Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Danica RevillaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Danica RevillaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet
by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/
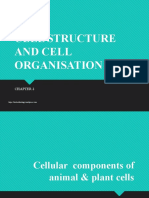
Functions of Cells Osmotic Solutions (cont) Cell Structures (cont)
Basic unit of life H2O moves H2O moves Cell remains Nucleolus
Cell metabolism and energy release into cell out intact
- in nucleus
LYSIS (burst) Crenation (shrinks) Location
Synthesis of molecules
Communication - produce ribosomes that are then
Cell Structures Function transported to the cytoplasm
Reproduction and inheritance
Cytoplasm Ribosome
Whole Cell Activity - Location Inside cell - attached to rough endoplasmic
Location reticulum (RER) or free-floating in
A cells characteristics are determined by the - Jelly-like fluid
cytoplasm
type of proteins it produces Characterist
ic - Produce proteins
Proteins' function is determined by genetics
- Function Give cell shape and hold Function
Information in DNA provides the cell with a cade
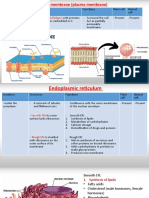
organelles in place RER (Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum)
for its cellular processes
Nucleus (not part of the cytoplasm) - Cytoplasm
Osmosis - Location Center of cell Location
- All cells contain nucleus at some - Membranes with ribosomes
What is Diffusion of water across a cell
Characterist point Characte attached
it? membrane
ristic
ics
Osmotic the force required to prevent
- Function Houses DNA - Site of protein synthesis
Pressure movement of water across cell
Function
membrane Nuclear Envelope
SER (Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum)
A measure of the tendency of water to move by - Location: edge of nucleus
osmosis across a selectively permeable - Cytoplasm
Nuclear Pores
membrane Location
- Location Surface of nucleus
- membranes with no ribosomes
Osmotic Solutions - Function Where materials pass in and out Characte
of nucleus ristic
Hypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic
Chromosome - Site of lipid synthesis
Solutions Solutions Solutions
Function
- Location Inside nucleus
- lower higher Equal
Golgi Apparatus
concentration concentration concentrati - Made of DNA and proteins
of solutes of solutes ons of Characterist - Cytoplasm
outside cell outside cell solutes ic Location
Higher higher Water - Function Part of genetic makeup - Closely, packed stacks of
concentration concentration doesn't Characte membranes
Chromatin
of H2O outside of H2O inside move ristic
- Location Inside nucleus
cell cell - Collect, sort, package, and
- Loosely coiled chromosomes
Function distribute proteins and lipids
Characterist
Secretory Vesicle
ic
- Cytoplasm
Location
- Distributes materials out of cell
Function
By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 1 of 4. https://apollopad.com
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet
by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/
Cell Structures (cont) Movement through the Cell Membrane Endocytosis
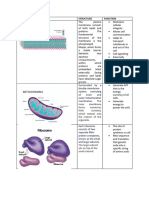
Lysosome - Cell membrane - Enzymes, glycogen, What is Process that brings materials into
selectively and potassium are it? cell using vesicles
- Location Cytoplasm
determines what can found in higher
1. Cell eating (solid particles)
- Function Enzymes that digest foreign pass in and out of the concentrations INSIDE
Phagocyto
material
cell the cell
sis
Mitochondria
- Sodium, calcium, - Nutrients must be 2. Cell drinking (liquid particles)
- Location Cytoplasm and chloride are able to enter the cell Pinocytosi
found in higher and waste products
- Contains folds (cristae) s
concentrations must be able to exit
Characteristic 3. Receptor mediated endocytosis
OUTSIDE the cell the cell
s
1. Directly through O2 and CO2 (small
- Function Produces ATP Cytoskeleton
diffusion (passive): molecules)
What is is? - Cells framework
Main Components of a cell 2. Facilitated - proteins that extend
- Made of proteins
diffusion (passive) from one side of the
Plasma or cell membrane Functions - Provide support
through membrane cell membrane to other
Organelles - Size, shape and - Hold organelles in place
channels:
charge (+/-) determine - enable cell to change
Cytoplasm
what can go through shape
- Ex. Na+ passes Types of Cytoskeleton
Jobs of the Cell Membrane
through Na+ channels
Microtubules - Largest diamete
1. Separate the inside from the outside of the
3. Carrier - bind to molecules, - Provide structural
cell
molecules: transport them across, support
2. Enable the immune system to recognize the and drop them off - Form cilia and flagella
cell as self or non-self --> marker glycoproteins
4. Vesicles: - Can transport a Intermediate - Medium diameter
or glycolipids
variety of materials filaments - maintain cell shape
3. Attach cells together or to the extracellular - Fuse with cell
Microfilaments - Smallest diameter
matrix --> adhesion proteins membrane
- Involved in cell
4. Receive signals from outside the cell and movement
transmit the signals to inside the cell -->
receptor proteins
Cell Division
5. Selectively transport substances from inside
to outside the cell, or outside to inside the cell - Formation of 2 daughter cells from a single
via transport mechanisms parent cell
- Uses mitosis and meiosis
- each cell (except sperm and egg) contains 46
chromosomes (diploid)
By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 2 of 4. https://apollopad.com
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet
by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/
Cell Division (cont) Cell Membrane (cont) Mediated Transport Mechanisms (cont)
- Sperm and egg contain 23 chromosomes Nonpolar Regions - "tails" Counter - a diffusing substance moves in
(haploid) - hydrophobic porter direction opposite to that of
- away from H2O protein transported substance
Mitosis
- Cell division that occurs in all cells except sex cell membrane consists of phospholipids,
cells cholesterol (for strength and flexibility), and Microtubules of the Cytoskeleton
proteins
- Forms 2 daughter cells Centriole - Composed of 9 microtubules
1. Interphase: 46 chromosomes Centrosome - 2 centrioles oriented
Diffusion
perpendicular to one another.
2. Prophase: Chromosomes doubled to 92
What is movement of molecules from areas Plays a role in mitosis
3. Prometaphase: Nucleus dissolves and it? of high to low concentration
Flagella
microtubules attach to centromeres
Solution solid, liquid, or gas that contains
4. Metaphase: Chromosomes align at middle - Location Cell surface
one or more solutes
of cell - 1 per cell
Solute Substance added to solvent that
Characterist
5. Anaphase: Separated chromosomes pulled dissolves
apart ic
Solvent Substance such as H2O that
- Function move cell, Eg. Sperm
6. Telophase: Microtubules disappear cell solute is being added to
division begins Cilia
Is energy no
7. Cytokinesis: Two daughter cells formed required? - Location Cell Surface
each with 46 chromosomes
- Many per cell
Mediated Transport Mechanisms Characterist
Cell Membrane ic
Facilitat - diffusion with aid of a carrier
Funtions: - Selective barrier molecule - Function Move materials across cell's
ed
-Encloses cytoplasm - requires no ATP surface
diffusio
Extracellular Material outside of cell n - passive transport Microvilli
Intracellular Material inside cell Active - moves substance from low to high - Location Cell Surface
membrane transpor concentration - Shorter than cilia
Fluid Mosaic a 2D liquid in which t - required ATP Characterist
Model phospoholipids and proteins Ex. Sodium-potassium pump ic
diffuse easily Cotrans - a diffusing substance moves in - Function Increase surface area
Made of phospholipids form a double port same direction as a transported
phospholipids layer or bilayer substance
DNA
and proteins
Double helix
Polar Region - "heads"
- hydrophilic Deoxyribose-phosphate backbone
- exposed to H2O Nucleotide base pairs
Backbone = sugar (ribose-phosphate)
By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 3 of 4. https://apollopad.com
Cell Structure and Function Cheat Sheet
by Morghay123 via cheatography.com/53154/cs/14396/
DNA (cont)
Gene Expression
- information in DNA directs protein synthesis
- nucleotide sequence of a gene determines amino acid sequence of
specific protein
- Enzymes regulate chemical reactions
- Uses transcription and translation
Flow of Genetic Information
Central Dogma DNA - transcribe - RNA -
translate - Protein
Transcription
- Process by which DNA is read - Occurs in the nucleus
- Produces mRNA - mRNA contains codons
- Codons: set of 3 nucleotide bases that code for a particular amino
acid
Translation
- Process by mRNA is converted into - Produces proteins
amino acids (polypeptides)
- Codons pair with anticodons
- anticodons: 3 nucleotide bases carried by tRNA
By Morghay123 Published 20th January, 2018. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
cheatography.com/morghay123/ Last updated 20th January, 2018. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
Page 4 of 4. https://apollopad.com
You might also like
- H2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFDocument5 pagesH2 Biology Notes On Cell Structure Cell Organelles PDFAnonymous 0iTAS7No ratings yet
- Cheatt Sheet #2Document2 pagesCheatt Sheet #2layanhaliloNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lec Module 3Document6 pagesZoology Lec Module 3Camille AlzolaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- (Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio NotesDocument11 pages(Organelles & Cellular Structures) H1 Bio Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Exercise 2Document5 pagesThe Cell: Exercise 2Jasmine Nicole EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument8 pagesCells and TissuesA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell StructureririNo ratings yet
- Cells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusDocument8 pagesCells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusHazimah MohiddinNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document2 pagesGroup 3Rane MandapatNo ratings yet
- Cells: Hap - Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesCells: Hap - Cell BiologyKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- CellDocument36 pagesCellwnslthmangulad05No ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Grayka QuiapoNo ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane Endoplasmic Re Culum: Structure & Composi OnDocument1 pagePlasma Membrane Endoplasmic Re Culum: Structure & Composi OnShein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Terms of Use: Graphics Used in This PackDocument15 pagesTerms of Use: Graphics Used in This PackclauspNo ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Outline: Introduction To The CellDocument3 pagesOutline: Introduction To The Cellvinnie0905No ratings yet
- Slides 06 CellularStructure CellBiologyDocument14 pagesSlides 06 CellularStructure CellBiologyCamila HerreraNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 (The Cell)Document6 pagesActivity 2 (The Cell)Sophia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Vinay IP Bio Notes (Updated)Document136 pagesVinay IP Bio Notes (Updated)Vinay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1Document4 pagesBiology Lesson 1Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)Document2 pagesCell As A Unit of Life (Science Form 1 - Short Notes)jrpyroNo ratings yet
- Biochem PrelimsDocument25 pagesBiochem Prelimslcpanaligan4175antNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document10 pagesCell 3OscarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document153 pagesLecture 3Miya GordNo ratings yet
- Omnis Cellua e Cellula, Which All Cells Only Arise From Pre-Existing CellsDocument3 pagesOmnis Cellua e Cellula, Which All Cells Only Arise From Pre-Existing CellsArvie Jane De TorresNo ratings yet
- Ocr A Level Biology CheatsheetDocument21 pagesOcr A Level Biology CheatsheetminaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cheatsheet PDFDocument21 pagesBiology Cheatsheet PDFAhmad Mubashar80% (5)
- 02 - Cell Worksheet Factory CardsDocument5 pages02 - Cell Worksheet Factory Cardsangeladel484No ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument65 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanLauren ChikwehwaNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument41 pagesBiology NotesJess DecostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their Functionsllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal Cell ChartDocument1 pagePlant Animal Cell ChartKram YnothnaNo ratings yet
- MC3 - Lecture Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMC3 - Lecture Activity 1 PDFFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Bab 2Document31 pagesBio F4 Bab 2Alwani FarahiNo ratings yet
- B1 - Trilogy Cells - Knowledge GoalDocument2 pagesB1 - Trilogy Cells - Knowledge GoalmagentaihdNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell LabelDocument1 pagePlant Cell LabelAllen TagatacNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell StructureDocument1 page1.1 Cell Structuremii chanrNo ratings yet
- Cell+Structure 1Document38 pagesCell+Structure 1madhubalaNo ratings yet
- 02 - The CellDocument91 pages02 - The CellDASHNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - 2 - Cell Organelles - 1Document26 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - 2 - Cell Organelles - 1shreya ravindranNo ratings yet
- 5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2018Document2 pages5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2018GUCCINONo ratings yet
- CELLDocument18 pagesCELLGabriel RamosNo ratings yet
- 96 (1) Tissue and OrgansDocument81 pages96 (1) Tissue and OrgansbillNo ratings yet
- La CelulaDocument50 pagesLa CelulaMarcos Yactayo Yactayo gutierrezNo ratings yet
- OL Comprehensive BiologyDocument180 pagesOL Comprehensive Biologyo8viiNo ratings yet
- Draw A Simple Eukaryotic Cell and Label All The Parts CompletelyDocument3 pagesDraw A Simple Eukaryotic Cell and Label All The Parts CompletelyJan Edward Abarientos MandaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio MidtermDocument4 pagesCell Bio MidtermCó Tên KhôngNo ratings yet
- Cellular PhysiologyDocument32 pagesCellular Physiologyانس ابوهيبة0% (1)
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument64 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanAdham EtmanNo ratings yet
- Clear My Choice: Not Yet Answered Marked Out of 1.00Document7 pagesClear My Choice: Not Yet Answered Marked Out of 1.00medodiabNo ratings yet
- Sedimen UrinDocument73 pagesSedimen UrinHerbanu PramonoNo ratings yet
- ImmunityDocument44 pagesImmunitysatishNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9Document17 pagesThe Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9hareem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Pathology MCQ PDFDocument32 pagesPathology MCQ PDFAmanullah100% (1)
- HINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareDocument4 pagesHINANAY SSG 4 Antepartum CareHenie Louise HinanayNo ratings yet
- ERBEJETDocument8 pagesERBEJETHossain TanjilaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function 2016Document11 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and Function 2016GunnNo ratings yet
- ADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesADIL BSN - 1C Manual Endocrine Systembernadil01No ratings yet
- MCQ On Gynecological CytologyDocument28 pagesMCQ On Gynecological CytologyVincent Muhayimana100% (4)
- Module in Science 9 First Quarter Week 6 Parts of A ChloroplastDocument2 pagesModule in Science 9 First Quarter Week 6 Parts of A ChloroplastKaryll ColumnaNo ratings yet
- Sliding Filament Model of ContractionDocument3 pagesSliding Filament Model of ContractionRATU ZULFI AMALIAHNo ratings yet
- A Sporadic Case of Delayed Implantation After In-Vitro Fertilization in The Human?Document4 pagesA Sporadic Case of Delayed Implantation After In-Vitro Fertilization in The Human?gardener10No ratings yet
- PETROMASTOIDDocument7 pagesPETROMASTOIDAhlen Chris TuazonNo ratings yet
- Case Study On ANC WITH Severe Anemia FINALDocument53 pagesCase Study On ANC WITH Severe Anemia FINALSoumya Rajeswari100% (1)
- Human ReproductionDocument96 pagesHuman Reproductionsanya razaNo ratings yet
- Unique Presentation of Submandibular Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUnique Presentation of Submandibular Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Case Report and Review of LiteratureInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Stem Cell TechnologyDocument48 pagesIntroduction of Stem Cell TechnologyR. EssoNo ratings yet
- The Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionDocument192 pagesThe Essential Review Guide For Passing The Mblex Licensing Exam 2017 EditionSabrina Marie100% (3)
- PBL Eye No1,2,3Document9 pagesPBL Eye No1,2,3adelaNo ratings yet
- Bleeding and ThrombosisDocument27 pagesBleeding and Thrombosisswathi bsNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument8 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumShahab Saqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Neuroblastoma IHCDocument4 pagesNeuroblastoma IHCSyedNo ratings yet
- Session #14 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document8 pagesSession #14 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- The Mechanism of Food AlergyDocument3 pagesThe Mechanism of Food AlergyWasiti Puji RahayuNo ratings yet
- Group 5. Movements Of: Gastrointestinal TrackDocument18 pagesGroup 5. Movements Of: Gastrointestinal TrackHusseinNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q2 - Week 3-Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument48 pagesG7 Science Q2 - Week 3-Levels of Biological OrganizationJessa-Bhel AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Ontario - Schedule of Benefits 2021Document970 pagesOntario - Schedule of Benefits 2021Raj LoganathanNo ratings yet
- ML Biology Chapter 08Document44 pagesML Biology Chapter 08Evans Junior T. MuvutiNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document3 pagesModule 9Gia Joy B. PardeNo ratings yet