Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AGK - Electrics 1 Introduction S1
Uploaded by
Cemalettin öztoprak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesatpl
Original Title
AGK_Electrics 1 Introduction S1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentatpl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views11 pagesAGK - Electrics 1 Introduction S1
Uploaded by
Cemalettin öztoprakatpl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
AGK Electrics
Lesson 1: Introduction and Basic Principles
Aircraft Electrical System
• Electrics is about the creation, distribution and
storage of power.
• Electronic devices need electrical power in order to
function and electrical systems will require electronic
systems for control purposes.
• Generates electrical energy to be used by
components
• Light training aircraft 14 volt DC system
• Larger twin turbine aircraft 28 volt DC system
• Modern jet airliner 115/200 V AC system
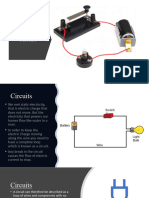
Electrical Currents
• An electric current is produced when electrons are
encouraged to flow through a conductor.
• Current flow when circuit is complete or closed
• One direction only is direct current or DC.
• When electrons first move one way and then back
the other way is alternating current or AC.
• Direct current - one direction
• Alternating current - changes direction
The Atom
• An electron is part of an atom. Every
substance we know of is made up of a
number of atoms, different materials
having different make up of their
atoms.
• An atom consists of Protons (which
have a positive charge) Electrons
(which have a negative charge) and
Neutrons which have no charge.
The Atom
• Each atom has the same number of
electrons as protons therefore making
the atom electrically neutral.
• Electrons surround the nucleus may be
encouraged to move from atom to atom
referred to as ‘free electrons’
• Electrons which resist movement
between atoms are referred to as
insulators.
• Electrons that can be moved from atom
to atom through the structure are
referred to as conductors.
Materials
• Insulators - bound electrons resist
movement
• Conductors - movable electrons
• Semiconductors act like an insulator but
after processing can be made to act like a
conductor.
The Driving Force
• Battery supplies energy to push electrons
through a closed circuit
Electromotive Force
• Battery has two electrodes separated by an electrolyte.
• Contains many ions.
• Very electrically conductive
Chemical reaction removes electrons from one
electrode and adds them to the other.
Negatively charged electrons in the conductor are
attracted towards the positive terminal.
Produces a positive terminal and a negative terminal.
Electromotive Force
• The difference in charge between the two
electrodes is the electrical potential.
• Provides the motive force to move electrons around
the circuit
• Closed circuit – current flows, open circuit – no
current flows.
• Negative to positive is called ‘electron flow’
assumed flow from positive to negative
‘conventional flow’
You might also like
- Ortiz-PPT Electricity, Electromagnetism, Alternators, MotorsDocument49 pagesOrtiz-PPT Electricity, Electromagnetism, Alternators, MotorsJose Maria Ortiz100% (1)
- Good Morning: Grade 5-St - PaulDocument27 pagesGood Morning: Grade 5-St - PaulLouie Ramos IralNo ratings yet
- Electricity Intro Powerpoint 2017Document10 pagesElectricity Intro Powerpoint 2017api-325864985No ratings yet
- 02-Lecture-BE-Fundamentals ConectpsDocument14 pages02-Lecture-BE-Fundamentals ConectpsAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument15 pagesElectrical Energyanuj sethNo ratings yet
- Low Frequency Currents 1st BPT ChiragDocument221 pagesLow Frequency Currents 1st BPT ChiragchiragNo ratings yet
- Study of Components Part I (Resistors) - 1Document34 pagesStudy of Components Part I (Resistors) - 1Atharva DhumalNo ratings yet
- Electrical SystemsDocument30 pagesElectrical Systemsshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument32 pagesCircuitsaleenawaltersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 BennetDocument54 pagesChapter 05 BennetpapipapiiNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Grade 9Document9 pagesElectricity - Grade 9nidda beeNo ratings yet
- FC-03-Basic Electrical & Electronics PDFDocument298 pagesFC-03-Basic Electrical & Electronics PDFDinesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document34 pagesLecture 01Zahin KhanNo ratings yet
- Building ConstructionDocument13 pagesBuilding Constructionaakash purohitNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Chap 7 - Electricity (Autosaved)Document41 pagesForm 2 - Chap 7 - Electricity (Autosaved)YeLynTanNo ratings yet
- X PPT CH 12 ElectricityDocument12 pagesX PPT CH 12 ElectricityAakritiNo ratings yet
- Y4 UNIT 5 Electricity & MagnetismDocument67 pagesY4 UNIT 5 Electricity & MagnetismPavithra SinnananNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Electrical Circuits - PowerpointDocument48 pagesElectricity and Electrical Circuits - PowerpointtuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Electrical Theory and CircuitsDocument142 pagesUnit 1 - Electrical Theory and CircuitsBinodSah100% (1)
- Building Electrical SystemsDocument24 pagesBuilding Electrical SystemsCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Electricity 5Document30 pagesElectricity 5Devika ManiNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: For: Navodaya School KidsDocument22 pagesElectrostatics: For: Navodaya School KidsVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electricity NotesDocument24 pagesElectricity NotesTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Lessons 7 & 8 Types of Electricity & Parts of CircuitDocument49 pagesScience 5 Lessons 7 & 8 Types of Electricity & Parts of Circuitclyde domingoNo ratings yet
- Practical English 1: Universidad Internacional Del EcuadorDocument16 pagesPractical English 1: Universidad Internacional Del EcuadorfabinhobajNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - IntroductionDocument38 pagesWeek 1 - Introductionmohammad aljihad bin mohd jamal FJ1No ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument23 pagesPRELIMJames SelibioNo ratings yet
- Ee-101 Basic Electrical Engineering: Voltage & Current Engr. Mashal Fatima Lecture No 1Document25 pagesEe-101 Basic Electrical Engineering: Voltage & Current Engr. Mashal Fatima Lecture No 1Mashal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Utilities Module 1Document24 pagesUtilities Module 1Camille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- PDF BirleşmişDocument287 pagesPDF BirleşmişZAMAZİNGONo ratings yet
- CBR PhilosophyDocument9 pagesCBR Philosophykhairina rangkutiNo ratings yet
- Q1L7 ElectricityDocument61 pagesQ1L7 ElectricityCarmella Raguindin100% (1)
- The Simple CircuitDocument10 pagesThe Simple CircuitMonique ReidNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics CHAPTER 3Document39 pagesMechatronics CHAPTER 3NahomNo ratings yet
- Unit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsDocument21 pagesUnit II Electrical Circuits: Basic Circuit Element and Their CombinationsMonte CarloNo ratings yet
- Main Topic Ce0053Document49 pagesMain Topic Ce0053JOSHUA MEYER ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Electricity ElectromagnetismDocument73 pagesElectricity ElectromagnetismDanish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electronics by Sir JoelDocument47 pagesElectronics by Sir JoelDann SarteNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesElectricity and MagnetismLakwatserong GuroNo ratings yet
- Electricity 5Document13 pagesElectricity 5Yakoob LiyaudeenNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Electricity: UNIT-1Document32 pagesBasic Concepts of Electricity: UNIT-1santhoshkumar KVNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PassiveActiveDocument25 pagesLesson 2 PassiveActiveManuel SapaoNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Electromagnetism - Alternators-MotorsDocument14 pagesElectricity - Electromagnetism - Alternators-MotorsfrankNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument37 pagesBasic Electronicsanon_692888401No ratings yet
- INTRO MOD 2 Fundamentals Rev2015 JuneDocument275 pagesINTRO MOD 2 Fundamentals Rev2015 Junesrikanth jeripothulaNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Revision NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Revision NotesAnsh DhandiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Unit 3: Electricity: Chapter 8: Ohm's LawDocument19 pagesGrade 9 Science Unit 3: Electricity: Chapter 8: Ohm's LawSquazzyNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Class X Science Subhasish MohantaDocument31 pagesElectricity: Class X Science Subhasish MohantasubhaNo ratings yet
- Class X - Electricity PPT Final ModifiedDocument32 pagesClass X - Electricity PPT Final Modified9C31 MOHNISH MNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document77 pagesLecture 1عقيل الفهداويNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits - Learning OutcomesDocument10 pagesElectrical Circuits - Learning OutcomesonaaaaangNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit ComponentsDocument40 pagesElectrical Circuit Componentsdarcyforan97No ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.Document49 pagesLecture 1-Electrical Elements - Series & Parallel Circuits.MAENYA BRUCE OYONDINo ratings yet
- Unit-1 DC CircuitsDocument44 pagesUnit-1 DC CircuitsLatha BarlaNo ratings yet
- Components of A CircuitDocument14 pagesComponents of A Circuitapi-310503032No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Electricityjustin christopher antonioNo ratings yet
- Systems 4 Hydraulic Principles S15 PDFDocument37 pagesSystems 4 Hydraulic Principles S15 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 9 Practical CircuitsDocument23 pagesAGK - Electrics 9 Practical CircuitsCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 13 Switches 21Document21 pagesAGK - Electrics 13 Switches 21Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 10 Semiconductors (1) S1Document16 pagesAGK - Electrics 10 Semiconductors (1) S1Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 1 Introduction S1Document11 pagesAGK - Electrics 1 Introduction S1Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 22 AC Motor 8 S1Document8 pagesAGK - Electrics 22 AC Motor 8 S1Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 22 AC Motor 8 S1Document8 pagesAGK - Electrics 22 AC Motor 8 S1Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 21 AC Generation 41 S21 PDFDocument41 pagesAGK - Electrics 21 AC Generation 41 S21 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 20 AC Power 11 S3Document12 pagesAGK - Electrics 20 AC Power 11 S3Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Engines 18 Exhaust System PDFDocument24 pagesEngines 18 Exhaust System PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 13 Switches 21Document21 pagesAGK - Electrics 13 Switches 21Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Systems 10 Pneumatic Systems PDFDocument21 pagesSystems 10 Pneumatic Systems PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Engines 22 APU PDFDocument14 pagesEngines 22 APU PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Systems 4 Hydraulic Principles S15 PDFDocument37 pagesSystems 4 Hydraulic Principles S15 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Engines 22 APU PDFDocument14 pagesEngines 22 APU PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Systems 12 Anti-Icing De-Icing S29 PDFDocument65 pagesSystems 12 Anti-Icing De-Icing S29 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Systems 14 Fire and Smoke Protection S23 PDFDocument59 pagesSystems 14 Fire and Smoke Protection S23 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- GDH PPL (A) Question Bank (Eng)Document358 pagesGDH PPL (A) Question Bank (Eng)CafeNet Girne100% (2)
- Systems 15 Oxygen Systems S51 PDFDocument76 pagesSystems 15 Oxygen Systems S51 PDFCemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics July 2013 PDFDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics July 2013 PDFH S Vishwa NathNo ratings yet
- Imagine:: The Stanford Team's Solar Car, SolsticeDocument5 pagesImagine:: The Stanford Team's Solar Car, SolsticestanscimagNo ratings yet
- Report of Safety and Health OrganizationDocument1 pageReport of Safety and Health OrganizationМарк Артём Лимот АпаллаNo ratings yet
- M.sc. Thesis EEDI (Final Copy)Document164 pagesM.sc. Thesis EEDI (Final Copy)manon16050% (2)
- Ibr BookDocument33 pagesIbr BookRaja JayachandranNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Thermalia (R) Dual (55-140) Dual H (35-90) - ExA - 111016Document28 pagesBrochure - Thermalia (R) Dual (55-140) Dual H (35-90) - ExA - 111016Nur Rachman HardiantoNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Energy in Food and During Physical ActivityDocument25 pagesMeasurement of Energy in Food and During Physical Activitykrissh20No ratings yet
- 1 50 MechanicsDocument8 pages1 50 MechanicsMarco AlfantaNo ratings yet
- Controladores Dixell Xm678d GBDocument14 pagesControladores Dixell Xm678d GBReinaldo MarquesNo ratings yet
- IE Rules 1956 As Amended On 25 Dec, 2000 by Central Electricity Board On 26 June, 1956 by Section 37 of Indian Electricity Act, 1910Document3 pagesIE Rules 1956 As Amended On 25 Dec, 2000 by Central Electricity Board On 26 June, 1956 by Section 37 of Indian Electricity Act, 1910ARNAB KAMILYANo ratings yet
- 03.5 - FPFF - Fire Preventing and FightingDocument78 pages03.5 - FPFF - Fire Preventing and FightingkunaalNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II - (2014-2015) Subject: SCIENCE Class: VIII Time 2: 30 Hrs. + 30 Mins For OTBA M.M. 60 General InstructionsDocument3 pagesSUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II - (2014-2015) Subject: SCIENCE Class: VIII Time 2: 30 Hrs. + 30 Mins For OTBA M.M. 60 General InstructionsMd ImranNo ratings yet
- CMAT Model Question - 4Document11 pagesCMAT Model Question - 4Ankit SubediNo ratings yet
- D 5682 - 95 Rdu2oditotuDocument4 pagesD 5682 - 95 Rdu2oditotuwpwmhatNo ratings yet
- Ik-Flex SheetsDocument8 pagesIk-Flex SheetsSathish P Sathish PalanichamyNo ratings yet
- BE MechDocument218 pagesBE MechBala RaviNo ratings yet
- Chem Principles 7e ISM Focus 04 Even FINALDocument62 pagesChem Principles 7e ISM Focus 04 Even FINALSelma MeloNo ratings yet
- Btech Civil 7to8semDocument62 pagesBtech Civil 7to8semfanishNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fuel Reserves - Cherrish Khera, 2060, AECC EVS Assignment 2022Document12 pagesNuclear Fuel Reserves - Cherrish Khera, 2060, AECC EVS Assignment 2022Gautam DohareyNo ratings yet
- Hit 7300 Epd PDFDocument44 pagesHit 7300 Epd PDFkupeoNo ratings yet
- Manual de Utilizare Ventilator MUB - 100 - 710DV - SileoDocument24 pagesManual de Utilizare Ventilator MUB - 100 - 710DV - SileopintileirobertNo ratings yet
- Grundfos - CR 15 10 A F A E HQQE PDFDocument15 pagesGrundfos - CR 15 10 A F A E HQQE PDFdimasNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar On VFDDocument17 pagesTechnical Seminar On VFDRadhika Priyadarshini100% (7)
- Hy Wire CarsDocument21 pagesHy Wire CarsNaresh VarikolluNo ratings yet
- 9701 s10 Ms 21Document8 pages9701 s10 Ms 21Hubbak Khan100% (1)
- CHM 1045 Chapter 1 Worksheet - AnswersDocument4 pagesCHM 1045 Chapter 1 Worksheet - AnswersLarry MolinerosNo ratings yet
- Clg920 ExcavatorDocument2 pagesClg920 Excavatortomas liu100% (1)
- Datasheet - Product Insert 6inch 750psi 300ansiDocument1 pageDatasheet - Product Insert 6inch 750psi 300ansihendry_hdwNo ratings yet
- H21SEM: Group A13Document28 pagesH21SEM: Group A13TsukomaruNo ratings yet