Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A 'Methodical' History of Language Teaching
Uploaded by
bertaniamine7Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A 'Methodical' History of Language Teaching
Uploaded by
bertaniamine7Copyright:
Available Formats
Classes are taught in the mother tongue, with little
active use of the target language.
Much vocabulary is taught in the form of lists of
isolated words.
Long, elaborate explanations of the intricacies of
Pedagogical practices in general (including
g rammar are given.
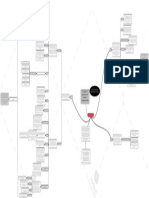
The grammar translation method is a method of t heoretical underpinnings and related research).
Methodology
teaching foreign languages derived from the W hatever considerations are involved in 'how to
Grammar provides the rules for putting words classical method of teaching Greek and Latin, which teach' are methodological.
together, and instruction often focuses on the form The major characteristics of Grammar Translation focused on grammatical rules, memorization of The Grammar Translation Method
and inflection of words. v ocabulary and of various declensions and
Theoretically well-informed positions and beliefs
conjugations, translations of texts, doing written
a bout the nature of language, the nature of language
exercises. A pproach
Reading of difficult classical texts is begun early. learning, and the applicability of both to pedagogical
s ettings.
Little attention is paid to the content of texts, which
are treated as exercises in grammatical analysis. A generalized set of classroom specifications for
Approach, Method, and Technique Method
accomplishing linguistic objectives.
Often the only drills are exercises in translating
d isconnected sentences from the target language A 'Methodical' History Curriculum/syllabus
Designs for carrying out a particular language
into the mother tongue. p rogram.
of Language Teaching
Little or no attention is given to pronunciation. A ny of a wide variety of exercises, activities, or
Technique tasks used in the language classroom for realizing
lesson objectives.
he series method was discovered by Gouin the
T
h ard way after spending 1 year in Germany trying to
learn German by memorizing its grammar. Inspired
b y his three-year-old nephew, he created the Series Gouin and the Series Method
Method, which taught learners directly and
conceptually a series of connected sentences that
are easy to perceive.
Classroom instruction was conducted exclusively in
the target language.
Only everyday vocabulary and sentences were
taught.
Oral communication skills were built up in a
carefully traded progression.
eaching methods have been changing through time
T
and almost every quarter of a century a new method Changing Winds and Shifting Sands
Grammar was taught inductively. The basic premise of the Direct Method was similar emerged.
to that of Gouin's Series Method, namely, that
s econd language learning should be more like first
New teaching points were taught through modeling
The main principles of the Direct Method language learning - lots of oral interaction, The direct Method
and practice.
s pontaneous use of the language, no translation
b etween first and second languages, and little to no
Concrete vocabulary was taught through analysis of grammatical rules.
emonstration, objects, and pictures; abstract
d Language is more than a system for
v ocabulary was taught by association of ideas. communication. It involves whole person, culture,
educational, developmental communicative
Both speech and listening comprehension were p rocesses.
taught.
Learning involves the whole person. It is a social
Correct pronunciation and grammar were p rocess of growth from childlike dependence to self-
emphisized. d irection and independence.
Community Language Learning
New material is presented in dialogue form. No specific objectives, but near-native mastery is
the goal.
There is dependence on mimicry, memorization of
s et phrases, and over-learning. No set syllabus. Course progression is topic-based;
learners provide the topics. Syllabus emerges from
learners' intention and the teacher's reformulations.
Structures are sequenced by means of contrastive
analysis and taught one at a time.
Memorization of whole meaningful texts is
recommended.
Structural patterns are taught using repetitive drills.
earning occurs through suggestion, when learners
L
here is little or no grammatical explanation.
T are in a deeply relaxed state. Baroque music is used
he WWII heightened the need for Americans to
T
Grammar is taught by inductive analogy rather than to induce this state.
b ecome orally proficient in the languages of both
b y deductive explanation.
their allies and their enemies. Thus, the US military
Suggestopedia
invented what came to be known as the Army he objective is to deliver advanced conversational
T
Vocabulary is strictly limited and learned in context. The main characteristics of the ALM Specialized Training Program (also known as the The Audiolingual Method competence quickly. Leaners are required to master
A rmy Method) to provide special and intensive p rodigious lists of vocabulary pairs, although the
language courses that focused on aural/oral skills. In g oal is understanding, not memorization.
There is much use of tapes, language labs, and
1950s, the Army Method came to be known as the
v isual aids.
A udiolingual Method.
The syllabus consists of 1200-word dialogues
Great importance is attached to pronunciation. g raded by vocabulary and grammar.
Very little use of the mother tongue by teachers is ach language is composed of elements that give it
E
p ermitted. a unique rhythm and spirit. Functional vocabulary
and core structure are key to the spirit of the
language.
Successful responses are immediately reinforced.
rocesses of learning a second language are
P
There is a great effort to get students to produce fundamentally different from L1 learning. L2
error-free utterances. learning is an intellectual, cognitive process.
his was not so much a method as it was an
T
approach that emphasized a conscious awareness of Surrender to the music of the language, silent
There is a tendency to manipulate language and rules and their applications to second language Cognitive Code Learning awareness then active trial.
d isregard content. 'Designer' Methods of the Spirited Seventies The Silent Way
learning, considering the children's brain to be pre-
equipped with a system of rules. he objective is near-native fluency, correct
T
p ronunciation, basic practical knowledge of the
g rammar of the L2. Leaners learn how to learn a
language.
Syllabus consists of structural lessons planned
a round grammatical items and related vocabulary.
Items are introduced according to their grammatical
complexity.
It has a structuralist, grammar-based view of
language.
L2 learning is the same as L1 learning;
comprehension before production is imprinted
through carrying out commands.
Total Physical Response
The objective is to teach oral proficiency to produce
learners who can communicate uninhibitedly and
intelligibly with native speakers.
Sentence-based syllabus with grammatical and
lexical criteria being primary, but focus on meaning,
n ot form.
The essence of language is meaning. Vocabulary,
n ot grammar, is the heart of language.
There are two ways of L2 language development: '
a cquisition' - a natural subconscious process, and '
learning' - a conscious process. Learning cannot
lead to acquisition.
The Natural Approach
Designed to give beginners and intermediate learners
b asic communicative skills. Four broad areas; basic
p ersonal communicative skills (oral/written);
academic learning skills(oral/written).
Syllabus is based on selection of communicative
activities and topics derived from learner needs.
You might also like
- Math Workshop, Grade 4: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade 4: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeNo ratings yet
- Terminology of MethodologyDocument1 pageTerminology of MethodologyFernanda FunezNo ratings yet
- Math Workshop, Grade 2: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeFrom EverandMath Workshop, Grade 2: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeNo ratings yet
- Korean Language 4B WB SampleDocument22 pagesKorean Language 4B WB Samplekamatpace70No ratings yet
- Korean Language 4A WB SampleDocument22 pagesKorean Language 4A WB Sampleseri ChannelNo ratings yet
- Unit Approaches, Methods and Techniques in English Language Teaching (Elt)Document8 pagesUnit Approaches, Methods and Techniques in English Language Teaching (Elt)Mil CondeNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental IsaDocument5 pagesMapa Mental IsaIsabel OliveraNo ratings yet
- Grammar-Introduction (S) NewDocument66 pagesGrammar-Introduction (S) Newfrusciante100% (1)
- Exam in Cae 216Document6 pagesExam in Cae 216Janrey RamosNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis of Charlie Chaplin's SpeechDocument9 pagesDiscourse Analysis of Charlie Chaplin's SpeechJudith MachisacaNo ratings yet
- Lingüística Aplicada - ApuntesDocument30 pagesLingüística Aplicada - ApuntesJose ALCONCHEL IRANZONo ratings yet
- Cuadro Comparativo MethodsDocument17 pagesCuadro Comparativo Methodsbraian montegmontNo ratings yet
- ELT 6 - Teaching and Assessment of Grammar - C2 - L2 - ActivitySheetsDocument4 pagesELT 6 - Teaching and Assessment of Grammar - C2 - L2 - ActivitySheetsEsperanza BuwatNo ratings yet
- Preface: How To Use This BookDocument22 pagesPreface: How To Use This BookNga NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingDocument32 pagesThe Nature of Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingJessemar Solante Jaron WaoNo ratings yet
- Time-Line: French Department - YEAR 8 Course, Scheme of Work 2019-2020Document6 pagesTime-Line: French Department - YEAR 8 Course, Scheme of Work 2019-2020MonaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Resume December 2022Document3 pagesTeaching Resume December 2022Maria BNo ratings yet
- Task - ApproachesDocument8 pagesTask - ApproachesGen MallariNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Approaches, Methods and TechniquesDocument10 pagesThe Nature of Approaches, Methods and TechniquesHeidy Teresa Morales100% (1)
- Methods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of CultureDocument11 pagesMethods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of CultureTania LpzNo ratings yet
- Methods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of CultureDocument11 pagesMethods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of CultureAminaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of CultureDocument11 pagesMethods of Teaching Grammar. Types of Grammatical Skills: St. Petersburg State University of Culture가르리예바마랄라No ratings yet
- MNJ 2017 1 (1) 40 PDFDocument3 pagesMNJ 2017 1 (1) 40 PDFAsmina Medag-mamaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document18 pagesPresentation 1Lorilee JoyNo ratings yet
- Korean Language 1B SB SampleDocument21 pagesKorean Language 1B SB Sample하지hachiiNo ratings yet
- Mapa LexicologiaDocument3 pagesMapa LexicologiaMariana OsorioNo ratings yet
- Caparing TableDocument4 pagesCaparing TableNgọc HồNo ratings yet
- Part One The Nature of Approaches and MethodsDocument1 pagePart One The Nature of Approaches and Methodsbertaniamine7No ratings yet
- Language Teaching Approach MatricesDocument13 pagesLanguage Teaching Approach MatricesJessie L. Labiste Jr.90% (10)
- Tema 12 CEN - GrammarDocument28 pagesTema 12 CEN - GrammarminimunhozNo ratings yet
- Shimizu JapaneseLanguageEducators 2002Document16 pagesShimizu JapaneseLanguageEducators 2002Ruben MaresNo ratings yet
- Luo - Plo1 - Edte602 Linking Experience To Theory PaperDocument5 pagesLuo - Plo1 - Edte602 Linking Experience To Theory Paperapi-549590947No ratings yet
- Annual Planning A1 - 1 PDFDocument10 pagesAnnual Planning A1 - 1 PDFAnonymous ibSRqUNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluation ToolDocument2 pagesMonitoring and Evaluation ToolCamelle Medina100% (1)
- Comparing TESOL Approaches and MethodsDocument12 pagesComparing TESOL Approaches and MethodsIsaías CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Grammar-Translation Method breakdownDocument3 pagesGrammar-Translation Method breakdownMissKientha Sexzzy Siirathu CopernieztaNo ratings yet
- Idiom Translation Strategies in EFL LearnersDocument13 pagesIdiom Translation Strategies in EFL Learnersimy faithNo ratings yet
- IMPLEMENTATION PhaseDocument7 pagesIMPLEMENTATION PhaseJanelyvie AgustinNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Second Language Teaching Methods and ApproachesDocument10 pagesAn Overview of Second Language Teaching Methods and ApproachesDammar Singh SaudNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Grammar Translation Method (GTMDocument5 pagesSWOT Analysis of Grammar Translation Method (GTMAgastya PribumiNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 3 - English Grammar K.03Document8 pagesKelompok 3 - English Grammar K.03iresgaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Translation: Akhmal R. Eki L. Fikri M. Surya A. Syahid ADocument7 pagesGrammar Translation: Akhmal R. Eki L. Fikri M. Surya A. Syahid ASyahid AlbannaNo ratings yet
- What Does Teaching Grammar Communicatively MeanDocument5 pagesWhat Does Teaching Grammar Communicatively MeanDani ZehraNo ratings yet
- Pedagogical Grammar ReportDocument19 pagesPedagogical Grammar Report잔돈No ratings yet
- Methodologies of Translation: V. Jai Vasumathi Valli RaniDocument4 pagesMethodologies of Translation: V. Jai Vasumathi Valli RaniHADJER DIBNo ratings yet
- Korean Language 1B WB SampleDocument22 pagesKorean Language 1B WB Sample하지hachii100% (1)
- Curricular Plans For Teaching With An Intercultural Communication OrientationDocument8 pagesCurricular Plans For Teaching With An Intercultural Communication OrientationMan BidamNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Conversational Shadowing On Teaching and Learning Conditional SentencesDocument15 pagesThe Effect of Conversational Shadowing On Teaching and Learning Conditional SentencesJesus ValdesNo ratings yet
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument6 pagesGrammar Translation MethodDonGato XDNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Curriculum ExamDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Curriculum ExamScarlett LisboaNo ratings yet
- Foreign Languages Teaching MethodsDocument2 pagesForeign Languages Teaching MethodsKevin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eed 102 Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesEed 102 Midterm ReviewerHershey Gwyneth SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Mersin University: Elt DepartmentDocument21 pagesMersin University: Elt DepartmentFatma SavaşNo ratings yet
- English Methodology CourseDocument21 pagesEnglish Methodology CourseAntonio Briceño VerasteguiNo ratings yet
- TNG of GrammarDocument15 pagesTNG of GrammarDaffodilsNo ratings yet
- He Audiolingual Method: StructuralismDocument2 pagesHe Audiolingual Method: StructuralismKathy'totszki OrtizNo ratings yet
- Template - Summary Table of Teaching MethodsDocument4 pagesTemplate - Summary Table of Teaching MethodsTấn Tài VõNo ratings yet
- Second Language Teaching MethodsDocument3 pagesSecond Language Teaching MethodsHernán ArizaNo ratings yet
- 1st Exam - EDENG 1Document3 pages1st Exam - EDENG 1Joy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- Language Teaching Approach MatricesDocument23 pagesLanguage Teaching Approach MatricesJessieLabisteJr.100% (1)
- Moot Problem For ICA - NMIMS - June 2021Document3 pagesMoot Problem For ICA - NMIMS - June 2021AayushiNo ratings yet
- Led PowerpointDocument35 pagesLed PowerpointArunkumarNo ratings yet
- q2 Wk1 Worksheet1 Music8Document10 pagesq2 Wk1 Worksheet1 Music8Michie Maniego - GumanganNo ratings yet
- Flexible Architectural Design and User Participation: January 2012Document5 pagesFlexible Architectural Design and User Participation: January 2012amlaNo ratings yet
- Advenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129Document32 pagesAdvenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129JMJPILOT75% (4)
- Supercritical CO2 Extraction: A Clean Extraction MethodDocument6 pagesSupercritical CO2 Extraction: A Clean Extraction MethodPrincess Janine CatralNo ratings yet
- 0611CT1001net PDFDocument272 pages0611CT1001net PDFAdrian M FahriNo ratings yet
- June 10Document16 pagesJune 10rogeliodmngNo ratings yet
- Competences Needed in Testing - Handout Manual PDFDocument97 pagesCompetences Needed in Testing - Handout Manual PDFCristina LucaNo ratings yet
- EVE 32 07eDocument45 pagesEVE 32 07eismoyoNo ratings yet
- Improving Oil Recovery with EOR/IOR MethodsDocument1 pageImproving Oil Recovery with EOR/IOR MethodsMuhammad Fawwad ObaidaNo ratings yet
- Report For Court, Sale of Dowling College Brookhaven CampusDocument26 pagesReport For Court, Sale of Dowling College Brookhaven CampusRiverheadLOCALNo ratings yet
- Technical Lead with 9 years' experience in .NET, Angular and AzureDocument2 pagesTechnical Lead with 9 years' experience in .NET, Angular and AzureModi SandeepNo ratings yet
- Doctor Who - In-Vision 074 - Resurrection of The Daleks PDFDocument19 pagesDoctor Who - In-Vision 074 - Resurrection of The Daleks PDFTim JonesNo ratings yet
- Human Rights EducationDocument149 pagesHuman Rights EducationLeonard MamergaNo ratings yet
- Bohol - Eng5 Q2 WK8Document17 pagesBohol - Eng5 Q2 WK8Leceil Oril PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Encounters 3Document4 pagesEncounters 3lgwqmsiaNo ratings yet
- Guns and Thighs by Ram Gopal Verma PDFDocument100 pagesGuns and Thighs by Ram Gopal Verma PDFSoma ShekharNo ratings yet
- Decision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningDocument14 pagesDecision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningZara ImranNo ratings yet
- The Law of One Study Guide - Section 4Document16 pagesThe Law of One Study Guide - Section 4Kyle Ordway100% (2)
- G3335-90158 MassHunter Offline Installation GCMSDocument19 pagesG3335-90158 MassHunter Offline Installation GCMSlesendreNo ratings yet
- Ship Constructor Structure TutorialDocument237 pagesShip Constructor Structure TutorialRodrigo Horta100% (1)
- Handbook+of+Global+Tuberculosis+Control - Chapter 5 - 2Document17 pagesHandbook+of+Global+Tuberculosis+Control - Chapter 5 - 2Dyah MustikawatiNo ratings yet
- Advertising ContractDocument3 pagesAdvertising Contractamber_harthartNo ratings yet
- Aqa Textiles Gcse Coursework Grade BoundariesDocument4 pagesAqa Textiles Gcse Coursework Grade Boundariesrqaeibifg100% (2)
- An Umbrella For Druvi: Author: Shabnam Minwalla Illustrator: Malvika TewariDocument12 pagesAn Umbrella For Druvi: Author: Shabnam Minwalla Illustrator: Malvika TewariKiran Kumar AkulaNo ratings yet
- PESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesDocument1 pagePESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesMac Corleone0% (1)
- Isoenzyme ClassifiedDocument33 pagesIsoenzyme Classifiedsayush754No ratings yet
- FisikaDocument46 pagesFisikaNurol Hifzi Putri RizkiNo ratings yet
- Research On Evolution Equations Compendium Volume 1Document437 pagesResearch On Evolution Equations Compendium Volume 1Jean Paul Maidana GonzálezNo ratings yet