Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Job Safety and Environment
Uploaded by
mohammad ashpakCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Job Safety and Environment
Uploaded by
mohammad ashpakCopyright:
Available Formats
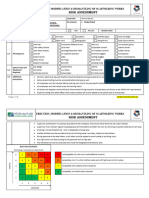
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
ACTIVITY OR TASK: Installation of Staircase and Hand Rails – Welding, Heights and Crane Usage Site Location:
JSA Preparation Project:
Date:
Work Team
Job Number:
Job Area JSA Number: CSI329 JSA Revision: 1.7
2. HAZARD IDENTIFICATION Identify hazards that may be present by ticking items on the list below. 3. PRECAUTIONS: hard hat, safety glasses, safety boots compulsory
WORK LOCATION HAZARDOUS AREA Food Safety ADDITIONAL PRECAUTIONS PERMITS
Difficult Entry/Exit Hazardous Substances - attach MSDS to Food Grade Lubricants Gloves: type = Welding Gloves x Hot Work x
Oxygen Deficiency JSA Approved Chemicals only Goggles/Glass’s Excavation
Oxygen Excess Working at Heights x Welding/Grinding Guidelines Full Face Shield X Confined Space
Engulfment (trench collapse) Remote Area Loose items removed High Visibility Vest X Hazardous Work Clearance
Poisonous Gas Present Motor Room Hazards Taints Harness X Access to Area
Temperature Extremes Toxic Substances Product Zones protected Fire Extinguishers X High Voltage Access
Defined Confined Space Potential for Difficult Rescue Pest control/doors Barricades or Tape X Scaffolding
Explosive Gas Present Anti-contamination Guidelines Ventilation Roof Access Ext
Working Alone Is consultation with QA requried Steel Cap Boots X Fire System
Allergen Risk Lighting Lockout Removal
HIGH RISK HAZARDS No Raw Materials in area Erect Scaffolding to access Working at Heights x
Falling Objects X Flamm. Materials Present Screens/partions/drop sheets Respirator or Dust mask
Poor Lighting Sharp Materials X Glass on Register Erect Warning signs X
Slippery Surfaces Suspended loads X Jewellery Removed Personal Locks or Tag system
Multiple Electrical Feeds Poor Visibility Group isolation
Trip Hazards X Inhalable Dusts/Fibres Dress Code Welding screen X
Electrical Hazards - LV High Noise Levels Phone Inspected Fall Arrest systems
Electrical Hazards - HV Use of Chemicals Welding Face Shield X
Fire/Smoke Elevated Work Platform X Hearing Protection X
Moving Machinery X Difficulty to Communicate amongst workers X Plastic Overalls
Manual Handling X Tools & Equipment X Gas Watcher
Steam Heat/ Sunlight/ Radiation X Safety Observer X
Ladders used in the task Traffic Movement X Acid Suit
Working at Heights X Working near Operation Processing Lines Phone/Radio/PA X
Working near Crane & Crane X Live Rails Procedure/SOP X
Runways
Residual Pressure Pneumatics Waste Disposal
Cutting/Drilling/Grinding X Uncontrolled Energy Release MSDS
Welding x Oxy cutting
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
EMERGENCY CONTACT INFORMATION Take 5 For Safety
The Five Step risk management process:
POLICE / FIRE / AMBULANCE (0) - 000 OR 112 (MOBILES) 1. Define the context
Preparation
DEPARTMENTAL REP 2. Identify tasks, activities, work processes and practices for assessment
H & S OFFICER
Step 1 Identify Hazards
POISONS INFORMATION 13 11 26
NATURAL GAS SUPPLIER 1300 763 106
Step 2 Assess and prioritise risks
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Call (0) 000 and notify emergency personnel
Step 3 Decide on control measures including heirarchy of control
2. Administer First Aid (DRABCD)
3. Notify Area Manager for all emergency events.
Step 4 Implement control measures
4. Notify Chief Fire Warden if Fire event
5. Notify H & S Manager/Officer and/or Injury Management Step 5 Monitor and review
Coordinator of all emergency Events
6. Secure the Work Area, LOTO Equipment if necessary.
4. Risk Rating Table The objective of rating the risk is to lower the risk by initiating the risk control measures.
The score is noted in the JSA risk score column on the next page – both before & after risk control measures have been nominated.
Likelihood Score
5. Almost
1. Rare 2. Unlikely 3. Possible 4. Likely
Certain
5. Catastrophic
Consequence Score
Death or multiple life threating
injuries. 5 10 15 20 25
4. Major
Life threatening injury or multiple 1 -3 Low Risk
serious injuries causing
hospitalisation. 4 8 12 16 20
3. Moderate
Serious injury causing
hospitalisation or multiple medical
4-6 Moderate Risk
treatment cases. 3 6 9 12 15
2. Minor
Minor injury or First Aid Treatment 8 - 12 High Risk
Case. 2 4 6 8 10
1. Insignificant
Injuries or ailments not requiring 15 - 25 Extreme Risk
medical treatment. 1 2 3 4 5
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
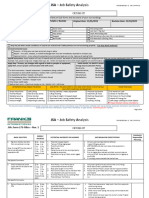
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
ACTIVITY OR TASK: Installation of Staircase and Hand Rails – Welding, Heights and Crane Usage JSA Number: CSI329 JSA Revision: 1.7
Risk Rating Recommended Corrective Action or Procedure Risk Rating
Sequence of Basic Job Steps Potential Safety & Determine what actions are necessary to eliminate or minimise all hazards that could
Step Break down Job into steps. Each step should Environmental Hazards/Impacts Use table on the
lead to an accident, injury, illness or environmental incident. The risk must be reduced Of the risk
previous page to following
No. accomplish a major task and be logical. Identify the hazards (health and safety or
score risk or controlled to a level that is acceptable before work commences. corrective action
Logical Environmental Aspects environmental) associated with each step, Indicate who is to perform the action where applicable against each action
sequence examine each to find all possible risk factors
C L # C L #
Competent work team to perform task (licenses & competencies)
Adequate consultation with all relevant people, adequate competent
supervision throughout task
Proper job and equipment planning for task
Inexperience workers, inadequate Ensure all approved controls and prevention measures are discussed and
consultation, inadequate understanding of JSA is discussed with all persons involved in the work.
1 Pre-job Meeting/Toolbox 4 2 8 2 2 4
job/equipment, Site hazards and emergency Site induction for team all members as required by site.
procedures not known
All personnel to wear mandatory PPE (Hard Hats, High Vis clothing, Safety
Footwear, Safety Eyewear)
Identification of Emergency equipment, procedures & contacts
In the event of an emergency all persons must move to the nearest exit and
muster point.
All personnel to attend daily toolbox
Risk of injury due to low awareness of work
environment. Take 5, be aware of hazards.
2 Identify work area/Site Establishment 3 2 6 Ensure all site rules and guidelines are met. 2 1 2
Unauthorised access/egress
Unsafe conditions Consider other trade operations within the work area and maintain
reasonable co-operation and communication.
Ensure adequate communication to team leaders and to work groups
3 Notify other teams of the works Noise / Traffic / area access / Fumes 3 2 6 2 1 2
adjacent
Injury / damage as a result of incorrect
4 Assess if a Permit To Work is required 3 3 9 Obtain correct PTW for the task. Training in PTW system. 3 1 3
information
Check isolations with operator at worksite before commencing work if
isolations are required.
Injury / damage to plant as a result of Use personal safety locks.
5 Isolations 4 3 12 2 2 4
incorrect isolations
Ensure that line is de-energized before commencing work.
Test for effective isolation.
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
At the start of any shift, basic warm up exercises should be conducted (as
would be conducted for most sporting activities) before commencing the
manual task.
Plan the task, identifying the route and ensure it is clear of any obvious slip
Over-exertion, potential body strain / sprain. and trip hazards.
Ensure no one is working below the work area and if necessary
Dropping materials / tools, crush injuries. barricades/signage must be erected around the work area. A spotter maybe
necessary and is to a hard hat if items could fall.
Stand as close to the load / object as possible to avoid reaching or over
Caught between surfaces, crush injuries to stretching.
hand/fingers.
Lift and carry materials, tools and equipment. Ensure a good grip before exerting force to lift, push or pull the object / tool.
6 Transport equipment and materials to job site. 4 3 12 4 1 4
Keep the load as close to the body as possible, this will reduce the strain on
Job Site Establishment
the lower back.
Slip, trip, fall. When turning, use the full body, rather then twisting at the waist.
Steel capped footwear must be worn at all times.
Struck by other plant.
Gloves should be worn where hand injuries are possible from hot, sharp or
rough surfaces. Site induction, wearing of hi vis clothing, isolate area if in a
UV exposure causing sunburn / heat stress. trafficable area by cones/bunting.
Two man lift for heavy equipment, use of vehicle loading crane for heavier
equipment
Use of sunscreen, hardhats to be worn, work under shade where available,
have regular rest breaks depending on weather
Moving machinery with possibility of Create exclusion area. Check floor for water, oil, Be aware of other plant
7 Barricade off work area collisions or impact resulting in personnel 4 2 8 operating in the area (boom/scissor/fork/etc). 3 1 6
injury or equipment damage. Slips, trips Clear all unrequired personnel from work area.
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
Ensure all tool and extension leads have a current (within 3 months) test tag
fitted to each lead.
Conduct a visual inspection of the leads and tool prior to each use. If any
defects are identified, do not use the tool and hand it to the site manager for
repair.
Electricity, potential electrocution
Ensure power tool is turned off prior to connecting power.
Ensure a residual current device (RCD) is fitted to the electrical distribution
High speed moving parts, potential board where the power lead is inserted. If not, use a portable RCD unit.
laceration and entanglement risks
Operate power tool If using a portable RCD unit, test to ensure it is working and then reset.
8 (cut, drill, grind material) 4 3 12 Ensure all guards are fitted to the power, DO NOT use if guards are 4 1 4
Noise missing.
Ensure all clothing is tucked in to avoid entanglement with any moving
Flying particles, including hot sparks parts.
Always wear eye protection and hearing protection when using all power
tools. If necessary gloves should be worn to protect the hands from flying
Fire, potential burns
particles and hot materials.
Ensure other site workers are not at risk from flying particles, if necessary,
position screens to contain flying particles.
Ensure all flammable materials are removed from the immediate work area
and if necessary, ensure a fire extinguisher is available.
At the start of any shift, basic warm up exercises should be conducted (as
would be conducted for most sporting activities) before commencing the
manual task.
Plan the task, identifying the route and ensure it is clear of any obvious slip
and trip hazards.
Over-exertion, potential body strain / sprain.
Ensure no one is working below the work area and if necessary
barricades/signage must be erected around the work area. A spotter maybe
Dropping materials / tools, crush injuries. necessary and is to a hard hat if items could fall.
Stand as close to the load / object as possible to avoid reaching or over
stretching.
Caught between surfaces, crush injuries to
hand/fingers. Ensure a good grip before exerting force to lift, push or pull the object / tool.
9 Lifting hand rails and fixing into place. 4 3 12 4 1 4
Keep the load as close to the body as possible, this will reduce the strain on
Slip, trip, fall the lower back.
When turning, use the full body, rather then twisting at the waist.
Prolonged poor posture, reaching, exposure Steel capped footwear must be worn at all times.
to vibration Gloves should be worn where hand injuries are possible from hot, sharp or
rough surfaces.
Rotate tasks within work group or take regular short breaks to prevent
prolonged exposure to manual tasks.
Maintain adequate work heights, approx. 900mm high.
Avoid stooping, trunk twisting and exerting high forces with rotation.
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
Ensure job is set up as per safe welding procedures. Only trained personnel
Electrocution:
4 3 12 to carry out welding. Fit earth clamp securely to job. 4 1 4
Welders must wear flame resistant work clothing and supplied leather PPE
Burns: where applicable. Wear gloves if required to protect hands and arms.
3 3 9 2 2 4
Wear welders shield with filter shade No. 7 to 15 inclusive. Wear AS1337
Eye injury (weld flash): safety spectacles under welding shields.
3 3 9 2 2 4
Use welding screens or blankets to shield arc from other personnel.
Welders assistants MUST WEAR anti weld flash eye protection to AS1337 if
10 Welding of hand rails Radiation and sparks: assistant required to look at the arc, then the same protection as welder is
3 3 9 2 2 4
required.
2 4 8 2 2 4
Fumes: Ensure adequate fresh air is around weld area and that fumes are efficiently
extracted away from the local work area.
3 3 9 A suitable fire extinguisher MUST BE ON HAND at all times welding is in 2 2 4
Fire:
progress. Check condition and date of extinguisher prior to starting job.
2 4 8 Complete hot work permit 2 2 4
Communication failure –forms RQD
WORKING FROM EWP
A thorough inspection of all equipment must be conducted prior to its use.
Inspections should check for;
1. General wear and tear
2. Cuts and tears to webbing
11 Inspect fall arrest equipment Damaged fall arrest equipment 4 3 12 3 2 6
3. Signs of damage to stitching
4. Stretching of the lanyard.
5. Welding burns to webbing
Conduct a visual inspection of the EWP and complete the EWP logbook
prior to operation.
12 Pre-operation Inspection of EWP 3 3 9 3 1 3
Any faults identified need to be reported to the Site Manager and the EWP
NOT used until all faults have been repaired.
Person responsible to identify / install an anchor point must do so without
risk of falling. Elevated work platforms, ladders or scaffold must be used to
access the anchor point.
Only approved anchor points and slings can be used as an anchor point or
Falls from height attachment to the anchor point.
13 Identify / Install an anchor point 4 3 12 3 2 6
The anchorage point of the fall arrest system should be positioned to ensure
that the static restraint line does not allow the person wearing the system to
free-fall.
Fall prevention to be used when working under 6.4M, rather than only fall
arrest.
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
Ground surfaces must be inspected to ensure sufficient compaction to
operate on, if in doubt seek advice from the Site Manager.
When operating on sloping ground, outriggers need to be fully extended and
pinned/locked into position. Outrigger stabilising pads may need to be
supported by concrete or timber beams in a pigsty packing structure.
Unstable or uneven ground surface,
potential rollover of EWP. Check with Site Manager to ensure work area is clear of underground
services before operating EWP.
Check for and ensure no overhead power lines are within the following
Underground services, potential damage to distances; 2 meters from distribution lines and 6m from transmission lines.
services. Additional control measures are required if the work is within the above
distances and the task is NOT to continue until adequate controls are in
place.
Overhead power lines, potential
14 Start-up and positioning of EWP 4 3 12 4 1 4
electrocution. Check for and ensure no overhead obstructions or protruding hazards are
within the work area. If identified, ensure all occupants of the EWP are
aware of the hazard and the EWP is positioned and operated well clear of
Overhead obstructions, crush / impact the hazard.
injuries.
Ensure all workers are well clear of the EWP. EWP operator is to stop if
obstructions or workers are in close proximity to travel route.
General Public / Traffic interaction, potential A spotter / traffic controller must be positioned in the immediate work area
collision and crush injuries for the duration of the task.
Where required, barricading and signage must be positioned to warn
pedestrians and drivers of the EWP activity.
EWP operator is to give way to all other traffic and pedestrians, unless
managed by a traffic controller.
All occupants must wear a full body harness and be attached to the
designated anchor point at all times when operating a EWP.
Fall from Boom Lift basket
All tools must be stored in an adequate storage box to ensure they are kept
off the basket floor and cannot fall from the basket.
15 Operate and Mobilise EWP 4 3 12 4 1 4
Tools and materials falling from Ensure no one is working below the raised platform/basket and if necessary
basket/platform, potential struck by injuries barricades and signage must be erected around the work area.
to other workers.
Materials (pipes, steel, etc) should be secured adequately to prevent
movement during operation and not simply laid over hand rails of EWP
WORKING WITH CRANE
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
Conditions not suitable for type of work,
increasing the danger / risk of work hazards.
Unsafe Access Ensure conditions for carrying out works are suitable.
Safe access to be provided to working area at all times including adequate
Arrive on site and review work
16 4 3 12 lighting to all areas. 4 1 4
conditions Insufficient lighting
Lighting towers to be positioned as required.
All plant to complete daily pre-start inspection.
Windy Conditions
Raining
Crane to be positioned as per lifting plan provided by crane company.
Hit by moving plant Crane supervisor to check crane position.
Ticketed crane operators to operate crane.
17 Setup & erection of cranes Damage to services 4 4 16 Ensure crane set-up does not clash with services. 3 2 6
Crane set up as per manufactures guidelines.
Crane overturn Ensure overhead and underground services are located prior to set up.
Refer to crane company SWMS for full details
Staircase is to be lifted within the cranes safe working radius and in
accordance with SWMS and Lift plan.
Crane overturn
SWL not to be exceeded
18 Lifting of staircase 5 4 20 Only licensed dogman to sling and unhook loads. 3 2 6
Crushed/ hit by structure
Lifting equipment to be inspected prior to use and certified as per Australian
Standards/ crane safety specifications.
No person to be under suspended structure when positioning load.
Keep body away from underneath of structure till it is located just above its
final position (fingers,body etc)
19 Locating staircase into position Crushed/ hit by structure 4 3 12 Use tag lines to locate and assist placement of staircase 3 2 6
Crane dogman to control staircase.
Two way radios to be used by all.
19 Release of crane load Hit by falling objects 5 4 12 No person or plant to be under the load when it is released. 5 1 5
Crane to be positioned as per lifting plan provided by crane company.
Hit by moving plant Crane supervisor to check crane position.
Ticketed crane operators to operate crane.
20 Demobilisation of cranes and truck Damage to services 4 4 16 Ensure crane set-up does not clash with services. 3 2 6
Crane set up as per manufactures guidelines.
Crane overturn Ensure overhead and underground services are located prior to set up.
Refer to crane company SWMS for full details
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA) / SAFE WORK METHOD STATEMENT
At the start of any shift, basic warm up exercises should be conducted (as
would be conducted for most sporting activities) before commencing the
manual task.
Plan the task, identifying the route and ensure it is clear of any obvious slip
Over-exertion, potential body strain / sprain.
and trip hazards.
Stand as close to the load / object as possible to avoid reaching or over
Dropping materials / tools, crush injuries. stretching.
Ensure a good grip before exerting force to lift, push or pull the object / tool.
Caught between surfaces, crush injuries to Keep the load as close to the body as possible, this will reduce the strain on
hand/fingers. the lower back.
Pack-up Clean up job site. Lift and carry
16 materials, tools and equipment. Transport 4 2 8 When turning, use the full body, rather then twisting at the waist. 2 1 2
equipment and materials to workshop.
Steel capped footwear must be worn at all times.
Slip, trip, fall. Gloves should be worn where hand injuries are possible from hot, sharp or
rough surfaces.Site induction, wearing of hi vis clothing, isolate area if in a
trafficable area by cones/bunting.
Struck by other plant.
Two man lift for heavy equipment, use of vehicle loading crane for heavier
equipment
UV exposure causing sunburn / heat stress.
Use of sunscreen, hardhats to be worn, work under shade where available,
have regular rest breaks depending on weather
Leave the work area clean, tidy and safe, Return tools to workshop, rubbish
in bins.
Access equipment must be available to access a fallen worker on site at all
times when using a fall arrest system.
Adequate means of access include, elevated work platforms, forklift with
17 Rescue of a fallen worker Falls from height 4 3 12 approved man cage, and crane with man box or mobile scaffold. 2 3 6
Adequately trained workers must also be available to operate any access /
rescue equipment.
Refer to Post Fall recovery Plan
Revision Date: July 2012 THIS DOCUMENT IS UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA)
CONSULTATION & SIGN-OFF RECORD
Points to Consider when Completing this JSEA: (this list is not inclusive – simply a prompt)
Does a work procedure/ existing JSEA relate to this job?
Have all relevant personnel been trained in the appropriate procedures?
Do all relevant personnel hold the required competencies / authorisations required for the task(s)? – Have these
been identified?
Have all relevant parties been notified and included?
Is signage required?
Are there special PPE requirements?
Is there an MSDS that needs to be referred to and made accessible?
Is there a permit required for the job and is it available?
Have all existing and recommended controls been noted on the above table and explained to those involved?
Are any new hazards being introduced – if so, are they adequately controlled to ensure an acceptable level of risk is
maintained?
Are there any mechanical aids or special tools / equipment that need to be made available?
Have the monitoring requirements been considered?
Environmental Issues: Erosion and sediment controls/ chemical and oil spills/ fauna and flora/ dust/ noise/ vibration/
public complaints
I confirm by my signature below, that I have attended a briefing on the requirements of the attached Job Safety &
Environment Analysis and agree to perform the work in the manner detailed on it. I confirm that copies of the relevant
Permits, MSDS's, Isolation Plans etc. have been reviewed.
Installation of Staircase and Hand Rails – Welding,
JSA NAME JSA No: CSI329 Rev:1.7
Heights and Crane Usage
CLIENT SIGN ON (Supervisor/Site Manager/Area Manager)
NAME (Please print) SIGNATURE DATE
TASK WORK TEAM
NAME (Please print) SIGNATURE DATE
THIS SAFE WORK BRIEFING / TRAINING WAS CARRIED OUT BY (responsible person at that location) :
Name: Signature: Date:
Client sign off (once complete)
Site / Project Manager sign off (document reviewed)
Revision Date: September 2010
JOB SAFETY & ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS (JSA)
Revision Date: September 2010
You might also like
- Job Safety Analysis for Instrument Sample Point InstallationDocument3 pagesJob Safety Analysis for Instrument Sample Point InstallationNasrullah JanNo ratings yet
- JSA Safety AnalysisDocument3 pagesJSA Safety AnalysisLusy Gusti EfendiNo ratings yet
- 011.TBSHE JSA 005 Pipelaying WorkDocument8 pages011.TBSHE JSA 005 Pipelaying Worknellaika puspa dewi100% (1)
- JSA G17 Lift Container With CraneDocument4 pagesJSA G17 Lift Container With Cranesetiawanaji407No ratings yet
- Crane Safety TipsDocument4 pagesCrane Safety Tipssetiawanaji407100% (1)
- Hard Hat, Safety Glasses, Safety Boots Compulsory: PowerDocument9 pagesHard Hat, Safety Glasses, Safety Boots Compulsory: PowerEbeneshwar Anthony71% (7)
- JSA G20 Scaffolding Erection DismantlingDocument4 pagesJSA G20 Scaffolding Erection DismantlingemmyNo ratings yet
- Job Safety AnalysisDocument13 pagesJob Safety AnalysisnagarjunaNo ratings yet
- JSA Analysis of Rudder Shaft Seal Tightening (less than 40 charsDocument2 pagesJSA Analysis of Rudder Shaft Seal Tightening (less than 40 charsIlya BordonosovNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis KFS-IMSF-HRA-01-Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis KFS-IMSF-HRA-01-Job Safety AnalysisAmit ChahandeNo ratings yet
- JSA - Scissor - Lift 2023Document4 pagesJSA - Scissor - Lift 2023syed khaja misbhuddinNo ratings yet
- JSA ReportDocument2 pagesJSA ReportVinod GuptaNo ratings yet
- Permanent Facilities Storage ProtectionDocument2 pagesPermanent Facilities Storage ProtectionMOHAMMED RIYAN TNo ratings yet
- JSA Welding & GrindingDocument2 pagesJSA Welding & GrindingtaufikNo ratings yet
- SP02 JSA Form EnglishDocument5 pagesSP02 JSA Form Englishmartina19No ratings yet
- Event Safety ChecklistDocument2 pagesEvent Safety ChecklistDeba RinaNo ratings yet
- 007ABGJHA007 Rebar WorkDocument4 pages007ABGJHA007 Rebar WorkALBILAL HSENo ratings yet
- JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS FOR WELDINGDocument2 pagesJOB SAFETY ANALYSIS FOR WELDINGSravan Dasari100% (3)
- Chop Saw PDFDocument3 pagesChop Saw PDFAnonymous YrCsoYgNo ratings yet
- Panel Rev00Document4 pagesPanel Rev00asdasd asdasdNo ratings yet
- Master Builders SA - Safe Work Method Statement - Timber Roof Truss Installation CraneDocument6 pagesMaster Builders SA - Safe Work Method Statement - Timber Roof Truss Installation CraneDaniel JulianNo ratings yet
- 002 ABGJHA002 Lifting of Materials Less Than 1 TonDocument3 pages002 ABGJHA002 Lifting of Materials Less Than 1 TonALBILAL HSENo ratings yet
- Safe - Work - Method - Statement - Roof - Truss - Installation V1.0Document8 pagesSafe - Work - Method - Statement - Roof - Truss - Installation V1.0hurairamughal666No ratings yet
- Weekly site inspection summaryDocument2 pagesWeekly site inspection summaryDark FantasyNo ratings yet
- JSA For Lift Personnel in Scissor LiftDocument6 pagesJSA For Lift Personnel in Scissor Liftnawalmaftah23No ratings yet
- PT Swadaya Graha: Form Jsa Work SheetDocument6 pagesPT Swadaya Graha: Form Jsa Work SheetArief SyaifudinNo ratings yet
- JHA For Mobile Crane 1 PDFDocument6 pagesJHA For Mobile Crane 1 PDFSethu MathanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Job Hazard/Task Assessment: Check All Applicable Hazards That May Be Present Before or During The Task(s)Document1 pagePre-Job Hazard/Task Assessment: Check All Applicable Hazards That May Be Present Before or During The Task(s)varpin71No ratings yet
- CERI-JSA-2023-02 - JSA Hot WorksDocument12 pagesCERI-JSA-2023-02 - JSA Hot Worksdiaf bilalNo ratings yet
- JSA - CERI Scaffold Erection PDFDocument11 pagesJSA - CERI Scaffold Erection PDFdiaf bilalNo ratings yet
- AEC-L-84649 Site Safety & Observation - Report EO #04Document10 pagesAEC-L-84649 Site Safety & Observation - Report EO #04riazulh106No ratings yet
- Ppe Hazard AssessmentDocument4 pagesPpe Hazard AssessmentNeha PatelNo ratings yet
- EHSMS09 Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Formand Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS)Document4 pagesEHSMS09 Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Formand Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS)yanaNo ratings yet
- ABRA For E-HouseDocument10 pagesABRA For E-HouseSatish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Workplace Hazard Assessment Form: Task Hazard(s) PPE Required Notes DepartmentDocument2 pagesWorkplace Hazard Assessment Form: Task Hazard(s) PPE Required Notes DepartmentMashur Al JunaibiNo ratings yet
- ERECTION, MODIFICATION & DISMANTLING OF SCAFFOLDING WORKS - Risk assessment - REV01Document10 pagesERECTION, MODIFICATION & DISMANTLING OF SCAFFOLDING WORKS - Risk assessment - REV01SolimanNo ratings yet
- JHA Template BlankDocument5 pagesJHA Template BlankChristopher Newby100% (1)
- Appendix A SPA FormDocument2 pagesAppendix A SPA FormMohamed HadjkacemNo ratings yet
- JSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019Document11 pagesJSA 173 - CRT RIG UP - Updated 21.10.2019tafhim rashidNo ratings yet
- SAFE WORK PERMIT HAZARDSDocument6 pagesSAFE WORK PERMIT HAZARDSSuud SenanNo ratings yet
- Work Permit Sample For Contractro TresDocument6 pagesWork Permit Sample For Contractro TresretheepNo ratings yet
- Fuel Transfer Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesFuel Transfer Safety AnalysisIlya BordonosovNo ratings yet
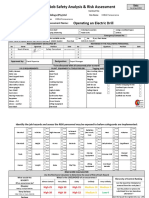
- Job Safety Analysis & Risk Assessment: Operating An Electric DrillDocument6 pagesJob Safety Analysis & Risk Assessment: Operating An Electric DrillH.J KENo ratings yet
- TRA - Amine System Degreasing - October 14, 2018Document9 pagesTRA - Amine System Degreasing - October 14, 2018Ijaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis - T-Wall InstallationDocument5 pagesJob Safety Analysis - T-Wall InstallationALBILAL HSENo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TemplateDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment TemplateKirunda AndrewNo ratings yet
- Job Safety AnalysisDocument3 pagesJob Safety AnalysisAndhy DhannyNo ratings yet
- RoutineJobHazardAnalysis 000Document2 pagesRoutineJobHazardAnalysis 000sugiyanto100% (1)
- 2 - HirarcDocument4 pages2 - HirarcMohd Fadli100% (3)
- Matriks APD GGSDocument75 pagesMatriks APD GGSAditiya PradanaNo ratings yet
- JHA Dryer Hot CommissioningDocument5 pagesJHA Dryer Hot CommissioningJowel MercadoNo ratings yet
- Form JSADocument2 pagesForm JSADella DwinovaliaNo ratings yet
- JHA 58-A - CML & CIG 4,5 Pump Header & Water Line Modification - DIP2Document3 pagesJHA 58-A - CML & CIG 4,5 Pump Header & Water Line Modification - DIP2cmgent2022No ratings yet
- Blank - JSADocument3 pagesBlank - JSAjwesgibsonNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: Location Date New Revised Jsa No. Task Supervisor Analysis by Approved byDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Location Date New Revised Jsa No. Task Supervisor Analysis by Approved byDavid GlawsonNo ratings yet
- PPE Matrix for Job Tasks Under 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesPPE Matrix for Job Tasks Under 40 CharactersSiva Naga Prasad TadipartiNo ratings yet
- TBT 53 Skid Steer PDFDocument2 pagesTBT 53 Skid Steer PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- TBT 18 Equipment Getting On Off PDFDocument2 pagesTBT 18 Equipment Getting On Off PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- TBT 50 Roof Collapse PDFDocument2 pagesTBT 50 Roof Collapse PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- TBT 54 TT-Skin-Cancer PDFDocument2 pagesTBT 54 TT-Skin-Cancer PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- TBT - 47 - Preventing Falls From Scaffolding PDFDocument2 pagesTBT - 47 - Preventing Falls From Scaffolding PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- CPWR RF Frequency TBTDocument2 pagesCPWR RF Frequency TBTmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- TBT 22 Falls Extension Ladders PDFDocument2 pagesTBT 22 Falls Extension Ladders PDFmohammad ashpakNo ratings yet
- Here The Whole Time ExcerptDocument18 pagesHere The Whole Time ExcerptI Read YA100% (1)
- Introduction to Honda automotive companyDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Honda automotive companyfarhan javaidNo ratings yet
- Fcra Act 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesFcra Act 2010 PDFKateNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE-10 BảnDocument5 pagesPRACTICE-10 BảnBinh Pham ThanhNo ratings yet
- CRIMINAL LAW 101Document7 pagesCRIMINAL LAW 101Rimwel GarafilNo ratings yet
- A CHAIN OF THUNDER: A Novel of The Siege of Vicksburg by Jeff ShaaraDocument13 pagesA CHAIN OF THUNDER: A Novel of The Siege of Vicksburg by Jeff ShaaraRandom House Publishing Group20% (5)
- Contract-Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesContract-Case AnalysisAakriti BakhadyoNo ratings yet
- англійська 11 final altered PDFDocument192 pagesанглійська 11 final altered PDFАнна НазаренкоNo ratings yet
- Monetizing Judgments DatasheetDocument9 pagesMonetizing Judgments DatasheetJohnWilliams100% (4)
- Protein Expression HandbookDocument118 pagesProtein Expression HandbookLuis Arístides Torres SánchezNo ratings yet
- Credits Is Hereby Given To Mrs. Jaylynne Escalona, Mscrim For Her Substantial Contribution As Regards To This NotesDocument15 pagesCredits Is Hereby Given To Mrs. Jaylynne Escalona, Mscrim For Her Substantial Contribution As Regards To This NoteseuniceNo ratings yet
- Indus Script - WikipediaDocument55 pagesIndus Script - WikipediaMuhammad Afzal BrohiNo ratings yet
- Eyewitness EvidenceDocument55 pagesEyewitness EvidencenatstarterNo ratings yet
- Public High School Teachers' Strategies for Addressing Challenges in Conducting Action ResearchDocument75 pagesPublic High School Teachers' Strategies for Addressing Challenges in Conducting Action ResearchMilbert Loyloy SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Zomer Development Company, Inc Vs Special 20th Division of CADocument20 pagesZomer Development Company, Inc Vs Special 20th Division of CACJNo ratings yet
- FPSC@FPSC - Gove.pk: Sector F-5/1, Aga Khan Road, Islamabad Email: UAN:-051-111-000-248Document9 pagesFPSC@FPSC - Gove.pk: Sector F-5/1, Aga Khan Road, Islamabad Email: UAN:-051-111-000-248Ayaz AliNo ratings yet
- Identify statements that match birthday party picturesDocument1 pageIdentify statements that match birthday party picturesprotogina100% (1)
- Snorkel: Rapid Training Data Creation With Weak SupervisionDocument17 pagesSnorkel: Rapid Training Data Creation With Weak SupervisionStephane MysonaNo ratings yet
- Liming Heavy Industry Introduction NewDocument7 pagesLiming Heavy Industry Introduction NewJohnny DoeNo ratings yet
- Already GoneDocument3 pagesAlready GoneladymyaNo ratings yet
- Supervision Assigment 1Document18 pagesSupervision Assigment 1Wendimu Nigusie100% (3)
- 1964-1986 OMC Sterndrive ManualDocument572 pages1964-1986 OMC Sterndrive ManualBarry Pieters75% (4)
- Puromines Vs CA DigestDocument2 pagesPuromines Vs CA DigestBea Alonzo100% (1)
- The Small Trees High Productivity Initiative: Principles and Practice in High Density Orchard DesignDocument1 pageThe Small Trees High Productivity Initiative: Principles and Practice in High Density Orchard DesignPutchong SaraNo ratings yet
- Scheme Samsung NT p29Document71 pagesScheme Samsung NT p29Ricardo Avidano100% (1)
- HR Generalist SyllabusDocument4 pagesHR Generalist Syllabusdugdugdugdugi100% (1)
- Srimad Bhagavatam 2nd CantoDocument25 pagesSrimad Bhagavatam 2nd CantoDeepak K OONo ratings yet
- Leadership: Dr. Sayedul Islam Sayed MD Resident, Psychiatry (BSMMU)Document34 pagesLeadership: Dr. Sayedul Islam Sayed MD Resident, Psychiatry (BSMMU)Sayedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Service GuideDocument185 pagesMaintenance and Service GuidenstomarNo ratings yet
- ch-1 Phy MEASUREMENT AND MOTIONDocument2 pagesch-1 Phy MEASUREMENT AND MOTIONRakesh GuptaNo ratings yet