Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Q3 Nerv - System
Uploaded by
Sophia Anama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesKLSANADGJBYIWEADBKIJWASILIK
Original Title
SCIENCE Q3 NERV.SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKLSANADGJBYIWEADBKIJWASILIK
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesScience Q3 Nerv - System
Uploaded by
Sophia AnamaKLSANADGJBYIWEADBKIJWASILIK
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
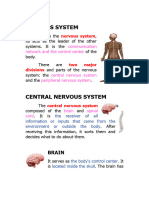
NERVOUS SYSTEM The central nervous system
is the body's processing
centre.
In biology, the nervous
system is the highly complex The BRAIN is a complex
part of an animal that organ that controls
coordinates its actions and thought, memory,
sensory information by emotion, touch, motor
transmitting signals to and skills, vision, breathing,
from different parts of its temperature, hunger and
body. every process that
regulates our body.
Nerve cells (neurones) are Together, the brain and
'excitable' cells which can spinal cord that extends
transduce a variety of from it make up the central
stimuli into electrical nervous system, or CNS.
signals, continuously
sending information about
the external and internal
environment (in the form of 1. CEREBRUM- the largest
sequences of action part of the brain. It is
potentials) to the central divided into two
nervous system (CNS). hemispheres, or halves,
called the cerebral
PARTS OF THE hemispheres. Areas within
NERVOUS SYSTEM the cerebrum control
muscle functions and also
control speech, thought,
The emotions, reading, writing,
central nervous syste and learning.
m (CNS) is made up of the
brain and spinal cord. It is 2. Cerebellum - is a part of
one of 2 parts of the your brain located at the back of
nervous system. The other your head, just above and
part is the peripheral behind where your spinal cord
nervous system, which connects to your brain itself.
consists of nerves that The name “cerebellum” comes
connect the brain and spinal from Latin and means “little
cord to the rest of the body. brain.” For centuries, scientists
believed your cerebellum's job regulation, acting as a sort of
was to coordinate your muscle relay station for auditory and
movements. visual information.
3. Brainstem- has many basic
functions, including regulation of 7. Thalamus is your body's
heart rate, breathing, sleeping, information relay station. All
and eating. It also plays a role in information from your body's
conduction. All information senses (except smell) must be
relayed from the body to the processed through your thalamus
cerebrum and cerebellum and before being sent to your brain's
vice versa must traverse the cerebral cortex for
brainstem. interpretation. Your thalamus
also plays a role in sleep,
4. Medulla- is where your wakefulness, consciousness,
cardiovascular and respiratory learning and memory.
systems link together into a
united system that controls your 8. Hypothalamus- a structure
heart rate, breathing, blood deep in your brain, acts as your
pressure and more. Manages body's smart control coordinating
other automatic processes. These center. Its main function is
are things that your body often to keep your body in a stable
does without you having to think state called homeostasis. It does
about them. its job by directly influencing
your autonomic nervous system or
5. Pons- is a part of your by managing hormones.
brainstem, a structure that links Within the spinal column
your brain to your spinal cord. lies the spinal cord, a
It handles unconscious processes vital aspect of the central
and jobs, such as your sleep- nervous system (CNS). The
wake cycle and breathing. It also three primary roles of the
contains several junction points spinal cord are to send
for nerves that control muscles motor commands from the
and carry information from senses brain to the body, send
in your head and face. sensory information from
the body to the brain, and
6. Midbrain is associated coordinate reflexes.
with vision, hearing, motor
control, sleep/wake, arousal
(alertness), and temperature
You might also like
- PE NeuronDocument3 pagesPE Neuronlucy ocampoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesNervous SystemRaazia HaseebNo ratings yet
- Report in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Document27 pagesReport in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Francia VenancioNo ratings yet
- Nervous SytemDocument24 pagesNervous SytemShaine MalunjaoNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument71 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive Systemsnathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADocument5 pagesNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerNo ratings yet
- Report in Physiological Psy. Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesReport in Physiological Psy. Nervous SystemFrancia VenancioNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Biology and PsychologyDocument23 pagesModule 2: Biology and Psychologyshain aldovinoNo ratings yet
- 3rd QuarterlyDocument7 pages3rd QuarterlyArque John Bertumen AbieraNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous Systemmarjeanlorana342No ratings yet
- Major Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellDocument6 pagesMajor Divisions and Parts of The Nervous System The Nerve CellAllysa Mae MoraNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Nervous System Lesson 2023Document72 pagesGrade 10 Nervous System Lesson 2023Kim DagaragaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemJason TaburnalNo ratings yet
- Identify The Parts and Functions of The Nervous System Distinguish The Divisions of The Nervous System Using A Concept MapDocument27 pagesIdentify The Parts and Functions of The Nervous System Distinguish The Divisions of The Nervous System Using A Concept MapChamain MarreroNo ratings yet
- Week 20 - Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesWeek 20 - Nervous SystemEraNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PPT - Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesAnaphy PPT - Nervous SystemJamaica TuellaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemPatricia BonganayNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemChloeNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument34 pagesBiological Basis of Behaviouralizaakif3No ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3: Module 3: by Ma'am Lea Rose A. SabasDocument29 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3: Module 3: by Ma'am Lea Rose A. Sabascharlesairondc1223No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesThe Nervous SystemAkheyla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument17 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAasma IsmailNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous SystemJoana RoxasNo ratings yet
- Science 10 ReportDocument3 pagesScience 10 ReportJeremiah Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerAudije, John Michael M.No ratings yet
- 8 The Need To Have A Central Control SystemDocument1 page8 The Need To Have A Central Control SystemGrace Ann MeronNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 NotesDocument3 pagesQuarter 3 NotesMichelle AlarcioNo ratings yet
- NSDocument37 pagesNSVanessa Joy SaavedraNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Nervous System Group 1Document45 pagesThe Human Body Nervous System Group 1Bai Nornica Abutazil UttoNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 04Document7 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 04megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewerDocument292 pagesGR 10 Revieweradrianigop29No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemOm TipsetwarNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesNervous Systemphoebecruz636No ratings yet
- Biological Bases, AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiological Bases, AssignmentBenjii CarlosNo ratings yet
- Body Control and ResponseDocument51 pagesBody Control and ResponseAngelyn AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiologyzairis21No ratings yet
- Biology 10Document3 pagesBiology 10Dwayne BaldozaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - ResearchDocument9 pagesSCIENCE - Researchmarealyn.hermida.camachoNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorSyed Huzayfah FaisalNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument47 pagesPeripheral Nervous SystemMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesNervous SystemAnn SerratoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab Disc 7Document44 pagesAnaphy Lab Disc 7BSLMS1D - Depasupil, Laurice Ann A.No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Systemanaliane azucenaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument85 pagesNervous SystemiamyouseokNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Crib Sheet (Mtes)Document3 pagesGeneral Biology II Crib Sheet (Mtes)JerseyNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Function of Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesCoordinated Function of Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemPosionous SubstancesNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesThe Nervous SystemMarivic AberinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesNervous System Flyer PDFKawaii GlamourNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Nervous System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- CVD Case StudyDocument23 pagesCVD Case StudyMsRhyxelle80% (5)
- Stanford Medicine Conductive Hearing LossDocument2 pagesStanford Medicine Conductive Hearing LossStrawberry ShortcakeNo ratings yet
- Organon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityDocument46 pagesOrganon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityLailatuz ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- Confo (Autosaved)Document30 pagesConfo (Autosaved)Prince KumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy of Edentulous Oral CavityDocument33 pagesApplied Anatomy of Edentulous Oral CavitymanaalNo ratings yet
- Dural Venous Sinus Azam SirDocument6 pagesDural Venous Sinus Azam SirLaserdotNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Thyroid and Parathyroid GlandsSidiq AboobakerNo ratings yet
- LipflpbotoxDocument4 pagesLipflpbotoxAlexandra Luz StodieckNo ratings yet
- Neurolocalization in PediatricsDocument66 pagesNeurolocalization in PediatricsNigussie MershaNo ratings yet
- What Does Your "Homunculus" Look Like?: Mapping Your Brain PurposeDocument3 pagesWhat Does Your "Homunculus" Look Like?: Mapping Your Brain PurposeClarissa PottsNo ratings yet
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) : Presented by Vajarala AshikhDocument34 pagesElectroencephalogram (EEG) : Presented by Vajarala Ashikhzohaib100% (1)
- Anatomy of NoseDocument8 pagesAnatomy of Noserizgah jawas100% (1)
- 8.2 Reading GuideDocument2 pages8.2 Reading GuideGrant HasletonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Revisi KonsDocument28 pagesAnatomy Revisi KonsGun Gun GunawanNo ratings yet
- The Neural Basis of Romantic LoveDocument6 pagesThe Neural Basis of Romantic LoveBooster CNo ratings yet
- Neuroimage: Clinical: Julia Andre, Marco Picchioni, Ruibin Zhang, Timothea ToulopoulouDocument9 pagesNeuroimage: Clinical: Julia Andre, Marco Picchioni, Ruibin Zhang, Timothea ToulopoulouEdisonNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument57 pagesAnatomical TerminologyAlicina DaleNo ratings yet
- The Valves of The Throat and Their Functioning in Tone, Vocal Register and Stress Laryngoscopic Case StudiesDocument36 pagesThe Valves of The Throat and Their Functioning in Tone, Vocal Register and Stress Laryngoscopic Case StudiesFelipe TabaresNo ratings yet
- CSF Rhinorrhea ReviewDocument7 pagesCSF Rhinorrhea ReviewPranave PNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Maxilla and MandibleDocument56 pagesAnatomy of Maxilla and Mandiblesoni bistaNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument13 pagesThyroidczarmaine29No ratings yet
- Koka Dhe QafaDocument57 pagesKoka Dhe QafaMarsiano Qendro100% (1)
- Quick Review - Fossa of RosenmullerDocument4 pagesQuick Review - Fossa of RosenmullerDavis KallanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Reconstructive Surgery of Defects of The Jaws PARTDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Reconstructive Surgery of Defects of The Jaws PARTMohammedNo ratings yet
- ENTssssssDocument15 pagesENTsssssssurg absiteNo ratings yet
- Dr. Bipul Rajbhandari PG Resident Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics Peoples Dental College and HospitalDocument27 pagesDr. Bipul Rajbhandari PG Resident Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics Peoples Dental College and Hospitalphanirg100% (1)
- Anatomy of The BrainDocument21 pagesAnatomy of The BrainChathiya Banu KrishenanNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy of The NeckDocument79 pagesBasic Anatomy of The NeckAlyssa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination. 2019 - 123400Document41 pagesNervous Coordination. 2019 - 123400Princess NekabariNo ratings yet
- Abducens NerveDocument13 pagesAbducens Nerveelena morettiNo ratings yet