Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Broadband Techniques-1
Uploaded by
kimemma0630 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesThis document discusses multiplexing techniques for increasing bandwidth utilization in communication channels. It introduces wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM), describing their basic concepts and types. WDM allows multiple optical signals to be transmitted simultaneously on an optical fiber using different wavelengths. TDM divides the channel into time slots to transmit multiple signals. Synchronous TDM assigns fixed time slots while asynchronous TDM uses variable slots based on data amounts. The document aims to design a 10 Gbps optical receiver for next-generation optical networks.
Original Description:
Original Title
broadband techniques-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses multiplexing techniques for increasing bandwidth utilization in communication channels. It introduces wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM), describing their basic concepts and types. WDM allows multiple optical signals to be transmitted simultaneously on an optical fiber using different wavelengths. TDM divides the channel into time slots to transmit multiple signals. Synchronous TDM assigns fixed time slots while asynchronous TDM uses variable slots based on data amounts. The document aims to design a 10 Gbps optical receiver for next-generation optical networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesBroadband Techniques-1
Uploaded by
kimemma063This document discusses multiplexing techniques for increasing bandwidth utilization in communication channels. It introduces wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM), describing their basic concepts and types. WDM allows multiple optical signals to be transmitted simultaneously on an optical fiber using different wavelengths. TDM divides the channel into time slots to transmit multiple signals. Synchronous TDM assigns fixed time slots while asynchronous TDM uses variable slots based on data amounts. The document aims to design a 10 Gbps optical receiver for next-generation optical networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Zagazig University
Faculty of Engineering
Electronics and Communication Department
Graduation Project 2022-2023
The broadband techniques that can be utilized to extend the
circuit bandwidth
Student Names
Alaa Ahmed Salah Shaheen
Supervisor: Dr. Ahmed Reda & Dr. Ahmed Wahba
01
Outlines
❑ Introduction
❑ Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
❑ Time Division Multiplexing
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 02
Outlines
❑ Introduction
❑ Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
❑ Time Division Multiplexing
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 03
Introduction
❑ Generally, a communication channel can carry only one signal
at any moment in time. This waste bandwidth.
❑ Using multiplexing to overcome this drawback .
❑ By using the multiplexing technique, we can easily send
multiple signals simultaneously over a communication channel
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 04
Without Multiplexing vs With Multiplexing
Without Multiplexing With Multiplexing
Carries only one signal at any moment in time. Carries three signals simultaneously.
large amount of bandwidth is wasted. uses only one communication channel
the bandwidth is effectively used.
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 05
Multiplexing
❑ Multiplexing is the process of combining multiple signals into
one signal.
❑ The device that does multiplexing, can be called as a MUX
❑ Types of Multiplexing
• Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
• Time Division Multiplexing
-Synchronous TDM -Asynchronous TDM
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 06
Outlines
❑ Introduction
❑ Wavelength Division Multiplexing
❑ Time Division Multiplexing
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 07
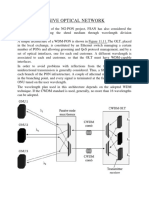
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
❑ Wavelength division multiplexing is a technology that increases
the bandwidth of a of a optical fiber . Several different signal
can be transported simultaneously on the fiber
❑ WDM techniques are of two types:
• Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
• Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 08
Wavelength Division Multiplexing
❑ Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
• Transmit a large number of optical signals simultaneously
• Has the ability to transmit up to 80 channels with (0.8 nm) spacing.
• Signal is transmitted a long distance.
❑ Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing
• Has the ability to transport up to 18 optical signals per optical fiber.
• It is designed for short distance
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 09
Outlines
❑ Introduction
❑ Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
❑ Time Division Multiplexing
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 10
Time division multiplexing
❑ Time division multiplexing (TDM) :The channel is divided into
equal fixed-length time slots . TDM is commonly used to
increase data transmission efficiency.
❑ Time Division Multiplexing is mainly classified into two types:
❑ Synchronous TDM (Time Division Multiplexing)
❑ Asynchronous TDM (Time Division Multiplexing)
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 11
Synchronous TDM
❑ Each signal is transmitted in fixed time slots regardless if the
device has any data to transmit or not.
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 12
Asynchronous TDM
❑ The time slots are not fixed but vary depending on how much
data is transmitted
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU 13
Thanks!
10 Gbps Optical Receiver for XG(S)-PON ONU XX
You might also like
- Mux and DeMux (FOT)Document33 pagesMux and DeMux (FOT)Arjun YadavNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Hybrid WDM-TDM Passive Optical Network (PON) and TDM NG-PONDocument3 pagesPerformance Analysis of Hybrid WDM-TDM Passive Optical Network (PON) and TDM NG-PONerpublicationNo ratings yet
- DWDM - Creating Bandwidth For Broadcast ContributionDocument6 pagesDWDM - Creating Bandwidth For Broadcast ContributionMahesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument9 pagesWavelength Division MultiplexingEdison CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ch-2Document112 pagesUnit 1 ch-2jyothinarne07No ratings yet
- 4 WDM Technology BasicsDocument78 pages4 WDM Technology BasicsSunil Satya100% (1)
- Wavelength-Division Multiplexing - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesWavelength-Division Multiplexing - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaaxextremeNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth UtilizattionDocument22 pagesBandwidth Utilizattion82Neha PalNo ratings yet
- High Speed SSSWZCDocument30 pagesHigh Speed SSSWZCSinghshNo ratings yet
- High Speed 1.6 Tbps Hybrid TWDM-OfDDocument29 pagesHigh Speed 1.6 Tbps Hybrid TWDM-OfDSinghshNo ratings yet
- PONDocument22 pagesPONYátish BáthlaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Systems Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)Document29 pagesFiber Systems Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)Sahil SunejaNo ratings yet
- Wavelength-Division MultiplexingDocument8 pagesWavelength-Division MultiplexingAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- The WavelengthDocument7 pagesThe WavelengthSahil KNo ratings yet
- OfdmDocument8 pagesOfdmTech TronieNo ratings yet
- Modulation and MultiplexingDocument18 pagesModulation and MultiplexingchrisjosewanjiraNo ratings yet
- Wavelength-Division MultiplexingDocument16 pagesWavelength-Division MultiplexingAtul VermaNo ratings yet
- WDM and DWDM MultiplexingDocument113 pagesWDM and DWDM MultiplexingtonzkosgeiNo ratings yet
- A High Capacity 512 Split Hybrid WDM/TDM-PON Architecture Using DPSK Downstream and Intensity Re-Modulation For Upstream Colorless TransmissionDocument8 pagesA High Capacity 512 Split Hybrid WDM/TDM-PON Architecture Using DPSK Downstream and Intensity Re-Modulation For Upstream Colorless TransmissionshahabniaziNo ratings yet
- Hybrid WDM-TDM PON Architectures and DWBA Algorithms: Luyin Zhou, Xiaofei Cheng, Yong-Kee Yeo, Lek Heng NgohDocument6 pagesHybrid WDM-TDM PON Architectures and DWBA Algorithms: Luyin Zhou, Xiaofei Cheng, Yong-Kee Yeo, Lek Heng Ngohendi marNo ratings yet
- 01 WDM Technology ComponentsDocument109 pages01 WDM Technology ComponentskalphieNo ratings yet
- Wavelength Division MultiplexingDocument7 pagesWavelength Division MultiplexingJorge RzezakNo ratings yet
- English Presentation - CWDMDocument15 pagesEnglish Presentation - CWDMJennie SmithNo ratings yet
- WDM Passive NetworkDocument6 pagesWDM Passive NetworkDo Xuan HuuNo ratings yet
- MCC Probable QNS PDFDocument21 pagesMCC Probable QNS PDFAbhijeet ShitoleNo ratings yet
- DWDM PPT Industrial SeminarDocument29 pagesDWDM PPT Industrial SeminarRajat Goel100% (1)
- OFDMDocument17 pagesOFDMAbhilasha AbhiNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Utilization: by Malvika KaushikDocument18 pagesBandwidth Utilization: by Malvika KaushikTanzeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing PresentationDocument22 pagesMultiplexing Presentationscribd01No ratings yet
- Multiplexing PresentationDocument22 pagesMultiplexing Presentationpisces1202No ratings yet
- Multiplexing PresentationDocument22 pagesMultiplexing PresentationYogeshkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Infinera IEEE OTN OverviewDocument25 pagesInfinera IEEE OTN OverviewMario RandolphNo ratings yet
- MWC OldGold SolutionsDocument35 pagesMWC OldGold Solutionsarjun neupaneNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)Document18 pagesUnit - 2: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)Gaurav MorghareNo ratings yet
- EL, Lec4,5,6 CS Week 2 CompiledDocument52 pagesEL, Lec4,5,6 CS Week 2 CompiledMariam IrfanNo ratings yet
- OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)Document20 pagesOFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)Muhammad Sheharyar AshrafNo ratings yet
- Technologies For Future Wavelength DivisDocument8 pagesTechnologies For Future Wavelength DivisTran Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistancesDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Chromatic Scattering in 2 8 Channel at 4 10 Gbps at Various DistanceswahbaabassNo ratings yet
- Analysis With Gain and Power For Better Coverage of FTTH Network Using WDM PON ArchitectureDocument9 pagesAnalysis With Gain and Power For Better Coverage of FTTH Network Using WDM PON ArchitectureHashmat MohamadNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Unit IIIDocument12 pagesComputer Network Unit IIIPinjari Soyab ShakilNo ratings yet
- WDMDocument16 pagesWDMParag MahajaniNo ratings yet
- 2.11 Tunnel Coverage PDFDocument5 pages2.11 Tunnel Coverage PDFgagan_555No ratings yet
- Reseaux MobilesDocument48 pagesReseaux MobilesFaba KamburutaNo ratings yet
- RF/Microwave Systems: Planning, Design & DeploymentDocument39 pagesRF/Microwave Systems: Planning, Design & DeploymentQuddus OkeleNo ratings yet
- Radio Network Planning Tool For DVB-H / DVB-SH Broadcast: (C) by AWE Communications 1Document56 pagesRadio Network Planning Tool For DVB-H / DVB-SH Broadcast: (C) by AWE Communications 1ZaidYemenNo ratings yet
- Method and Modelling For Allocating Wavelength in WDM Passive Optical NetworksDocument10 pagesMethod and Modelling For Allocating Wavelength in WDM Passive Optical Networkssemselvan794694No ratings yet
- CSE 4215/5431: Mobile Communications: Suprakash DattaDocument66 pagesCSE 4215/5431: Mobile Communications: Suprakash DattaKarthikeyan RamajayamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document55 pagesUnit 3Hema DarshanaNo ratings yet
- OFDM HistoryDocument17 pagesOFDM HistoryDekris DarutamaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of SDH TechnologyDocument46 pagesEvolution of SDH Technologysatiz143844100% (2)
- Week 4 Course ProjectDocument10 pagesWeek 4 Course ProjectIssy JosephNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing Tdma, Fdma, CdmaDocument24 pagesMultiplexing Tdma, Fdma, Cdmakashi13No ratings yet
- Guided By:: Submitted By: Shuchi Jani Enrol - No. MU09MCS019Document30 pagesGuided By:: Submitted By: Shuchi Jani Enrol - No. MU09MCS019bhoop_sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Aceess NetworksDocument13 pagesUnit 5 Aceess NetworksDivyanshu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 01-0-WCDMA Wireless Principle and Key Technology-102Document101 pages01-0-WCDMA Wireless Principle and Key Technology-102Cedrick MakambuNo ratings yet
- Emerging Optical Broadband Access Networks From TDM PON To Ofdm PonDocument5 pagesEmerging Optical Broadband Access Networks From TDM PON To Ofdm Ponendi marNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Proceedings of The International Conference On Computational Intelligence and Sustainable TechnologiesDocument758 pagesProceedings of The International Conference On Computational Intelligence and Sustainable Technologieskimemma063No ratings yet
- The Mechanism of The Arithmetic Logic UnitDocument12 pagesThe Mechanism of The Arithmetic Logic Unitkimemma063No ratings yet
- Automatic Control ExerciseDocument26 pagesAutomatic Control Exercisekimemma063No ratings yet
- 2346 ArticleTextinPDFFormat 6324 2 10 20180410Document7 pages2346 ArticleTextinPDFFormat 6324 2 10 20180410kimemma063No ratings yet
- Lab 3ADocument8 pagesLab 3Akimemma063No ratings yet
- Graduation Project 2022-2023: Exploring Available 10 Gbps Photodetectors and Their SpecificationsDocument14 pagesGraduation Project 2022-2023: Exploring Available 10 Gbps Photodetectors and Their Specificationskimemma063No ratings yet
- GunnDocument2 pagesGunnkimemma063No ratings yet
- Criteria For ExtempoDocument2 pagesCriteria For Extempoaljon tusingNo ratings yet
- The MetamorphosisDocument30 pagesThe MetamorphosisALY SHABANNo ratings yet
- Design Fabrication of A Solar Powered Stirling EngineDocument65 pagesDesign Fabrication of A Solar Powered Stirling EngineSirajus Salekin [Id:37]No ratings yet
- Ecu TestDocument5 pagesEcu TestWawan SatiawanNo ratings yet
- Eq Public PDFDocument15 pagesEq Public PDFmoisesNo ratings yet
- Oaa000009 Sigtran Protocol Issue2.0-20051111-ADocument37 pagesOaa000009 Sigtran Protocol Issue2.0-20051111-AFranceNo ratings yet
- Wicking Bed Notes 1Document9 pagesWicking Bed Notes 1Mak NNo ratings yet
- What Is Granite and How Is It FormedDocument2 pagesWhat Is Granite and How Is It FormedPedro Carlos PicapiedraNo ratings yet
- What Is New in PTV Vissim 6Document21 pagesWhat Is New in PTV Vissim 6tekbir1981No ratings yet
- MP 2Document2 pagesMP 2Jorge ParraNo ratings yet
- Reflection Math 1040 ProjectDocument2 pagesReflection Math 1040 Projectapi-260891512No ratings yet
- Isotropic Linear Elastic Stress ConcentrationDocument19 pagesIsotropic Linear Elastic Stress ConcentrationIoan-Lucian StanNo ratings yet
- mb1319 L433Document25 pagesmb1319 L433Pablo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- GED102 Module 3 Project: Group Members: Raynard Yu John Luis Arce Miguel Agustin Galang Paul Cauman Renz Eugene GurionDocument6 pagesGED102 Module 3 Project: Group Members: Raynard Yu John Luis Arce Miguel Agustin Galang Paul Cauman Renz Eugene GurionqwertasdfgNo ratings yet
- A2 English Coursework ConclusionDocument7 pagesA2 English Coursework Conclusionbatesybataj3100% (2)
- CH 0 JKDocument5 pagesCH 0 JKAli Al-AsadiNo ratings yet
- 30 Footwear Developer Interview Questions and AnswersDocument16 pages30 Footwear Developer Interview Questions and Answersthanh2501No ratings yet
- Relationship DevelopmentDocument42 pagesRelationship DevelopmentIntan Putri Cahyani100% (1)
- Signal Processing I: Sebastián Roldán Vasco Sebastianroldan@itm - Edu.coDocument28 pagesSignal Processing I: Sebastián Roldán Vasco Sebastianroldan@itm - Edu.coDaniela GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Part Book D9T TWG Vol 1Document953 pagesPart Book D9T TWG Vol 1iwan nawiNo ratings yet
- Quiz IiDocument9 pagesQuiz IiElma FebrianaNo ratings yet
- The Seven Organisational Levels of DiscourseDocument9 pagesThe Seven Organisational Levels of DiscourseEddy Kloprogge100% (1)
- Mux 2700Document16 pagesMux 2700obioji100% (1)
- Jackson SafetyDocument40 pagesJackson SafetyMarisol Gonzalez (Soly)No ratings yet
- Billings Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyDocument19 pagesBillings Et Al-2018-Journal of Clinical PeriodontologyCristian CulcitchiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 S1.2.2 Mathematical Language and Symbols (Truth Tables)Document12 pagesLecture 4 S1.2.2 Mathematical Language and Symbols (Truth Tables)Dum AccountNo ratings yet
- MT8000 User Manual WinView HMI EazyBuilderDocument428 pagesMT8000 User Manual WinView HMI EazyBuilderhiloactive100% (2)
- Guan, Chen - 2012 - Modeling The Relative Efficiency of National Innovation Systems-AnnotatedDocument14 pagesGuan, Chen - 2012 - Modeling The Relative Efficiency of National Innovation Systems-Annotatedrleonardo_ochoa6263No ratings yet
- Process Simulation and Control Using AspenDocument331 pagesProcess Simulation and Control Using Aspenfarshidian96% (27)
- GYFSTH-12OM3 OPTEG 12 FibersDocument3 pagesGYFSTH-12OM3 OPTEG 12 FibersLeonisa GoezNo ratings yet