Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clampers EPC LAB Updated Latest4.12.23
Uploaded by
ganeshrpujarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Clampers EPC LAB Updated Latest4.12.23
Uploaded by
ganeshrpujarCopyright:
Available Formats
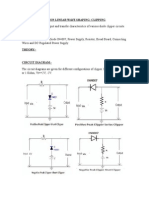
BIASED CLIPPERS AND CLAMPERS
Aim : To design and test biased clipping and clampers circuits using MULTI SIM.
Tools Required : PC loaded with MULTI SIM Software.
Component Required:
SL NO Component Value/Number
1 Diode 1N4007G
2 Resistor 100Ω,1kΩ,10kΩ,100 kΩ
3 Capacitor 100µF
Theory:-
Clippers:
The circuit with which the waveform is shaped by removing (or clipping) a portion of the applied
wave is known as a clipping circuit. Clippers are networks that employ diodes to clip away portions of an
input signal without distorting the remaining part of the applied signal. These clipper circuits transfer a
selected portion of the input waveform to the output. Diode clipping circuits are used to prevent a
waveform from exceeding some particular limit in either negative or positive or both sides of it. This is
achieved by connecting the diode in series or in parallel circuit. Variable DC voltage is connected in the
circuit to achieve required level of clipping. By using different levels of DC voltages, it is possible to get
different level of clipping in positive and negative side. The circuit with which the waveform is shaped by
removing a portion of the applied wave is known as a clipping circuit.
These clipper circuits are also called as limiters. Following the important diode clippers are
1)Positive clippers 2)Negative clippers 3)Biased clippers 4)Combinational clippers
There are generally two categories of clippers: series and parallel to load. In series configuration
diode is in series with the load, but in parallel the diode is parallel to load.
Clampers:
Clamper is a circuit that "clamps" a signal to a different DC level without changing the
appearance (or Shape) of the applied signal. The different types of clampers are positive, negative and
biased clampers. A clamping network must have a capacitor, a diode and a resistive element. The
magnitude of R and C must be chosen such that the time constant RC is large enough to ensure that
the voltage across the capacitor does not discharge significantly during the interval the diode is not
conducting. By connecting suitable DC voltage in series with the diode, the level of swing can be
varied.
A circuit that places either the Positive or Negative peak of a signal at a desired fixed DC level
is known as clamping circuit. The operation of a clamper is based on the principle that charging time of a
capacitor is made very small as compared to its discharging time.
1. Positive Clamper Circuit without reference
Circuit diagram Expected waveform Practical waveform
Fig 1. Positive Clamper Circuit without reference
2. Negative Clamper Circuit without reference
Circuit diagram Expected waveform Practical waveform
Fig 2. Negative Clamper Circuit without reference
3. Positive Clamper Circuit with reference
Design
Let negative peak be clamped at Vo(min)= -4V
From Fig 1 given below , Vo(min)= -Vref - Vᵞ
Therefore Vref= -Vo(min) - Vᵞ =-(-4) – 0.6 = 3.4V
Circuit diagram Expected waveform Practical waveform
Fig3. Positive Clamper Circuit with reference
4. Negative Clamper Circuit with reference
Design
Let positive peak be clamped at Vo(max)=+4V
From Fig given above , Vo(max)=Vref + Vᵞ
Therefore Vref=Vo(max) - Vᵞ =4 – 0.6 =3.4V
Circuit diagram Expected waveform Practical waveform
Fig4. Negative Clamper Circuit with reference
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Clamper EPC LAB Updated Latest4.12.23Document3 pagesClamper EPC LAB Updated Latest4.12.23ganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- SodaPDF Converted AKOL LAB6Document21 pagesSodaPDF Converted AKOL LAB6ballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsFrom EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNo ratings yet
- 938 Aurora Boulevard, Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument10 pages938 Aurora Boulevard, Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMikko OmanaNo ratings yet
- عملي دوائر اليومDocument27 pagesعملي دوائر اليوممعاً إلى الجنةNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Electronics1 PDFDocument19 pagesLesson 3 - Electronics1 PDFLapugot, Anne Carla, Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- عملي دوائر اليوم2Document24 pagesعملي دوائر اليوم2معاً إلى الجنةNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- 7-Study The Diode ClippingDocument4 pages7-Study The Diode ClippingMohsin TariqNo ratings yet
- EC &LD-Lab ManualDocument50 pagesEC &LD-Lab ManualEk naye din ki shuruwat kroNo ratings yet
- Epc LabDocument9 pagesEpc LabganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- ClamperDocument4 pagesClamperJhoanna Mae Q. AmaroNo ratings yet
- Electroinc Experiment 3Document9 pagesElectroinc Experiment 3forsan15432No ratings yet
- Non Linear Wave Shaping ClippingDocument5 pagesNon Linear Wave Shaping ClippingManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Beee Exp 7Document8 pagesBeee Exp 7aman vermaNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator Manual PDFDocument73 pagesMultivibrator Manual PDFAvijitRoyNo ratings yet
- EL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 04Document6 pagesEL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 04Jawwad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab Manual - Updated - 103726Document93 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab Manual - Updated - 103726Yangannagari VineelareddyNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - 5: Submitted ToDocument5 pagesLab Report - 5: Submitted ToSaif UR RahmanNo ratings yet
- Clippers 0 PDFDocument6 pagesClippers 0 PDFNadineNo ratings yet
- Exp 7-Clipper ClamperDocument3 pagesExp 7-Clipper ClamperNidhish Milind SonavaleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Electronics1Document30 pagesLesson 3 - Electronics1Ron Neil MicosaNo ratings yet
- Clamping Circuits (Diode)Document4 pagesClamping Circuits (Diode)Manjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Analog System Design ExperimentsDocument27 pagesAnalog System Design ExperimentsAnsh BhaganiaNo ratings yet
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- 1104 - Clamper Circuit PDFDocument7 pages1104 - Clamper Circuit PDF1101 MilonNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document9 pagesLab 0549 - 103 - Umair HossainNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument45 pagesEDC Lab ManualChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- Non Linear Wave ShapingDocument4 pagesNon Linear Wave Shapingh9emanth4No ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Clippper and Clamper CircuitsDocument7 pagesLab 4 - Clippper and Clamper CircuitseyobNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument8 pagesDiode Applicationsمعتصم الكاملNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EC II Format 2Document53 pagesLab Manual EC II Format 2nishavs100% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesPDC Lab ManualKumar Goud.K90% (10)
- EC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswersDocument83 pagesEC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswerssunandaalurNo ratings yet
- Clipper CircuiDocument8 pagesClipper Circuiwaqar_baloch_070% (1)
- Diode and Its ApplicationsDocument39 pagesDiode and Its ApplicationsUsama SidhuNo ratings yet
- EEE 234L Spring 2022 - Lab Sheet 3Document6 pagesEEE 234L Spring 2022 - Lab Sheet 3Mahmud Sazzad MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4,5Document22 pagesExperiment 4,5Aryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument61 pagesElectronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory: Lab ManualSrihari Y.sNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2Document92 pagesLab Manual 2Joyce GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- EDC ManualDocument34 pagesEDC ManualRahul Mahar100% (1)
- Unit 1 Lecture 2 - RevDocument40 pagesUnit 1 Lecture 2 - RevMohak KumarNo ratings yet
- Bemt 2Document34 pagesBemt 2Sai GanthodNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With Orcad Pspice 10.5Document36 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual With Orcad Pspice 10.5Muhammad Ahtisham Asif100% (2)
- 2 Pulse CircuitsDocument74 pages2 Pulse CircuitsWaqar Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- SNDT ManualDocument42 pagesSNDT ManualDhaval BhojaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document12 pagesLab 3whole usesNo ratings yet
- DAGA Lab6Document19 pagesDAGA Lab6Kristan Oneal DagaNo ratings yet
- Edc-Open Ended Lab: BEE - 56 A Capt Adnan Ahmad KhanDocument5 pagesEdc-Open Ended Lab: BEE - 56 A Capt Adnan Ahmad Khanadnan3ahmad3khan-2No ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentDocument58 pagesExperiment 1: Aim of The ExperimentAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- Cruzat Lat Mulingbayan LabNo.1 PDFDocument25 pagesCruzat Lat Mulingbayan LabNo.1 PDFRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- EEE 111 Diode Applications: Topic 2 (Chapter 2)Document54 pagesEEE 111 Diode Applications: Topic 2 (Chapter 2)Naruto DragneelNo ratings yet
- 117766110-PDC-Lab-Manual 4Document46 pages117766110-PDC-Lab-Manual 4Suda KrishnarjunaraoNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Diode Applications: PurposeDocument3 pagesLab 2 Diode Applications: Purposeabraham8085No ratings yet
- Exp.4 FloresDocument4 pagesExp.4 FloresBrittney Mhey FloresNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics SylubusDocument5 pagesIndustrial Electronics SylubusganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- Bescom GSTN No: 29Aaccb1412G1Z5Document2 pagesBescom GSTN No: 29Aaccb1412G1Z5ganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- Dayananda Sagar College of EngineeringDocument15 pagesDayananda Sagar College of EngineeringganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- Epc LabDocument9 pagesEpc LabganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- 3semTT 2023Document3 pages3semTT 2023ganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- ESP and ETS Integration PlansDocument2 pagesESP and ETS Integration PlansganeshrpujarNo ratings yet
- Latex TutorialDocument27 pagesLatex TutorialSalman AhmadNo ratings yet
- HD 70 CDocument101 pagesHD 70 CPhamVanGiangNo ratings yet
- Dataram RAMDisk Users ManualDocument20 pagesDataram RAMDisk Users ManualBabis ArbiliosNo ratings yet
- Ic Assignment 2Document1 pageIc Assignment 2Nilven GastardoNo ratings yet
- Сравнит. лингвистикаDocument22 pagesСравнит. лингвистикаАнастасия ДобровольскаяNo ratings yet
- Gear Manufacturing ProcessDocument30 pagesGear Manufacturing ProcessSanjay MehrishiNo ratings yet
- Aviation Service ManualDocument28 pagesAviation Service ManualArmo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Calculations of The EFG Tensor in DTN Using GIPAW With CASTEP and QE SoftwareDocument12 pagesCalculations of The EFG Tensor in DTN Using GIPAW With CASTEP and QE SoftwareAllen MNo ratings yet
- Communication ManagementDocument20 pagesCommunication Managementmandalapu_devi5240No ratings yet
- Understand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)Document2 pagesUnderstand Concept of Multi-Rate Signal Processing: (Autonomous College Affiliated To University of Mumbai)nicO neeNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Systems, 9th Edition: Chapter 9Document50 pagesAutomatic Control Systems, 9th Edition: Chapter 9physisisNo ratings yet
- 10 - Starting and ReversingDocument4 pages10 - Starting and ReversingAisha Zaheer100% (3)
- Assigment Sheet Tast 2 Aina MardianaDocument10 pagesAssigment Sheet Tast 2 Aina MardianaAina MardianaNo ratings yet
- How To Implement A Distributed CommonJ Work Manager ESDocument20 pagesHow To Implement A Distributed CommonJ Work Manager ESAbmel Salim LopessierNo ratings yet
- 3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanaDocument14 pages3681 113533 1 SM - , mutasiCVKaroseriLaksanataufiq hidayatNo ratings yet
- Applied Dynamics PDFDocument862 pagesApplied Dynamics PDFLeonardo Mereles100% (1)
- DBMS Practice QueestionsDocument2 pagesDBMS Practice QueestionsAbhibhava Bhatt VIII [E] 4No ratings yet
- Sap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFDocument52 pagesSap PP 01 Organizational Structure Overview PDFMahesh KamdeyNo ratings yet
- Pega Interview PreperationDocument35 pagesPega Interview PreperationPramodh SSNo ratings yet
- 100 Irregular Plural Nouns ListDocument3 pages100 Irregular Plural Nouns Listjinesham007No ratings yet
- Motor Protection: Module #2Document32 pagesMotor Protection: Module #2Reymart Manablug50% (2)
- Studyprotocol Open Access: Yue Yan, Yalin Zhan, Xian 'E Wang and Jianxia HouDocument7 pagesStudyprotocol Open Access: Yue Yan, Yalin Zhan, Xian 'E Wang and Jianxia HouGery KrismawanNo ratings yet
- MATHSDocument221 pagesMATHSAbdulai FornahNo ratings yet
- Ch02HullOFOD9thEdition - EditedDocument31 pagesCh02HullOFOD9thEdition - EditedHarshvardhan MohataNo ratings yet
- R134a HXWC Series Water Cooled Screw Flooded Chillers Cooling Capacity 200 To 740 Tons 703 To 2603 KW Products That Perform PDFDocument16 pagesR134a HXWC Series Water Cooled Screw Flooded Chillers Cooling Capacity 200 To 740 Tons 703 To 2603 KW Products That Perform PDFmohamad chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2B 6th SemesterDocument28 pagesMini Project 2B 6th SemesterRohit Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Information Data and ProcessingDocument10 pagesInformation Data and ProcessingarshdeepsinghdhingraNo ratings yet
- Report Builder ENGDocument94 pagesReport Builder ENGfran reyNo ratings yet
- Evolution of C-Si: PV Cell TechnologiesDocument52 pagesEvolution of C-Si: PV Cell TechnologiesFábio VelôzoNo ratings yet