Professional Documents
Culture Documents
19 Meconium Aspiration
19 Meconium Aspiration
Uploaded by
Yassboy MsdOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
19 Meconium Aspiration
19 Meconium Aspiration
Uploaded by
Yassboy MsdCopyright:
Available Formats
SOP 19: NCU
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
A condition in which a newborn aspirated meconium-stained amniotic fluid
after passing meconium in-utero and develops respiratory distress
Risk Factors Clinical Features
- Post-term delivery - Onset: Immediately or a few hours after birth
- Fetal distress - Respiratory distress
- Perinatal asphyxia - Cyanosis/hypoxia
- Maternal infection or - Meconium-stained skin/umbilical cord/nails
morbidity e.g. - Pulmonary hypertension
diabetes, hypertension - Signs of post-term delivery
Management Investigations
Evidence of meconium-stained amniotic fluid ✓ Continuous pulse
AND floppy neonate, bradycardia, and/or oximetry
apnoea? ✓ Chest x-ray
Yes No
✓ ECG
✓ Blood gas analysis
(metabolic acidosis?)
Suction of meconium ✓ Septic work-up
immediately after
delivery
Supportive Care
Temperature
regulation and
Dry and stimulate the baby minimal handling
Maintain Systolic
Is the baby breathing? Blood Pressure >
Pulmonary BP
Yes No
Adequate
Resuscitate and stabilize sedation if on
ventilator
Options depending on severity of disease: ✓ Antibiotic therapy
✓ Oxygen therapy ✓ Surfactant therapy
✓ Consider CPAP or mechanical ventilation ✓ ECMO in severe cases
WHO (2016) Surfactant for meconium aspiration syndrome in term and late preterm infants
You might also like
- (PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Mei 2020-1-Unlocked PDFDocument155 pages(PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Mei 2020-1-Unlocked PDFnayNo ratings yet
- 2.03B Fetal Assessment Part 2 (Dr. Candelario) PDFDocument7 pages2.03B Fetal Assessment Part 2 (Dr. Candelario) PDFjay lorenz joaquinNo ratings yet
- Meconium AspirationDocument7 pagesMeconium AspirationDelphy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care LectureDocument65 pagesNewborn Care LectureNichole daFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Emergencies: Amanda Louise Du, MD, DPPS, DPSNBM Pediatrician-NeonatologistDocument44 pagesDelivery Room Emergencies: Amanda Louise Du, MD, DPPS, DPSNBM Pediatrician-NeonatologistLyn LynNo ratings yet
- For Delivery FDAR ChartingDocument5 pagesFor Delivery FDAR ChartingLyca Mae Aurelio100% (2)
- Newborn ResuscitationDocument24 pagesNewborn Resuscitationsagi mu100% (2)
- Endrenal Reyzelin M.-Concept Map & NCPDocument5 pagesEndrenal Reyzelin M.-Concept Map & NCPReyzelinNo ratings yet
- 20 - Neonatal InfectionsDocument4 pages20 - Neonatal InfectionsYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- 17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Document60 pages17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Lutfi HakimNo ratings yet
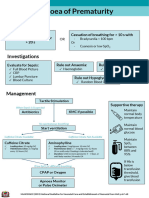
- 17 Apnoea PrematurityDocument1 page17 Apnoea PrematurityYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- F-IMNCI Chart BookletDocument45 pagesF-IMNCI Chart BookletGunda SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Monitoring: Causes of Fetal Compromise During LaborDocument10 pagesIntrapartum Monitoring: Causes of Fetal Compromise During LaborlicencaNo ratings yet
- PromDocument1 pagePromwedishaNo ratings yet
- Recognizing The Ill NewbornsDocument29 pagesRecognizing The Ill NewbornsMay MayNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Disorders 4Document33 pagesCommon Neonatal Disorders 4Laishram Deeva ChanuNo ratings yet
- Management of Normal Labour ChartDocument1 pageManagement of Normal Labour ChartwedishaNo ratings yet
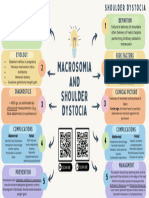
- Macrosomia and Shoulder DystociaDocument1 pageMacrosomia and Shoulder Dystociaelmajek.yehiaNo ratings yet
- VEAL CHOP With Interventions and OutcomesDocument1 pageVEAL CHOP With Interventions and Outcomesayngn13No ratings yet
- 1 - A Sem 9 Osce Discussion Set Mey 1Document21 pages1 - A Sem 9 Osce Discussion Set Mey 1Phoebe ThumNo ratings yet
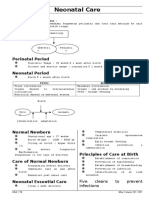
- Neonatal CareDocument3 pagesNeonatal CareAlmira Ulfa Utari NasutionNo ratings yet
- TH TH TH NDDocument3 pagesTH TH TH NDNguyen TaNo ratings yet
- Revisi Bidan Mei 2021 HPPDocument78 pagesRevisi Bidan Mei 2021 HPPNurye MsglowbeautyNo ratings yet
- Induction AND Augmentation OF LabourDocument42 pagesInduction AND Augmentation OF LabourDakshayini MbNo ratings yet
- Summary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseDocument1 pageSummary - Hyaline Membrane DiseaseJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- MCN 2Document13 pagesMCN 2Peter Angelo GeleraNo ratings yet
- CIM by Shahid Zafar LNCONDocument3 pagesCIM by Shahid Zafar LNCONJalil KhanzzNo ratings yet
- Pediatri 2Document165 pagesPediatri 2YUYUM100% (2)
- (Anak) TX Bayi Baru LahirDocument39 pages(Anak) TX Bayi Baru LahirWorldhealthNo ratings yet
- MCN MidtermsDocument4 pagesMCN MidtermsMutya XDNo ratings yet
- CPD Concept MapDocument1 pageCPD Concept MapShandle Dynne Baena100% (1)
- Golden OurDocument89 pagesGolden OurRosmauliana DamanikNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 9 10 2010 0-42-42 R Neonatal-ResuscitationDocument21 pages9 10 2010 0-42-42 R Neonatal-ResuscitationSamsiah ChaNo ratings yet
- Care of NeonatesDocument7 pagesCare of NeonatesJankaruroNo ratings yet
- RLE 107 FDAR Immediate Care of The NewbornDocument6 pagesRLE 107 FDAR Immediate Care of The NewbornLizelle DavidNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis CuiDocument23 pagesDrug Analysis CuiMark Christian CuiNo ratings yet
- Neonatologi SMT 7Document39 pagesNeonatologi SMT 7Zulfikar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument10 pagesLabor and DeliveryCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia: Group 3Document21 pagesEclampsia: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Document4 pagesWorksheet Pedia (Sanaani)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY and CASE ANALYSISDocument6 pagesDRUG STUDY and CASE ANALYSISMa. Kaile Shyla LlacarNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation - AdvancedDocument17 pagesResuscitation - Advancedmarkus_danusantosoNo ratings yet
- RJP Neonatus - ChristDocument65 pagesRJP Neonatus - Christerna moetNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument4 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromePGDME 20192020No ratings yet
- Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment: National Neonatology ForumDocument6 pagesEmergency Triage Assessment and Treatment: National Neonatology ForumSatya Prakash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric MeasurementsDocument3 pagesAnthropometric Measurementssabao kizuiteNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Achalasia & Pyloric StenosisDocument1 page1.0 Achalasia & Pyloric StenosisRaman kangNo ratings yet
- Acute Conditions of The NewbornDocument5 pagesAcute Conditions of The NewbornCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDiseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- MCN Day 2Document7 pagesMCN Day 2Jekka Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DR TLJPH Drug Study - Sali Mari Tamayo Bsn3aDocument5 pagesDR TLJPH Drug Study - Sali Mari Tamayo Bsn3aSALIMARI TAMAYONo ratings yet
- NRP Basics OPNF 7th EdDocument8 pagesNRP Basics OPNF 7th EdRazil AgilNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument6 pagesNeonatal SepsisAisyah ShawtyNo ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous Vagina Delivery: Group 11: Case PresentationDocument9 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vagina Delivery: Group 11: Case PresentationMikes CastroNo ratings yet
- Prom & AromDocument1 pageProm & AromthedewltNo ratings yet
- Health Information System Guidelines (HISG)Document80 pagesHealth Information System Guidelines (HISG)Yassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - DHIS 2 Concepts and Data ModelDocument11 pagesModule 3 - DHIS 2 Concepts and Data ModelYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- Admission Guidebook 2023 - 24Document205 pagesAdmission Guidebook 2023 - 24Yassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- MPDSR Gudeline Final Aproved 6 - 11 - 2019Document96 pagesMPDSR Gudeline Final Aproved 6 - 11 - 2019Yassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- SESSION 8 - Anti-Malaria DrugsDocument48 pagesSESSION 8 - Anti-Malaria DrugsYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- 15 ShockDocument1 page15 ShockYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- 20 - Neonatal InfectionsDocument4 pages20 - Neonatal InfectionsYassboy MsdNo ratings yet
- CABULADocument26 pagesCABULAYassboy MsdNo ratings yet