Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure
Uploaded by
s2128226Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure
Uploaded by
s2128226Copyright:
Available Formats
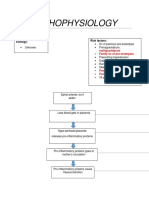
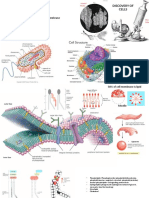
CELL STRUCTURE CHARACTERISTICS FUNCTIONS Abnormalities/
Transport
Cellular membrane Trilamar compartmentalization
Lipid and protein organise enzyme for
Carbs effective biochemical
Dynamic (Fluid mosaic interaction
model) selectively permeable
barrier
Transporting solutes
Responding to external
signal
Interaction for adjacent
cells
Energy transduction
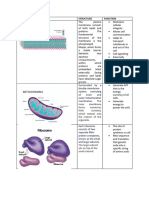
Mitochondria Can fuse with one Contain DNA, ribosome Disorder
another or split into and enzyme. RNA and mutation in
two protein are synthesised mitochondrial
Two membranes in matrix, not DNA/mtDNA
Outer – 50% lipid intermembrane space Inherited
Inner bacterial like – Cristae – ATP machinery maternally
75% protein, locate Proliferation
cardiolipin, porin Carbohydrate mitochondria
metabolism – TCA cycle Premature
aging
Peroxisome Membrane bound Oxidative metabolism Zellweger
vesicles with oxidative Oxidise long chain fatty syndrome
enzymes acids Lack enzyme
Form by splitting from Synthesise
preexisting organelle plasmalogens in neuron Adrenoleukodyds-
Glyoxysome(plant) cells trophy
Export preformed Fatty acid
proteins accumulate in
H2O2 formed, is broken brain,
down by catalase destruct
myelin sheath
SER In endocrine cell synthesis of steroid
In liver detoxification
In muscle cell sequestration of calcium ion
into cytoplasm
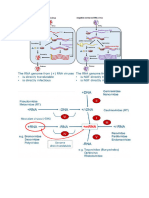
RER On ribosomes Polypeptide synthesis Messenger RNA
(secreted, integral binds to free
membrane, soluble ribosome
proteins) Nascent protein
On “free” ribosomes Human genome, cytosolic, synthesised on
peripheral membrane, ribosome have
nuclear protein their signal
sequence
recognised by SRP
SRP interact with
Processing nascent/newly a SRP receptor
synthesised protein Ribosome interact
-carbo added by with translocon
oligosaccharltransferase SRP-RIBOSOME-
- RER is packed with NASCENT PEPTIDE
chaperones to assist in CHAIN COMPLEX
folding and contain protein binds to ER
disulfide isomerase to add GTP-binding
disulfide bonds protein helps the
release of SRP
Upon entering
RER lumen, the
signal sequence is
cleaved by signal
peptidase
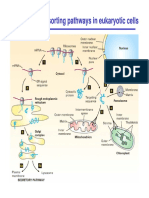
Transport vesicles Donor compartment Biosynthetic – modify & Fuse to form the
budding transport ER G intermediate
Receptor Secretory- constitutive & compartment
Recipient regulated COP II-coated
compartment fusion vesicles move
materials from ER
forward to ERGIC
to Golgi
COP I-coated
vesicles move
materials
backwards
Golgi Apparatus Stack of flattened Cis Golgi network sorts Vesicular
cisternae protein for the ER od transport model
Functional next Golgi station Cargo is shuttled
compartments Trans Golgi network fr CGN to CGMGN
Cis- sort protein proteins to to MGN to
Trans- membrane/ MGTGN to TGN in
intracellular destination vesicles
Glycoslyation, assembly Clathrins-coated
of carbo in glycolipid, vesicles move
glycoprotein, sequence materials from
them into TGN to
Lysosomal protein is oligosaccharides with endosomes,
phosphorylated/tagged enzyme lysosomes and
with mannose residue so glycosyltransferases(α-
they are recognised by mannosidase I, GlcNac-
(MPRs) mannose-6- transferase I, α-m iI,
phosphate receptors GlcNac-t Ii, fucosyl &
galactosyl- t, Sialyl- t
Lysosome Organelle turnover Lysosomal
Autophagy when fuse storage disorder –
with autophagosome absence of
To digest damaged lysosomal enzyme
organelle thus accumulated
material cause
Tay-Sachs disease
You might also like
- Decriptive Anatomical Terminology Body PlanesDocument2 pagesDecriptive Anatomical Terminology Body Planesskyler andrada100% (1)
- USMLE STEP 1 CHECKLIST @lifeinwhitecoatDocument23 pagesUSMLE STEP 1 CHECKLIST @lifeinwhitecoatGlorivy E. Mora Gonzalez100% (3)
- Trauma MaksilofacialDocument69 pagesTrauma MaksilofacialgedepambudiNo ratings yet
- Thirty Day CleanseDocument2 pagesThirty Day CleanseChelaru AlinaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Risk Assessment CHEMICAL 1Document5 pagesRisk Assessment CHEMICAL 1tracey_chrystalNo ratings yet
- Waec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesDocument8 pagesWaec 2021 Biology Practical: BOTH HAVE: I. Large Neural Canal Ii. Transverse Process Iii. Neural SpinesJacob Spiritual100% (2)
- Main Functions of ProteinDocument3 pagesMain Functions of ProteinsweetwaffleNo ratings yet
- Succunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageSuccunylcholine (Anectine) : University of San Carlos College of Nursing Drug StudyFederico AndalesNo ratings yet
- Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Soft Tissue SurgeryDocument944 pagesMaster Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery Soft Tissue SurgeryAbotaleb Mohd100% (15)
- Pathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document38 pagesChapter 1synap5esNo ratings yet
- Cheatt Sheet #2Document2 pagesCheatt Sheet #2layanhaliloNo ratings yet
- EOC Review Packet StudentDocument15 pagesEOC Review Packet Studentjjman epicNo ratings yet
- Summary ShortDocument10 pagesSummary ShortDelon van den AkkerNo ratings yet
- Virology TableDocument10 pagesVirology TableFrances Ijeoma ObiakorNo ratings yet
- AP Bio CH 15Document17 pagesAP Bio CH 15Jhun Banual ZaspaNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Organelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesDocument6 pagesOrganelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesAine CebedoNo ratings yet
- Translation and Proteins: The Products of TranscriptionDocument10 pagesTranslation and Proteins: The Products of TranscriptionRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- H2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFDocument5 pagesH2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFAnonymous 0iTAS7No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument4 pagesCell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet: by ViaDanica RevillaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument19 pagesProtein SynthesisRara Aulia IINo ratings yet
- 10RepCM MamalapatDocument2 pages10RepCM MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21, Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesLecture 21, Protein SynthesisNariopolusNo ratings yet
- 4.03 Intracellular Traffic, Protein Sorting and BiosignalingDocument16 pages4.03 Intracellular Traffic, Protein Sorting and BiosignalingMiguel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36 - Translation and Protein TargetingDocument24 pagesLecture 36 - Translation and Protein TargetingFarisha SultanNo ratings yet
- Bio Compare and ContrastDocument2 pagesBio Compare and ContrastRhea SivakumarNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio MidtermDocument4 pagesCell Bio MidtermCó Tên KhôngNo ratings yet
- Protein Trafficking: I. OverviewDocument15 pagesProtein Trafficking: I. OverviewAndrea Erika Loyola SolisNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lec TransesDocument9 pagesBiochem-Lec TransesK CruzNo ratings yet
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument15 pagesCell BiologySinchan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- Gen. Micro (Trans 004)Document3 pagesGen. Micro (Trans 004)Cristian Kenneth TrillanesNo ratings yet
- Cell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkDocument5 pagesCell STRUCTURE and Function Worksheet. HomeworkMichael WrightNo ratings yet
- Biomol BiomedikFera Ibrahim08032018Document95 pagesBiomol BiomedikFera Ibrahim08032018PMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- Study Guide For Prokaryotic Cell UltrastructureDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Prokaryotic Cell UltrastructureFetalvero EddieNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell StructureDocument2 pages2.1 Cell StructureZarmina KhanNo ratings yet
- 5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2018Document2 pages5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2018GUCCINONo ratings yet
- 10 PlasmidsDocument17 pages10 Plasmidsparduman kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Transcriptional Control in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument13 pagesLecture Transcriptional Control in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesTony_Tonique_Q_1649No ratings yet
- Translation 160204065032Document79 pagesTranslation 160204065032Sai SundeepNo ratings yet
- Gene To Protein FlashcardsDocument2 pagesGene To Protein FlashcardsTim DAVISNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - The CellDocument39 pagesLecture 1 - The CellBianca AnguloNo ratings yet
- Comparison DNA and RNADocument2 pagesComparison DNA and RNAMani MentalNo ratings yet
- Control of Eukaryotic Genes: AP BiologyDocument21 pagesControl of Eukaryotic Genes: AP BiologyGabe GallagherNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec 3Document2 pagesBio Lec 3lilliaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Endoplasmic Re Culum: Structure & Composi OnDocument1 pagePlasma Membrane Endoplasmic Re Culum: Structure & Composi OnShein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mbt1 B Cloning Expression 14 15Document91 pagesMbt1 B Cloning Expression 14 15Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Genetika Dan Ekspresi Gen Pada EukariotDocument36 pagesGenetika Dan Ekspresi Gen Pada EukariotRaditya Indah TofaniNo ratings yet
- Fig. 2.15 Rnai Method For Gene: 2.14 Recombinant Protein Expression and Purifi CationDocument13 pagesFig. 2.15 Rnai Method For Gene: 2.14 Recombinant Protein Expression and Purifi CationJuliana DiazNo ratings yet
- Transcription and The Control of Gene RegulationDocument66 pagesTranscription and The Control of Gene Regulationerenyorulmaz143No ratings yet
- Mesozoic Era PresentationDocument1 pageMesozoic Era PresentationKingZhytt DrizNo ratings yet
- ANA LAB Cell MembraneDocument30 pagesANA LAB Cell MembraneAlessandra Franchesca CortezNo ratings yet
- Microbial Genetics: and BiotechnologyDocument77 pagesMicrobial Genetics: and BiotechnologyRoderick BalceNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellsDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal CellsCharisse Sheree PuentenegraNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Processing of Rna: The Steps of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: DNADocument8 pagesTranscription and Processing of Rna: The Steps of Gene Expression in Prokaryotic Cells: DNACindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- BMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationDocument15 pagesBMD-3201 - Trans 2.2 - Cells and Tissue ContinuationOwen RoldanNo ratings yet
- Reaya 3rd PeriodicalDocument16 pagesReaya 3rd PeriodicalRhenz San PedroNo ratings yet
- Fiche 1 EGREDocument2 pagesFiche 1 EGREkhouloud djebabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter #2: Cell Structure Eukaryotic Cell Structure:: Murein Mucopeptide PeptidoglycanDocument3 pagesChapter #2: Cell Structure Eukaryotic Cell Structure:: Murein Mucopeptide PeptidoglycanElle ReyesNo ratings yet
- 10RepCM MamalapatDocument2 pages10RepCM MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- Why Regulation of Gene Expression Is Important?Document36 pagesWhy Regulation of Gene Expression Is Important?api-3700537No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- Organelles Part 1-Making ProteinsDocument28 pagesOrganelles Part 1-Making ProteinscoryguntherNo ratings yet
- CHEM14LAB - Experiment 1Document10 pagesCHEM14LAB - Experiment 1Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument67 pagesThe EarNathanNo ratings yet
- STEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022Document1 pageSTEP1 Sample Pass Report 2022M. Baidar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Railway Recruitment Board ExaminationDocument51 pagesRailway Recruitment Board ExaminationobroirohitNo ratings yet
- Sleep Quality and Stress: A Literature Review.: June 2015Document10 pagesSleep Quality and Stress: A Literature Review.: June 2015Mia Kichelle OliverosNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants in Traumatic Brain Injury: Neuroprotective Mechanism(s)Document44 pagesMedicinal Plants in Traumatic Brain Injury: Neuroprotective Mechanism(s)Dmytro DemashNo ratings yet
- Transitional EpitheliumDocument7 pagesTransitional EpitheliumsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors: Stroke PreventionDocument2 pagesRisk Factors: Stroke PreventionPanduRespatiNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries and Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesDental Caries and Diabetes MellitusAgung HartadwitamaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument4 pagesQuestion Bankop GamingNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture ImpressionsDocument222 pagesComplete Denture ImpressionsAmar BimavarapuNo ratings yet
- Invivo Omega Series Model 1445 1400 Mri Service ManualDocument98 pagesInvivo Omega Series Model 1445 1400 Mri Service ManualGerardo AlvaresNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Zoology-Rev-Test-4-Qn-By-Zta-Malappuram (1) - 230212 - 105754Document5 pagesHsslive-Xi-Zoology-Rev-Test-4-Qn-By-Zta-Malappuram (1) - 230212 - 105754എസ്സാർപി ഊരുചുറ്റൽ തുടരുന്നുNo ratings yet
- Lesson TemplateDocument6 pagesLesson TemplateAnonymous 9p23ZapzNo ratings yet
- NEJM 2014 Fundamentals of Lung AuscultationDocument7 pagesNEJM 2014 Fundamentals of Lung AuscultationFelipe CeaNo ratings yet
- Application PDF Manob - Deho PDFDocument8 pagesApplication PDF Manob - Deho PDFSayeedMdAzaharulIslamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesDocument17 pagesModule 1 Cells As The Basis of Life NotesNicholas MichailouNo ratings yet
- ACS Parotidectomy PDFDocument10 pagesACS Parotidectomy PDFadel santosNo ratings yet
- Trigger Point TheoryDocument3 pagesTrigger Point Theoryarun_chhedaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of PeriodontiaDocument57 pagesSeminar On Cementum: Shreya Das Intern Department of Periodontiashreya dasNo ratings yet