Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Post modification Chốt cuối bài
Uploaded by
Hạ Thu DươngOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Post modification Chốt cuối bài
Uploaded by
Hạ Thu DươngCopyright:
Available Formats
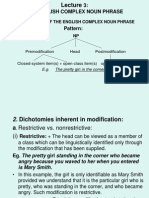
Review: Post- modification (p.
48) + Chốt cuối bài
Components of complex noun phrase:
- Head noun
- Pre- modifier
- Post- modifier
- Post- modifiers comprise all the items place after the head.
E.g:
The book that you recommended last week
The beautiful painting in the museum
The final episode of the popular TV show that aired last night
- These post- modifiers are realized by preposition phrase, finite clauses (or
relative clause), non- finite clauses, adjectives phrases, noun phrases or
adverbial phrases.
E.g:
+ Prepositional phrase: The girl in the red dress
+ Finite- clause: The girl who is wearing a red dress
+ Non-finite clause: The girl dressed in a red dress
+ Adjectives phrase: The girl beautiful in a red dress
+ Noun phrase: The girl, a dancer
+ Adverbial phrase:
- Major class of post-modification
+ Of-genetive
Has a close correspondence to 'have' sentences:
E.g: Genitive: “The chapters of the book” Corresponding ‘have’ sentence:
“The book has chapters”
Relate to 'be' sentences
E.g “The heart of the city” Corresponding ‘be’ sentence: “The heart is of the
city”
Be used to express the subject or object relation
Eg: The recognition of these results
+ Noun phrase:
Encode the information
Eg: The hotel Marriott
+ Adjectives phrase
Be regarded as a reduced relative clause
Eg: Something wrong
+ Prepositional phrase
Have a wide range of prepositions that can be used, including the complex
prepositions and those having participle forms
Place: The man on the bus
Time: The lesson on Monday
Manner: That woman with the glasses
+ Non-finite clause
To V: The plan to build a new stadium
V-ing participle, e.g: The cat sleeping in the shade
V-ed participle, e.g: The dog trained at the academy
+ Finite- clause
Can be restrictive or non-restrictive
Begin with relative pronouns: 'who', 'whom', 'whose', 'that' (personal);
'which', 'that', 'what' (non-personal); 'when', a preposition plus 'which' (time);
'where', a preposition plus 'which' (place); and 'why', 'for which' (reason).
While restrictive relative clauses help to define the head noun, the non-
restrictive ones give additional information to it.
Eg: The man who is standing in the corner
+ Adverbial
The room upstair
- Attention:
Their no grammatical limit to the number of post-modifiers occurring in a
noun phrase, considerations of style and comprehensibility will normally
keep them to one or two. Where we have more than one, the relative order
tends to depend on the related properties of length and class, with shorter
modifiers preceding longer ones, prepositional phrases preceding clauses
Eg:
The book on the table covered in dust hasn’t been read in years.
The woman in the green dress talking on the phone is my aunt.
You might also like
- Grammar Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesGrammar Cheat Sheeticon6970No ratings yet
- Arabic With Husna (Lesson 2) Unit 1 (0.2) Bayyinah TV Transcript NotesDocument4 pagesArabic With Husna (Lesson 2) Unit 1 (0.2) Bayyinah TV Transcript NotesMUSARRAT BANO100% (8)
- Language Worksheets For Grade 1Document3 pagesLanguage Worksheets For Grade 1David0% (2)
- Sudric Fictional LanguageDocument5 pagesSudric Fictional Languagemacaoidh2100% (2)
- Noun PhrasesDocument13 pagesNoun PhrasesLegends FunanzaNo ratings yet
- Reader's and Writer's Notebook - Gr4 - SEDocument3 pagesReader's and Writer's Notebook - Gr4 - SEChedy Chavez0% (1)
- Kinds of PhrasesDocument19 pagesKinds of PhrasesFarah AnjumNo ratings yet
- SyntaxDocument27 pagesSyntaxAreFharm BidinNo ratings yet
- Engleza SintaxaDocument144 pagesEngleza SintaxaSorina Ileana MesarosNo ratings yet
- Prepositional PhraseDocument5 pagesPrepositional PhraseMar Nie Morales ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Active VoiceDocument104 pagesPassive Voice and Active VoiceLuis Serrano CortezNo ratings yet
- Easy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishFrom EverandEasy Learning How to Use English: Your essential guide to accurate EnglishRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Structure of Noun Phrases in EnglishDocument6 pagesThe Structure of Noun Phrases in EnglishCamelia GalitNo ratings yet
- The Smallest Unit of Language That Has A Meaning of Its OwnDocument33 pagesThe Smallest Unit of Language That Has A Meaning of Its OwnabaclavaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar Reading 3Document10 pagesAdvanced Grammar Reading 3Ngọc ĐTNo ratings yet
- PHẦN NGỮ PHÁPDocument15 pagesPHẦN NGỮ PHÁPTư MaiNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns: Nhóm 1 1. Nguyễn Lê Anh Thuận 2. Huỳnh Lâm Xuân Hoanh 3. Đỗ Đức Phong 4. Lê Thanh Hào 5. Lê Ngọc ĐínhDocument11 pagesRelative Pronouns: Nhóm 1 1. Nguyễn Lê Anh Thuận 2. Huỳnh Lâm Xuân Hoanh 3. Đỗ Đức Phong 4. Lê Thanh Hào 5. Lê Ngọc Đínhđỗ đức phongNo ratings yet
- False TrueDocument8 pagesFalse TrueThảo Nguyễn Thị PhươngNo ratings yet
- Functions and Structure of NPDocument5 pagesFunctions and Structure of NPTrần Minh ThuNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument27 pagesNounsjanezahrenNo ratings yet
- PhrasesDocument14 pagesPhrasesSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Phrases: I. Lesson PointsDocument4 pagesUnit 5: Phrases: I. Lesson PointsHuong DangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note For SS2 (Week 3) - WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesLesson Note For SS2 (Week 3) - WPS OfficeSegun HursheeNo ratings yet
- Phrases - Clauses - SentencesDocument11 pagesPhrases - Clauses - SentencesHồ Trúc QuyênNo ratings yet
- PhrasesDocument35 pagesPhrasesNur Hanna AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrases: The Police Officer's DogDocument6 pagesNoun Phrases: The Police Officer's DogMustaqueNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar - PHRASESDocument15 pagesAdvanced Grammar - PHRASESTieu LinhNo ratings yet
- Complex Noun PhraseDocument7 pagesComplex Noun PhraseNgo Thi HueNo ratings yet
- نسخة PhrasesDocument6 pagesنسخة PhrasesRaghadNo ratings yet
- Language Profiency and Reading Comprehension - SSG CETs Review Program '19-'20Document186 pagesLanguage Profiency and Reading Comprehension - SSG CETs Review Program '19-'20Ernie McmillanNo ratings yet
- Adjective Normal PositionDocument13 pagesAdjective Normal PositionThet NaungNo ratings yet
- 4A06 Nguyen Kim Phung The Structure of Noun Phrase in English and VietnameseDocument19 pages4A06 Nguyen Kim Phung The Structure of Noun Phrase in English and VietnamesethinhptitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AdjectivesDocument54 pagesChapter 14 Adjectives耿雨栋No ratings yet
- Practiceteaching 151210032826Document30 pagesPracticeteaching 151210032826Diomedes ColarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document17 pagesChapter 6thị hương nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Ts 5Document4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Ts 5Afifa FauziahNo ratings yet
- Grammar Unit 5Document5 pagesGrammar Unit 5Phúc ThịnhNo ratings yet
- English Basic GrammerDocument7 pagesEnglish Basic GrammerKrish NithyanNo ratings yet
- Studies of English.: Simple PresenteDocument8 pagesStudies of English.: Simple PresenteluizNo ratings yet
- University Grammar of English: Quirk, GreenbaumDocument17 pagesUniversity Grammar of English: Quirk, Greenbaumnora khaledNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Duy Long100% (1)
- "The Bridge" High SchoolDocument16 pages"The Bridge" High SchooljawahirsamiNo ratings yet
- Introductory Concepts 1Document8 pagesIntroductory Concepts 1mostarjelicaNo ratings yet
- Basic English GrammarDocument78 pagesBasic English GrammarPbNo ratings yet
- Adjectives - Seminarski RadDocument11 pagesAdjectives - Seminarski RadBlagica ZivicNo ratings yet
- Dps Grammar Stage 1Document3 pagesDps Grammar Stage 1api-198669584No ratings yet
- Uses and Position of PrepositionsDocument2 pagesUses and Position of Prepositionsalethea40877No ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument86 pagesAdjectives and Adverbssaadi mziriNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri ToeicDocument17 pagesTugas Mandiri ToeicBunga Divi IswaraNo ratings yet
- Seminarski Rad: Student: ProfesorDocument12 pagesSeminarski Rad: Student: ProfesorMilicevic NikolaNo ratings yet
- Isang Dosenang Klase NG High School Students: Jessalyn C. SarinoDocument8 pagesIsang Dosenang Klase NG High School Students: Jessalyn C. SarinoMary Jane Reambonanza TerioteNo ratings yet
- LEC FILO III LECTURE 5 Relative-Clauses - Boricean Teodora - Re-A, Anul 3Document12 pagesLEC FILO III LECTURE 5 Relative-Clauses - Boricean Teodora - Re-A, Anul 3Boricean TeodoraNo ratings yet
- Lec Filo Iii Lecture 5 Relative ClausesDocument12 pagesLec Filo Iii Lecture 5 Relative ClausesLaura ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Student - Version - RELATIVE CLAUSES Ly Thuyet - BT Trac NghiemDocument8 pagesStudent - Version - RELATIVE CLAUSES Ly Thuyet - BT Trac Nghiemphương thuNo ratings yet
- A Noun PhraseDocument7 pagesA Noun Phrasescribder994realNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument31 pages8 Parts of SpeechPASACAS, MARY ROSE P.No ratings yet
- Week 2 Syntax - Functional WordsDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Syntax - Functional WordsMinh Trâm VũNo ratings yet
- Noun Phrase LectureDocument2 pagesNoun Phrase Lecturewaqarali78692No ratings yet
- MODULE 7 - PrepositionsDocument4 pagesMODULE 7 - PrepositionsGwyneth Mogol100% (1)
- Are Your Signs and Labels Confusing?: Messages For Manufacturing PersonnelDocument1 pageAre Your Signs and Labels Confusing?: Messages For Manufacturing Personnelkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- EIC 4 Practice Exercises Unit 8Document4 pagesEIC 4 Practice Exercises Unit 8Trung Trần Lý QuốcNo ratings yet
- Marked TonicityDocument2 pagesMarked TonicityFacundo IbáñezNo ratings yet
- Speakout 1e Starter Scope and SequenceDocument4 pagesSpeakout 1e Starter Scope and SequenceFaraj RahilNo ratings yet
- CyrillizationDocument25 pagesCyrillizationKarelBRGNo ratings yet
- Grade K Developmental Stages of Writing English SpanishDocument1 pageGrade K Developmental Stages of Writing English Spanishapi-293887577No ratings yet
- Segment 2.4 (Verbal Roots)Document4 pagesSegment 2.4 (Verbal Roots)Santosh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive PronounsDocument1 pagePersonal Pronouns Possessive Adjectives Possessive PronounsTeh ban lengNo ratings yet
- Comparative and SuperlativeDocument2 pagesComparative and Superlativeيعرب زيدانNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: CombinationsDocument2 pagesLesson 2: CombinationsmanigyawaliNo ratings yet
- So-Such & PracticeDocument39 pagesSo-Such & Practicebaktiar ansharNo ratings yet
- Morpheme Bases: Prepared By: Hassan Fakhir Birhat Jamal Supervisor:Ahmed JabarDocument7 pagesMorpheme Bases: Prepared By: Hassan Fakhir Birhat Jamal Supervisor:Ahmed Jabarberhat zardagomeNo ratings yet
- Grammar NotesDocument5 pagesGrammar NotesNana ZainNo ratings yet
- English HistoryDocument7 pagesEnglish HistorySam FoxNo ratings yet
- Sekcija-Angliski JazikDocument5 pagesSekcija-Angliski JazikIlka Pandilovska DimitrijevskaNo ratings yet
- Personal Best B1+ Unit 7 Reading TestDocument3 pagesPersonal Best B1+ Unit 7 Reading Testhongochaphuong080205No ratings yet
- SOLT Serbian Module 5 Lesson 1Document16 pagesSOLT Serbian Module 5 Lesson 1Goryan NikolenkoNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1Document3 pagesHand Outs - 05242022 - Subject Verb Agreement 1Skye MaiaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses - EFLnetDocument4 pagesVerb Tenses - EFLnetDaley JamesNo ratings yet
- E4E - Passive IIDocument4 pagesE4E - Passive IIRenan PaivaNo ratings yet
- Possessive Adjectives PPT ExerciseDocument1 pagePossessive Adjectives PPT ExerciseCristian ChioloNo ratings yet
- Planificare Anuala Click On 3 Clasa A 9a L2Document10 pagesPlanificare Anuala Click On 3 Clasa A 9a L2Carmen Maria FluturaşNo ratings yet
- Formation and Usage of The Imperative Mood in EnglishDocument4 pagesFormation and Usage of The Imperative Mood in EnglishresearchparksNo ratings yet
- MID TERM EXAM 4th EditionDocument2 pagesMID TERM EXAM 4th EditionisaiasferNo ratings yet
- The English Tenses: S ED Will ShallDocument9 pagesThe English Tenses: S ED Will ShallAnonymous wIlqpnk7BwNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Japanese LanguageDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of The Japanese LanguageJune CostalesNo ratings yet