BOLDSTEPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, NYANYA-ABUJA
SS1 FIRST TERM
COMPUTER PROJECT
TITLE:
COMPUTER HARDWARE
BY:
MURTALA HAMMAD MUA'ZU
DATE:
5TH OCTOBER, 2023.
1
� DEDICATION
I dedicate this project to God Almighty who grant me the necessary wisdom and
knowledge to accomplish this task and to my ever loving parents Mr. /Mrs. Murtala-
Muazu for their relentless support and encouragements during the course of this project.
2
� ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Firstly, I thank Allah Almighty for making all things possible.
I want to specially acknowledge my computer teacher Mr. Halifax for his numerous
contributions, encouragements and positive impact, and who ensure that I am well
equipped and trained in character and learning. I also record my appreciation to the entire
staff of Boldsteps International School Nyanya, FCT, Abuja.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude and appreciation to my beloved Parents
Mr./Mrs. Murtala - Muazu and my brother for their encouragements and overwhelming
support to complete this project. Thank you.
3
� TABLE OF CONTENTS
Title page…………………………………..…………..…….…………………………………………….1
Dedication……………………………………………………………...…………………………...….….2
Acknowledgement ……………………………………….……………………..…………………..……..3
Table of contents……………………………………….……..…………………...………………………4
CHAPTER ONE
Introduction…………………………………………………………..………………………….………..5
What is Computer Hardware……..……………………………………….………………..……………..5
Examples of computer hardware…………………………………...……………………………………..5
Categories of computer hardware……………………………………..…………………………………..5
CHAPTER TWO
System Unit………………………………………...……………………………………………………...6
Components Of System Unit (1)………………...…………..…………………………………………….6
Input Devices………………………………………………………..…………………………………….6
Display Devices…………………………………………………...………………………………………7
External Devices…………………...……………………..……………………………………………….8
CHAPTER THREE
Components Of System Unit Ii………………………………..…………………..……………………....9
The System Board……………………………………………………..……………..…..………………..9
Central Processing Unit (CPU)…………………………………………………………………………..10
CHAPTER FOUR
Memory Or Storage Unit:……………………..…………………………………….……………………11
Random Access Memory. …………………….………………………………...……………………….11
Read-Only Memory …………………………………………………………….……………..…………11
Hard Drive……………………………………………………………………………………..…………11
Control Unit …………………………………………………………………………………….………..11
Arithmetic Logic Unit……………………………………………………………………………………12
Power Supply………………………………………………………….…………………………………12
CHAPTER FIVE
Cooling System…………………………………………………………………………………………..13
Heat Sinks ………….……………………………………..……………………………………………..13
Fan………………………………………………………………………………………………………..13
Thermal Compound ……………………………………………………………………………………...14
Liquid Cooling System………………………………………………..………………………………….14
SUMMARY……………………...……………..………………………………………………………..15
CONCLUSION………………………………...……..………………………………………………….15
REFERENCE ………………………………...……...…………………………………………………..15
4
� CHAPTER ONE
INTRODUCTION
What is Computer Hardware
Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements that constitutes a computer system. These are
the physical components of the computer system. They are the tangible parts that can be seen and
touched.
Hardware Components of a computer is also refers to the collection of physical parts of a computer
system that we can touch or feel. This includes the computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. It also
includes all the parts inside the computer case, such as the hard disk drive, motherboard, video card, and
many others.
EXAMPLES OF COMPUTER HARDWARE.
The following are examples of hardware. The first 9 components listed usually belong to the internal
category, and the other 11 are typically external.
1. Motherboard 11. Keyboard
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU) 12. Mouse
3. Power Supply 13. Printer
4. Random Access Memory (RAM) 14. Speakers
5. Hard Disk Drive (HDD) 15. External Hard Drive
6. Video Card 16. Desktop Image Scanner
7. Solid-State Drive (SSD) 17. Projector
8. Optical Disc Drive (e.g. BD drive, DVD 18. Joystick
drive, CD drive) 19. Headphones
9. Card Reader (e.g. SD, SDHC) 20. USB Flash Drive
10. Monitor
CATEGORIES OF COMPUTER HARDWARE
The hardware components of a computer or personal computer are categorized into 4 primary
categories: -
a. System Unit
b. Display Device
c. Input Devices
d. External Devices
5
� CHAPTER TWO
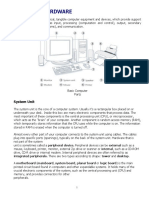
SYSTEM UNIT
A System Unit is the main component of a personal computer, which houses the other devices
necessary for the computer to function. It is comprised of a chassis and the internal components
of a personal computer such as the system board (mother board), the microprocessor, memory
modules, disk drives, adapter cards, the power supply, a fan or other cooling device and ports
for connecting external components such as monitors, keyboards, mice, and other devices.
COMPONENTS OF SYSTEM UNIT (I)
Display Devices
A display device is a personal computer component and is an output device that enables user to
view the text and graphical data associated with a computer program. Display devices
commonly connect to the system unit via a cable, and they have controls to adjust the settings
for the device. They vary in size and shape, as well as the technology used.
Display Device
a. Input Devices
An input device is a personal computer component that enables users to enter data or
instructions into a computer. The most common input devices are keyboards and computer
mice. Input devices can connect to the system via a cable or a wireless connection.
6
�7
�b. External Devices
Any peripherals devices that are not housed inside the system unit are inherently external
devices. A personal computer’s functionality can be enhanced by connecting different types of
external devices to the system unit, often called peripherals devices. These devices typically
provide alternative input or output methods or additional data storage. External devices are
connected to the system unit via a cable or wireless connection. Some of them have their own
power source and some draw power from the system.
There are several categories of external devices.
External Devices Functionality
Microphone Provides audio input
Digital camera Provides graphical input
Scanner Provides graphical input
Speaker Provides audio output
Printer Provides printed output
Provides communication with other
Network device computers, such as access to the Internet.
External device Provides additional data storage
8
� CHAPTER THREE
COMPONENTS OF SYSTEM UNIT II
The System Board
I. Central Processing Unit
II. Memory
III. Power Supplies
IV. Cooling Systems etc.
I. THE SYSTEM BOARD
The system board is the personal computer component that acts as the backbone for the
entire computer system as it serves as a single platform to connect all of the parts of a computer
together. It connects the CPU, memory, hard drives, optical drives, video card, sound card, and
other ports and expansion cards directly or via cables. System Board is also known as
motherboard. It consists of a large, flat circuit board with chips and other electrical components
on it.
Some popular manufacturers of the motherboard are: -
Intel
Asus
Gigabyte
Biostar
Msi
System Board or Motherboard
9
� CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), sometimes called microprocessor or just processor, is
the real brain of the computer and is where most of the calculations take place.
Some popular manufacturers / designers of the CPU are: -
Intel
AMD
Qualcomm
Media Tek
NVIDIA
Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of the following features: -
CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
It controls the operation of all parts of the compute
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Now, the CPU itself has following three components: -
Memory or Storage Unit
Control Unit
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
CPU
Memory Unit
Input Unit Control Unit Output Unit
Arithmetic &
Logic Unit
10
� CHAPTER FOUR
MEMORY OR STORAGE UNIT:
This unit stores data, instructions & results for processing andstores the final results of processing
before these results are released to an output device. It is also responsible for the transmission of all
inputs and outputs.
Random Access Memory – RAM. Where information is stored temporarily when a program is
run. Information is automatically pulled into memory, we cannot control this. RAM is cleared
automatically when the computer is shutdown or rebooted. RAM is volatile (non-permanent).
Read Only Memory – ROM. More permanent than RAM. Data stored in these chips is
nonvolatile -- it is not lost when power is removed. Data stored in these chips is either
unchangeable or requiresa special operation to change. The BIOS is stored in the CMOS, read-
only memory.
Hard Drive – Where you store information permanently most frequently. This is also
nonvolatile.
Control Unit (CU) : This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not
carry out any actual data processing operations.
11
� Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU): All calculations are performed in the Arithmetic Logic
Unit (ALU) of the computer. It also does comparison and takes decision. The ALU can
perform basic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc and does
logic operations viz, >, <, =, ‘etc. Whenever calculations are required, the control unit
transfers the data from storage unit to ALU once the computations are done, the results are
transferred to the memory unit by the control unit and then it is send to the output unit for
displaying results.
II. Power Supply
Power Supply known as switch-mode power supply (SMPS) is an electronic circuit that
converts power using switching devices that are turned on and off at high frequencies, and
storage components such as inductors or capacitors to supply power when the switching
device is in its non-conduction state.
Switching power supplies have high efficiency and are widely used in a variety of electronic
equipment, including computers and other sensitive equipment requiring stable and efficient
power supply.
SMPS
12
� CHAPTER FIVE
COOLING SYSTEM
Cooling may be required for CPU, Video Card, Mother Board, Hard Drive, etc. Without
proper cooling, the computer hardware may suffers from overheating. This overheating causes
slow downs, system error messages, and crashing. Also, the life expectancy of the PC's
components is likely to diminish. The following are commonly used techniques for cooling the
PC or Server components:
Heat Sinks
CPU/Case Fans
Thermal Compound
Liquid Cooling Systems
Heat Sinks: The purpose of a heatsink is to conduct the heat away from the processor or any
other component (such as chipset) to which it is attached. Thermal transfer takes place at the
surface of a heatsink. Therefore, heat sinks should have a large surface area. A commonly used
technique to increase the surface area is by using fins. A typical processor heat sink is shown
in the figure below:
Intel Dual Core Xeon LGA 771 heatsink
Fan: The Fan is primarily used to force cooler air in to the system or remove hot air out of the
system. A fan keeps the surrounding cooler by displacing air around the heatsink and other parts
of the computer. A typical CPU fan is shown below.
CPU Fan Heatsink with Fan
13
�Thermal Compound: A thermal compound is used for maximum transfer of heat from CPU
to the heatsink. The surface of a CPU or a heatsink is not perfectly flat. If you place a heatsink
directly on a CPU, there will be some air gaps between the two. Air is a poor conductor of heat.
Therefore, an interface material with a high thermal conductivity is used to fill these gaps, and
thus improve heat conductivity between CPU and heat sink.
Liquid Cooling Systems: Like a radiator for a car, a liquid cooling system circulates a liquid
through a heat sink attached to the processor. First, the cooler liquid passes through the heatsink,
and then gets hot due to transfer of heat from the processor to the heatsink. Then the hot liquid
passes through the radiator at the back of the case, and transfers the heat to the secondary
coolant (air). Now, the liquid is cool enough to pass through the hot processor heatsink, and the
cycle repeats. The chief advantage of LCS (Liquid Cooling System) is that the cooling takes
place very efficiently (since liquids transfer heat more efficiently than air/solids). The dis-
advantages include bulkier cooling system, cost, and additional reliability issues associated with
LCS.
14
� SUMMARY
Hardware (sometimes abbreviated to HW) can be defined as the physical components that a computer
system needs to function. This distinguishes it from software, which consists of written instructions that
tell the physical components what to do.
The components that make up hardware can be categorized as being either internal or external.
Internal components are those installed inside the computer, typical examples being the motherboard,
power supply, and central processing unit (CPU).
External components are connected to the outside of the computer; these can also be referred to as
peripherals, or peripheral devices, common examples being the monitor, keyboard, and mouse.
Some examples of computer hardware are;
1. Motherboard
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
3. Power Supply
4. Random Access Memory (RAM)
5. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
6. Video Card
7. Solid-State Drive (SSD)
8. Optical Disc Drive (e.g. BD drive, DVD drive, CD drive)
9. Card Reader (e.g. SD, SDHC)
10. Monitor
11. Keyboard
12. Mouse
13. Printer
14. Speakers
15. External Hard Drive
16. Desktop Image Scanner
17. Projector
18. Joystick
19. Headphones
20. USB Flash Drive
CONCLUSION
Through this project I have gained some comprehensive knowledge of computer software. I encourage
everyone who comes across this material to study and digest its contents make further research for better
understanding of computer software.
REFERENCE
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-GQmtITMdas
http://www.dspmuranchi.ac.in/pdf/Blog/Input,%20Output%20and%20Memory%20Devices.pdf
compnote.blogspot.com
inspire.education.gov.ng
Computer Studies of Senior Secondary Education by Hiit Plc
15