUD KAMELNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 2Document127 pagesEc8395 Ce Notes 2makNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications and Information Theory Lecture 1Document10 pagesDigital Communications and Information Theory Lecture 1Sunila AkbarNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Notes EEE400 Wk1Document5 pages02 Lecture Notes EEE400 Wk1Wafula DerrickNo ratings yet
- PRINCOMM ReviewerDocument4 pagesPRINCOMM Reviewerrick reyNo ratings yet
- Bio MimeticDocument20 pagesBio MimeticRajat PratapNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Communication SystemsDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Communication SystemsNeelamAsifNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems: - It Is The Act of Transmission of InformationDocument31 pagesCommunication Systems: - It Is The Act of Transmission of InformationSingh PushparajNo ratings yet
- Communication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Document22 pagesCommunication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Deepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Overview of Some of The Topics We Will Study in This Course: EE 341, Autumn'21Document7 pagesOverview of Some of The Topics We Will Study in This Course: EE 341, Autumn'21vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electronic CommunicationDocument17 pagesFundamental of Electronic CommunicationLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Pendahuluan PDFDocument81 pagesBab 1 Pendahuluan PDFalfianNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1 - Chapter 1Document5 pagesLecture Notes 1 - Chapter 1sohailahmed714319No ratings yet
- WCN-Wireless Communications and NetworksDocument28 pagesWCN-Wireless Communications and Networkslaiba noorNo ratings yet
- Computer Network (503) - Unit IIDocument29 pagesComputer Network (503) - Unit IIKashishNo ratings yet
- 02 DataTransmission TVMDocument44 pages02 DataTransmission TVMTrinnette07No ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesCommunication Systemsmaria.rehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Electronic CommunicationDocument18 pagesUnit 6 Electronic CommunicationDr G VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Com Chap 1 Lec 1Document33 pagesCom Chap 1 Lec 1Anwar MohammedNo ratings yet
- TOBB ETU Bil457/Bil557 Wireless Networks September 24, 2008Document93 pagesTOBB ETU Bil457/Bil557 Wireless Networks September 24, 2008faziNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 3Document39 pagesData Communication & Computer Networks: Week # 3Shoaib AtiqNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document91 pagesModule 4mahendra naikNo ratings yet
- Sahil DcsDocument28 pagesSahil DcsPrasun SinhaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Analogue N Digital SignalsDocument40 pagesPresentation On Analogue N Digital SignalsnancykapoorNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Lecture Notes: Department of Electronics and Communications Microwave-I Notes By-Girraj SharmaDocument142 pagesAnalog Communication Lecture Notes: Department of Electronics and Communications Microwave-I Notes By-Girraj SharmaER_GIRRAJNo ratings yet
- Basic CommunicationDocument24 pagesBasic CommunicationSiam hasanNo ratings yet
- EE 370 Communications Engineering I Chapter 1 - INTRODUCTIONDocument16 pagesEE 370 Communications Engineering I Chapter 1 - INTRODUCTIONAbdulaziz Al-ShammariNo ratings yet
- RF PropogationDocument59 pagesRF PropogationAnonymous aey2L8z4No ratings yet
- Review of Fourier SeriesDocument16 pagesReview of Fourier SeriesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 23 SamplingDocument13 pages23 SamplingMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 24 Multiplexing TechniquesDocument27 pages24 Multiplexing TechniquesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Network Models - Exercise Question With SolutionDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Network Models - Exercise Question With SolutionMd Saidur Rahman Kohinoor86% (92)
- Review of Signals and SystemsDocument12 pagesReview of Signals and SystemsMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- Fourier TransformDocument24 pagesFourier TransformMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Effects of NonlinearitiesDocument6 pages6 Effects of NonlinearitiesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Sampling and Signal ReconstructionDocument15 pages1 Sampling and Signal ReconstructionMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- 20 FM Demodulators PLLDocument9 pages20 FM Demodulators PLLMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 7p4 Transmission Rates of Typical ServicesDocument8 pages7p4 Transmission Rates of Typical ServicesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Sampling Pulse Modulation TDM and Aliasing v3Document9 pages3 Sampling Pulse Modulation TDM and Aliasing v3Mohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- 7p7 Demodulation Ask PSK DPSK FSKDocument6 pages7p7 Demodulation Ask PSK DPSK FSKMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- 19 Pre-Emphasis and De-EmphasisDocument8 pages19 Pre-Emphasis and De-EmphasisMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- 5 Quantization NonuniformDocument6 pages5 Quantization NonuniformMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 19 Pre-Emphasis and De-EmphasisDocument8 pages19 Pre-Emphasis and De-EmphasisMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- 1 ACS IntroductionDocument63 pages1 ACS IntroductionMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 10 FM ReceiverDocument9 pages10 FM ReceiverMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 18 FM Demodulators-Foster Seeley and Ratio DetectorDocument22 pages18 FM Demodulators-Foster Seeley and Ratio DetectorMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 7 SSB SC DetectionDocument17 pages7 SSB SC DetectionMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 8 VSB Generation and DetectionDocument15 pages8 VSB Generation and DetectionMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 15 FM Problems-Indirect FMDocument9 pages15 FM Problems-Indirect FMMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 7 Geenration of Wideband FM-SPECTREDocument12 pages7 Geenration of Wideband FM-SPECTREMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- SSBSC Modulation TechniqueDocument39 pagesSSBSC Modulation TechniqueYaganti pavan saiNo ratings yet
- 7p5 Mary Multi Amplitude and Orthogonal SignallingDocument12 pages7p5 Mary Multi Amplitude and Orthogonal SignallingMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 2 AliasingDocument8 pages2 AliasingMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Amplitude Modulator TypesDocument18 pages3 Amplitude Modulator TypesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 10 Angle ModulationDocument23 pages10 Angle ModulationMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 7p1 Line CodesDocument11 pages7p1 Line CodesMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 6 T1 Carrier SystemDocument11 pages6 T1 Carrier SystemMohamed shabanaNo ratings yet
- 7p2 Pulse Shaping and Nyquist For Zero ISIDocument15 pages7p2 Pulse Shaping and Nyquist For Zero ISIMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- Melsec-Q Ethernet (UDP) Driver: Mitsubishi Electric CorpDocument13 pagesMelsec-Q Ethernet (UDP) Driver: Mitsubishi Electric CorpJansen SoejarsonoeNo ratings yet
- Bca 503 PDFDocument3 pagesBca 503 PDFDARK ViSIoNNo ratings yet
- Target CoDeSys Reference Manual enDocument238 pagesTarget CoDeSys Reference Manual enShivaperumal.K EEENo ratings yet
- Lighting Control ApplicationGuide - Parking PDFDocument4 pagesLighting Control ApplicationGuide - Parking PDFDionie DavidNo ratings yet
- H12-211-Enu V14.02 PDFDocument194 pagesH12-211-Enu V14.02 PDFalmamydiakho0% (1)
- Manual Icom IC 7000Document166 pagesManual Icom IC 7000Carlos KropfNo ratings yet
- EC8701 Antennas and Microwave EngineeringDocument3 pagesEC8701 Antennas and Microwave EngineeringPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Cours 01 - CampusNetworkDesignDocument29 pagesCours 01 - CampusNetworkDesignAbdelkader MechiNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 Configuration GuideDocument1,722 pagesRTN 950 Configuration GuideWilliam Fernandes100% (2)
- House Automation Using TelegramDocument17 pagesHouse Automation Using TelegramNaveen DhaaramNo ratings yet
- AT Commands PDFDocument68 pagesAT Commands PDFashleshNo ratings yet
- hdr4 8 8050 720p Sdi DVR ManualDocument39 pageshdr4 8 8050 720p Sdi DVR ManualPlinio FernandezNo ratings yet
- History of The InternetDocument17 pagesHistory of The InternetFerdinand A. RamosNo ratings yet
- Huawei ESight Storage Manager Data SheetDocument2 pagesHuawei ESight Storage Manager Data SheetemcviltNo ratings yet
- WOOFY GPON DESIGN BLDG Case 1 VER2Document4 pagesWOOFY GPON DESIGN BLDG Case 1 VER2renedosrNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology: Jalandhar, PunjabDocument45 pagesNational Institute of Technology: Jalandhar, PunjabGaurav SachdevaNo ratings yet
- No ND IP Embassy Type Calling Station IdDocument21 pagesNo ND IP Embassy Type Calling Station IdIkhsan Dwirana MoetaqienNo ratings yet
- Configuration Management (SRAN9.0 01)Document26 pagesConfiguration Management (SRAN9.0 01)mailsianNo ratings yet
- Quectel EC20 R2.1 LTE Specification V1.2Document2 pagesQuectel EC20 R2.1 LTE Specification V1.2TrungTrầnNo ratings yet
- Thomson Vibe Cp7000Document3 pagesThomson Vibe Cp7000Vilasak ItptNo ratings yet
- Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM)Document221 pagesDigital Radio Mondiale (DRM)Alexandre VitorNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS XR Getting Started GuideDocument344 pagesCisco IOS XR Getting Started GuideMares MarianNo ratings yet
- CyberPower DS PDU41004 (5) en v1Document2 pagesCyberPower DS PDU41004 (5) en v1Yeung Chau HoNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson ST15 Xperia Mini Trоubleshooting Guide - Electrical Rev1Document10 pagesSony Ericsson ST15 Xperia Mini Trоubleshooting Guide - Electrical Rev1Aron VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Unifi ApDocument10 pagesDatasheet Unifi ApjaanfesiNo ratings yet
- KX 21Document18 pagesKX 21Kang OpikNo ratings yet
- COM02 Activity 2Document6 pagesCOM02 Activity 2Claire AragoncilloNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report ON Implement Communication System Using Steganography Using Audio FilesDocument17 pagesMicro Project Report ON Implement Communication System Using Steganography Using Audio Files19IF001 Chaitali AkhareNo ratings yet
- Seminar PPT On 5G TechnologyDocument12 pagesSeminar PPT On 5G TechnologyPriyanshu Mangal91% (11)
- Signals and transmission mediaDocument108 pagesSignals and transmission mediaDeepakPradhan100% (1)