Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
luzonaljur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageProtein synthesis is a process where polypeptide chains are formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the cell, requiring a coded DNA sequence, enzymes, messenger RNA to carry DNA's code to ribosomes, and transfer and ribosomal RNA. DNA contains genetic code transmitted through traits. Amino acids are organic molecules used to form proteins, with RNA types transporting amino acids and DNA code for protein assembly regulated by DNA and occurring in the nucleus and ribosomes.
Original Description:
Original Title
protein synthesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProtein synthesis is a process where polypeptide chains are formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the cell, requiring a coded DNA sequence, enzymes, messenger RNA to carry DNA's code to ribosomes, and transfer and ribosomal RNA. DNA contains genetic code transmitted through traits. Amino acids are organic molecules used to form proteins, with RNA types transporting amino acids and DNA code for protein assembly regulated by DNA and occurring in the nucleus and ribosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageProtein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
luzonaljurProtein synthesis is a process where polypeptide chains are formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the cell, requiring a coded DNA sequence, enzymes, messenger RNA to carry DNA's code to ribosomes, and transfer and ribosomal RNA. DNA contains genetic code transmitted through traits. Amino acids are organic molecules used to form proteins, with RNA types transporting amino acids and DNA code for protein assembly regulated by DNA and occurring in the nucleus and ribosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
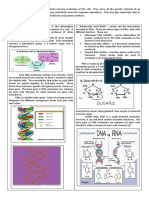
Protein synthesis- is a process in which polypeptide chains are
formed from coded combinations of single amino acids inside the
cell. The synthesis of new polypeptides requires a coded
sequence, enzymes, and messenger, ribosomal, and transfer
ribonucleic acids (RNAs). Protein synthesis occurs within a cell's
nucleus and ribosomes and is regulated by DNA and RNA.
DNA - is an organic chemical of complex molecular structure
found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and in many
viruses. DNA codes genetic information for the transmission
of inherited traits. Double-stranded sugar phosphate
(deoxyribose) (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Amino acid- any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a
primary amino group (―NH2), an acidic carboxyl group
(―COOH), and an organic R group (or side chain) that is unique
to each amino acid
RNA - a single-stranded sugar phosphate (ribose)
Messenger RNA (mRNA) - brings information from the DNA in the
nucleus to the protein manufacturing area, the cytoplasm.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - holds tightly to the mRNA using its
information to assemble the amino acids in the correct order.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) - supplies amino acids to the ribosome to
be assembled as a protein.
You might also like
- Physical ScienceDocument15 pagesPhysical SciencelovelyNo ratings yet
- DNA WPS OfficeDocument14 pagesDNA WPS OfficeRylle ParkNo ratings yet
- Genetics VocabDocument2 pagesGenetics VocabMinseo Neal ChangNo ratings yet
- Nu Cleo ShitDocument4 pagesNu Cleo ShitPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Dna TranslationDocument16 pagesDna Translation2C Lamsin, Estelle NerieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Genetic ControlDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Genetic ControlCor GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Dna 1Document31 pagesDna 1Dr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids and NucleotidesWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Bio Study GuideDocument2 pagesBio Study GuidetaraNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology (Zeb 361)Document7 pagesMolecular Biology (Zeb 361)Jacob WalterNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument56 pagesDna and Rna StructureZeah RealNo ratings yet
- Presentation Pit Pit 1Document16 pagesPresentation Pit Pit 1michsantosNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesOrganic Molecule:: Nucleic Acidsako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code & Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesGenetic Code & Protein SynthesisMarilyn BagayNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument44 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleGxmini playsNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochemistry FinalsKc CalderonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Camille Claire A. Bernabe BSN 1Document17 pagesNucleic Acid: Camille Claire A. Bernabe BSN 1Carl Michael BernabeNo ratings yet
- RNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8Document2 pagesRNA NOTES For SUMMATIVE TEST On BIOTECH 8Nadia KhanNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- 5th Part Nucleic AcidDocument3 pages5th Part Nucleic AcidAichal HmjNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocument55 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- 456-Microbio-Topics - 3Document3 pages456-Microbio-Topics - 3Margot JonesNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument47 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistryjohn2001royNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Eckert Minerva Deland Flip Part 1Document34 pagesGenetics: Eckert Minerva Deland Flip Part 1Carl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- CAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 6 - Nucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesCAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 6 - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesisstephen areriNo ratings yet
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocument45 pagesHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocument2 pagesWeek 10 Nucleic Acid ChemistryRochelle NabaunagNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument6 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidLouiseNo ratings yet
- GenesDocument16 pagesGeneshifzaaijaz366No ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages28ib7zlrsyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649Document8 pagesNucleic Acid: Name: Miss Rabaya Akter ID: 1922247649SymumNo ratings yet
- Mol Basis of InheritanceDocument74 pagesMol Basis of InheritanceNishita BharaliNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) : Adnan BhanwadiaDocument24 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA) : Adnan BhanwadiaTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- RNA - Level I - 14 Jan 2010Document7 pagesRNA - Level I - 14 Jan 2010safemindNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids OnlineDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids OnlineIsabel DizonNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument10 pagesNucleic Acidslovely carilloNo ratings yet
- NucleotideDocument5 pagesNucleotideReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- LECTURE NUCLEIC ACIDSDocument4 pagesLECTURE NUCLEIC ACIDSj9694052No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectDocument18 pagesNucleic Acids Rna World Biotech ProjectSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ReportDocument15 pagesNucleic Acid Reportmumu memeNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of ProtiensDocument10 pagesSynthesis of ProtiensJeth JuradoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesMarie WrightNo ratings yet
- Dna RnaDocument2 pagesDna RnaralphNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesProtein SynthesisRussel OtillaNo ratings yet
- Reaya 3rd PeriodicalDocument16 pagesReaya 3rd PeriodicalRhenz San PedroNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pagesOrganic Molecule:: Nucleic AcidsCharles SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Biol313 M5Document2 pagesBiol313 M5Fares SamirNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)Document18 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA)Serap BayramNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation by Dr. Mesut KarahanDocument26 pagesTranscription and Translation by Dr. Mesut KarahanEmily ClementhNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- Notes On DNADocument1 pageNotes On DNAChristina VlietNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument41 pagesBiochemIram KhanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism AllDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism AllRaufur Rahman AkandaNo ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet