Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 10 - Mathematics
Uploaded by
April Mae Rodriguez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageThe document outlines the essential learning competencies for 10th grade mathematics organized by quarter. It includes 12 competencies to be covered in Quarter 1 focused on patterns, algebra, and geometric sequences. Quarter 2 covers 5 competencies focused on polynomial functions and relations among chords, arcs, angles. Quarter 3 includes 8 competencies on counting principles, permutations, combinations, and probability. Quarter 4 mentions proving theorems related to chords, arcs, and angles but provides no additional details.
Original Description:
Original Title
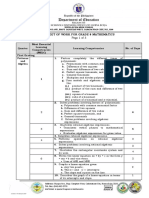
GRADE 10 – MATHEMATICS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the essential learning competencies for 10th grade mathematics organized by quarter. It includes 12 competencies to be covered in Quarter 1 focused on patterns, algebra, and geometric sequences. Quarter 2 covers 5 competencies focused on polynomial functions and relations among chords, arcs, angles. Quarter 3 includes 8 competencies on counting principles, permutations, combinations, and probability. Quarter 4 mentions proving theorems related to chords, arcs, and angles but provides no additional details.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageGrade 10 - Mathematics
Uploaded by
April Mae RodriguezThe document outlines the essential learning competencies for 10th grade mathematics organized by quarter. It includes 12 competencies to be covered in Quarter 1 focused on patterns, algebra, and geometric sequences. Quarter 2 covers 5 competencies focused on polynomial functions and relations among chords, arcs, angles. Quarter 3 includes 8 competencies on counting principles, permutations, combinations, and probability. Quarter 4 mentions proving theorems related to chords, arcs, and angles but provides no additional details.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
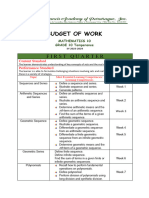
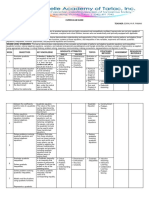
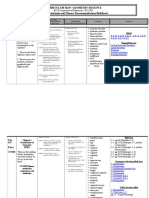
GRADE 10 – MATHEMATICS
Most Essential Learning No. of Days
Quarter Learning Competencies
Competencies (MELC) Taught
Quarter 1
1. Generates patterns.
1 • Illustrates patterns and relationships. 4
11. Illustrates
• Cites the that
situations center-radius form of the equation
generate patterns.
of a circle.
2. Illustrates an arithmetic sequence.
18
2 • Solves quadratic equations by completing 4
4
the square.
3. 12. Determines
Determines the center
arithmetic andand
means radius
nth of a circle
term of angiven
its equation
arithmetic and vice versa.
sequence.
3 4
13. Graphs a circle and other geometric figures on the
19 4
Patterns coordinate plane.
and 4. 14. Solvesaproblems
Illustrates geometric involving geometric figures on the
sequence.
20 4
Algebra coordinate plane.
4
Quarter 3
5. Differentiates a geometric sequence from 4
1. Illustrates the permutation of objects.
an arithmetic sequence.
• Illustrates the Fundamental Counting
6. Determines geometric means and nth term of a
5 21 Principle through a tree diagram or by listing
geometric sequence.
method. 4 4
7. Finds the sum
• Uses FCPof tothe terms the
visualize of apossible
given finite
number
or infinite geometric
of arrangements. sequence.
6 8. Solves problems involving sequences. 4
2. Derives the formula for finding the number
9. Performs division of polynomials
of permutations using at
of objects taken longa time.
division
N r and synthetic division.
7
22 3. Solves problems involving permutations. 4 4
23 4. Illustrates the combination of objects. 4
10. Proves the Remainder Theorem and the Factor
5. Differentiates permutation from combination of
24 Theorem.
objects taken at a time.
11. 6.
Factors polynomials. 4
Derives the formula for finding the number
of combinations of n objects taken r at a
Statistics
8 time. 4
And
Probability 7. Solves problems involving permutations
25 4
and combinations
9 8. Illustrates
12. Illustrates events, and
polynomial union and intersection
equations. 4
of events.
13. Solves problems involving polynomials
• Uses Venn Diagrams to represent sets, subsets,
26 and polynomial equations. 4
and set operations.
10 4
• Illustrates the union and intersection of sets
and the difference of two sets.
Quarter 2 9. Illustrates the probability of a union of two events.
11 27 • Illustrates
1. Illustrates an experiment,
polynomial functions. outcome,
Patterns 4
sample space
2. Graphs polynomial functions. and event. 4
and • Finds the probability of a simple event.
Algebra 12 3. Solves problems involving polynomial functions. 4
10.
4. Derives Finds the probability
inductively
of A ∪ B
the relations .
among chords,
13 28 4 4
arcs, central angles, and inscribed angles.
5. Proves theorems related to chords, arcs, central
29 11. Illustrates
angles, mutuallyangles.
and inscribed exclusive events. 4
12.
5.1Proves theorems related toprobability.
Solves problems involving chords, arcs, central
14 30 4 4
angles.
Quarter 4 5.2. Proves theorems related to inscribed
Geometry 1. Illustrates
angles. the following measures of
position: quartiles,
6. Illustrates secants, tangents, decilessegments,
and percentiles.
and
15 a. a Illustrates the following measures 4
sectors of circle.
7. Proves theorems of position: quartiles,
on secants, tangents, and
16 31 b. Illustrates the following measures
4
segments. 4
8. Solves problems of position: deciles and percentiles
on circles.
9. Derives the distance formula.
Statistics 10. Applies the distance formula to prove some 4
17 2. Calculates a specified measure of position
And 32 geometric properties. 4
(e.g. 90th percentile) of a set of data.
Probability 33 3. Interprets measures of position. 4
34 - 35 4. Solves problems involving measures of position. 8
5. Formulates statistical mini-research.
36 - 37 8
6. Uses appropriate measures of position and other
38 - 40 statistical methods in analyzing and interpreting 12
research data.
You might also like
- (Winter 2021) : CS231A: Computer Vision, From 3D Reconstruction To Recognition Homework #0 Due: Sunday, January 17Document2 pages(Winter 2021) : CS231A: Computer Vision, From 3D Reconstruction To Recognition Homework #0 Due: Sunday, January 17Nono Nono100% (1)
- A. Pogorelov-Geometry PDFDocument317 pagesA. Pogorelov-Geometry PDFThirdocean100% (2)
- How To SolderDocument16 pagesHow To SolderIan Holdeman100% (1)
- Forensic Audit Report of BKR Foods Pvt. LTDDocument7 pagesForensic Audit Report of BKR Foods Pvt. LTDA Kumar LegacyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Enhanced Oil Recovery: by Engr. Hassan AzizDocument83 pagesPrinciples of Enhanced Oil Recovery: by Engr. Hassan AzizKhalid Waheed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Maths GCSE Higher Syllabus PDFDocument3 pagesMaths GCSE Higher Syllabus PDFSam DeanNo ratings yet
- (Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Document477 pages(Algebra Logic and Applications 6) - Exercises in Algebra - A Collection of Exercises, in Algebra, Linear Algebra and geometry-CRC Press (1996)Jesús Eduardo Dimas Ramírez100% (1)
- CV For Civil EngineerDocument6 pagesCV For Civil EngineerRAREEENo ratings yet
- MELCS Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesMELCS Pre CalculusLiedi Brigette100% (4)
- AS Pure Sample Edexcel PDFDocument33 pagesAS Pure Sample Edexcel PDFSemaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesMarc Angelo C. CruzNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Math10Document2 pagesBudget of Work Math10Chelsie May ReyesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 10Document3 pagesBudget of Works Grade 10EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 9Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 9EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 9Document2 pagesBOW in MATH 9Joshua ServitoNo ratings yet
- BOW V3.0 Math 9Document2 pagesBOW V3.0 Math 9Jessebel AndresNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationODETTE GENOVA100% (1)
- Math 9 Bow Q1Document2 pagesMath 9 Bow Q1Hans Jhayson CuadraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide - Grade 9 (Mathematics)Document5 pagesCurriculum Guide - Grade 9 (Mathematics)Genciano CambalonNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Curriculum Mapvirginia taguibaNo ratings yet
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 10Document10 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 10Ella Q. EngcoNo ratings yet
- (Diagnostic Test in Grade 10 Math) : Table of SpecificationDocument3 pages(Diagnostic Test in Grade 10 Math) : Table of SpecificationMARLON DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- G10Document3 pagesG10Janen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Bow-Math 10Document5 pagesBow-Math 10marissa turlaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade-10: K-12 Basic Education Curriculum Scope & Sequence 2021Document2 pagesMathematics Grade-10: K-12 Basic Education Curriculum Scope & Sequence 2021Maita Jane ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Document5 pagesSyllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- Division of Davao Del Norte Mathematics Grade 10-Scope and Sequence First QuarterDocument3 pagesDivision of Davao Del Norte Mathematics Grade 10-Scope and Sequence First QuarterLesil ValleNo ratings yet
- TOS and KEY GRADE 10 - Achievement Test 2022Document7 pagesTOS and KEY GRADE 10 - Achievement Test 2022Erwin Joaquin CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsDocument6 pagesEdexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsWandaNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 8Document3 pagesBOW in MATH 8Eric ManotaNo ratings yet
- Tos Math 10Document2 pagesTos Math 10Nico TulaliNo ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideEdralyn PamaniNo ratings yet
- Sjs Switch Curriculum Grade 10Document5 pagesSjs Switch Curriculum Grade 10maria cristinaNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsDocument3 pagesPivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsMarife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- Daily Curriculum Map: SUBJECT: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 9 UNIT/STRANDS: Quarter I TeachersDocument4 pagesDaily Curriculum Map: SUBJECT: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 9 UNIT/STRANDS: Quarter I TeachersJesmar SantillanNo ratings yet
- MATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFDocument81 pagesMATH GRADE 9 1st QTR PDFMarcus John Vincent C. KeNo ratings yet
- v6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFDocument21 pagesv6wA3TTFyk8aJy8f8qZw PDFnoneofyourbusinessNo ratings yet
- 2021 Technical Mathematics ATP GRADE 11Document3 pages2021 Technical Mathematics ATP GRADE 11radinneofentse67No ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Subject Areas Per Grade LevelDocument13 pagesCurriculum Map Subject Areas Per Grade LevelMaria Sheila OtlangNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 8Document4 pagesBudget of Works Grade 8EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IDocument9 pagesEngineering Mathematics IIbrahim AliNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Document3 pagesYear 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Hannah LeeNo ratings yet
- 2019 Third Quarterly Examination Table of Specification: Division of Davao Del Norte Division Unified Test in G-10 MathDocument5 pages2019 Third Quarterly Examination Table of Specification: Division of Davao Del Norte Division Unified Test in G-10 MathLesil ValleNo ratings yet
- 2022 T1 Y10am SSDocument1 page2022 T1 Y10am SSWOON RAY MINGNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-18 at 12.29.53 PMDocument3 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-18 at 12.29.53 PMmehrNo ratings yet
- Maths KS5Document4 pagesMaths KS5georgia.cuzucNo ratings yet
- Math-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezDocument8 pagesMath-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezCharizz DominguezNo ratings yet
- Geometry Regents Curriculum Map 2013-14Document20 pagesGeometry Regents Curriculum Map 2013-14Diamond JonesNo ratings yet
- Aqa Further Maths WorkbookDocument58 pagesAqa Further Maths Workbook18mckenzieaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Wise Plan of "Multivariable Caculus": Contact: 03002999903Document6 pagesLecture-Wise Plan of "Multivariable Caculus": Contact: 03002999903faiqa yousafNo ratings yet
- 007 Compulsory MathDocument17 pages007 Compulsory Mathamar nath vermaNo ratings yet
- TEST-RESULTS-Grade 10Document2 pagesTEST-RESULTS-Grade 10Rodel AringoNo ratings yet
- CIE Short SyllabusDocument5 pagesCIE Short SyllabusBijoy SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification (TOS)Document2 pagesTable of Specification (TOS)ALLYSA KRISTINE M. TALAGTAGNo ratings yet
- Budget of WorkDocument4 pagesBudget of WorkRysy May Gomez ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Topic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsDocument4 pagesTopic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsmosulNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Teacher's GuideDocument326 pagesMathematics: Teacher's Guidechan pinkNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Subject: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 9Document7 pagesCurriculum Map: Subject: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 9joan niniNo ratings yet
- MayamotNHS-Q2-Least MasteredDocument2 pagesMayamotNHS-Q2-Least MasteredAaron James LicoNo ratings yet
- CMO 13 S. 2008 Annex III COURSE SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE BSCpE PROGRAMDocument52 pagesCMO 13 S. 2008 Annex III COURSE SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE BSCpE PROGRAMMichellePascualPullonNo ratings yet
- Analisis CP X IpasDocument7 pagesAnalisis CP X IpasRemi OliviraNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Diri Kelas 7Document10 pagesEvaluasi Diri Kelas 7kristianasillyNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Math 10Document4 pages1st Quarter Math 10April Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Content Knowledge and Pedagogy 2Document5 pagesContent Knowledge and Pedagogy 2April Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument14 pagesCirclesApril Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Math 10Document8 pagesLesson Plan in Math 10April Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MathDocument317 pagesMathApril Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- GEH-Mark VIe UCCA Serial ModbusDocument29 pagesGEH-Mark VIe UCCA Serial ModbustestvsptestNo ratings yet
- NetGear Task TSK-MVC-20230109000274 13KRW0104Document3 pagesNetGear Task TSK-MVC-20230109000274 13KRW0104Ir VanNo ratings yet
- Shortcut AutocadDocument3 pagesShortcut AutocadDjoko Dwi IrwantoNo ratings yet
- GPS Submittal PDFDocument32 pagesGPS Submittal PDFshankar05No ratings yet
- Function CatalogueDocument591 pagesFunction CatalogueAshish PatwardhanNo ratings yet
- SWOT Tool MBDocument8 pagesSWOT Tool MBMichael DuggerNo ratings yet
- Midtermbm11lm#1 FractionDocument10 pagesMidtermbm11lm#1 FractionjulianneNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Decision 1 Lesson 7 - Linear Programming: Formulating A Problem As A Linear Programming ProblemDocument4 pagesLesson Notes - Decision 1 Lesson 7 - Linear Programming: Formulating A Problem As A Linear Programming ProblemsparrowjakazzNo ratings yet
- Contract No. Mk/Tt/16-01: It Is Agreed As FollowsDocument4 pagesContract No. Mk/Tt/16-01: It Is Agreed As FollowsNhi LanNo ratings yet
- ARDUINODocument28 pagesARDUINOAshmad Syed100% (1)
- Image ProcessingDocument12 pagesImage Processingsiddharth.20bcun006No ratings yet
- Product CatalogueDocument44 pagesProduct CatalogueTo Van TinhNo ratings yet
- Kerberos FunctionalityDocument8 pagesKerberos Functionalityjimm gamerNo ratings yet
- Earning and Stock Split - Asquith Et Al 1989Document18 pagesEarning and Stock Split - Asquith Et Al 1989Fransiskus ShaulimNo ratings yet
- JellDocument1 pageJellMuhammad DanuNo ratings yet
- Preca Solutions BrochureDocument16 pagesPreca Solutions BrochurePMC - PRECANo ratings yet
- Sunny Steel Enterprise LTD.: Collect Steel Pipe and Fitting ResourcesDocument7 pagesSunny Steel Enterprise LTD.: Collect Steel Pipe and Fitting ResourcesAngirekula gopi krishnaNo ratings yet
- National Company Law Tribunal Chennai Special Bench (Court I)Document7 pagesNational Company Law Tribunal Chennai Special Bench (Court I)Parimal KashyapNo ratings yet
- DDV V-S Su Ub B: Compact High Power SubwooferDocument4 pagesDDV V-S Su Ub B: Compact High Power SubwooferGobitobiNo ratings yet
- 2 - LLMNRNBT-NS Poisoning With Out CredsDocument1 page2 - LLMNRNBT-NS Poisoning With Out CredsabdelrahemNo ratings yet
- Capacities (Refill) : Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument2 pagesCapacities (Refill) : Operation and Maintenance ManualERIC ERICNo ratings yet
- Sas Prog 1Document2 pagesSas Prog 1Supriyo SamantaNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Lesson 1 - Written Task - HiyasDocument3 pagesQ2 - Lesson 1 - Written Task - HiyasGaming IndustryNo ratings yet
- ARO Pump ManualDocument8 pagesARO Pump Manualrazaq athabNo ratings yet
- Premill Horizontal Roller Mill enDocument6 pagesPremill Horizontal Roller Mill enrecaiNo ratings yet