Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STM 008 1st Quarter
STM 008 1st Quarter
Uploaded by
Kassandra Gayle Olmodo Sardoncillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThe document outlines various biological concepts related to nutrition, respiration, excretion, genetics, and cell processes. It defines important terms like autotrophs, heterotrophs, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and the central dogma of biology. Several forms of tropism in plants and taxis in animals are described, as well as Gregor Mendel's discoveries of the laws of inheritance and segregation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines various biological concepts related to nutrition, respiration, excretion, genetics, and cell processes. It defines important terms like autotrophs, heterotrophs, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and the central dogma of biology. Several forms of tropism in plants and taxis in animals are described, as well as Gregor Mendel's discoveries of the laws of inheritance and segregation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageSTM 008 1st Quarter
STM 008 1st Quarter
Uploaded by
Kassandra Gayle Olmodo SardoncilloThe document outlines various biological concepts related to nutrition, respiration, excretion, genetics, and cell processes. It defines important terms like autotrophs, heterotrophs, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and the central dogma of biology. Several forms of tropism in plants and taxis in animals are described, as well as Gregor Mendel's discoveries of the laws of inheritance and segregation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1st Quarter
Friday, 24 February 2023 10:47 am
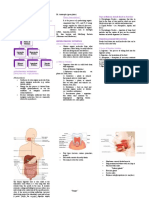
Nutrition Activities by which living things obtain raw Excretion Non-Mendelian Genetics:
- One is considered a living thing when it possesses the 7 materials from the environment and transport (removal of waste) - Co-Dominance
characters of life. them into their cells ○ When both alleles are expressed equally
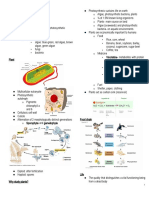
- Plants are considered AUTOTROPHS, produces their own PLANTS ANIMALS ▪ Ex. White + red petals
Respiration A process that requires oxygen; • Photosynthesis - Excretion System - Incomplete Dominance
food CO2 is produced and must be removed by the
- Animals are considered HETEROTHROPIC, cannot produce • Respiration - Cellular System ○ When both are present/blended
body; • Transportation ▪ Ex. BB x bb = 100% Bb
their own food. where metabolism takes place
- Plants : Photosynthesis ▪ Black + White = Grey
- Animals : Cellular Respiration Heterotrophic A mode that depends only on some living things to Chemical Occurs in the cells of living organisms all the time to ○ Intermediate dominance
- Plants: (-tropism) Nutrition get food Reaction carry out the life processes - Sex-linked traits
○ Thermotropism Herbivores Only eats plants ○ Not only carries the genes that determine male and female traits but also those for some
Excretion The removal of metabolic waste products from the other characteristics as well
○ Phototropism body of an organism
Carnivores Only eats meat ○ Basta katu XX ug XY
○ Geotropism
○ Thigmotropism Omnivores Eats both plants and meat Oxygen Waste/product produced during photosynthesis
○ Hydrotropism Carbon Waste/product produced in respiration - Polygenic Trait
Parasitic Organisms that get their nutrition by attaching
- Animals: (-taxis) Dioxide ○ A combination of genes
Nutrition themselves or to a host
○ Geotaxis - Pleiotropy
Saprophytic Get nutrients from things that are decomposing Water The waste removed during transpiration ○ One gene to many traits
○ Chemotaxis Nutrition
○ Aerotaxis Excretory Helps maintain internal chemical homeostasis and
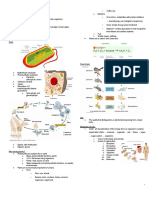
○ Phototaxis Photosynthesis A process where plants use light from the sun to System prevents damage to the body Central Dogma
○ Thigmotaxis convert CO2 from the air and water from the soil Cellular Metabolic reactions and processes that take place - The process by which the instructions in DNA are converted into a functional product
into sugar to feed plants and provide O2 into the - 1958 by Francis Crich
○ Chemotaxis respiration in the cell of organisms to convert biochemical
air energy from nutrients into ATP Gene Expressions
- Phototropism - light response in Plants
- Transcription
○ Positive Phototropism - growth towards light source Thigmotropism A movement in response to touch or contact
○ DNA to RNA
○ Negative Phototropism - growth away from the light Geotropism Growth in plants in response to gravity Gregor Mendel ○ Nucleus
- 3 processes of excretion - Discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance
Chemotaxis Migratory response that is elicited by chemicals - Replication
○ Photosynthesis - Law of Segregation ○ Old DNA to new DNA
○ Respiration Thermotropism Movement in response to heat ○ Each inherited trait is defined by a gene pair ○ Nucleus
○ transpiration Phototaxis Animal's response towards/away from stimulus ○ Gene separates from each other so that each gamete - Translation
carries only one allele for each gene ○ RNA to Proteins
Hydrotropism Plants movement in response to water ○ Two alleles to form a gamete ○ Site - Cytoplasm
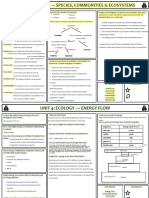
Cellular - Characteristic of life Phototropism -plants movement in response to light - Law of Independent Assortment
Organization - Means that living things are made of cells -movement in response to chemicals ○ Genes are sorted separately from one another
- Law of Dominance DNA RNA
Types of - Sexual (Humans) Irritability An excitation response to stimulus
Reproduction - Asexual (Bacteria) ○ Alternate forms of a gene that expresses the for that is Adenine Uracil
dominant
Asexual -when a single cell divides to form two daughter ADAPTABILITY Thymine Thymine
○ Off-springs will exhibit only the dominant train In the
cells that are genetically identical to parent cells phenotype Cytosine Cytosine
sexual -producing offspring w/ the union of gametes PLANTS ANIMALS ○ Dominant Trait: Guanine Guanine
- Hydrophytes - Living together ▪ One of the traits will always suppress the other,
Homeostasis - Maintains a stable internal environment
- Hygrophytes - Mitigation thereby expressing itself
- The ability of the organism to maintain
- Halophytes - Hibernation ○ Recessive Trait
internal condition Recombined DNA
- Xerophytes - Artificial Bigness ▪ The suppressed trait
Heredity Genetic information passed down from - DNA made artificially
- Mesophytes - Camouflage Allele
generation to another STEPS:
- Mimicry - One or two more versions of a gene
1. DNA Extraction
Adaptation The ability to change overtime in response to - phytes - refers to a Homozygous
a. Extract DNA's from desired organism
the environment taxonomic group of - If two alleles are the same
2. Gene Cloning
plants/algae Heterozygous
Stimuli Detectable change om the internal and external a. Cloning to separate single gene from the next of the genes extracted
- If the alleles are different
environment; 3. Gene Design
the reason behind every action or response a. Genetic engineers design the gene to work once inside a different organism
4. Transformation
Irritability Organisms ability to respond to stimuli
a. Inserted into the cell
Reproduction The process by which plants and animals 5. Backcross Breeding
produce off-springs a. Crossed w/ elite breeding lines using traditional plant breeding methods to combine the
Ovule The egg in carpel of the plants desired traits of elite parents of the transgene into a single line
Applications of Recombined DNA:
Gonads Organs producing the reproductive cell
- Food industry
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Medical Research
- Agricultural Industry
STM 008 Page 1
You might also like
- Bizantium and The Northern Islands Sneak PreviewDocument32 pagesBizantium and The Northern Islands Sneak PreviewStefano Chiaramonti100% (1)
- ABB Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger CatalogeDocument49 pagesABB Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger CatalogeSEO BDM100% (1)
- Hemophilia and Factor Assay PDFDocument17 pagesHemophilia and Factor Assay PDFSumaira JunaidNo ratings yet
- Omelianenko I Hands On Neuroevolution With Python PDFDocument359 pagesOmelianenko I Hands On Neuroevolution With Python PDFAleksa Bogdanovic100% (4)
- Direct To TOEFL iBT Answer KeyDocument44 pagesDirect To TOEFL iBT Answer KeyLeonid Pastukhov54% (13)
- AS 400 IntroductionDocument3 pagesAS 400 IntroductionRichaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument11 pages6.1 Types of NutritionNoor Hidayah SambliNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Drainage Plan and ReportDocument26 pagesStormwater Drainage Plan and ReportBeau HumeNo ratings yet
- SystematicsDocument24 pagesSystematicsMARCOS RODSEL CUADRASAL MATEONo ratings yet
- Zoolfun Notes PDFDocument13 pagesZoolfun Notes PDFRlan Gerard Manero100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 Feasibility Study For Dance StudioDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 4 Feasibility Study For Dance StudioAlexander0% (1)
- Caie Igcse: BiologyDocument32 pagesCaie Igcse: BiologySamyuktha TIPSNo ratings yet
- Frosio QuestionsDocument3 pagesFrosio QuestionsAS Dev100% (2)
- Genbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerDocument11 pagesGenbio 1 1ST Grading ReviewerTodo Roki100% (1)
- General Biology Notes 3Document10 pagesGeneral Biology Notes 3Zanark Evan100% (1)
- Bio1 - Unit 1 LectureDocument7 pagesBio1 - Unit 1 LectureCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Sop PraptiDocument6 pagesSop PraptiRikhil NairNo ratings yet
- TDS - SnSO4 Regal - (Eng)Document2 pagesTDS - SnSO4 Regal - (Eng)Rana Tahor100% (1)
- Genbio Reviewer (1st Sem)Document2 pagesGenbio Reviewer (1st Sem)Kassandra Gayle Olmodo SardoncilloNo ratings yet
- NMAT BotanyDocument35 pagesNMAT BotanyXavier AbainzaNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument31 pagesBotanyStephany Mae ChiNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument4 pagesLife ProcessesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument207 pagesBiologyAhmed WaelNo ratings yet
- ST ND RD TH TH TH TH THDocument8 pagesST ND RD TH TH TH TH THOsoNo ratings yet
- Puputok Na Ugat Ko Sa Ulooo AAAAHHHHHH Genbio MidtermsDocument9 pagesPuputok Na Ugat Ko Sa Ulooo AAAAHHHHHH Genbio Midtermscassyleen03No ratings yet
- Different Branches of Biology Different Branches of Botany: 5 Theories About The Origin ofDocument2 pagesDifferent Branches of Biology Different Branches of Botany: 5 Theories About The Origin ofEzekiel CruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document4 pagesGen Bio 2Drake AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Light Energy Chemical Energy and Carbohydrate ATPDocument32 pagesBiology: Light Energy Chemical Energy and Carbohydrate ATPNicole LamNo ratings yet
- Botany For NMATDocument26 pagesBotany For NMATMARBIE KATE PEROJANo ratings yet
- Zoology Reviewer 2022Document30 pagesZoology Reviewer 2022Lana Venice BolinaoNo ratings yet
- STM008 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSTM008 ReviewerCatherine Sanchez RosarioNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Mode of Reproduction: Sharlene Solo XII - St. Helena General Biology 2Document4 pagesMode of Reproduction: Sharlene Solo XII - St. Helena General Biology 2kenjie bustilloNo ratings yet
- Biology - November 2017Document1 pageBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18 Apr 2023Document25 pagesAdobe Scan 18 Apr 2023meryamNo ratings yet
- Bio Brain MapsDocument37 pagesBio Brain MapsNEERU JINDALNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 26 03 Sample Botany 1Document17 pagesNEET UG 26 03 Sample Botany 1Md FaijalNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Organismal Biology 2Document33 pagesSession 1 Organismal Biology 2Betty IrezariNo ratings yet
- Biolab2 Report FinalDocument14 pagesBiolab2 Report FinalKriztle de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Teacher)Document32 pagesChapter 6 (Teacher)ajakazNo ratings yet
- The Individual in An Ecosystem: Individual: Fundamental Units of Populations, Communities, Ecosystems and BiomesDocument12 pagesThe Individual in An Ecosystem: Individual: Fundamental Units of Populations, Communities, Ecosystems and BiomesEthan HuntNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewDocument6 pagesBiology Reviewmj espanolaNo ratings yet
- Bio Rev Dig System 2.0Document5 pagesBio Rev Dig System 2.0Christine Ann GotanNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory 63fcd53c82e726483f1cfcda 877Document34 pagesCaie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory 63fcd53c82e726483f1cfcda 877Family TimeNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument34 pagesBiology NotesMwangala ANo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument26 pagesLife ProcessesJungli GodNo ratings yet
- Bio 1202 Lecture Notes EditDocument52 pagesBio 1202 Lecture Notes EditBundeh SughnenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Characteristics of LifeDocument29 pagesLesson 4 Characteristics of Liferosie sialanaNo ratings yet
- Science 5º Tema1Document7 pagesScience 5º Tema1elenaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: General Biology 2Document5 pagesNutrition: General Biology 2Thea DegraciaNo ratings yet
- EnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDocument47 pagesEnviEng MRII 0894 PDFDaniel MalapitanNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification PDFDocument4 pagesBiological Classification PDFDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- iGCSE Edexcel Biology All ContentDocument162 pagesiGCSE Edexcel Biology All Contenticonman030No ratings yet
- Biology Sol ReviewDocument8 pagesBiology Sol ReviewhtyhongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- ANP101 Lesson Note - AbiojaDocument10 pagesANP101 Lesson Note - Abiojaabiolaelizabeth255No ratings yet
- NARATopic4 - RevisionMat 1Document4 pagesNARATopic4 - RevisionMat 1naraNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument5 pagesGen BioCloudy HeavenNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems andDocument31 pagesPlant and Animal Organ Systems androselyn acpacNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture Animation PPTDocument47 pages01 Lecture Animation PPTMary JewelNo ratings yet
- GenBio1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio1 Reviewerangeladmana09No ratings yet
- NARATopic4 RevisionMatDocument4 pagesNARATopic4 RevisionMatnaraNo ratings yet
- Organismal BiologyDocument30 pagesOrganismal BiologyLeamonique AjocNo ratings yet
- 1a the Science of Life (预读班)Document46 pages1a the Science of Life (预读班)J20230 彭振城HENRY PHANG ZHEN CHENGNo ratings yet
- 8 MicrobiologycramsheetDocument2 pages8 Microbiologycramsheetapi-326958203No ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument1 pageDiversity in Living OrganismsAdarshNo ratings yet
- Weak Points NotesDocument15 pagesWeak Points NotesJana GhonaimNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v23Document34 pagesCaie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v23sg024220565No ratings yet
- What Is Life?: Biology, Science, and How We Study ThingsDocument33 pagesWhat Is Life?: Biology, Science, and How We Study ThingsSer IvanNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Species - EcosystemsDocument1 page4.1 Species - EcosystemsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document21 pagesLecture 4Gia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- Bonding, Grounding, and Surge Protection Products and Low Voltage Panel ComponentsDocument14 pagesBonding, Grounding, and Surge Protection Products and Low Voltage Panel Componentspatitay036817No ratings yet
- Part 61 MOS Vol 1Document74 pagesPart 61 MOS Vol 1Jake BlatchfordNo ratings yet
- IDb5e0db2f1-1996 Fiat Punto ManualDocument2 pagesIDb5e0db2f1-1996 Fiat Punto ManualBryant Tairua100% (1)
- Cinefantastique Vol 07 No 3-4 1978Document96 pagesCinefantastique Vol 07 No 3-4 1978VanderNo ratings yet
- N61-1544-000-0001 Honeywell Aerospace APU Overview-BroDocument4 pagesN61-1544-000-0001 Honeywell Aerospace APU Overview-BroIventNo ratings yet
- Causes of DeforestationDocument3 pagesCauses of DeforestationZakaria GhaniNo ratings yet
- Rissner, Christoph - Seminar - Mind MapsDocument23 pagesRissner, Christoph - Seminar - Mind MapsvoodoogodsNo ratings yet
- AT&T Alascom NetworkDocument1 pageAT&T Alascom NetworkrbskoveNo ratings yet
- 018 - BBA (B&I) - 3rd & 5th SEM - DECLARE - RESULT - DEC2020Document105 pages018 - BBA (B&I) - 3rd & 5th SEM - DECLARE - RESULT - DEC2020vansham malikNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document12 pagesLec 1TanujHandaNo ratings yet
- Conflict in Europe 1935Document13 pagesConflict in Europe 1935jessica_choy_4No ratings yet
- Jensen Series 600VA Parts DWGDocument1 pageJensen Series 600VA Parts DWGSergioNo ratings yet
- Microleakage A Review: Vitro Detection of MicroleakageDocument8 pagesMicroleakage A Review: Vitro Detection of MicroleakageAayushi VaidyaNo ratings yet
- PR-ization of News and The New Media PDFDocument14 pagesPR-ization of News and The New Media PDFAlexis Koronakis-AspiotisNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Energy and Environmental Applications of Glass: Richard K. Brow, Melodie L. SchmittDocument9 pagesA Survey of Energy and Environmental Applications of Glass: Richard K. Brow, Melodie L. SchmittSupriya RaiNo ratings yet
- GTL 1x4Document4 pagesGTL 1x4Ronald TesoroNo ratings yet
- Breakout Trading Strategies Quick GuideDocument10 pagesBreakout Trading Strategies Quick GuideTim KanikaNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation of Seafood Processing Plant Effluent: Collection and Biochemical Analysis of EffluentDocument10 pagesBioremediation of Seafood Processing Plant Effluent: Collection and Biochemical Analysis of EffluentAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet