Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences Between Steady-State and Dynamic Simulation
Uploaded by
Mustafa AhsanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences Between Steady-State and Dynamic Simulation
Uploaded by
Mustafa AhsanCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences
between
Steady-state
simulation and
Dynamic
simulation
Chemsys Innovative Solutions
Differences between Steady-state
simulation and Dynamic simulation
Steady-State Dynamic
Simulation Simulation
Analyzes the behavior of a system at a Analyzes the behavior of a system over
fixed, steady operating point. It time, considering transient conditions
Definition assumes equilibrium and calculates and dynamic behavior. Tracks the
steady-state values for variables of response of variables during changing
interest. conditions.
Time-invariant analysis. Assumes the Time-dependent analysis. Considers
system remains at a fixed operating changes and transitions over time.
Time point throughout the analysis. Evaluates transient behavior and dynamic
Consideration response to varying inputs and
disturbances.
Assumes the system is in a state of Recognizes that the system experiences
equilibrium, with balanced inputs and changes and transitions over time. May
Equilibrium outputs. involve multiple equilibrium states or
adjusting to changes in
inputs/disturbances.
Typically assumes constant or fixed Considers varying inputs and disturbances
inputs throughout the analysis. during the simulation. Reflects the
Inputs dynamic nature of the system.
Focuses on calculating steady-state Tracks the transient response and
values for variables of interest. dynamic behavior of variables over time.
Response Provides a snapshot of system Captures system behavior during
behavior under steady conditions. transient periods or changes in
inputs/disturbances.
Evaluates system stability at the fixed Examines stability during dynamic events
operating point. Examines stability or disturbances. Considers factors like
Stability margins, eigenvalues, or frequency transient response, oscillations, and
response. stability criteria.
Used for initial design, steady-state Useful for system response evaluation,
optimization, and performance control system design, transient analysis,
Applications analysis. Provides insights into system and understanding dynamic interactions
behavior under steady conditions. between system components.
Determining the power output of a Studying the response of a control system
power plant under steady operating to a sudden change in input.
Example conditions.
You might also like
- Global Stability Properties of Equilibria Periodi - 1996 - Applied MathematicalDocument13 pagesGlobal Stability Properties of Equilibria Periodi - 1996 - Applied MathematicalNestorNo ratings yet
- Report SeminarDocument23 pagesReport SeminarpradnyaekadNo ratings yet
- 01 - M&S-Introduction To Modeling and SimulationDocument40 pages01 - M&S-Introduction To Modeling and Simulationumair fastNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Two Marks QuestionDocument41 pagesControl Systems Two Marks QuestionSk WajuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Continuous Dynamic Systems ModelingDocument23 pagesChapter 3 - Continuous Dynamic Systems Modelinggetachew workuNo ratings yet
- EC2255-Solved Problems in Control System IV Semester ECEDocument182 pagesEC2255-Solved Problems in Control System IV Semester ECEBEKHITI BelkacemNo ratings yet
- HCHE 322 Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument8 pagesHCHE 322 Lecture 1 - IntroductionBrian MasauliNo ratings yet
- Alvarez Johndave Bsece412 Ass#1Document4 pagesAlvarez Johndave Bsece412 Ass#1MelanieNo ratings yet
- Modelling Concepts and ClassificationDocument11 pagesModelling Concepts and ClassificationAshley MendozaNo ratings yet
- Time ResponseDocument7 pagesTime Responseeugeni madaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument17 pages04 - Chapter 1 PDFAnonymous KhhapQJVYtNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionslo803421No ratings yet
- StateDocument176 pagesStateurstranger0No ratings yet
- Closed Loop ResponseDocument8 pagesClosed Loop ResponseJoydeep Choudhury 20UCH030No ratings yet
- KIG 4001 Control Engineering (Group 4) : Time Response AnalysisDocument29 pagesKIG 4001 Control Engineering (Group 4) : Time Response AnalysisNurul Iman Nur ElahiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledProxy EmailNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument12 pagesControl Systemsoyebowale.emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Cyber Physical SystemDocument7 pagesModelling of Cyber Physical SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- An Online Wide-Area Direct Coordinated Control Architecture For Power Grid Transient Stability Enhancement Based On Subspace IdentificationDocument12 pagesAn Online Wide-Area Direct Coordinated Control Architecture For Power Grid Transient Stability Enhancement Based On Subspace IdentificationtusharshharmaNo ratings yet
- Auto Reviewer Vikings OnlyDocument17 pagesAuto Reviewer Vikings OnlyRick James RojasNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium-Independent Dissipativity With Quadratic Supply RatesDocument15 pagesEquilibrium-Independent Dissipativity With Quadratic Supply RatesHamed PourazadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transient Stability: Starrett Mini-Lecture #1Document16 pagesIntroduction To Transient Stability: Starrett Mini-Lecture #1Hadi MahmudiNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering: For Third YearDocument9 pagesControl Engineering: For Third YearsaidikNo ratings yet
- Week 1&2Document19 pagesWeek 1&2Yahya MateenNo ratings yet
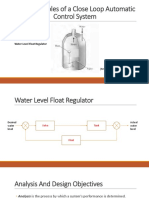
- More Examples of A Close Loop Automatic Control System: Water-Level Float RegulatorDocument11 pagesMore Examples of A Close Loop Automatic Control System: Water-Level Float RegulatorAkiHiro San CarcedoNo ratings yet
- Q2. Give An Example of Each A. Stochastic Model B. Continuous Model C. Discrete Model D. Static Model E. Dynamic ModelDocument2 pagesQ2. Give An Example of Each A. Stochastic Model B. Continuous Model C. Discrete Model D. Static Model E. Dynamic Modelsheena RomNo ratings yet
- Slides CPC PDFDocument536 pagesSlides CPC PDFJam imtiaz100% (1)
- @2 - Mathematical Modeling of Control System ?Document52 pages@2 - Mathematical Modeling of Control System ?Mir Md Mofachel HossainNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - L1 - Introduction and Basic Concepts of ControlDocument33 pagesWeek 1 - L1 - Introduction and Basic Concepts of ControlOlerile AnaniaNo ratings yet
- Modelling - Chapter 3Document121 pagesModelling - Chapter 3TÍN Phạm Nguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignDocument14 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Pms 40 WordsDocument2 pagesPms 40 WordsTahreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- Classifications of SystemsDocument14 pagesClassifications of Systemsياسين خالدNo ratings yet
- CHE 57 Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHE 57 Midterm Exam ReviewerProxy EmailNo ratings yet
- DynamicModel7 3 PDFDocument224 pagesDynamicModel7 3 PDFArcangelo Di TanoNo ratings yet
- Prelims Report: Che-529 Process Dynamics and ControlDocument17 pagesPrelims Report: Che-529 Process Dynamics and ControlMariel ManiboNo ratings yet
- Develop Systems With Stability (INF 5) FINALDocument7 pagesDevelop Systems With Stability (INF 5) FINALEmmanuel David Beltran RodriguezNo ratings yet
- IOE 474 Exam Review2Document20 pagesIOE 474 Exam Review2skempa1No ratings yet
- Adaptive Control - Wikipedia PDFDocument20 pagesAdaptive Control - Wikipedia PDFig: sidaryNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control Chapter 1Document19 pagesIndustrial Control Chapter 1Qayyum AqasyahNo ratings yet
- 2 - Generator Model Validation PDFDocument62 pages2 - Generator Model Validation PDFRaihan KamilNo ratings yet
- Bifurcation Control of Nonlinear - SinhaDocument8 pagesBifurcation Control of Nonlinear - SinhaThiago CésarNo ratings yet
- Dhan Kumar Rai 0701CM171013 Vi Sem Assignment 1 On Chemical Process ControlDocument4 pagesDhan Kumar Rai 0701CM171013 Vi Sem Assignment 1 On Chemical Process ControlYng Dmb Broke GuyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document19 pagesLecture 1FarooqNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 AIM: Absolute Stability, Relative Stability, and Steady-State ErrorDocument8 pagesExperiment 1 AIM: Absolute Stability, Relative Stability, and Steady-State ErrorSaranshNo ratings yet
- Intro To Control TheoryDocument15 pagesIntro To Control TheoryDavid AmarteyNo ratings yet
- Simulation 4 UnitDocument81 pagesSimulation 4 UnitsatyamicNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control Using Multiple ModelsDocument17 pagesAdaptive Control Using Multiple Modelsfarid22f2002No ratings yet
- Control Systems: Module: Modelling of SystemsDocument19 pagesControl Systems: Module: Modelling of Systemsee210002004No ratings yet
- Ec3351 Control SystemsDocument18 pagesEc3351 Control SystemsParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Course Code: KKEK 3152 Modeling of Chemical ProcessesDocument47 pagesCourse Code: KKEK 3152 Modeling of Chemical ProcessesRishi KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2sheena RomNo ratings yet
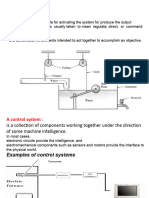
- 1 Control Pres 1Document27 pages1 Control Pres 1Ahmed ShabanNo ratings yet
- Introduction 23Document16 pagesIntroduction 23Ggfgsgege GegsgsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Physical Modelling 1Document28 pagesPhysical Modelling 1Kotadpp KumarNo ratings yet
- Reference ReportDocument24 pagesReference ReportMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PMC & Engineering ContractorDocument2 pagesDifference Between PMC & Engineering ContractorMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Final PrintDocument5 pagesFinal PrintMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Averil Nivya ReportDocument35 pagesAveril Nivya ReportMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice-March2021v1Document78 pagesEngineering Practice-March2021v1Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Mohsin Hashmi - ResumeDocument6 pagesMohsin Hashmi - ResumeMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Das Ew 0010 Iso 01Document3 pagesDas Ew 0010 Iso 01Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Telephone Bills Format 2020-2021Document1 pageTelephone Bills Format 2020-2021Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
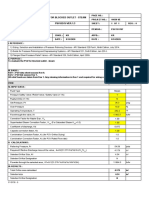
- Blocked Outlet - Steam - psv351707Document2 pagesBlocked Outlet - Steam - psv351707Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Blocked Outlet - Steam - psv351720Document2 pagesBlocked Outlet - Steam - psv351720Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Revamping Coke Gas Cleaning Plant PSV Data Sheet - Unit 351Document13 pagesRevamping Coke Gas Cleaning Plant PSV Data Sheet - Unit 351Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Revamping Coke Gas Cleaning Plant PSV List: Arcelor Mittal TemirtauDocument2 pagesRevamping Coke Gas Cleaning Plant PSV List: Arcelor Mittal TemirtauMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- When Excess Air Becomes Too MuchDocument3 pagesWhen Excess Air Becomes Too MuchMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Maximising Naphtha Through Hydrocracking Refinery of The FutureDocument25 pagesMaximising Naphtha Through Hydrocracking Refinery of The FutureMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Telephone Bill April 2020 To Aug 2020Document10 pagesTelephone Bill April 2020 To Aug 2020Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Sample Declaration Format (Rent Receipt Without PAN)Document1 pageSample Declaration Format (Rent Receipt Without PAN)Mustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Preventive Health Check Up BillsDocument1 pagePreventive Health Check Up BillsMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- SurahDocument5 pagesSurahMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- 5500 I.D. 1400 I.D. 1000: Vessel SpecificationDocument2 pages5500 I.D. 1400 I.D. 1000: Vessel SpecificationMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- 5 Petrochemical Projects in Europe You Need To Know AboutDocument1 page5 Petrochemical Projects in Europe You Need To Know AboutMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Vessel Specification: Sonatrach Hassi Messaoud (Algerie) 1BD0933 110 - VDUDocument2 pagesVessel Specification: Sonatrach Hassi Messaoud (Algerie) 1BD0933 110 - VDUMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Design As A Social Practice The Experience of New Build Schools Harry DanielsDocument41 pagesDesign As A Social Practice The Experience of New Build Schools Harry DanielsnatloznubNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Digital LeaderDocument28 pagesHow To Be A Digital LeaderSeta A WicaksanaNo ratings yet
- Perbedaan Kadar Kolesterol Sebelum Dan Sesudah Dilakukan Brisk Walking Pada SiswaDocument8 pagesPerbedaan Kadar Kolesterol Sebelum Dan Sesudah Dilakukan Brisk Walking Pada SiswaEva RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFMostafa SalahNo ratings yet
- Developing The Psychological Capital of ResiliencyDocument7 pagesDeveloping The Psychological Capital of ResiliencyAnastasia EL SayyedNo ratings yet
- Internship Report 1Document27 pagesInternship Report 1Saarthak AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Entrep Mind.Document9 pagesReviewer in Entrep Mind.John Alpon CatudayNo ratings yet
- Review of Past LessonDocument30 pagesReview of Past LessonDiana Ross Dayrit DiazNo ratings yet
- Information Bulletin of TS DSC-2024Document24 pagesInformation Bulletin of TS DSC-2024Sugander SanthapuriNo ratings yet
- Is Mercury A:: Natural Benefic or Natural Malefic?Document1 pageIs Mercury A:: Natural Benefic or Natural Malefic?STELLA MALLIOTAKINo ratings yet
- Name: - Yr/Section: - Date: - Activity No. 1 Define and Illustrate The Process of Ridge Counting and Ridge TracingDocument6 pagesName: - Yr/Section: - Date: - Activity No. 1 Define and Illustrate The Process of Ridge Counting and Ridge TracingMardy Hoyohoy BarraquioNo ratings yet
- Modern Public School: HOLIDAY HOME WORK, 2021-2022 Class Xii, ScienceDocument23 pagesModern Public School: HOLIDAY HOME WORK, 2021-2022 Class Xii, Scienceaaditya sharmaNo ratings yet
- EN 10168 - 2004 - Steel Products - Inspection Documents PDFDocument12 pagesEN 10168 - 2004 - Steel Products - Inspection Documents PDFBogdanNo ratings yet
- CV - Elchin SalimovDocument3 pagesCV - Elchin SalimovMicRoToneNo ratings yet
- Arrays: Instructor's Manual Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesArrays: Instructor's Manual Table of ContentsLeonard GojerNo ratings yet
- New ScientistDocument60 pagesNew ScientistTrúc Phan Nguyên Thảo100% (1)
- Fe Ce 511 Prestressed ConcreteDocument6 pagesFe Ce 511 Prestressed ConcreteJeana Rick GallanoNo ratings yet
- The National Atlas-Printable MapsDocument2 pagesThe National Atlas-Printable MapsAlexandre RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Tender Evaluation Using Weighted Criteria For Building Works and ServicesDocument11 pagesGuidelines On Tender Evaluation Using Weighted Criteria For Building Works and Serviceschristopher hersantNo ratings yet
- Outline Impact of A TeacherDocument3 pagesOutline Impact of A TeacherShakirah SariNo ratings yet
- Ethics Part2 - BBColl2021Document26 pagesEthics Part2 - BBColl2021Michael MatshonaNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 1.3 PDFDocument12 pagesATPL Inst 1.3 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- SFS Academic Council Report On Map of The Modern World ChangesDocument7 pagesSFS Academic Council Report On Map of The Modern World ChangesJuliana BrintNo ratings yet
- Plant Design Project LogbookDocument4 pagesPlant Design Project Logbookمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Vision Test JaegerDocument1 pageVision Test JaegerManivannanMudhaliar100% (2)
- Styrolux 684D SBC Ineos TDS enDocument3 pagesStyrolux 684D SBC Ineos TDS enfabianmendez2875No ratings yet
- 8 ZAB - UN6080 Alarm and Event List v2.0.00-1 PDFDocument82 pages8 ZAB - UN6080 Alarm and Event List v2.0.00-1 PDFsrinivasNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id4377891Document35 pagesSSRN Id4377891MUHAMMAD SAFWAN AHMAD MUSLIMNo ratings yet
- Sabz Bagh11Document23 pagesSabz Bagh11Hassan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Paper 20230906104745Document96 pagesPaper 20230906104745afifkadriNo ratings yet