Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CONSTRUCTIVISM
Uploaded by
Phong Nguyễn Nhật0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesConstructivism views learning as an active process where learners construct new ideas based upon their current and past knowledge and experiences. It emphasizes that individuals create their own understanding and that social interactions, background knowledge, and environment play a role in cognitive development. Constructivism sees the learner as an active participant in the learning process rather than a passive recipient of information.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConstructivism views learning as an active process where learners construct new ideas based upon their current and past knowledge and experiences. It emphasizes that individuals create their own understanding and that social interactions, background knowledge, and environment play a role in cognitive development. Constructivism sees the learner as an active participant in the learning process rather than a passive recipient of information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesCONSTRUCTIVISM
Uploaded by
Phong Nguyễn NhậtConstructivism views learning as an active process where learners construct new ideas based upon their current and past knowledge and experiences. It emphasizes that individuals create their own understanding and that social interactions, background knowledge, and environment play a role in cognitive development. Constructivism sees the learner as an active participant in the learning process rather than a passive recipient of information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
CONSTRUCTIVISM
1. Constructivism views learning as a _____________ in which the learner
_______________________ or _____________ new ideas or concepts.
2. Each of us generates our own _____________ and _______________,
which we use to _______________ of our experiences.
3. Learning is simply the process of _____________ our ______________
to _______________ new experiences.
4. In the Constructivist theory the emphasis is placed on the _____________
or the _____________ rather than the _____________ or the
_____________.
5. The learner, therefore, _____________ his/her own conceptualizations
and solutions to problems.
6. Constructivists view learning as the result of _____________________.
Students learn by _____________ new _____________ together with
what they already know. People learn best when they ________________
their own _______________.
7. Learning is affected by the _____________ and the _____________ and
_____________ of the learner.
8. Learners are encouraged to _____________ their own solutions and to try
out ideas and _____________. They are given the opportunity to build on
_______________________.
9. ____ types of constructivism:
- cognitive constructivism which is about how the individual learner
understands things, in terms of __________________________ and
_______________________
- social constructivism which emphasises how meanings and
understandings grow out of ____________________________.
10. Jean Piaget’s theory of _____________ development suggested that
through processes of _____________and _____________, individuals
_____________ new knowledge from their experiences. He mentioned
_____________ stages in cognitive development.
11. Behaviorism treats learners as ________________, while constructivism
treats them as __________________ of information, making use of their own
past experiences (_____________) to _____________ their own knowledge.
12. Using an ____________________ to deal with a new object or situation is
called _____________.
13. Lev Vygotsky associated with _____________________ which
emphasized the effects of one’s _____________ have on learning.
14. Lev Vygotsky's notion of zone of _____________ development, is the
gap between a learner’s _____________ development determined by
independent problem-solving and the learner's _____________ level of
development.
16. According to Vygotsky, learning occurs with the assistance of
_____________ in Zone of Proximal Development
17. Learning is a search for _____________. Therefore, learning must start
with the issues around which students are _____________ trying to
_____________ meaning.
18. The learning process focuses on _____________ concepts, not
_____________ facts.
19. In order to teach well, we must understand the _________________
that students use to perceive the world and the _____________ they make to
support those models.
20. The purpose of learning is for an individual to _____________ his or her
own meaning, not just _____________ the “right” answers and _____________
someone else’s meaning.
21. _________________ & __________________________ are the
application of this theoretical background.
22. Constructivism calls for the _____________ of a ________________
curriculum. Instead, it promotes using curricula customized to the students’
______________________. Also, it emphasizes _____________ problem
solving.
23. Under the theory of constructivism, educators focus on making
_____________ between facts and fostering new _____________ in students.
Instructors tailor their teaching strategies to student responses and encourage
students to _____________, _____________, and _____________ information.
Teachers also rely heavily on _________________ questions and promote
_______________________ among students.
24. Constructivism calls for the elimination of _____________ and
_____________ testing. Instead, _______________ becomes part of the
learning process so that students play a larger role in judging their own progress.
25. Constructivism ...
emphasises _____________ and not _____________
encourages and accepts learner _____________ and _____________ sees
learners as creatures of will and purpose
thinks of learning as a _____________
encourages learner _____________
acknowledges the critical role of experience in learning
nurtures learners natural _____________
takes the learner's _______________________ into account
emphasises _________________ and _________________ when assessing
learning
bases itself on the principles of the __________________________ theory
makes extensive use of cognitive terminology such as _____________,
_____________ and _____________
considers _____________ the student learns
encourages learners to engage in _____________ with other students and
the teacher
supports ____________________ learning
involves learners in real world situations
emphasises the _____________ in which learning takes place
considers the _____________ and _____________ of the learner
provides learners the opportunity to _____________ new knowledge and
understanding from _____________ experience
You might also like
- Mindful Meditation Guide and Journal Mindfulness ExercisesDocument20 pagesMindful Meditation Guide and Journal Mindfulness ExercisesCetateanul PopescuNo ratings yet
- John Zeimbekis, Athanassios Raftopoulos - The Cognitive Penetrability of Perception - New Philosophical Perspectives (2015, Oxford University Press)Document480 pagesJohn Zeimbekis, Athanassios Raftopoulos - The Cognitive Penetrability of Perception - New Philosophical Perspectives (2015, Oxford University Press)jesus vergaraNo ratings yet
- Teaching Reflective Learning in Higher Education A Systematic Approach Using Pedagogic Patterns by Mary Elizabeth Ryan (Eds.)Document233 pagesTeaching Reflective Learning in Higher Education A Systematic Approach Using Pedagogic Patterns by Mary Elizabeth Ryan (Eds.)Okong PhituNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps How To Improve Memory, Writer Smarter, Plan Better, Think Faster, and Make More Money (PDFDrive)Document94 pagesMind Maps How To Improve Memory, Writer Smarter, Plan Better, Think Faster, and Make More Money (PDFDrive)varta baterijaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century QuestionnaireDocument9 pages21st Century QuestionnaireCynthia Unay100% (2)
- Learning and Teaching in Adult Education: Contemporary TheoriesFrom EverandLearning and Teaching in Adult Education: Contemporary TheoriesNo ratings yet
- 21st Century QuestionnaireDocument6 pages21st Century QuestionnaireLiezl Sabado82% (17)
- Module 14 ActivityDocument5 pagesModule 14 ActivityAlyssa Aile NonatoNo ratings yet
- EDU301 - General Methods of Teaching (QUIZ 1-2-3) (PAST GRAND QUIZ) (MID TERM MCQS) FINAL TERM (ALL IN ONE FILE)Document23 pagesEDU301 - General Methods of Teaching (QUIZ 1-2-3) (PAST GRAND QUIZ) (MID TERM MCQS) FINAL TERM (ALL IN ONE FILE)Dua ZahraNo ratings yet
- MIL QuizDocument2 pagesMIL QuizKirk Kervin OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Lte - 8Document8 pagesLte - 8Judy Ann PalingcodNo ratings yet
- 1 Shs Daily Lesson Log DLL Template Oral CommunicationDocument12 pages1 Shs Daily Lesson Log DLL Template Oral CommunicationKristine Bernadette MartinezNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 Vygotskys Socio Cultural TheoryDocument5 pagesMODULE 9 Vygotskys Socio Cultural TheoryDelmar Acyatan100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Views About Learning: ExercisesDocument10 pagesLesson 1: Views About Learning: ExercisesSonny Rivas100% (5)
- UploadDocument36 pagesUploadbahiyah71100% (3)
- EDU406 (CURRENT MCQs FINAL TERM)Document1 pageEDU406 (CURRENT MCQs FINAL TERM)Ribqa ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Edu301 Combine FileDocument84 pagesEdu301 Combine FileMisbah Hanif100% (2)
- Edu301 (Quiz 1) (Mid Term MCQS) Final Term (All in One File)Document38 pagesEdu301 (Quiz 1) (Mid Term MCQS) Final Term (All in One File)DARK COBRA YT100% (1)
- 1st Monthly Test PR1Document4 pages1st Monthly Test PR1Renen Millo BantilloNo ratings yet
- An Exercise To Determine Your Educational PhilosophyDocument2 pagesAn Exercise To Determine Your Educational PhilosophyCrisa Marie Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1. Using The Information You Read in The Materials, Give Your Stand To The Following Argument About Learner-CenterednessDocument6 pagesActivity 1. Using The Information You Read in The Materials, Give Your Stand To The Following Argument About Learner-CenterednessLovely Joy Benavidez BarlaanNo ratings yet
- What Makes Students Learn Effectively?Document33 pagesWhat Makes Students Learn Effectively?Papitik PhotographyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Teaching Science 2Document2 pagesFinal Exam in Teaching Science 2Angela AgonosNo ratings yet
- The Teaching Profession ActivityDocument41 pagesThe Teaching Profession ActivityBliss RoenNo ratings yet
- Instructional Observation FormDocument2 pagesInstructional Observation FormCrisel NombilaNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz For English 3-1Document1 pageLong Quiz For English 3-1Lourene May ApolinaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1,1page 3 Exercise For PrintDocument3 pagesChapter 1,1page 3 Exercise For PrintRoselyn GilapayNo ratings yet
- Constructivist ClassroomDocument3 pagesConstructivist ClassroomFionna Grace Rojas TonidoNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1.B UndergradDocument13 pagesUNIT-1.B UndergradNiheiNo ratings yet
- Eastern Mindoro College: Prelim Examination in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEastern Mindoro College: Prelim Examination in Curriculum DevelopmentJaymar MagtibayNo ratings yet
- EDU301 General Methods of Teaching (Grand Quiz) (MCQs 62 )Document2 pagesEDU301 General Methods of Teaching (Grand Quiz) (MCQs 62 )Ayesha Noor Ayesha Noor75% (4)
- Set 2 Teaching ApproachesDocument10 pagesSet 2 Teaching ApproachesDavidEzekiel Zaragoza Caña CarilloNo ratings yet
- Educ 7-Quiz 1.3 REVIEWERDocument3 pagesEduc 7-Quiz 1.3 REVIEWERErica LeysonNo ratings yet
- Eastern Mindoro College: Prelim Examination in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEastern Mindoro College: Prelim Examination in Curriculum DevelopmentJaymar MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Tle 1 Pre Final ExamDocument3 pagesTle 1 Pre Final Exammerlyn sanchoNo ratings yet
- ILTED - Module IV - 17 MayoDocument30 pagesILTED - Module IV - 17 MayoMaría luz NuñezNo ratings yet
- TCP Task 1 PrelimDocument8 pagesTCP Task 1 PrelimReymondNo ratings yet
- Form For Demontration ObservationDocument2 pagesForm For Demontration ObservationBelinda MagdaleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Adriane Tingzon100% (1)
- Answer Key Building BridgesDocument6 pagesAnswer Key Building BridgesMaricris Galman SalamatNo ratings yet
- EDFLCT Chapter 2Document13 pagesEDFLCT Chapter 2Kim GenandaNo ratings yet
- Part 5. Methods of Teaching and IMs EDITEDDocument44 pagesPart 5. Methods of Teaching and IMs EDITEDJamaica Kaye GantalaoNo ratings yet
- EDUC 403/603 Core Competency Self-Diagnostic AssessmentDocument4 pagesEDUC 403/603 Core Competency Self-Diagnostic AssessmentMarina KennedyNo ratings yet
- T A L P: by David J. VoelkerDocument8 pagesT A L P: by David J. VoelkerKomathi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 1 1Document7 pagesActivity 2 1 1Joyce NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Rating Sheet-Demo and LPDocument2 pagesRating Sheet-Demo and LPJim Boy BumalinNo ratings yet
- Sir A Teaching ProfDocument85 pagesSir A Teaching ProfRoselyn Gilapay78% (9)
- Grade 11 Methods of Enquiry WsDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Methods of Enquiry Wsvandanapandey.apslucknowNo ratings yet
- Grading ShitDocument2 pagesGrading ShitChandrikka MandeNo ratings yet
- The Learning Environment Observation 1: Getting Acquainted With Cooperating School and ClassDocument12 pagesThe Learning Environment Observation 1: Getting Acquainted With Cooperating School and ClassMariacris CarniceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task No. 12Document2 pagesAssessment Task No. 12Ma.Rodelyn OcampoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination in PR1Document2 pagesMidterm Examination in PR1Jessa SumayangNo ratings yet
- Module1 ACTIVITYDocument3 pagesModule1 ACTIVITYdylyn jane gallegoNo ratings yet
- English Presentation GuideDocument3 pagesEnglish Presentation GuidePatrícia FariaNo ratings yet
- A. Fill-In The KWL Chart With The Needed Information in The KWL ChartDocument13 pagesA. Fill-In The KWL Chart With The Needed Information in The KWL ChartBelle Herminigildo AngelesNo ratings yet
- In Class Assignment (Interdisciplinary)Document2 pagesIn Class Assignment (Interdisciplinary)fitree.0821No ratings yet
- Teacher-Centered Student-CenteredDocument5 pagesTeacher-Centered Student-CenteredArvin LlanetaNo ratings yet
- FS 4 Episode 5.Document7 pagesFS 4 Episode 5.Charles Kenn Mantilla65% (17)
- PED 8 w1 ACTDocument1 pagePED 8 w1 ACTroesajanisselagare73No ratings yet
- Department of Education Region VI Melchor Memorial School IncDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education Region VI Melchor Memorial School IncAna Melissa JarobillaNo ratings yet
- Editable Learning Packet Template - SENIOR HIGH SCHOOLDocument4 pagesEditable Learning Packet Template - SENIOR HIGH SCHOOLHARLEY L. TANNo ratings yet
- Aquino-Jenny-D. 4Document5 pagesAquino-Jenny-D. 4Jenny Derrayal AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ilted Module IIDocument23 pagesIlted Module IIMaría luz NuñezNo ratings yet
- Learning For Life: Empowering Students Through Personalized EducationFrom EverandLearning For Life: Empowering Students Through Personalized EducationNo ratings yet
- English To The Max - 1,200 Questions That Will Maximize Your English PowerDocument62 pagesEnglish To The Max - 1,200 Questions That Will Maximize Your English PowerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- 8 đề TS10Document32 pages8 đề TS10Phong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hk1 TIENG ANH 12 Nam 2021 2022Document8 pagesDe Thi Hk1 TIENG ANH 12 Nam 2021 2022Phong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Bu I 5Document2 pagesBu I 5Phong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document6 pagesTest 3Phong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- CLT AnswerDocument3 pagesCLT AnswerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- ALM AnswersDocument3 pagesALM AnswersPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism AnswerDocument3 pagesBehaviorism AnswerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Constructivism AnswerDocument4 pagesConstructivism AnswerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Affective Factors AnswerDocument3 pagesAffective Factors AnswerPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)Document3 pagesCommunicative Language Teaching (CLT)Phong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Direct MethodDocument8 pagesDirect MethodPhong Nguyễn NhậtNo ratings yet
- Science 5-Dlp-June 13, 2023Document4 pagesScience 5-Dlp-June 13, 2023Rachelle PedroNo ratings yet
- ELC612 Learning and CognitionDocument10 pagesELC612 Learning and CognitionVIJAYALAKSHMI A/P SANKARANARAYANAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
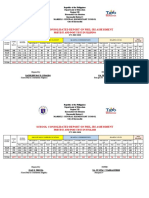
- School Consolidated Report On Phil-Iri Assessment: Pretest and Post Test in FilipinoDocument6 pagesSchool Consolidated Report On Phil-Iri Assessment: Pretest and Post Test in FilipinoKathleen Kay SubaldoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology - Assignment 1Document2 pagesIntroduction To Psychology - Assignment 1Sheiza SheikhNo ratings yet
- Edt 315 Module 4 Lesson Plan Template Fixed AccessDocument4 pagesEdt 315 Module 4 Lesson Plan Template Fixed Accessapi-642840473No ratings yet
- GCP TilleyDocument71 pagesGCP Tilleyapi-608529636No ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions For HEDocument13 pagesFinal Exam Questions For HEAliya Nicole CNo ratings yet
- PLAN DE CLASE DEMOSTRATIVA INGLÉS BÁSICA SUPERIOR 8vo BBDocument13 pagesPLAN DE CLASE DEMOSTRATIVA INGLÉS BÁSICA SUPERIOR 8vo BBelizabeth englishNo ratings yet
- TitluDocument2 pagesTitluCosmin NitaNo ratings yet
- 8 Week LRC Class Program CorrectedDocument7 pages8 Week LRC Class Program CorrectedMaLuisaMallaNo ratings yet
- Malto, Richelle Ann: Rubric For Assessing Teacher Intern'S Daily Demonstration Teaching Performance Name of Teacher ADocument4 pagesMalto, Richelle Ann: Rubric For Assessing Teacher Intern'S Daily Demonstration Teaching Performance Name of Teacher Aapi-712919764No ratings yet
- Final PortfolioDocument17 pagesFinal PortfolioDiego PradaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 4 Module 1Document3 pagesEDUC 4 Module 1DUNGOG AYESSANo ratings yet
- FS ManualDocument22 pagesFS ManualMARJOLIZ BIASONNo ratings yet
- Principles of Language AssessmentDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Language AssessmentDannahNo ratings yet
- MyELT - PW1 - U8 - RW - Lesson A - Reading 1Document6 pagesMyELT - PW1 - U8 - RW - Lesson A - Reading 1Quân Nguyễn Lê MinhNo ratings yet
- BC WORK - Anamika DebDocument12 pagesBC WORK - Anamika DebHarshal FuseNo ratings yet
- Demonstrasi Kontekstual Topik 2 - PemahamanDocument1 pageDemonstrasi Kontekstual Topik 2 - Pemahamanalya nurlhNo ratings yet
- Bilişsel Süreçler Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesBilişsel Süreçler Reflection PaperSoner AkımalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Creative WritingDocument41 pagesLesson 5 Creative Writingantoniagabriel salinasNo ratings yet
- Meet 11 Reading Main IdeaDocument13 pagesMeet 11 Reading Main IdeaNaya RaaNo ratings yet
- 5.training Delivery Modes and MethodsDocument8 pages5.training Delivery Modes and MethodsJAN MARISH TUNGOLNo ratings yet
- RTP - English9 Q3 Week 2 FinalDocument8 pagesRTP - English9 Q3 Week 2 FinaljhanceedebbieNo ratings yet
- Week7 Gen-Math Bunny Wilson EditedDocument9 pagesWeek7 Gen-Math Bunny Wilson EditedLorena MaglonzoNo ratings yet
- Bandura Power PointDocument30 pagesBandura Power PointLinh Ha NguyenNo ratings yet