Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Integument System: The Skin Accessory Organs
Uploaded by
RANGSINEE SUWANNASUKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Integument System: The Skin Accessory Organs
Uploaded by
RANGSINEE SUWANNASUKCopyright:
Available Formats
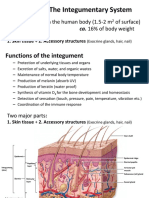
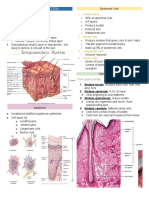
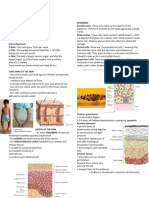
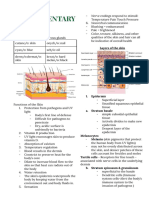
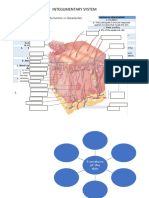
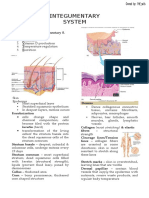
The functions of skin On most of your body the skin is around 2mm thick.
On the
the skin soles of your feet it is much thicker, while on your eyelids
accessory organs
it is only 0.5mm thick.
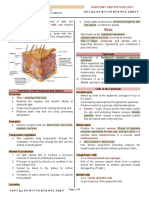
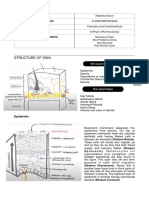
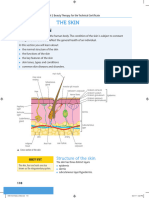
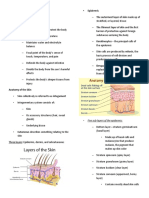
Epidermis
Regulation of body temperature Two layers; dead outermost
Protection from dehydration and infection layer and inner living layer
Respond to temperature, pressure and pain Keratin
Excretion of water, salts and urea (nitrogenous In humans, the skin accounts for about 7% of the total body weight Melanin
waste) and has a total surface area of about 1.8 square meters. No blood vessels
First defensive barrier of immune response
the ultraviolet rays of sun light stimulate the •
BAT €0 Dermis
any
The integument system
deep epidermis to produce vitamin D (calciferol) Collagen
Many blood vessels
Skin color
fµ -
• Be .
*
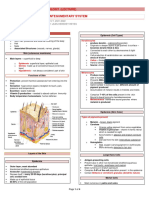
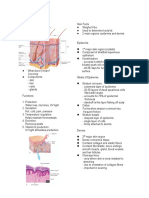
The Functions of hair
Hair
Nerve endings
Sensory receptors
Three skin pigments Warmth ; less in man than other Glands; sweat & sebaceous
Melanin: the most important mammals Smooth muscles
Carotene: from carrots and yellow vegies Sense light touch of the skin
Hair follicles
Hemoglobin: the pink of light skin Protection ; scalp
Melanin in granules passes from melanocytes toHair growth: averages 2 mm/wk
Active: growing
Hypodermis
keratinocytes in stratum basale
Resting phase then shed Mainly fat storage
Digested by lysosomes
Hair color Contains larger blood vessels &
Variations in color Amount of melanin for black or brown larger nerve fibers
Protection from UV light Distinct form of melanin for red
White: decreased melanin and air
bubbles in the medulla Nail disorders Skin disorders
Nails
Hard keratin
Grows from nail matrix
Hair disorders
Except nipples and part of
Sebaceous (oil) glands
external genitalia
Except palms and soles ,Produce
Prevent overheating
sebum by holocrine secretion
Produced in response to stress
,Oils and lubricates
as well as heat
You might also like
- Its-Skin 2Document37 pagesIts-Skin 2Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Integumentary System (Notes)Document5 pagesAnaphy - Integumentary System (Notes)Beatriz NideaNo ratings yet
- Skin Appendages and FunctionsDocument24 pagesSkin Appendages and FunctionsChris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemDocument27 pagesPowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1Document15 pagesBIOL 2210 Chapter 6, Integument System-1KellyPatrick SpencerNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Document1 pageIntegumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Shiem TrabocNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Functions and StructureDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System Functions and StructureLly Isidoro100% (2)
- Presentation On Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesPresentation On Integumentary SystemMd. Shahriar Arif 2122064630No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- 5 - IntegDocument8 pages5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Week 17 Integumentary SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 17 Integumentary System1203-Abuyuan, AechelleNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntegumentary SystemreinajoannaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleDocument8 pagesStructure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleRakshita GroverNo ratings yet
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PptintegsystemDocument64 pagesChapter 5 PptintegsystemlorinsyacderminnatNo ratings yet
- Beauty Therapy 1Document6 pagesBeauty Therapy 1Ekram MagedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ANAPHY The Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesChapter 5 ANAPHY The Integumentary Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Corneum and Is Directly Exposed To TheDocument3 pagesCorneum and Is Directly Exposed To Theydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- 6 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages6 Integumentary SystemPrincess kyle anicoyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System IncludesDocument29 pagesIntegumentary System IncludesRhena TogoresNo ratings yet
- M5 HAPP LecDocument9 pagesM5 HAPP LecM SNo ratings yet
- Skin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPDocument59 pagesSkin Physiology: Lecturer:Dr Herman Mulijadi MS, SPKPJosephine SNo ratings yet
- HUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS: INTEGUMENTARY AND SKELETALDocument3 pagesHUMAN ORGAN SYSTEMS: INTEGUMENTARY AND SKELETALDenine Dela Rosa OrdinalNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReviewerMark GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesLecture 9 Integumentary SystemJoshtwotown EarnshawNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab QuizDocument12 pagesAnaphy Lab QuizScout Beauty JHOINo ratings yet
- L3 Rec1 IntegumentDocument21 pagesL3 Rec1 IntegumentMORAKINYONo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet No. 5 Integumentary SystemDocument15 pagesLab Worksheet No. 5 Integumentary SystemKarylle Ezra GulifardoNo ratings yet
- Skin Histology 1Document72 pagesSkin Histology 1ace danielNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy 1 With NotesDocument23 pagesGeneral Anatomy 1 With NotesCesar marquesesNo ratings yet
- Skin Histology GuideDocument39 pagesSkin Histology GuideRuby BhattyNo ratings yet
- 01-INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM TheoryDocument9 pages01-INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Theorykapil RajputplNo ratings yet
- Angee 11Document4 pagesAngee 11lunadawsonesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3-4Document13 pagesAnatomy 3-4Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesIntegumentary SystemALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Part 1Document4 pagesActivity 2 Part 1Alejandra IndaNo ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System 1Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: DermisDocument11 pagesThe Integumentary System: DermisAnonymous AVSgz8UNo ratings yet
- PHCPD01 Unit 6 Part 1 PDFDocument5 pagesPHCPD01 Unit 6 Part 1 PDFAmber LugtuNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System MazonDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System MazonMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Chapter+7 +Integumentary+SystemDocument16 pagesChapter+7 +Integumentary+Systemmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesIntegumentary SystemEllysa Endrina BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Skin Structure and FunctionsDocument25 pagesSkin Structure and FunctionsUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaDocument8 pagesSkin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 3 IntegralDocument3 pagesAnaphy Topic 3 Integral박제라No ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Functions of Human SkinDocument7 pagesThe Anatomy and Functions of Human SkinPau De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Study Guide AnswersDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Study Guide Answersapi-33050097583% (6)
- Functions of Integumentary SystemDocument20 pagesFunctions of Integumentary SystemMa. Rita Concepcion TungulNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegeDocument62 pagesThe Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegetanarNo ratings yet
- Workbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveDocument5 pagesWorkbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveAmbaw PutiiNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY - Midterms ReviewerDocument15 pagesANAPHY - Midterms ReviewerTiffany WongNo ratings yet
- NeoNotes Derma HighlightedDocument32 pagesNeoNotes Derma Highlightedyomna.saaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ANAPHY Notes 4Document5 pagesIntegumentary System ANAPHY Notes 4Alloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Epidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueDocument2 pagesEpidermis Dermis Hypodermis or Subcutaneous TissueCarmehlyn BalogbogNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemOddysa EstorqueNo ratings yet
- PSORIASISDocument9 pagesPSORIASISDianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. The Human HairDocument30 pagesChapter 5. The Human HairqwertNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument22 pagesAnaphyarold bodoNo ratings yet
- Jarvis 12 Skin Hair NailsDocument11 pagesJarvis 12 Skin Hair NailsSarah C. SnooksNo ratings yet
- Seborrehic DermatitisDocument25 pagesSeborrehic DermatitisHallidayNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument1 pageConnective TissueDr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Beauty Content Bible - Sneak Peek 30 1-17Document17 pagesBeauty Content Bible - Sneak Peek 30 1-17Bagus Deddy AndriNo ratings yet
- 9621 NAM Luminesce APT200Document23 pages9621 NAM Luminesce APT200عيسى العسيريNo ratings yet
- 3W Clinic 3W Clinic BB Cream Wrinkle Intensive: Discounted Price: 200.00Document28 pages3W Clinic 3W Clinic BB Cream Wrinkle Intensive: Discounted Price: 200.00esteban batalaoNo ratings yet
- Treating Burns in ChildrenDocument62 pagesTreating Burns in ChildrenMusa yohana75% (4)
- WEEK 4 LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues & Integumentary System - UY-OCODocument7 pagesWEEK 4 LAB EXERCISE - Fundamental Types of Tissues & Integumentary System - UY-OCOBianca LouiseNo ratings yet
- CUTANEOUS ALLERGY MECHANISMS AND TESTINGDocument26 pagesCUTANEOUS ALLERGY MECHANISMS AND TESTINGThiti JessadaromNo ratings yet
- Non-Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Daphne Thioly-Bensoussan, MDDocument17 pagesNon-Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Daphne Thioly-Bensoussan, MDdominiqueNo ratings yet
- New York Medicaid APG CrosswalkDocument6,734 pagesNew York Medicaid APG CrosswalksdpetesrhsNo ratings yet
- Andrews' Diseases of The Skin 1e 2018Document578 pagesAndrews' Diseases of The Skin 1e 2018Ivanildo100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Integumentary System AssignmentDocument2 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Integumentary System AssignmentRitchell Dahl TumacaNo ratings yet
- Tissue SaltsDocument11 pagesTissue SaltsMatthewRyanTippett100% (2)
- Order Form UAE - 01-01-2023Document2 pagesOrder Form UAE - 01-01-2023Mohammad BelalNo ratings yet
- Eritroderma - Bolognia 4th EditionDocument15 pagesEritroderma - Bolognia 4th EditionAisyahNo ratings yet
- Types of Skin LesionsDocument5 pagesTypes of Skin LesionsZielledee100% (2)
- Chemical Peeling With Trichloroacetic Acid and Lactic Acid For Infraorbital Dark CirclesDocument6 pagesChemical Peeling With Trichloroacetic Acid and Lactic Acid For Infraorbital Dark CirclesAna Claudia Kordelos DinizNo ratings yet
- Modul Kulit SsDocument22 pagesModul Kulit Ssshafiraa29No ratings yet
- Kosmetik: N o Nama Barang Ukura N Stok Harga Harga Jual LabaDocument6 pagesKosmetik: N o Nama Barang Ukura N Stok Harga Harga Jual LabaAhmad FatoniNo ratings yet
- PDYP SampleDocument18 pagesPDYP SampleBillW2010100% (1)
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument49 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsPukazhvanthen Paramanandhan100% (1)
- Product Price List 2021: Shop Online With Convenience On My Forever India AppDocument3 pagesProduct Price List 2021: Shop Online With Convenience On My Forever India AppFirdous AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System NotesDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System NotesJose Enrico SumayaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument4 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityMarjorie Jofel Cerrudo PaciaNo ratings yet
- Head Toe Physical AssessmentDocument2 pagesHead Toe Physical Assessmentzbestgurl100% (2)
- 706f PDFDocument15 pages706f PDFVictor BazanNo ratings yet