Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCH3U - Unit 5 Cheat Sheet
SCH3U - Unit 5 Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
syednasifahmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SCH3U - Unit 5 Cheat Sheet
SCH3U - Unit 5 Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
syednasifahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
SCH3U - Unit 5 “Cheat” Sheet
Between: Oppositely Charged Particles(s), Polar Molecules(s,l,g), Non-Polar Molecules (s,l,g)
Stronger Force → Weaker Force
Law Formula Extra Space
Boyle’s Law 1 ℃ to K:
𝑉 ∝ 𝑝
| 𝑃1𝑉1 = 𝑃2𝑉2 K = ℃ + 273.15
Charle’s Law 𝑉1 𝑉2 K to ℃
𝑉∝𝑇 | 𝑇1
= 𝑇2
℃ = K - 273.15
Pressure = force / area
Gay Lussac’s 𝑃1 𝑃2
Law 𝑃∝𝑇 | 𝑇1
= 𝑇2
Combined 𝑃1𝑉1 𝑃2𝑉2
Gas Law 𝑇1
= 𝑇2
Avogadro’s 𝑛1 𝑛2
Law 𝑛 ∝ 𝑉 | 𝑉1
= 𝑉2
Ideal Gas 𝑘𝑃𝑎 · 𝐿
𝑃𝑉 = 𝑛𝑅𝑇, 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑛 = 8. 314 𝑚𝑜𝑙
Law ·𝐾
*Formulas can be re-arranged to isolate specific variables
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures: “in a mixture of non-reacting gases, the total pressure exerted
is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.”
1 𝑎𝑡𝑚 = 760 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝑔 = 760 𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑟 = 101325 𝑃𝑎 = 101. 325 𝑘𝑃𝑎 = 1. 01325 𝑏𝑎𝑟 = 14. 7 𝑝𝑠𝑖
𝑚𝑅𝑇
● Molar mass 𝑀 = 𝑃𝑉
𝑚 𝑃𝑀 𝑀
● Density 𝑣
= 𝑅𝑇
;D= 𝑉𝑚
, where Vm is molar volume
Pressure Celsius Temp. Kelvin Temp. Molar Volume of an Ideal Gas
STP 101.325 kPa 0℃ 273.15 K 22.4 L/mol
SATP 100.0 kPa 25℃ 298.15 K 24.8 L/mol
You might also like
- Introduction To Physical ChemistryDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Physical ChemistryRheanne SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Real-GasesDocument9 pagesLecture 4-Real-GasesScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- 4th WeekDocument7 pages4th WeekMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- At DarshanDocument127 pagesAt DarshanBabaluNo ratings yet
- Thermo Rev Mod2Document6 pagesThermo Rev Mod2Mikasa AckermanNo ratings yet
- Gas LawDocument1 pageGas Lawaira sharidaNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 - Part 2Document15 pagesModule - 4 - Part 2AckshayaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gases - Real Gases - 2020-2Document42 pagesProperties of Gases - Real Gases - 2020-2Aeriel May PliegoNo ratings yet
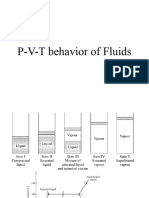
- PVT BehaviourDocument21 pagesPVT Behaviourkartik44No ratings yet
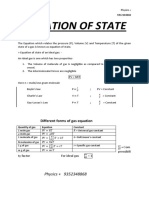
- Equation of StateDocument7 pagesEquation of StateJack SparrowNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws PDFDocument12 pagesGas Laws PDFMara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas Laws: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesWeek 3: Ideal Gases and Ideal Gas Laws: ObjectivesMarc Jairro GajudoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 Final Term NotesDocument9 pagesChemistry 1 Final Term NotesnicolassarragaNo ratings yet
- asset-v1-DelftX+TP102x+3T2016+type@asset+block@Formula Sheet ATPDocument12 pagesasset-v1-DelftX+TP102x+3T2016+type@asset+block@Formula Sheet ATPkennethmsorianoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture 21, 22, 23 & 24: ThermometersDocument4 pagesSummary of Lecture 21, 22, 23 & 24: ThermometersStevenChandraNo ratings yet
- GASES-CHM130 by DELZYDocument15 pagesGASES-CHM130 by DELZYmisakisuki7No ratings yet
- KEYPROBLEMSET GAS LAWSDocument16 pagesKEYPROBLEMSET GAS LAWSClark AggabaoNo ratings yet
- CHEM20024 Lecture Notes 11 - Free Energy and EquilibriumDocument27 pagesCHEM20024 Lecture Notes 11 - Free Energy and EquilibriumEzriel QuantumNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry - Lecture 3Document20 pagesEngineering Chemistry - Lecture 3El Sayed ZakariaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMSET GAS LAWSDocument16 pagesPROBLEMSET GAS LAWSClark AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirDocument22 pagesGas Laws: Pressure, Volume, and Hot AirKevin SimanjorangNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes 3rd MasteryDocument3 pagesChem Notes 3rd MasteryblezieNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Ideal Gas LawDocument15 pages3.4 Ideal Gas LawfaridaisepicNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Notes PDFDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 5 Notes PDFlavkush singhNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document14 pagesLec 2أمجد هاتف منفي جفالNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws HandoutDocument10 pagesGas Laws HandoutVenu ReddyNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Mapùa University School of Chemical, Biological, Materials Engineering and SciencesDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Mapùa University School of Chemical, Biological, Materials Engineering and SciencesJE BuanNo ratings yet
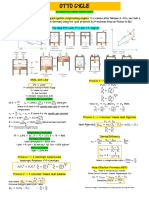
- The Ideal Otto CycleDocument1 pageThe Ideal Otto CycleNurlaila DalidigNo ratings yet
- Engineers & Doctors Inn: Physics Xii (Formulae - 1)Document2 pagesEngineers & Doctors Inn: Physics Xii (Formulae - 1)Meer UmarNo ratings yet
- Claysius Clapeyron Lab ExperimentDocument11 pagesClaysius Clapeyron Lab Experimentmohamad munzir100% (1)
- 6 Gaseous State 2023Document11 pages6 Gaseous State 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Thermodynamics I Basics and First LawDocument34 pagesLesson 6 - Thermodynamics I Basics and First Lawjaydi.maat.02No ratings yet
- Chap 13 Gas Laws & Kinetic Theory SummaryDocument2 pagesChap 13 Gas Laws & Kinetic Theory SummarySyakirah MunirNo ratings yet
- L2 States of MatterDocument53 pagesL2 States of MatterAaryan ChodankarNo ratings yet
- CHM 221Document12 pagesCHM 221Necherem MissionNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gases (Report)Document19 pagesProperties of Gases (Report)Rex LapisNo ratings yet
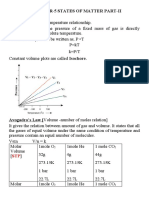
- Class-11 Chemistry Chapter-5 States of Matter Part-IIDocument7 pagesClass-11 Chemistry Chapter-5 States of Matter Part-IINevin ShajiNo ratings yet
- Multiphase Systems - Part IDocument20 pagesMultiphase Systems - Part I랄뚜기No ratings yet
- PVT Properties of Hydrocarbon Systems: 02MAZNW - Fluid Mechanics in Porous MediaDocument50 pagesPVT Properties of Hydrocarbon Systems: 02MAZNW - Fluid Mechanics in Porous MediaFaraj27No ratings yet
- CheemmmmmmmmmmmmDocument4 pagesCheemmmmmmmmmmmmarabela albairaNo ratings yet
- 4Q Chemistry G10Document9 pages4Q Chemistry G10vyn bringinoNo ratings yet
- CP Ch5Document33 pagesCP Ch5Ahmad RaghebNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 - Lecture 1Document69 pagesPhysics 2 - Lecture 1Abonin, Carl Ivan D.L.No ratings yet
- 7 ThermalDocument69 pages7 ThermalKingsonNo ratings yet
- TDY1 - Les 3 EngDocument28 pagesTDY1 - Les 3 EngBrandon GesterkampNo ratings yet
- Equations of State and PVT AnalysisDocument37 pagesEquations of State and PVT AnalysisJanickNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics Part 1 - Basic Fluid MechanicsDocument23 pagesFluid Statics Part 1 - Basic Fluid MechanicsEro RosalNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument85 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure SubstancesKIM ASHLEY CARRILLONo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionDocument4 pagesAtmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionjenduekieNo ratings yet
- 11) Gas Laws - Second Edition - 1551343848Document9 pages11) Gas Laws - Second Edition - 1551343848ungaranigundla sachivalayamNo ratings yet
- Gas IdealDocument10 pagesGas IdealAlexis CGNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesThermodynamicsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws-1Document8 pagesGas Laws-1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Week 1 2 Gas Laws LECTUREDocument49 pages4th Quarter Week 1 2 Gas Laws LECTUREJohn Albert Tubillo ChingNo ratings yet
- N M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review CenterDocument4 pagesN M (Joules) FT LB Newton LB M FT: Inhinyero Review CenterPaulyne TuganoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equation SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Equation SheetFabiola RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet