Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G10
Uploaded by
Janen Joy Baniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesG10
Uploaded by
Janen Joy BanielCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
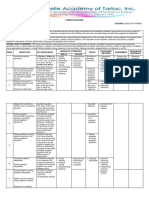
Number of
Quarter Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC)
Days Taught
generates patterns.
illustrates an arithmetic sequence 5
determines nth term of an arithmetic sequence
determines arithmetic means
5
determines sum of the terms of a given arithmetic sequence.
illustrates a geometric sequence.
5
differentiates a geometric sequence from an arithmetic sequence.
determines geometric means, nth term of a geometric sequence and sum of the
5
terms of a given finite or infinite geometric sequence
solves problems involving sequences. 5
performs division of polynomials using long division and synthetic division.
proves the Remainder Theorem and Factor Theorem
factors polynomials. 5
proves the Rational Root Theorem.
5
illustrates polynomial equations.
solves problems involving polynomials and polynomial equations. 5
illustrates polynomial functions.
5
understand, describe and interpret the graphs polynomial functions.
solves problems involving polynomial functions. 5
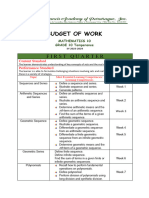
2 derives inductively the relations among chords, arcs, central angles, and
5
inscribed angles.
proves theorems related to chords, arcs, central angles, and inscribed angles. 5
illustrates secants, tangents, segments, and sectors of a circle. 5
proves theorems on secants, tangents, and segments.
solves problems on circles. 5
applies the distance formula to prove some geometric properties. 5
illustrates the center-radius form of the equation of a circle.
5
determines the center and radius of a circle given its equation and vice versa.
graphs and solves problems involving circles and other geometric figures on the
5
coordinate plane.
illustrates the permutation of objects. 5
illustrates the combination of objects. 5
differentiates permutation from combination of n objects taken r at a time. 5
solves problems involving permutations and combinations 5
illustrates events, and union and intersection of events. 5
illustrates the probability of a union of two events.
3
5
finds the probability of (A u B).
illustrates mutually exclusive events. 5
solves problems involving probability. 5
illustrates the following measures of position: quartiles, deciles and percentiles. 5
calculates a specified measure of position (e.g., 90th percentile) of a set of data. 5
interprets measures of position. 5
4 solves problems involving measures of position. 5
formulates statistical mini-research. 10
uses appropriate measures of position and other statistical methods in analyzing
10
and interpreting research data.
BUDGET OF WORK (BOW)
GRADE 10 – MATHEMATICS
S.Y. 2023-2024
You might also like
- TOS and KEY GRADE 10 - Achievement Test 2022Document7 pagesTOS and KEY GRADE 10 - Achievement Test 2022Erwin Joaquin CabigaoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade-10: K-12 Basic Education Curriculum Scope & Sequence 2021Document2 pagesMathematics Grade-10: K-12 Basic Education Curriculum Scope & Sequence 2021Maita Jane ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works Grade 10Document3 pagesBudget of Works Grade 10EJ TrinidadNo ratings yet
- (Diagnostic Test in Grade 10 Math) : Table of SpecificationDocument3 pages(Diagnostic Test in Grade 10 Math) : Table of SpecificationMARLON DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Grade Quarter Content TopicsDocument2 pagesGrade Quarter Content TopicsKen Matthew OlivaNo ratings yet
- Sample TQ Math 10Document2 pagesSample TQ Math 10Leah Orfiano MarticioNo ratings yet
- Division of Davao Del Norte Mathematics Grade 10-Scope and Sequence First QuarterDocument3 pagesDivision of Davao Del Norte Mathematics Grade 10-Scope and Sequence First QuarterLesil ValleNo ratings yet
- G11 Scheme of WorkDocument6 pagesG11 Scheme of WorkmyeboockNo ratings yet
- TEST-RESULTS-Grade 10Document2 pagesTEST-RESULTS-Grade 10Rodel AringoNo ratings yet
- MELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Document18 pagesMELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Marife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide - Grade 9 (Mathematics)Document5 pagesCurriculum Guide - Grade 9 (Mathematics)Genciano CambalonNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - MathematicsDocument1 pageGrade 10 - MathematicsApril Mae RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MayamotNHS-Q2-Least MasteredDocument2 pagesMayamotNHS-Q2-Least MasteredAaron James LicoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 10Document10 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 10Ella Q. EngcoNo ratings yet
- MayamotNHS-Q1-Least MasteredDocument2 pagesMayamotNHS-Q1-Least MasteredAaron James LicoNo ratings yet
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification (TOS)Document2 pagesTable of Specification (TOS)ALLYSA KRISTINE M. TALAGTAGNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)Document6 pages1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)graman65No ratings yet
- Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesCurriculum GuideEdralyn PamaniNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanNo ratings yet
- K To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSDocument12 pagesK To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSV.G. Lopez AspirinNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Mission Academy: Manticao Misamis OrientalDocument21 pagesMindanao Mission Academy: Manticao Misamis OrientalJayhia Malaga Jarlega100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region IV-A (CALABARZON) Division of Rizal Table of SpecificationODETTE GENOVA100% (1)
- Budget of Work Math10Document2 pagesBudget of Work Math10Chelsie May ReyesNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Higher Checklist 2017: Maths DepartmentDocument4 pagesEdexcel Higher Checklist 2017: Maths DepartmentJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-TOS-Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesGrade 10-TOS-Diagnostic TestTonet Salago CantereNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Document5 pagesSyllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.No ratings yet
- 007 Compulsory MathDocument17 pages007 Compulsory Mathamar nath vermaNo ratings yet
- Math F231Document4 pagesMath F231Shantanu MishraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Teacher's GuideDocument326 pagesMathematics: Teacher's Guidechan pinkNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesMarc Angelo C. CruzNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CurriculumDocument14 pagesMathematics Curriculumacharyasampada180No ratings yet
- Math-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezDocument8 pagesMath-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezCharizz DominguezNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Bow Q1Document2 pagesMath 9 Bow Q1Hans Jhayson CuadraNo ratings yet
- Annual Program XDocument3 pagesAnnual Program XPurwanti WahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- Title Marine Engineering MathematicsDocument10 pagesTitle Marine Engineering MathematicsgunapalshettyNo ratings yet
- Maths GCSE Higher Syllabus PDFDocument3 pagesMaths GCSE Higher Syllabus PDFSam DeanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-18 at 12.29.53 PMDocument3 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-18 at 12.29.53 PMmehrNo ratings yet
- Bow-Math 10Document5 pagesBow-Math 10marissa turlaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Document3 pagesYear 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Hannah LeeNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Diri Kelas 7Document10 pagesEvaluasi Diri Kelas 7kristianasillyNo ratings yet
- RS9687 - RS9455 - COMPULSARY CURRICULUM GRADE 11-12 MathematicsDocument17 pagesRS9687 - RS9455 - COMPULSARY CURRICULUM GRADE 11-12 MathematicsJitendra Raj KarkiNo ratings yet
- Math7-Diagnostic Test TOS Q1Document9 pagesMath7-Diagnostic Test TOS Q1Jdrew BautistaNo ratings yet
- TOS For Gen MathDocument3 pagesTOS For Gen MathAbegail PanangNo ratings yet
- Promes KLS 7Document18 pagesPromes KLS 7Asvinda RosidahNo ratings yet
- Math ProblemsDocument33 pagesMath ProblemsWeand YbanezNo ratings yet
- OASMATH7 THDocument3 pagesOASMATH7 THkalebg100No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Teacher'S Report On The Results of The Regional Mid-Year AssessmentRodel AringoNo ratings yet
- Math 111 SyllabusDocument8 pagesMath 111 Syllabusapi-327140356No ratings yet
- Edexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsDocument6 pagesEdexcel AS and A-Level Modular MathematicsWandaNo ratings yet
- Most Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Document14 pagesMost Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Mary Jane De YroNo ratings yet
- G 11 AddmaDocument5 pagesG 11 AddmaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Subject Areas Per Grade LevelDocument13 pagesCurriculum Map Subject Areas Per Grade LevelMaria Sheila OtlangNo ratings yet
- BOW in MATH 8Document3 pagesBOW in MATH 8Eric ManotaNo ratings yet
- NEB Maths Syllabus XI & XIIDocument17 pagesNEB Maths Syllabus XI & XIIBhanu Aryal100% (1)
- MayamotNHS-Q3-Least MasteredDocument2 pagesMayamotNHS-Q3-Least MasteredAaron James LicoNo ratings yet
- Least Learned ConsolidatedDocument8 pagesLeast Learned ConsolidatedLee GorgonioNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Math 17-bDocument3 pagesCourse Guide Math 17-bJames Albert AquinoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Subject: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 10Document6 pagesCurriculum Map: Subject: Mathematics Grade Level: Grade 10joan niniNo ratings yet
- Educ 203Document13 pagesEduc 203Janen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Cot2 S.y.23-24 VaDocument7 pagesCot2 S.y.23-24 VaJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- MIS Midterm ExamDocument1 pageMIS Midterm ExamJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Math RulesDocument2 pagesMath RulesJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- A. Content Standard: School Quarter Teacher Week Subject DateDocument5 pagesA. Content Standard: School Quarter Teacher Week Subject DateJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Hurricane: WeatherDocument2 pagesAtlantic Hurricane: WeatherJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Educ 201Document2 pagesEduc 201Janen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Cyclones NotesDocument1 pageCyclones NotesJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Where On Google Earth Is Carmen SandiegoDocument1 pageWhere On Google Earth Is Carmen SandiegoJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Pacific Hurricane SimulatorbyDocument2 pagesPacific Hurricane SimulatorbyJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps How To Make Research PaperDocument1 page5 Steps How To Make Research PaperJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Amazing GraceDocument1 pageAmazing GraceJanen Joy BanielNo ratings yet
- Writing The Précis: English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument10 pagesWriting The Précis: English For Academic and Professional PurposesDengDengNo ratings yet
- Synopsis OSCEDocument5 pagesSynopsis OSCEPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards " Asian Paints" (With Reference To Hightech Paint Shopee, Adoni)Document7 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Towards " Asian Paints" (With Reference To Hightech Paint Shopee, Adoni)RameshNo ratings yet
- Should Students Consider Taking A Gap Year Before Starting UniversityDocument20 pagesShould Students Consider Taking A Gap Year Before Starting Universityzahra321No ratings yet
- Accomplishment Teachers BoothDocument3 pagesAccomplishment Teachers Boothjosephine paulinoNo ratings yet
- Dementia Tri-Fold BrochureDocument2 pagesDementia Tri-Fold Brochureapi-27331006975% (4)
- IManager U2000 Single-Server System Software Installation and Commissioning Guide (Windows 7) V1.0Document116 pagesIManager U2000 Single-Server System Software Installation and Commissioning Guide (Windows 7) V1.0dersaebaNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided DraftingDocument7 pagesComputer Aided DraftingCarlito PantalunanNo ratings yet
- DLL For Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionDocument5 pagesDLL For Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionWareen CablaidaNo ratings yet
- Features of 21st Century HRD and Training ProgramsDocument9 pagesFeatures of 21st Century HRD and Training Programstvglacaba1213100% (1)
- Basketball Skills Assessment Tests (BSAT) : DribblingDocument3 pagesBasketball Skills Assessment Tests (BSAT) : DribblingPatricia QuiloNo ratings yet
- What The 'Bluest Eye' Knows About Them - Culture, Race, Identity - Christopher DouglasDocument29 pagesWhat The 'Bluest Eye' Knows About Them - Culture, Race, Identity - Christopher DouglasCaroline SouzaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - Lesson 2Document1 pageMedia and Information Literacy - Lesson 2Mary Chloe JaucianNo ratings yet
- What Is Potency - Exploring Phenomenon of Potency in Osteopathy in The Cranial Field - Helen Harrison - Research ProjectDocument105 pagesWhat Is Potency - Exploring Phenomenon of Potency in Osteopathy in The Cranial Field - Helen Harrison - Research ProjectTito Alho100% (1)
- How To Motivate Students in Learning English As A Second LanguageDocument2 pagesHow To Motivate Students in Learning English As A Second LanguagebulliinaNo ratings yet
- Position PaperDocument7 pagesPosition Papercocopitlabmix100% (3)
- Tugas ATDocument20 pagesTugas ATKhoirunnisa OktarianiNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON PLAN Oral Com Speech Context Q1Document5 pagesDAILY LESSON PLAN Oral Com Speech Context Q1Datu George100% (1)
- Solutions Manual For Power System Analysis and Design 5th Edition by Glover PDFDocument15 pagesSolutions Manual For Power System Analysis and Design 5th Edition by Glover PDFFrederick Cas50% (2)
- Effects of Music Notation Software On Compositional Practices and OutcomeDocument271 pagesEffects of Music Notation Software On Compositional Practices and OutcomeConstantin PopescuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Class IIIDocument36 pagesSyllabus Class IIIchandrakiranmeena14No ratings yet
- Inquiries, Investigation S and Immersion: Dr. Amelita J. DrizDocument26 pagesInquiries, Investigation S and Immersion: Dr. Amelita J. DrizAjilNo ratings yet
- Law Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityDocument1 pageLaw Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityFbarrsNo ratings yet
- Quality Work Refection Visual Arts Worksheet - Ofrenda Still LifeDocument3 pagesQuality Work Refection Visual Arts Worksheet - Ofrenda Still Lifeapi-543529133No ratings yet
- CNP 4Document22 pagesCNP 4Aregahagn NesruNo ratings yet
- Tpa 1Document11 pagesTpa 1api-501103450No ratings yet
- Comparing Numbers (2021 - 06 - 19 01 - 35 - 12 UTC) (2021 - 08 - 06 04 - 51 - 25 UTC)Document3 pagesComparing Numbers (2021 - 06 - 19 01 - 35 - 12 UTC) (2021 - 08 - 06 04 - 51 - 25 UTC)ALLinOne BlogNo ratings yet
- Shak-Kushan Abhilekhon Me Varnit Kshatrapa Avam MahaKshatrapaDocument7 pagesShak-Kushan Abhilekhon Me Varnit Kshatrapa Avam MahaKshatrapaAvinash PalNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Oral Medicine Oral DiagnosisDocument924 pagesTextbook of Oral Medicine Oral DiagnosisSonal100% (1)
- DLL Social ScienceDocument15 pagesDLL Social ScienceMark Andris GempisawNo ratings yet