Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ball Charge
Uploaded by
irfanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ball Charge
Uploaded by
irfanCopyright:
Available Formats
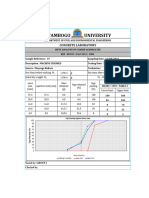
Raw Materials Granulometry:
Sampling Point Sieve %Retained
[mm]
25 12.5 9.5 4.75 2.36 1.18
A Mill Feed slag 100.00% 0.0 5.0 10.0 20.0 25.0 32.0
B Clay Mix. 0.00% 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
C1 Iron Ore 0.00% 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
C2 Limestone 0.00% 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
C3 Silica Sand 0.00% 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
100.0% 0.0 5.0 10.0 20.0 25.0 32.0
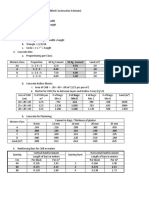
Max. Ball Size Calculation:
d80 [µm] ρ [g/cm3] Wi [kwh/t] K Ψ [%] Du [m] Ømax [mm]
slage 9000 2.83 10.35 335 73 3.65 62.1
Mix 0 0 0 0 0 0 #DIV/0!
Iron Ore 0 0 0 0 0 0 #DIV/0!
d80 [µm] Mesh: size of the sieveing where 80% of material is Passing
ρ [g/cm3] density of material
Wi [kwh/t] Work Index
K Factor (335 for dry grinding (OC or CC), 350 for wet grinding)
Ψ [%] % of Critical Speed (mill)
Du [m] Effective Di of the mill
Ømax [mm] Maximum Ball size
Ball Charge Distribution:
From to Slag Granulometry
Material: EB d180: d280: WB: Energy %Passing d280: WB: Energy Diam ton
Slag 10.35 7000 90 9.7 18.0% 85.0% 90 8.22 25.4% 60-50 13.7
5000 80 10.1 18.9% 80.0% 80 8.09 25.0% 50-40 13.5
4000 50 13.0 24.3% 75.0% 50 9.75 30.2% 40-30 16.3
2000 20 20.8 38.9% 30.0% 20 6.25 19.3% 30-25 10.4
53.6 100.0% 100% 54.0
10 10 EB: Bond ‘s work index,
`WB E B d180: fresh feed particle size for which there is 80 [%] of passing,
d 280 d180
d280: final product particle size for which there is 80 [%] of passing,
WB: specific energy consumption [kWh/t].
You might also like
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- Styrofoam ResultsDocument5 pagesStyrofoam Resultsmpairwe cliffortNo ratings yet
- Marshall Stability Test PDFDocument8 pagesMarshall Stability Test PDFAnonymous FO4sHLLONo ratings yet
- FM200 Cal1Document2 pagesFM200 Cal1Flash GuaranteeNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document7 pagesCH 1Clark Jallen RamosNo ratings yet
- Design of Shotcrete ConcreteDocument8 pagesDesign of Shotcrete ConcreteDevinder SokhiNo ratings yet
- Consistency Test of Cement: ResultsDocument11 pagesConsistency Test of Cement: Resultsnira365No ratings yet
- 5 To 10 MM AGGREGATE SIEVEDocument1 page5 To 10 MM AGGREGATE SIEVENajma BatoolNo ratings yet
- Odogwu 0359 - FinalDocument31 pagesOdogwu 0359 - FinalAbdullahi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Analisa Saringan Bahan: Asal: No. Saringan Berat B. Saringan Berat Kode MM Saringan Sampel TertahanDocument12 pagesAnalisa Saringan Bahan: Asal: No. Saringan Berat B. Saringan Berat Kode MM Saringan Sampel TertahanMaksi MilianusNo ratings yet
- Untitled1 PDFDocument36 pagesUntitled1 PDFJulius OgowewoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix DesignDocument12 pagesConcrete Mix DesignAnand.5No ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document2 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Noor MohdNo ratings yet
- Lab Test 2Document1 pageLab Test 2Kakulu Paul MutatiinaNo ratings yet
- 07 - Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregate (19-10mm) (Astm c136) (Rswtp-01-Hcg-qc-g00-Tp-0007)Document1 page07 - Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregate (19-10mm) (Astm c136) (Rswtp-01-Hcg-qc-g00-Tp-0007)Mahmudul MasumNo ratings yet
- COLUMNDocument53 pagesCOLUMNUmesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Estate Soil Investigation ResultsDocument10 pagesIndustrial Estate Soil Investigation ResultsGerryBoD.BagtasJr.No ratings yet
- Sieve and Hydrometer Results of Dry Bin Crosby TillDocument2 pagesSieve and Hydrometer Results of Dry Bin Crosby TillAJR365No ratings yet
- Quality Control Services Testing LabDocument2 pagesQuality Control Services Testing Labraju_420034520No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Material Q.T.ODocument10 pagesCivil Engineering Material Q.T.ONaison StanleyNo ratings yet
- Old Test SheetDocument13 pagesOld Test SheetImran SikandarNo ratings yet
- Filter Snd.Document8 pagesFilter Snd.Okello StevenNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials Granulometry and Ball Charge DesignDocument11 pagesRaw Materials Granulometry and Ball Charge DesignKaran_Agarwal_4807100% (2)
- Gradation Chart (Soil) : Sieve Size (MM)Document5 pagesGradation Chart (Soil) : Sieve Size (MM)Imtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Cone Penetration Test Result (Cpt/Sondir) : Testing Point S-1Document2 pagesCone Penetration Test Result (Cpt/Sondir) : Testing Point S-1rifqi bambangNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis ReportDocument1 pageSieve Analysis ReportBaluku BennetNo ratings yet
- M25 Mix Design 100 Recycled AggregateDocument9 pagesM25 Mix Design 100 Recycled AggregateRakesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Soil and Materials SurveyDocument17 pagesSoil and Materials SurveyDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Connesction Apex Hauncs l.6,8&7Document6 pagesConnesction Apex Hauncs l.6,8&7Khadafi Dwi AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Cost Index City 3 VDocument2 pagesCost Index City 3 VSHAILENDRANo ratings yet
- Estimates Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesEstimates Cheat SheetKyreen100% (1)
- Sand Sieve 7-2023Document2 pagesSand Sieve 7-2023hamedmustafa093No ratings yet
- Calculos Rampa - Cut and Fill Post PilllarDocument51 pagesCalculos Rampa - Cut and Fill Post PilllarCadelaguNo ratings yet
- D) Gradation of Coarse AggregateDocument6 pagesD) Gradation of Coarse Aggregatechitranjan4kumar-8No ratings yet
- Measuring rainfall runoff using hydrographsDocument6 pagesMeasuring rainfall runoff using hydrographsAmro Ahmad RosidinNo ratings yet
- Effects of Glass Fibers on Concrete PropertiesDocument10 pagesEffects of Glass Fibers on Concrete PropertiesChris ArtecoNo ratings yet
- Caracterizacao Dos InertesDocument7 pagesCaracterizacao Dos InertesHamilton PedroNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Test Calculations & Particle Size Distribution CurveDocument6 pagesSieve Analysis Test Calculations & Particle Size Distribution CurveZeeshan aliNo ratings yet
- CONSTRUCTION OF PATENGA CONTAINER TERMINAL (PCT) SIEVE ANALYSISDocument4 pagesCONSTRUCTION OF PATENGA CONTAINER TERMINAL (PCT) SIEVE ANALYSISEngr.Estiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- M40 Grade Concrete Mix Design As Per ACI MethodDocument7 pagesM40 Grade Concrete Mix Design As Per ACI Methodugrasen chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Elongation Index For Coarse Aggregate22mmDocument2 pagesElongation Index For Coarse Aggregate22mmMarwa AlasheebiNo ratings yet
- 06 - Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregate (19-5mm) (Astm c136) (Rswtp-01-Hcg-qc-g00-Tp-0006)Document1 page06 - Sieve Analysis of Coarse Aggregate (19-5mm) (Astm c136) (Rswtp-01-Hcg-qc-g00-Tp-0006)Mahmudul MasumNo ratings yet
- Sl. No Work Description Qty Unit: P.C.C Using WET MIX + CementDocument8 pagesSl. No Work Description Qty Unit: P.C.C Using WET MIX + CementrangarajanNo ratings yet
- M30 Concrete Mix DesignDocument4 pagesM30 Concrete Mix DesignrajupetalokeshNo ratings yet
- Coarse: Aggregate Test ResultsDocument24 pagesCoarse: Aggregate Test ResultsMahendar ErramNo ratings yet
- PT Paver Strength CalculationsDocument3 pagesPT Paver Strength CalculationsEr Narayan ApawatNo ratings yet
- Product information 【MIGHTY 21WH】Document2 pagesProduct information 【MIGHTY 21WH】Khin Sandi KoNo ratings yet
- CA (15-25 MM) Gradation For ConcreteDocument1 pageCA (15-25 MM) Gradation For ConcreteAdrian FrantescuNo ratings yet
- 10 SandDocument5 pages10 SandSAFE SERVICES LHRNo ratings yet
- HITUNGAN STEEL 1Document1 pageHITUNGAN STEEL 1lutfiNo ratings yet
- CIVN3004 LAB REPORT (Group 9)Document6 pagesCIVN3004 LAB REPORT (Group 9)Kavish DayaNo ratings yet
- SGL Datasheet SIGRAFINE Materials For Mechanical Applications ENDocument2 pagesSGL Datasheet SIGRAFINE Materials For Mechanical Applications ENMayur PattanshettiNo ratings yet
- VIL Aggregate Particle Size Distribution TestDocument1 pageVIL Aggregate Particle Size Distribution TestIsaiahogedaNo ratings yet
- 05 - SIEVE ANALYSIS OF COARSE AGGREGATE (10-5mm) (ASTM C136) (RSWTP-01-HUN-QC-G00-TP-0005)Document1 page05 - SIEVE ANALYSIS OF COARSE AGGREGATE (10-5mm) (ASTM C136) (RSWTP-01-HUN-QC-G00-TP-0005)Mahmudul MasumNo ratings yet
- Combined Gradation of Aggregates Project Consultant Contractor Mix Identification No. Sample Deasription Sampling Method Test Method LocationDocument9 pagesCombined Gradation of Aggregates Project Consultant Contractor Mix Identification No. Sample Deasription Sampling Method Test Method LocationAndrew MwambaNo ratings yet
- Concrete MixDocument69 pagesConcrete MixRATNA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Build Up RateDocument10 pagesBuild Up RateNurul Farhanah100% (2)
- Effects of Ash in ClinkerDocument16 pagesEffects of Ash in ClinkerirfanNo ratings yet
- Raw Mix Design SoftwareDocument6 pagesRaw Mix Design SoftwareIrfan Ahmed100% (1)
- Rawmix DesignDocument2 pagesRawmix DesignBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- OPC PILE DESIGN Calculation - (Complete) 2Document7 pagesOPC PILE DESIGN Calculation - (Complete) 2Irfan Ahmed0% (1)
- Cement Mill1CheckListforStartupDocument1 pageCement Mill1CheckListforStartupirfanNo ratings yet
- Fuel Price DifferenceDocument1 pageFuel Price DifferenceirfanNo ratings yet
- Conveyor CalculationDocument40 pagesConveyor CalculationAnonymous 5XvUbWynnNo ratings yet
- Coal ConversionDocument3 pagesCoal ConversionIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Rawmix DesignDocument2 pagesRawmix DesignBùi Hắc HảiNo ratings yet
- Heat AnalysisDocument33 pagesHeat AnalysisirfanNo ratings yet
- LINE-2 PYRO PROCESS SITE DATA FOR BHARATHI CEMENTS KADAPADocument44 pagesLINE-2 PYRO PROCESS SITE DATA FOR BHARATHI CEMENTS KADAPAirfanNo ratings yet
- Plant InvesticationDocument3 pagesPlant InvesticationirfanNo ratings yet
- Cement Clinker Calculus,: 2.0% Lime Stone 8.0% Clay 1.0% Iron Ore 2.0% Siliceous SandDocument4 pagesCement Clinker Calculus,: 2.0% Lime Stone 8.0% Clay 1.0% Iron Ore 2.0% Siliceous SandirfanNo ratings yet
- Bypass SystemDocument9 pagesBypass SystemirfanNo ratings yet
- MASS BALANCE SUMMARYDocument51 pagesMASS BALANCE SUMMARYirfan100% (1)
- Velocity Profiles: SLC 6-Stage II-String: Vol. Flow, WDocument1 pageVelocity Profiles: SLC 6-Stage II-String: Vol. Flow, WirfanNo ratings yet
- Cement Kiln Pyro BalanceDocument45 pagesCement Kiln Pyro BalanceirfanNo ratings yet
- By Pass System in The Dry ProcessDocument16 pagesBy Pass System in The Dry Processirfan100% (1)
- Barometric pressure and steam generation calculationsDocument4 pagesBarometric pressure and steam generation calculationsirfanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.1 Process Kiln SystemsDocument61 pagesLecture 5.1 Process Kiln SystemsirfanNo ratings yet
- Cast Astimaton For Local CoalDocument1 pageCast Astimaton For Local Coalirfan100% (1)
- Kiln FormulasDocument189 pagesKiln FormulasirfanNo ratings yet
- PDF Kiln Heat and Mass BalanceDocument20 pagesPDF Kiln Heat and Mass BalanceirfanNo ratings yet
- MEDIACalculator (Raw Mill2)Document4 pagesMEDIACalculator (Raw Mill2)irfanNo ratings yet
- 1705 N Technical Data: 1 Sprokets D.E N.DDocument1 page1705 N Technical Data: 1 Sprokets D.E N.DirfanNo ratings yet
- Coal Mixing Calculations:: Mineral MatterDocument2 pagesCoal Mixing Calculations:: Mineral MatterirfanNo ratings yet
- Heat AnalysisDocument33 pagesHeat AnalysisirfanNo ratings yet
- Radiation Calculation For Kiln 1 (From Kiln Outlet)Document32 pagesRadiation Calculation For Kiln 1 (From Kiln Outlet)irfanNo ratings yet
- Annex 16.1 & 16.2: Mill calculation plant dimensions and filling degree formulasDocument2 pagesAnnex 16.1 & 16.2: Mill calculation plant dimensions and filling degree formulasIrfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Coal GCV &NCVDocument1 pageCoal GCV &NCVirfanNo ratings yet
- Functions and Applications of Geosynthetics in Roadways: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesFunctions and Applications of Geosynthetics in Roadways: SciencedirectNurul SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Corrugated Board Grades GuideDocument3 pagesCorrugated Board Grades Guidejeziel salazar0% (1)
- En 10025 Equivalent CodingDocument56 pagesEn 10025 Equivalent CodingLeonardoNo ratings yet
- F 482 - 84 R99 Rjq4mi1sruqDocument7 pagesF 482 - 84 R99 Rjq4mi1sruqJuanNo ratings yet
- Manual Injection MoldingDocument5 pagesManual Injection MoldingM. AhmadNo ratings yet
- TEST 4 SolutionDocument2 pagesTEST 4 SolutionBasm IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Stress and StrainDocument72 pagesChapter 1 - Stress and StrainNazhan HaziqNo ratings yet
- Expanding Cryogenic Liquids with Flashing Liquid Expanders (FLEsDocument18 pagesExpanding Cryogenic Liquids with Flashing Liquid Expanders (FLEsPhilip ShihNo ratings yet
- IS 2190 - Fire ExtinguishersDocument35 pagesIS 2190 - Fire ExtinguishersNoel Federer SarkarNo ratings yet
- LASER FERITI CERTIFICATE OF QUALITYDocument1 pageLASER FERITI CERTIFICATE OF QUALITYdario_791473996No ratings yet
- Sae Technical Paper Series: Gerhard FischerDocument10 pagesSae Technical Paper Series: Gerhard FischerHakim Sakib100% (1)
- Engineering Structures: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesEngineering Structures: SciencedirectMahmoud AbbassNo ratings yet
- Nanocharacterisation, 2007, p.319 PDFDocument319 pagesNanocharacterisation, 2007, p.319 PDFMaria Ana Vulcu100% (1)
- Dupont Nomex 818: Technical Data SheetDocument6 pagesDupont Nomex 818: Technical Data SheetSNX11No ratings yet
- Jar Test Water TreatmentDocument5 pagesJar Test Water TreatmentKhaiiiNo ratings yet
- Equipment Design HW01Document4 pagesEquipment Design HW01Grin NikiforovNo ratings yet
- Drying of Pipelines Prior To Commissioning - CEPS A.SDocument6 pagesDrying of Pipelines Prior To Commissioning - CEPS A.Sim4uim4uim4uim4uNo ratings yet
- Dilutions Worksheet SolutionsDocument4 pagesDilutions Worksheet SolutionsAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification JKR RoadDocument3 pagesStandard Specification JKR RoadChin Thye100% (2)
- Stainless Steel: High Ni & CR Content Low (Controlled) InterstitialsDocument62 pagesStainless Steel: High Ni & CR Content Low (Controlled) Interstitialstbmari50% (2)
- Metal SizesDocument2 pagesMetal Sizesjohnphilip1No ratings yet
- Laundry Soap PDFDocument4 pagesLaundry Soap PDFAjay Prajapati100% (1)
- III-Basics of Continuum Mechanics-StressDocument22 pagesIII-Basics of Continuum Mechanics-StressMirza Muneeb AhsanNo ratings yet
- Hg ASTM Thermometers CatalogDocument4 pagesHg ASTM Thermometers CatalogmegacobNo ratings yet
- Atlas Users1Document1,533 pagesAtlas Users1Алексей ЗавгороднийNo ratings yet
- (Paper) IRC Rehabilitation of Sharavathi BridgeDocument24 pages(Paper) IRC Rehabilitation of Sharavathi BridgeRAJENDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Jr.C-120 - Jee-Adv - WTA-06 - Question PaperDocument15 pagesJr.C-120 - Jee-Adv - WTA-06 - Question PaperMurari MarupuNo ratings yet
- Compaction Test (Soil II)Document21 pagesCompaction Test (Soil II)ZaimHarith100% (1)
- CHAPTER 3 Phase Diagram TTT HT - 1stDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 3 Phase Diagram TTT HT - 1stAriff AziziNo ratings yet
- Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel - Part 2 - TWIDocument6 pagesWelding of Austenitic Stainless Steel - Part 2 - TWISumantaNo ratings yet