Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diversity of Materials in The Environment
Uploaded by
Angelika Tibayan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
DIVERSITY OF MATERIALS IN THE ENVIRONMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesDiversity of Materials in The Environment
Uploaded by
Angelika TibayanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
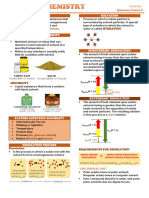
DIVERSITY OF MATERIALS IN THE ENVIRONMENT • A solid substance that dissolves completely in a of solute per unit volume, the solution
of solute per unit volume, the solution is said to be
SOLUTIONS given solvent is said to be soluble. concentrated.
Parts of a Solutions • Two liquids that completely mix in each other are • However, if the solution contains a relatively small
• The particles of solutions are too tiny to be seen by said to be miscible. amount of solute per unit volume, the solution is
the naked eye. Thus solutions appear to be • Solutes and solvents that differ in state and do not said to be diluted. This concentration of solutions
homogeneous. Solutions also cannot be filtered dissolve appreciably are insoluble. is only expressed qualitatively.
because particles of solutions can pass through • Solutes and solvents of the same state that do not • The concentration of solution is the amount of
the holes of filter paper. An unlike colloids, mix appreciably are immiscible. solute present in a given quantity of solution.
solutions do not scatter light. Saturated, Unsaturated, and Supersaturated Solutions Percent by Mass and Percent by Volume
• Solute is the material present in smaller amount. • A solution that has reached its maximum solubility Percent by Mass
• Solvent is the substance present in larger amount. is referred to as a saturated solution. • Percent by mass, or % (m/m) of solution, refers to
• The solvent is also referred to as the substance • An unsaturated solution is a solution that can still the mass of solute dissolved in 100 g solution. It
that dissolves, while the solute is the substance dissolved more solute in the given amount of has no unit because it is a ratio of mass expressed
that is dissolved. A solution that has water as the solvent at a given temperature. in grams.
solvent is generally termed as an aqueous • A supersaturated solution is prepared by setting a mass mass of solute
• %( ¿= x 100
solution. saturated solution at a higher temperature. mass mass of solution
Types of Solutions Factors Affecting Solubility • The mass of solution is obtained by adding the
• Solutions may be classified according to the state The Nature of Solute and Solvent mass of solute and the mass of solvent. The
of the solvent, according to their solubility, and • The solubility of some solutes depends on the equation is expressed this way:
according to their concentrations. nature of the solute and solvent • mass of solution = mass of solute + mass of
• Solutions exist in the three states of matter: solid, • Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes. solvent
liquid, and gas. Temperature Percent by Volume
• A solute or a solvent can either be a gas, liquid, or • Solids are usually more soluble in liquids at higher • Percent by volume, or % v/v, refers to the number
solid but the final state of the solution is temperatures. of milliliters of solute dissolved in 100 mL solution.
determined by the state of the solvent. • For instance, sugar dissolves faster in hot water volume of solute
Solubility than in cold. • % volume/volume = x 100
volume of solution
• The maximum amount of solute that is dissolved in Pressure Percent by Mass/ Volume
a given amount of solvent at a specific • Pressure does not affect the solubility of liquids • Percent by mass/ volume, or % (m/v), refers to the
temperature. It is usually expressed in grams of and solids. However, it greatly affects the solubility mass of solute dissolved in milliliters solution. It is
solute in exactly 100 g of solvent. of gases in liquids. calculated by dividing the grams of solute by the
• In the solution process, the terms soluble and Concentration of Solutions milliliters of solution and multiplying by 100.
miscible refer to solids dissolved in liquids and • Solutions may be classified on the basis of the mass of solute
liquids dissolved in liquids, respectively. amount of solvent and solute present in them. • % mass/volume = x 100
volume of solution
When a solution contains a relatively large amount
You might also like
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Lecture 3 - Solubility & DissolutionDocument16 pagesLecture 3 - Solubility & DissolutionSHANJIDA ALI RIANo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Solutions G7Document44 pagesSolutions G7Rlene May MateoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionDocument5 pagesConcentration of Solutionmargareth bumatayNo ratings yet
- Defining ConcentrationDocument7 pagesDefining ConcentrationMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Parts Per Million (PPM)Document2 pagesParts Per Million (PPM)welpNo ratings yet
- Solution1 PDFDocument2 pagesSolution1 PDFAhmad HasanNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2 Digital Note Taking TemplateDocument1 pageCHEM 2 Digital Note Taking Templatekasandra cristy galonNo ratings yet
- Weeks5 7solutionsDocument27 pagesWeeks5 7solutionsEmma LoreinNo ratings yet
- Larutan 1 PDFDocument21 pagesLarutan 1 PDFAnonymous 2xr3Y5VNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure Notes PDFDocument15 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure Notes PDFgkclubakshayaNo ratings yet
- Chem NotessssssssssssDocument5 pagesChem NotessssssssssssevanNo ratings yet
- 1 Solutions ReportDocument19 pages1 Solutions ReportDaphne Lianne DegayNo ratings yet
- Solution & Solubilit yDocument28 pagesSolution & Solubilit yChristine MalibiranNo ratings yet
- Edsci 112Document8 pagesEdsci 112Meah Angela GulacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Solutions PPT Grade 7Document17 pagesChapter 16 Solutions PPT Grade 7Tiffanie Mae Paredes100% (5)
- Learning Material 2: General Chemistry 2 PLM For February 26-March 5,2021Document5 pagesLearning Material 2: General Chemistry 2 PLM For February 26-March 5,2021Justeny TabbayNo ratings yet
- IPC-Solutions PPT-BordersDocument30 pagesIPC-Solutions PPT-BordersJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument92 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsPeter PanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryJared AlexanderNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument34 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406100% (1)
- Solutions - SolubilityDocument16 pagesSolutions - SolubilityÖmer KhanNo ratings yet
- Solubility of DrugsDocument147 pagesSolubility of Drugsharshagadia234No ratings yet
- SOLUTIONSDocument15 pagesSOLUTIONSdivinegrace.cruz.mnlNo ratings yet
- L 3 - SolutionsDocument51 pagesL 3 - SolutionsJayRiveraNo ratings yet
- Razzel Quinones Chemistry SolutionDocument5 pagesRazzel Quinones Chemistry SolutionRazzel QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- IV. Properties of SolutionDocument11 pagesIV. Properties of SolutionHania ABDULNo ratings yet
- Solubility and Distribution Phenomena: Aseel SamaroDocument89 pagesSolubility and Distribution Phenomena: Aseel Samaroveneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- SolubilityDocument59 pagesSolubilityNadem DreemNo ratings yet
- Chem Detailed Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesChem Detailed Lesson PlanGlen MillarNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Solution: Group 1Document27 pagesPhysical Properties of Solution: Group 1Althea BacordoNo ratings yet
- SATURATEDDocument20 pagesSATURATEDSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - Preparing of SolutionDocument22 pagesWEEK 3 - Preparing of SolutionQUENNIE BRIONESNo ratings yet
- 2.solutions FDocument33 pages2.solutions Fshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- Solubility and Distribution PhenomenaDocument89 pagesSolubility and Distribution Phenomenadesekar sejati100% (2)
- Solubility of Drugs PDFDocument66 pagesSolubility of Drugs PDFPrabhas MeherNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of SolutionsDocument22 pagesCharacteristics of SolutionsJunior LifeNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Solutions 2023Document39 pagesCH 2 Solutions 2023Kaleb Ashiko100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanGlen Millar100% (1)
- Solubility and DissolutionDocument87 pagesSolubility and Dissolutionm7md3del2015No ratings yet
- Solubility ExpressionsDocument7 pagesSolubility ExpressionsYuppie Raj100% (1)
- Class Xii 1,2,3 SolutionDocument50 pagesClass Xii 1,2,3 SolutionSubhasish SauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Solutionsahmedelhawary1561No ratings yet
- Water &MC: in Food SystemDocument23 pagesWater &MC: in Food SystemFISIA AQRORINANo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument32 pagesSolutionsMayuresh PanseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13aulectureslides 000 PDFDocument105 pagesChapter 13aulectureslides 000 PDFFrances Valerie Cambronero PaceteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument23 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsRacquel SupsupNo ratings yet
- 7 2 SolubilityDocument18 pages7 2 SolubilityJordan Bautista-EspirituNo ratings yet
- Solubility Notes Summary Physical Pharmacy PharmaceuticsDocument9 pagesSolubility Notes Summary Physical Pharmacy PharmaceuticsYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument25 pagesChemistryPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Solutions All inDocument85 pagesLesson 4 Solutions All inlacanilaoxyreljazeNo ratings yet
- Solution PCTDocument21 pagesSolution PCTpromisearinzechi4No ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-06-16 في 4.43.06 مDocument14 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-06-16 في 4.43.06 م11xgcxvcgcNo ratings yet
- Kimia Larutan: Moondra Zubir, PH.DDocument23 pagesKimia Larutan: Moondra Zubir, PH.DmaudysakinahNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument52 pagesSolutionsCarmina DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ChemistryDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Chemistrymaricar regidor100% (2)
- 8.1 Classifying SolutionsDocument8 pages8.1 Classifying SolutionsAngela JoyNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Chemistry Chapter 6 Lesson 2 - Concentration and SolubilityDocument15 pagesGrade 8 Chemistry Chapter 6 Lesson 2 - Concentration and SolubilityKarim AL-TijaniNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument32 pagesSolutionsAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- MicroorganismsDocument6 pagesMicroorganismsAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument2 pagesElements and CompoundsAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProcessDocument6 pagesInvestigatory ProcessAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument3 pagesSolutionAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesAcids and BasesAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Substances and MixtureDocument1 pageSubstances and MixtureAngelika TibayanNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope Forensics Letter PDFDocument50 pagesWire Rope Forensics Letter PDFAshley DeanNo ratings yet
- Regional Training of Teachers For Critical Content in Grade 8 ScienceDocument35 pagesRegional Training of Teachers For Critical Content in Grade 8 ScienceZeraNo ratings yet
- Passive Energy Dissipation Systems For StructuralDocument12 pagesPassive Energy Dissipation Systems For StructuralMichael Jhoan Rodriguez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapt 08Document21 pagesChapt 08Jesse McClure100% (5)
- Design and Analysis of Drive Shaft Using Kevlar/Epoxy and Glass/Epoxy As A Composite MaterialDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of Drive Shaft Using Kevlar/Epoxy and Glass/Epoxy As A Composite MaterialAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Implant Surface Modifications - A ReviewDocument6 pagesImplant Surface Modifications - A ReviewKlaudia SzymikNo ratings yet
- Tech Memo - y FactorDocument4 pagesTech Memo - y FactorsumitrochakrabortiNo ratings yet
- hlL3 - SSHT II 201213Document30 pageshlL3 - SSHT II 201213Will Morgan-EvansNo ratings yet
- What Factors Will Affect Paint GlossDocument5 pagesWhat Factors Will Affect Paint GlosseiearjunNo ratings yet
- FSC PaperDocument2 pagesFSC PaperRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Tubing ENDocument5 pagesInstrumentation Tubing ENLuis CasasNo ratings yet
- Base Plate DesignDocument21 pagesBase Plate Designtitir bagchi100% (1)
- Push Over Analysis PDFDocument28 pagesPush Over Analysis PDFSardimalAmirNo ratings yet
- Materials Science 10.53.11 PMDocument39 pagesMaterials Science 10.53.11 PMJane LeeNo ratings yet
- Graduate Vibrations ProjectDocument27 pagesGraduate Vibrations ProjectJohn AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsDocument11 pagesSample Design Calculation - Vessel Supported On LugsinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- Ihw 4Document7 pagesIhw 4LogoNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Fatigue Life Analysis of Rolling Bearings Based On Quasistatic ModelingDocument11 pagesResearch Article: Fatigue Life Analysis of Rolling Bearings Based On Quasistatic ModelingAkash SoodNo ratings yet
- Astm A321Document2 pagesAstm A321clevercog0% (1)
- 3RD Quarter Exam Smaw 12 NoteDocument2 pages3RD Quarter Exam Smaw 12 NoteBryan Borje100% (2)
- Unit 9 - WEEK 08: Assignment 08Document4 pagesUnit 9 - WEEK 08: Assignment 08Barani KumarNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Reinforced ConcreteDocument25 pagesBamboo Reinforced Concretestructuralengineers100% (1)
- PEC ReviewerDocument4 pagesPEC ReviewerJmNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis J David Irwin 11th Edition All Chapter Solutions Manual PDFDocument25 pagesBasic Engineering Circuit Analysis J David Irwin 11th Edition All Chapter Solutions Manual PDFStorie Everson ZoioNo ratings yet
- Wood Design AidDocument12 pagesWood Design AidbarrypeckertonNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit 03Document14 pagesBEE Unit 03PrasadNo ratings yet
- (E) Basic Study Pack - Optics - Sol - ch01Document13 pages(E) Basic Study Pack - Optics - Sol - ch01jeannieqintszyanNo ratings yet
- API 570 Course Notes - JoshiDocument173 pagesAPI 570 Course Notes - JoshiPrabhakar Kattula100% (3)
- Mistery of RZDocument5 pagesMistery of RZzlatkoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10Document7 pagesExperiment 10Deepan AdakNo ratings yet