Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Structure Outline
Uploaded by
Erin FindlayOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bone Structure Outline
Uploaded by
Erin FindlayCopyright:
Available Formats
Bone Structure Outline
Week
Date
Difficulty
Exam Date
Files
Notes
Notes 1
Reviewed For Exam
Structural Term meaning
Structure Meaning
tuberosity protrusion that is an attachment for muscles or CT
tubercle small rounded prominence for CT attachment
supra above
infra below
foramen opening - hole
fossa shallow depression
crest raised edge of bone
groove space in bone surface to allow blood vessels and nerves to enter
eminence projection
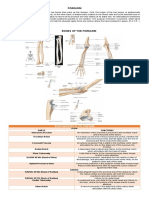
Thoracic Limb
Scapula
Structure Placement
Cranial angle angle on dorsal part of scapula
Bone Structure Outline 1
Structure Placement
Caudal angle angle on caudal part of scapula
Cranial border border closest skull
border closest to vertebrae, attachment of
Dorsal border
cartilage
Caudal border border closest to ribs
Supraspinous fossa surface dorsal to spine
Infraspinous fossa surface ventral to spine (largest surface)
Spine lateral ridge
Acromion wide end piece of spine
Hamate Process projection from acromion
only seen in cats, upper projection from hamate
Suprahamate Process (metacromion)
process
Supraglenoid tubercle cranial, distal placement of a small projection
dorsal to supraglenoid tubercle, small
Scapular notch
depression
Serrated face (medial) dorsal surface
subscapular fossa (medial) long depression below serrated face
coracoid process (medial) projection, dorsal to supragleniod tubercle
Infraglenoid tubercle (medial) small projection on right side of medial viewing
glenoid fossa socket on distal end
Humerus
Structure Placement
lateral to head of humerus, caudolateral to
Greater tubercle
lesser tubercle
small bony knob, medial and anterior to greater
Lesser tubercle
tubercle
space between greater and less tubercle, seen
intertubercle groove (lateral) - bicipital groove
in lateral view
tuberosity of teres minor (later) small depression behind head
crest of greater tubercle raised portion distal to greater tubercle
Bone Structure Outline 2
Structure Placement
deltoid tuberosity raised portion on the shaft
cranial -small depression to the left of deltoid
tuberosity for teres major
tuberosity, caudal - infra to lesser tubercle
brachialis groove (musculo-spiral) space on the majority of shaft, lateral view
radial fossa (cranial) depression above supratrochlear foramen
hole in distal part of humerus, nothing passes
supratrochlear foramen (dogs)
through
trochlea left distal portion connecting with capitulum
capitulum right distal portion connecting with trochlea
distal, inline with supratrochlear foramen
lateral epicondyle
(extension)
distal, medial and infra to supratrochlear
medial epicondyle
foramen (flexion)
olecranon fossa (caudal) depression on the distal portion
projection on lateral end, supra to olecranon
lateral supracondylar crest
fossa
condyle radial fossa, supratrochlear fossa and trochlea
Pectoral ridge (cats) supra to deltoid ridge
supracondyloid foramen (cats) opening on left side of humerus
coronoid fossa (cats) infra to supracondyloid foramen
Radius - bigger Ulna - longer
Structure Placement Structure Placement
small projection dorsal, semicircular
radial tuberosity olecranon
below head projection
projection at distal depression,
styloid process
end trochlear notch articulation with
trochlea of humerus
distal grooves (radial
spiral depression
groove) projection, forms
articulates with anconeal process trochlear notch. fits
capitular fovea articular fovea on into olecranon fossa
ulna
Bone Structure Outline 3
Structure Placement Structure Placement
distal, concave fovea projections from
coronoid process
articular face articulates with trochlear notch
carpal raised part distal to
distal articulation ulnar tuberosity medial coronoid
ulnar notch
with ulna process
capitular fovea and projection at distal
styloid process
head articular end
circumference depression between
radial notch
styloid process and coronoid processes
trochlea
articular face
dorsal to styloid
articular
process, articulation
circumference
with radius
Hindlimb
Acetabulum
Structure Placement
Acetabular Fossa cavity for articulation with fovea capitis
Acetabular notch ventral gap within ridge
Lunate surface deep to the rim, articular face
depression, dorsal to the margin of the hip
Greater ischiatic notch
bones
Iliopubic eminence connection of ilia and pubis, caudal
round ligament attached head of femur to acetabulum
Ilium
Structure Placement
Body of ilium dorsal portion of pelvic girdle
caudal dorsal iliac spine (tuber sacrale) small process from the back, top of ilia
caudal ventral iliac spine (tuber sacrale) small process from back, bottom of ilia
cranial dorsal iliac spine process caudal to iliac crest
cranial ventral iliac spine process cranial to iliac crest
Bone Structure Outline 4
Structure Placement
gluteal surface concave surface
most dorsal portion of ilium, palpable,
iliac crest
connection of muscles
tuber coxae hook, iliac tuberosity, ventral spines combined
tuber sacrale dorsal spines combined
wing of ilium two portions that extend towards vertebrae
Ischium
Structure Placement
ventral, lateral piece to make up the pelvic
Body of ischium
girdle
ischiatic spine articulation of ilium and ischium
ischiatic tuberosity pin, attachment for sacrotuberous ligament
ramus of ischium medial to obturator, fuses with ramus of pelvis
lesser ischiatic notch ventral to ischatic spine
obturator foramen opening between pubis and ischium
obturator sulcus small piece within the obturator
Pubis
Structure Placement
Body of pubis L-shaped, middle portion
caudal ramus medial border of obturator foramen
cranial border to obturator foramen, forms part
cranial ramus
of acetabulum
pecten sharp cranial border to cranial ramus
formed by right and left pectenes on ventral
pubic tubercle
midline
fusion of pubis symphyasis and ischii
Pelvic symphysis
symphysis
Femur
Bone Structure Outline 5
Structure Placement
pelvic osteology fovea capitis articulates with acetabulum
extensor fossa pit cranial to lateral epicondyle
facies aspera on the body, between the medial and lateral lips
femoral body “thigh”
spherical projection articulating with
femoral head
acetabulum
small cavity within head, provides attachment
fovea capitis femoris
for round ligament
femoral neck attaches the head to the neck
on distal cranial face, a deep groove for the
femoral trochlea
gliding of patella
greater trochanter lateral to head, insertion for gluteus muscles
distal, deep cavity, where the cruciate ligaments
intercondylar fossa
are found
distal to neck, small prominence seen in
intertrochanteric crest
mediocaudal aspect
lateral condyle attachment for lateral collateral ligaments
lateral epicondyle roughened prominence proximal to condyle
lateral supracondylar tuberosity caudal face, proximal to lateral condyle
mediocaudal aspect, distal to neck, small
lesser trochanter
prominence
medial condyle attachment for medial collateral ligaments
medial epicondyle roughened prominence proximal to condyle
medial supracondylar tuberosity caudal face, proximal to condyle
caudal face flattened, surrounded by medial
popiteal surface
and lateral supercondylar tuberosities
indistinct line distocaudal from greater
third trochanter
trochanter
deep space between head and greater
trochanteric fossa
trochanter
Tibia - shin
Bone Structure Outline 6
Structure Placement
body of tibia “true leg”, weight bearing bone
cranial border tibial crest, distal extension of tibial tuberosity
extensor groove cranial to lateral epicondyle
between surfaces of medial and later
intercondylar eminence
intercondylar tubercles
proximal projection for articulation with condyle
lateral condyle
of femur
proximal projection for articulation with condyle
medial condyle
of femur
medial malleolus distal articular surface
proximal end, deep pit dividing the condyles
popiteal notch
caudally
distal, two deep grooves that articulate with
tibial cochlea
talus
tibial tuberosity sharp prominence at cranial end
Fibula
Structure Placement
flattened, attached to tibia by interosseous
fibular body
membrane
proximally articulates with lateral condyle of
fibular head
tibia
lateral malleolus distal, palpable bony knob
Vertebrae
Axial skeleton - vertebral column and rib cage
Appendicular - pectoral girdle and limbs
C7 T13 L7 S3 Ca20-24
Spaces
space between of occipital condyles and cranial
Atlanto-occipital space
articular surface of atlas
Bone Structure Outline 7
atlanto-axial space space between c1 and c2
interarcuate space
thoracolumbar space between T13 and L1
Cervical vertebrae
C1 - ATLAS
Structure Placement
body reduced in mass
on C1, small depression for articulation of dens
fovea for dens
from C2
small ventral projection from caudal aspect of
ventral tubercle
body
modification of transverse processes into broad
wing
flat wings
proximal lateral and medial depression, notch is
alar notch (foramen)
in dogs/cats and foramen in all other species
caudolateral opening in the arch, cervical
lateral vertebral foramen
nerves passes
transverse foramen opening in the wing, vertebral artery passes
C2
Structure Placement
body spool-shaped
cranial articular surface articular fovea of articular processes
dens (odontoid process) prominent midline projection from cranial end
spinous process tall dorsal projection
transverse foramen opening cranial to transverse process
transverse process irregular caudoventral projection
Rest of cervical vertebrae
Structure Placement
transverse foramen absent in C7
Bone Structure Outline 8
Structure Placement
transverse process caudoventral projection
spinous process dorsal midline projection
caudal articular process caudal projection to the side of spinous process
cranial vertebral notch depression below spinous process
caudal vertebral notch depression below caudal articular process
costal fovea on C7, allows for the articulation of scapula
lamina dorsal part of arch
pedicles flattened dorsal part of arch
Thoracic
Structure Placement
vertebral foramen spinal cord passes through
mamilloarticular process small cranial projection
spinous process tall dorsal projection
caudal articular process 2 processes caudal to spinous process
accessory process medial projection to caudal articular process
transverse process lateral projection to caudal articular process
anticlinar pointed caudally, on T11, point of transition
Lumbar
Structure Placement
caudal vertebral notch aligns with cranial
intervertebral foramen vertebral notch and so on, creating opening for
spinal cord
accessory process caudal projection
transverse process long projection directed cranial
mamilloarticular (mamillary) process cranial short projection
cranial articular process projections
caudal articular process projections
spinous process long dorsal projection
Bone Structure Outline 9
Structure Placement
interarcuate space spaces between lumbar vertebrae arches
lumbosacral space space between L7 and sacrum
gel-like sac in between vertebrae bodies to
nucleus pulposus
provide shock absorption
ligament attaching spinous processes and
supraspinous ligament epaxial ligament in vertebrae column, known as
nuchae ligment
intraspinous ligament ligament inbetween spinous processes
interarcuate ligament attachment to arch
dorsal longitudinal ligament ligament across dorsal body of vertebrae
ventral longitudinal ligament ligament across ventral body of vertebrae
Sacrum
Structure Placement
sacral vertebrae each individual sacral vertebrae
spinous process tall dorsal projection
median sacral crest fusion of spinous processes
transverse process fused together with lateral sacral crest
promontary ventral articular process, articulates to L7
pelvic sacral foramina dorsal openings
surface that complements with auricular surface
auricular surface
of hip
sacroilia ligament attaches sacrum to ilia
Caudal
Structure Placement
body decreases in size after Ca2
arch decreases in size after Ca2
processes decreases in size after Ca2
small projection from hemal arch, does not fuse
hemal process
to body
Bone Structure Outline 10
Structure Placement
hemal arch bone v-shape arch on ventral aspect of caudal body
caudal articular process caudal projection
cranial articular process cranial projection
arch in horses incomplete, exposed
structures that attach to end of spinal cord,
caudal equina
gives innervention to tail (nerves)
Thorax
Ribs
Structure Placement
shaft body
projection to attach to transverse fovea of
tubercle
thoracic vertebrae
neck distal to head
angle distal to neck
costal groove attachment for coastal cartilage
Sternum
Structure Placement
manubrium first sternebra
sternebrae each individual sternum pieces
xiphoid process last sternebra
caudal attachment to xiphoid, attachment for
xiphoid cartilage
linea alba
costal arch asternal ribs, ribs 9-12
thoracic inlet consists of T1, 1st pair of ribs and manubrium
costochrondrial junction joint that joints ribs and cartilage
cartilage that is medial or lateral to
costal cartilage
intersternaebral cartilage
Bone Structure Outline 11
Structure Placement
intersternabra cartilage cartilage in between sternebra
Bone Structure Outline 12
You might also like
- Trunk Range of MotionDocument6 pagesTrunk Range of MotionacNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper ExtremitiesDocument1 pageBones of The Upper ExtremitiesChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- A New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullFrom EverandA New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Musculoskeletal System: AppendagesDocument16 pagesAnatomy of The Musculoskeletal System: AppendagesRyzeNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Shoulder?Document9 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Shoulder?VizaNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGeneral Anatomy of The Human BodyVarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityDocument12 pagesMuscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityKaren ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: Appendicular Skeleton: Cristagalliiiiii Anatomy Spring 14Document22 pagesLab 3: Appendicular Skeleton: Cristagalliiiiii Anatomy Spring 14trolling100% (1)
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and InsertionsFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Muscle Innervation Chart IIDocument7 pagesMuscle Innervation Chart IIkimsue9448No ratings yet
- Muscle Origin, Insertion and Action TableDocument12 pagesMuscle Origin, Insertion and Action TableCort07186% (14)
- Origin No JutsuuuuuuuuuDocument6 pagesOrigin No Jutsuuuuuuuuukristel amadaNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Thoracic LimbDocument10 pagesBones of The Thoracic LimbDelfin UrbanoNo ratings yet
- ForearmDocument4 pagesForearmVince Gabriel SotejoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Charts PDFDocument6 pagesMuscle Charts PDFVikrantNo ratings yet
- Barrios C 4 Parotid Gland and Infratemporal FossaDocument2 pagesBarrios C 4 Parotid Gland and Infratemporal FossaCarlo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Temporal Fossa & Infratemporal Fossa and Muscles of MasticationDocument22 pagesTemporal Fossa & Infratemporal Fossa and Muscles of Masticationpposs9220No ratings yet
- Summary of Nerves of Lower LimbDocument6 pagesSummary of Nerves of Lower LimbYusri Arif100% (6)
- Muscle Chart Upper ExtremityDocument3 pagesMuscle Chart Upper Extremitykep1313100% (1)
- Thoracic Wall To Upper Limb: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve SupplyDocument13 pagesThoracic Wall To Upper Limb: Muscle Origin Insertion Action Nerve SupplyShandria AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Bones of Upper LimbDocument13 pagesBones of Upper Limbapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy NotesDocument8 pagesNeuroanatomy NotesJustine May Gervacio100% (1)
- Muscles Crossing The Shoulder Joint: Movements of The Arm (Humerus)Document3 pagesMuscles Crossing The Shoulder Joint: Movements of The Arm (Humerus)sarahalaouieNo ratings yet
- Types of Bone Divided in To Four Classes: 1) Long Bone:dyaphysis (Body, Shaft), Epiphysis 2) Short Bone 3) Flate Bone 4) Irreglar BoneDocument31 pagesTypes of Bone Divided in To Four Classes: 1) Long Bone:dyaphysis (Body, Shaft), Epiphysis 2) Short Bone 3) Flate Bone 4) Irreglar Boneapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderDocument10 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Nerve Action Comment ShoulderAdam IrsyaddyraNo ratings yet
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 pagesSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴No ratings yet
- TEMPORAL AND INFRATEMPORAL FOSSAE Lecture-1Document62 pagesTEMPORAL AND INFRATEMPORAL FOSSAE Lecture-1Prashant Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- LIST OF MUSCLES and BONESDocument4 pagesLIST OF MUSCLES and BONESCyril Leigh Santos EstrellasNo ratings yet
- Head FactoidsDocument17 pagesHead FactoidsENo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomyfarahjurdi8No ratings yet
- Frog S Muscular System PDFDocument9 pagesFrog S Muscular System PDFVia CabardaNo ratings yet
- Gross B 2.20. Superficial Structures and Posterior Triangle of The NeckDocument6 pagesGross B 2.20. Superficial Structures and Posterior Triangle of The NeckShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 pagesElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- Upper Limb Muscles OnlyDocument7 pagesUpper Limb Muscles OnlyGwen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Labs 1 and 2: Muscular System Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Human Muscles: Unit 7, Muscle Tissue and Muscular SystemDocument10 pagesLabs 1 and 2: Muscular System Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Human Muscles: Unit 7, Muscle Tissue and Muscular SystemFranco AlminoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Temporal and Infratemporal FossaDocument8 pagesLecture 8 Temporal and Infratemporal Fossanatheer ayedNo ratings yet
- General Discription of MusclesDocument25 pagesGeneral Discription of Musclesapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Cat MusclesDocument5 pagesCat MusclesMisty VitoNo ratings yet
- UE Muscles OINADocument3 pagesUE Muscles OINAUshuaia Chely FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationDocument7 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb Muscles of The Back Superficial Back Proximal Distal Action InnervationKris GulleyNo ratings yet
- MUSCLES OINA LavarnDocument20 pagesMUSCLES OINA LavarnStray KidsNo ratings yet
- Lower Anatomy PT 2120Document29 pagesLower Anatomy PT 2120mahmoudmyoussef2001No ratings yet
- Basic Radiology PDFDocument104 pagesBasic Radiology PDFsimona mariana dutu100% (1)
- Кости На Горен КрайникDocument25 pagesКости На Горен КрайникEmma DanovaNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy - 9Document2 pagesGeneral Anatomy - 9ayaaqassimalmodafarNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Trans - MusclesDocument3 pagesGeneral Zoology Trans - MusclesKist Chealsea OjanoNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Joints - Quick Revision Table by Anatomy DecodedDocument8 pagesUpper Limb Joints - Quick Revision Table by Anatomy DecodedJuned LabbaiNo ratings yet
- SkullDocument26 pagesSkulldr.b1100100% (2)
- Muscles of The Human BodyDocument150 pagesMuscles of The Human BodyJoseph EpsteinNo ratings yet
- Tloy Inguinal Hernias Doc MedinaDocument11 pagesTloy Inguinal Hernias Doc MedinaJAM CHRISTINE MABBUNNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Bones: Bone Structure Bone Structure Clavicle UlnaDocument1 pageUpper Limb Bones: Bone Structure Bone Structure Clavicle Ulnaspeedy.catNo ratings yet
- Cranil ForaminaeDocument9 pagesCranil Foraminaemero1983No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy 11B 1 Semester, Sy 2017 LaboratoryDocument3 pagesNeuroanatomy 11B 1 Semester, Sy 2017 LaboratorymekonekoNo ratings yet
- U.L MusclesDocument4 pagesU.L Muscles54ytkq9mtgNo ratings yet
- Upper ExtremityDocument1 pageUpper ExtremityAiramel Shekina AlborNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocument11 pagesMuscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationNurul Afiqah Fattin AmatNo ratings yet
- Muscle OIAN - HandDocument3 pagesMuscle OIAN - Handanais MitchellNo ratings yet
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDocument3 pages2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanNo ratings yet
- A&P 1 Lab Exam 2 Review GuideDocument2 pagesA&P 1 Lab Exam 2 Review GuideMakenzie LyonNo ratings yet
- Thorax McqsDocument23 pagesThorax McqsBassamSheryanNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself ThoraxDocument29 pagesTeach Yourself ThoraxSambili Tonny100% (3)
- Figure Sculpting Tutorial ZbrushDocument10 pagesFigure Sculpting Tutorial ZbrushAfin Tulus N100% (5)
- People vs. Uycoque, Et Al., 246 SCRA 769, July 31, 1995Document18 pagesPeople vs. Uycoque, Et Al., 246 SCRA 769, July 31, 1995Harold Q. GardonNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesDocument2 pagesThorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesJean OpallaNo ratings yet
- Chest Wall Trauma: Sarah Majercik,, Fredric M. PieracciDocument9 pagesChest Wall Trauma: Sarah Majercik,, Fredric M. PieracciEviana AntikaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Sciences Diagnosis Laboratory Manual July 2008Document145 pagesClinical Sciences Diagnosis Laboratory Manual July 2008Michael KoontzNo ratings yet
- ARTHROLOGYDocument10 pagesARTHROLOGYAlina MoiseNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 5th Edition Saladin Full DownloadDocument34 pagesTest Bank For Anatomy and Physiology The Unity of Form and Function 5th Edition Saladin Full Downloadbrianbell06021999pfa100% (41)
- Lecture 3Document39 pagesLecture 3Anne XxNo ratings yet
- The Healing Art of Tenchi Seiki Te-AteDocument29 pagesThe Healing Art of Tenchi Seiki Te-AteJames Deacon100% (7)
- Sas 3 AnaphyDocument7 pagesSas 3 AnaphyClarrinne Geralence Galo RomoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 A.1 Axial BonesDocument7 pagesGroup 5 A.1 Axial BonesIsabella CariagaNo ratings yet
- Thoracotomy: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument19 pagesThoracotomy: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Preparations HistologyDocument6 pagesBone Marrow Preparations Histology365 DaysNo ratings yet
- Edan SE-2003 & SE-2012 Holter User ManualDocument43 pagesEdan SE-2003 & SE-2012 Holter User Manualfpanci100% (2)
- The Human Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Human Skeletal SystemHelenPetersenNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic WallDocument27 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic WallSamuel Pola Karta Sembiring100% (1)
- Corpsman Pt1Document140 pagesCorpsman Pt1David Radcliffe100% (1)
- Dim Mak AnatomyDocument6 pagesDim Mak Anatomyloy7100% (6)
- Anatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Document24 pagesAnatomy, Lecture 3, Thoracic Wall (1) (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Chest, Dr. Hasan Nyambe PDFDocument45 pagesStructure of Chest, Dr. Hasan Nyambe PDFAndi Meidin AnugerahNo ratings yet
- What Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Skeletal System?: Axial Skeleton AnatomyJared RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Document17 pagesThe Skeletal System Human Body (206) Axial Skeleton (80) Skull (28) A. Paired Bones (11x2 22)Leo Cordel Jr.No ratings yet
- Surface Anat of ThoraxDocument42 pagesSurface Anat of ThoraxSyed NangyalNo ratings yet
- OIA of Cat MusclesDocument8 pagesOIA of Cat Musclesksdfsd8903No ratings yet
- Muscles of The Thorax Back AbdomenDocument30 pagesMuscles of The Thorax Back AbdomenPeeyush100% (1)
- Autologous Rib Microtia Construction: Nagata TechniqueDocument15 pagesAutologous Rib Microtia Construction: Nagata Techniqueandi ilmansyahNo ratings yet
- Clavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyDocument24 pagesClavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyBishal Chauhan100% (1)