Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digcompedu Leaflet en
Digcompedu Leaflet en
Uploaded by
Raquel Romero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Digcompedu Leaflet En
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesDigcompedu Leaflet en
Digcompedu Leaflet en
Uploaded by
Raquel RomeroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
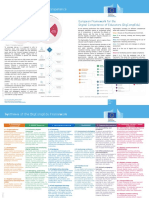
Assessing Educators' Digital Competence
European Framework for the
Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu)
As the teaching professions face rapidly changing DigCompEdu considers six different competences
demands, educators require an increasingly broad areas with a total of 22 competences.
set of competences. In particular the ubiquity of Area 1 focuses on the professional environment;
digital devices and the duty to help students
become digitally competent requires educators to Area 2 on sourcing, creating and sharing digital
develop their own digital competence. resources;
The DigCompEdu framework aims to capture these Area 3 on managing and orchestrating the use of
educator-specific digital competences. digital tools in teaching and learning;
The framework is directed towards educators at all Area 4 on digital tools and strategies to enhance
Figure 2: Conceptual approach
levels of education, from early childhood to higher assessment;
To encourage take-up, it is proposed to refer to
and adult education, including general and Area 5 on the use of digital tools to empower
proficiency levels using motivating role descriptors.
These can, however, be mapped onto the proficiency vocational training, special needs education, and learners;
levels used by the Common European Framework of non-formal learning contexts. It aims to provide a
general reference frame for developers of Digital Area 6 on facilitating learners' digital competence.
Reference for Languages (CEFR), ranging from A1
(Newcomer) to C2 (Pioneer). In general, the following Competence models, i.e. Member States, regional Areas 2 to 5 form the pedagogic core of the
characterisations apply: governments, national and regional agencies, framework. They detail the competences educators
Newcomers (A1) have had very little contact with digital educational organisations themselves, and public or need to possess to foster effective, inclusive and
tools and need guidance to expand their repertoire. private professional training providers. innovative learning strategies, using digital tools.
Explorers (A2) have started using digital tools without,
however, following a comprehensive or consistent
approach. Explorers need insight and inspiration to
expand their competences.#
Integrators (B1) use and experiment with digital tools for
a range of purposes, trying to understand which digital
strategies work best in which contexts.
Experts (B2) use a range of digital tools confidently,
creatively and critically to enhance their professional
activities. They continuously expand their repertoire of
practices.
Leaders (C1) rely on a broad repertoire of flexible,
comprehensive and effective digital strategies. They are
a source of inspiration for others.
Pioneers (C2) question the adequacy of contemporary
digital and pedagogical practices, of which they
themselves are experts. They lead innovation and are a
role model for younger teachers.
Figure 3: Proficiency progression
Figure 1: Overview of the DigCompEdu framework
For more information, please contact:
Christine.Redecker@ec.europa.eu
https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/digcompedu
Synthesis of the DigCompEdu Framework
6. Facilitating Learners' Digital
1. Professional engagement 2. Digital Resources 3. Teaching and Learning 4. Assessment 5. Empowering Learners
Competence
3.1 Teaching
6.1 Information and media literacy
To plan for and implement
5.1 Accessibility and To incorporate learning activities,
2.1 Selecting digital digital devices and resources in
inclusion assignments and assessments which
1.2 Organisational resources the teaching process, so as to
To ensure accessibility to require learners to articulate
communication To identify, assess and select enhance the effectiveness of learning resources and information needs; to find information
To use digital technologies to digital resources for teaching teaching interventions. To
enhance organisational 4.1 Assessment strategies activities, for all learners, and resources in digital environments;
and learning. To consider the appropriately manage and
communication with learners, orchestrate digital teaching To use digital technologies for including those with special to organise, process, analyse and
specific learning objective, needs. To consider and respond interpret information; and to compare
parents and third parties. To formative and summative
context, pedagogical approach, interventions. To experiment
contribute to collaboratively with and develop new formats assessment. To enhance the to learners' (digital) and critically evaluate the credibility
and learner group, when expectations, abilities, uses and and reliability of information and its
developing and improving diversity and suitability of
selecting digital resources and and pedagogical methods for misconceptions, as well as sources.
organisational communication instruction. assessment formats and
planning their use. contextual, physical or cognitive
strategies. approaches.
constraints to their use of digital 6.2 Digital communication &
3.2 Guidance
technologies. collaboration
2.2 Creating and modifying To use digital technologies and
To incorporate learning activities,
digital resources services to enhance the
4.2 Analysing evidence assignments and assessments which
1.2 Professional To modify and build on existing interaction with learners,
To generate, select, critically 5.2 Differentiation and require learners to effectively and
collaboration openly-licensed resources and individually and collectively,
analyse and interpret digital personalisation responsibly use digital technologies for
To use digital technologies to other resources where this is within and outside the learning
evidence on learner activity, To use digital technologies to communication, collaboration and civic
engage in collaboration with permitted. To create or co- session. To use digital
performance and progress, in address learners’ diverse participation.
other educators, sharing and create new digital educational technologies to offer timely and
order to inform teaching and learning needs, by allowing
exchanging knowledge and resources. To consider the targeted guidance and
learning. learners to advance at different 6.3 Digital content creation
experiences and collaboratively specific learning objective, assistance. To experiment with
levels and speeds, and to follow To incorporate learning activities,
innovating pedagogic context, pedagogical approach, and develop new forms and
individual learning pathways assignments and assessments which
practices. and learner group, when formats for offering guidance
and objectives. require learners to express themselves
designing digital resources and and support.
4.3 Feedback and planning through digital means, and to modify
planning their use. and create digital content in different
3.3 Collaborative learning To use digital technologies to
provide targeted and timely 5.3 Actively engaging formats. To teach learners how
1.3 Reflective practice To use digital technologies to
feedback to learners. To learners copyright and licenses apply to digital
To individually and collectively foster and enhance learner
To use digital technologies to content, how to reference sources and
reflect on, critically assess and 2.3 Managing, protecting collaboration. To enable learners adapt teaching strategies and
to provide targeted support, foster learners' active and attribute licenses.
actively develop one's own and sharing digital to use digital technologies as
based on the evidence creative engagement with a
digital pedagogical practice resources part of collaborative
generated by the digital subject matter. To use digital 6.4. Responsible use
and that of one's educational To organise digital content and assignments, as a means of
technologies used. To enable technologies within pedagogic To take measures to ensure learners'
community. make it available to learners, enhancing communication,
strategies that foster learners' physical, psychological and social
parents and other educators. collaboration and collaborative learners and parents to
understand the evidence transversal skills, deep thinking wellbeing while using digital
To effectively protect sensitive knowledge creation.
provided by digital and creative expression. To technologies. To empower learners to
digital content. To respect and open up learning to new, real- manage risks and use digital
1.4 Digital Continuous 3.4 Self-regulated learning technologies and use it for
correctly apply privacy and world contexts, which involve technologies safely and responsibly.
Professional Development To use digital technologies to decision-making.
copyright rules. To understand learners themselves in hands-on
(CPD) the use and creation of open support self-regulated learning
activities, scientific investigation 6.5 Digital problem solving
To use digital sources and licenses and open educational processes, i.e. to enable
or complex problem solving, or To incorporate learning activities,
resources for continuous resources, including their learners to plan, monitor and
in other ways increase learners' assignments and assessments which
professional development. proper attribution. reflect on their own learning,
active involvement in complex require learners to identify and solve
provide evidence of progress,
subject matters. technical problems, or to transfer
share insights and come up with
technological knowledge creatively to
creative solutions.
Figure 4: Synthesis of the DigCompEdu competence descriptors new situations.
You might also like
- Emotionally Focused Therapy - ManualDocument37 pagesEmotionally Focused Therapy - ManualEdy-Claude Okalla Bana67% (3)
- Learning and Development PackageDocument10 pagesLearning and Development PackageSonny Matias100% (7)
- Modified Fennema Math AttitudeDocument7 pagesModified Fennema Math AttitudeEx AtingGuro Partylist Cebrian83% (6)
- Deep Learning - Fundamentals, Theory and Applications 2019 PDFDocument168 pagesDeep Learning - Fundamentals, Theory and Applications 2019 PDFismake31100% (3)
- Modelos Lineales Generalizados Con Ejemplos en RDocument573 pagesModelos Lineales Generalizados Con Ejemplos en RJuan Manuel AntónNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument24 pagesFinal ReportDiego Andrew G RNo ratings yet
- Digcompedu Leaflet En-2017!10!09Document2 pagesDigcompedu Leaflet En-2017!10!09angieNo ratings yet
- Assessing Educators' Digital CompetenceDocument2 pagesAssessing Educators' Digital CompetenceNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- LD Upskilling of SHS Teachers of Empowering Technology and Media Information Literacy RepairedDocument15 pagesLD Upskilling of SHS Teachers of Empowering Technology and Media Information Literacy RepairedChris Marlowe YambaoNo ratings yet
- Handouts Tle107Document1 pageHandouts Tle107Miss'ElNo ratings yet
- Ced102 TransesDocument9 pagesCed102 TransesZedric EstapeNo ratings yet
- ICT Competency Standards For Philippine Pre-Service Teacher EducationDocument8 pagesICT Competency Standards For Philippine Pre-Service Teacher EducationDominique TacangNo ratings yet
- CPD Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesCPD Plan TemplateGia KhanhNo ratings yet
- Leanne Lawrence A. Bonaobra Iii Bsed Fil-C Activity 1Document1 pageLeanne Lawrence A. Bonaobra Iii Bsed Fil-C Activity 1Leannelawrence bonaobraNo ratings yet
- G12 E Tech - SyllabusDocument10 pagesG12 E Tech - Syllabusvagidiy697No ratings yet
- Ipcrf-Development Plan 2022Document1 pageIpcrf-Development Plan 2022Kimberly Ann DayonNo ratings yet
- Bsed Math 2B - Hubahib - Activity 2Document2 pagesBsed Math 2B - Hubahib - Activity 2Hines HubahibNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 Presentation 1 AnswerDocument3 pagesTTL 1 Presentation 1 Answerjooo meeeooowNo ratings yet
- Course Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 1Document12 pagesCourse Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 1Ever Shekhaina-XavierNo ratings yet
- TTL ReviewerDocument3 pagesTTL ReviewerAeverly V. QuetuaNo ratings yet
- Educ 6Document9 pagesEduc 6Regine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- TTL 2 NotesDocument8 pagesTTL 2 Noteskristelannantong3No ratings yet
- Module 1: Lesson 1 - Ict Competency Standards For Pre-Service Teacher EducationDocument2 pagesModule 1: Lesson 1 - Ict Competency Standards For Pre-Service Teacher EducationMarie RachelNo ratings yet
- Dccs Newsletter No 2 - enDocument4 pagesDccs Newsletter No 2 - enapi-457427318No ratings yet
- PoliciesDocument20 pagesPoliciesapi-411978564No ratings yet
- Handouts Cpe107Document2 pagesHandouts Cpe107Miss'ElNo ratings yet
- New LD Proposal Template EditableDocument16 pagesNew LD Proposal Template Editableneilmarc tomas100% (1)
- CASE 1 - FelizardoDocument1 pageCASE 1 - FelizardoANGELINNE FELIZARDONo ratings yet
- Developing Physics Digital Literacy Skill Diagnostic Test Assisted by Google Form For Senior High School StudentsDocument7 pagesDeveloping Physics Digital Literacy Skill Diagnostic Test Assisted by Google Form For Senior High School StudentsA SNo ratings yet
- Milestone AccomplishmentDocument2 pagesMilestone AccomplishmenthendrixNo ratings yet
- SPPD-lac-plan-mande-SIAGAO-IS FinalDocument9 pagesSPPD-lac-plan-mande-SIAGAO-IS FinalLuz Marie CorveraNo ratings yet
- LP1 - BEED & BSED 2 - PROF. ED. 5 - UNIT 1 - Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionDocument13 pagesLP1 - BEED & BSED 2 - PROF. ED. 5 - UNIT 1 - Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionJhazz GabietaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Ed 107 Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument14 pagesReviewer in Ed 107 Technology For Teaching and LearningJesille May Hidalgo Bañez100% (1)
- Ict Teacher Prof Dev Prog Course Outline April 2019Document28 pagesIct Teacher Prof Dev Prog Course Outline April 2019api-464043271No ratings yet
- Reviewer Ed107Document16 pagesReviewer Ed107Margareth De VillaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 2 Midterm NotesDocument16 pagesEDUC 2 Midterm NotesZymelle Princess FernandezNo ratings yet
- Trips" Have An Advantages Over A VideoDocument5 pagesTrips" Have An Advantages Over A VideoKim MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Digital Higher Education in The EU: Christine Redecker, PH.DDocument28 pagesDigital Higher Education in The EU: Christine Redecker, PH.DAdelina SilvaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesBon Anthony Tipdas100% (1)
- Educational Technology Action PlanDocument8 pagesEducational Technology Action PlanRENATO EGANGNo ratings yet
- ttl1 MidtermDocument62 pagesttl1 MidtermJo Michael Flores Agarma100% (1)
- ICT DOMAINS-RegineDocument3 pagesICT DOMAINS-RegineRegine GrefilNo ratings yet
- Activity Lesson 1Document3 pagesActivity Lesson 1RAIZEN LANIPA OBODNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Technology For Teaching and Learning KissieDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Technology For Teaching and Learning KissieAndrew C. BrazaNo ratings yet
- Module in Teaching and Learning 1 CHAPTER 1 1Document28 pagesModule in Teaching and Learning 1 CHAPTER 1 1Michel Jay Arguelles EspulgarNo ratings yet
- ICT Competency Standards (CHED-UNESCO), Policy, Standards and Guidelines (PSG) For Pre-Service Teacher EducationDocument5 pagesICT Competency Standards (CHED-UNESCO), Policy, Standards and Guidelines (PSG) For Pre-Service Teacher EducationPrincess Veah IlaoNo ratings yet
- EDUC206-MODULES ReviewerDocument48 pagesEDUC206-MODULES ReviewerIvy Novero SibuloNo ratings yet
- TTL1 W1Document7 pagesTTL1 W1Leah DiongcoNo ratings yet
- UNIT I: Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionDocument3 pagesUNIT I: Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionJhon Carlo DelmonteNo ratings yet
- SPPDDocument7 pagesSPPDNadya de LeonNo ratings yet
- Blended/Online Na Pagtuturo/Pagkatuto: Hamon Sa Mga Guro : Mr. Josemari V. CordovaDocument64 pagesBlended/Online Na Pagtuturo/Pagkatuto: Hamon Sa Mga Guro : Mr. Josemari V. CordovaRhodalyn P. BaluarteNo ratings yet
- Part Iv: Development Plans: 1.Kindergarten-Janice G. ParedesDocument7 pagesPart Iv: Development Plans: 1.Kindergarten-Janice G. ParedesRodnel Moncera100% (1)
- DEVELOPMENT PLAN Gerona Maria Christina 2022Document3 pagesDEVELOPMENT PLAN Gerona Maria Christina 2022MichelBorresValentinoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument52 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningGianna MichaelsNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 - ModulesDocument13 pagesTTL 1 - ModulesMohfry OoiiNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy Level & Administrative SupportDocument68 pagesDigital Literacy Level & Administrative SupportWish locker GirlNo ratings yet
- TTL KleinDocument2 pagesTTL KleinKleinNo ratings yet
- Part Iv Development Plans Ybanez ElnagraceDocument2 pagesPart Iv Development Plans Ybanez ElnagraceElna Grace Dicon-YbañezNo ratings yet
- Jhonalyn Individual Learning Plan-1Document15 pagesJhonalyn Individual Learning Plan-1Jhonalyn Toren-Tizon LongosNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning With Technology (TTL)Document6 pagesTeaching and Learning With Technology (TTL)Jana RaeNo ratings yet
- DCO Presents School Introduction To SDS and RAGDocument7 pagesDCO Presents School Introduction To SDS and RAGAnthony DunnNo ratings yet
- Ipcrf-Development PlanDocument4 pagesIpcrf-Development Planjohn stephen dingcongNo ratings yet
- Handouts Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument3 pagesHandouts Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningKhemme Lapor Chu Ubial100% (3)
- Digital Fluency Workshop SlidesDocument37 pagesDigital Fluency Workshop Slidesg-60553937No ratings yet
- Elearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersFrom EverandElearning Theories & Designs: Between Theory & Practice. a Guide for Novice Instructional DesignersNo ratings yet
- Brand StatementDocument7 pagesBrand Statementapi-371057862No ratings yet
- Development and EducationDocument12 pagesDevelopment and EducationarisNo ratings yet
- CSTP 3 Ocampo 09Document9 pagesCSTP 3 Ocampo 09api-635281515No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Students Attitudes Towards Mathematics in Two Different School SystemsDocument24 pagesA Comparative Study of Students Attitudes Towards Mathematics in Two Different School Systemsjoeisa presbiteroNo ratings yet
- Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesBudget of WorkAnna Karina100% (1)
- Assignment - Final - POL 101Document2 pagesAssignment - Final - POL 101Pinaki RanjanNo ratings yet
- Hamtig - Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesHamtig - Midterm ExamHnna HmtgNo ratings yet
- BUS 5153 Research Fall 2017Document14 pagesBUS 5153 Research Fall 2017Housi WongNo ratings yet
- 2013 Silabus Population Development and Social ChangeDocument8 pages2013 Silabus Population Development and Social ChangeGajah MadaNo ratings yet
- Pe Lesson Nov 17th - Gold RushDocument3 pagesPe Lesson Nov 17th - Gold Rushapi-273222612100% (1)
- WalkerrDocument24 pagesWalkerrMercedes FerrandoNo ratings yet
- Modules in Educ 11 Teaching InternshipDocument45 pagesModules in Educ 11 Teaching InternshipGEREMIAH MELGONo ratings yet
- 36-Rekap Validasi Data DosenDocument124 pages36-Rekap Validasi Data DosenKhalila KitchenNo ratings yet
- Holly Pich: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesHolly Pich: ObjectiveHolly ﺕ PichNo ratings yet
- Nurul Syafiqa Binti Ismail (Gs58268)Document5 pagesNurul Syafiqa Binti Ismail (Gs58268)Syaf IsmailNo ratings yet
- Education System Serbia PDFDocument23 pagesEducation System Serbia PDFTatjana Pop-AntoskaNo ratings yet
- Authentic Test BankDocument119 pagesAuthentic Test BankPaul john caguingNo ratings yet
- Contoh Proposal SkripsiDocument22 pagesContoh Proposal Skripsisurya megaNo ratings yet
- A Netnographic Examination of Constructive Authenticity in Victoria Falls TouristDocument8 pagesA Netnographic Examination of Constructive Authenticity in Victoria Falls TouristDeria Adi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Teacher-Student Relationships and Engagement PDFDocument22 pagesTeacher-Student Relationships and Engagement PDFRias Wita SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Tangazo La Kazi 6 Januari 2014Document45 pagesTangazo La Kazi 6 Januari 2014Aaron DelaneyNo ratings yet
- Inspiring StoriesDocument132 pagesInspiring StoriesRavi Dilawari [Aspire]No ratings yet
- Indian Medical Association: Family Security SchemeDocument2 pagesIndian Medical Association: Family Security SchemeAmol DhanvijNo ratings yet
- 2020 2021 SyllabusDocument28 pages2020 2021 SyllabusRifatul BariNo ratings yet